OSGi是在Java中定义动态模块的方法。 主要为Java实现的三个OSGi容器是Apache Felix , Eclipse Equinox和Knopflefish 。
为什么选择OSGi? 因为OSGi提供了将应用程序划分为多个模块的能力,并且那些模块易于与其他依赖项一起管理。 除此之外,它非常容易安装,更新,停止和删除没有停止引擎的模块(例如:Tomcat Web应用程序容器)。 我们可以使用多种实现方式来影响其他参考。
基于Web的Java框架主要有3个层(表示层,业务层和DAO层)。 在那里,我们可以将其分为三个基于OSGi的模块。 那么我们可以很容易地将错误修复到一层,而不会影响其他错误并重新启动我们的Web容器。 只是我们需要更新模块。
在OSGi世界中,输出是捆绑包,可以是Jar或War文件。 捆绑软件由Java类和其他资源以及一些其他元数据组成(向其他捆绑软件提供服务和软件包)。
我将使用Eclipse IDE创建我的第一个捆绑软件。 因为Eclipse IDe内置了Equinox容器(每个eclipse插件都是OSGi捆绑包)。
创建Eclipse插件项目
- 转到新建–>其他–>插件项目 ,然后单击下一步,将出现新项目创建对话框
- 提供项目名称和目标平台,如下所示。 然后点击下一步
项目名称: com.chandana.Hello.HelloWorld
目标平台:选择Stranded OSGi
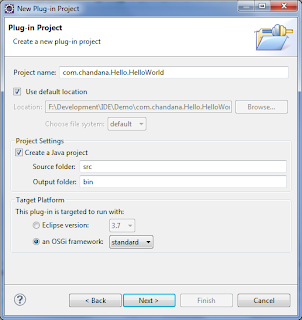
- 在下一个屏幕中,您可以更改捆绑包信息(这些信息可在MANIFEST.MF中找到,稍后我会提供详细信息),然后单击“下一步”按钮。
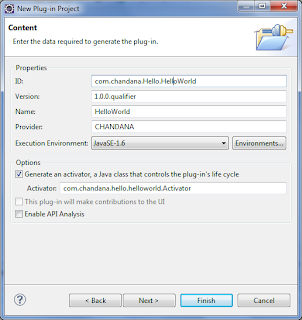
- 之后将出现OSGi项目模板选择对话框。选择Hello OSGi Bundle,然后单击Finish。
-
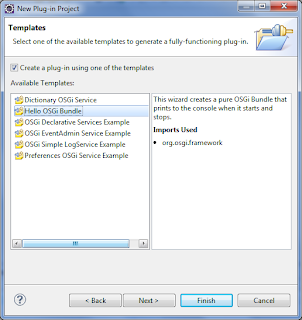
几秒钟后,Eclipse将生成Hello World Plug-In-Project(我几秒钟没有响应:))
在我的项目结构中是这样的:

Activator.java
package com.chandana.hello.helloworld;import org.osgi.framework.BundleActivator;
import org.osgi.framework.BundleContext;public class Activator implements BundleActivator {/** (non-Javadoc)* @see org.osgi.framework.BundleActivator#start(org.osgi.framework.BundleContext)*/public void start(BundleContext context) throws Exception {System.out.println("Hello World!!");}/** (non-Javadoc)* @see org.osgi.framework.BundleActivator#stop(org.osgi.framework.BundleContext)*/public void stop(BundleContext context) throws Exception {System.out.println("Goodbye World!!");}}Activator是实现BundleActivator的类 接口。 它已经停了 然后开始 方法。 当捆绑包启动或停止时,将调用这些方法 。 此束激活器类在MENIFEST.MF文件( 束激活器条目)中指定。
启动方法:
捆绑包启动时,OSGi容器将调用start方法。 我们可以使用此启动方法进行初始化的数据库连接,注册服务以供其他捆绑使用。 停止方式: 捆绑包停止时,OSGi容器调用stop方法。 我们可以使用此方法从服务注册表中删除服务,例如清理过程
清单文件
Manifest-Version: 1.0
Bundle-ManifestVersion: 2
Bundle-Name: HelloWorld
Bundle-SymbolicName: com.chandana.Hello.HelloWorld
Bundle-Version: 1.0.0.qualifier
Bundle-Activator: com.chandana.hello.helloworld.Activator
Bundle-Vendor: CHANDANA
Bundle-RequiredExecutionEnvironment: JavaSE-1.6
Import-Package: org.osgi.framework;version="1.3.0" Bundle-ManifestVersion
Bundle-ManifestVersion标头显示OSGi容器,该捆绑包遵循OSGi规范的规则。 值为2表示捆绑软件符合OSGi规范第4版。 值1表示它符合版本3或更早的版本。
捆绑名称
Bundle-Name标头定义捆绑的简短可读名称。
Bundle-SymbolicName
Bundle-SymbolicName标头指定捆绑包的唯一名称。 这是您在从其他捆绑包中引用给定捆绑包时将使用的名称。
捆绑版本
Bundle-Version标头是捆绑软件的版本号。
捆绑销售商
Bundle-Vendor标头是供应商的描述(例如,这是我的名字)。
进口包装
Import-Package指示此捆绑包还需要其他Java捆绑包(OSGi)。 我们称之为依赖性。
出口包装
导出包指示什么是捆绑包中的公共包,那些导出包可以从其他捆绑包中导入。
运行捆绑包:
- 对于“运行此项目”,请单击“运行”->“运行配置”,在OSGi Framework中,右键单击并创建新的“运行配置”。
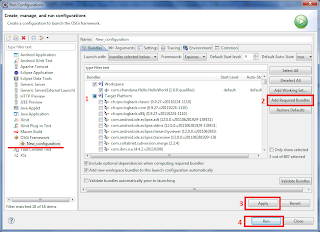
- 首先取消选中所有目标平台,然后单击“ 添加必需的捆绑包” 。
- 之后,单击“运行”按钮,应用更改并运行项目。
- 运行后,项目OSGi控制台显示如下。
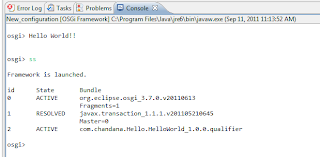
OSGi终端命令:
源代码
接下来,我将描述如何创建基于依赖的OSGi捆绑软件。
OSGi服务是一个Java对象实例,已向OSGi框架注册了一组属性。 可以通过服务注册表(通过类BundleContext执行)访问服务。 BundleActivator将在启动和停止时调用。 当BundleActivator调用start方法时,我们将注册我们的服务。 之后,任何捆绑包都可以访问该服务。
服务包:
在服务包中,您需要导出服务,并需要通过服务注册表进行注册。 当我们导出服务时,我们仅导出接口包。 与往常一样,这是从其他捆绑包中隐藏实现。
我已经创建了一个名为HelloService的示例OSGi项目。
清单文件
Manifest-Version: 1.0
Bundle-ManifestVersion: 2
Bundle-Name: HelloService
Bundle-SymbolicName: com.chandana.hello.HelloService
Bundle-Version: 1.0.0
Bundle-Activator: com.chandana.hello.helloservice.Activator
Bundle-Vendor: CHANDANA
Bundle-RequiredExecutionEnvironment: JavaSE-1.6
Import-Package: org.osgi.framework;version="1.3.0"
Export-Package: com.chandana.hello.service
Bundle-ActivationPolicy: lazy服务接口:
public interface HelloService { public String helloMethods();
}服务实施:
public class HelloServiceImpl implements HelloService {@Overridepublic String helloMethods() {String retValue = "Inside Hello Service method";return retValue;}
}边界激活剂:
public class Activator implements BundleActivator {ServiceRegistration serviceRegistration;/** (non-Javadoc)* @see org.osgi.framework.BundleActivator#start(org.osgi.framework.BundleContext)*/public void start(BundleContext context) throws Exception {System.out.println("Bundle Started.....!!!!!");HelloService service = new HelloServiceImpl();serviceRegistration = context.registerService(HelloService.class.getName(), service,null);}/** (non-Javadoc)* @see org.osgi.framework.BundleActivator#stop(org.osgi.framework.BundleContext)*/public void stop(BundleContext context) throws Exception {System.out.println("Bundle Stoped.....!!!!!");serviceRegistration.unregister();}
}使用发布的服务时,可以从另一个捆绑包中导入它。 因此需要为HelloClient创建另一个插件项目
捆绑内容
捆绑包上下文是OSGi运行时中单个捆绑包的上下文,它是在捆绑包启动时创建的。 捆绑包上下文可用于安装新捆绑包,通过其他捆绑包获取注册的服务以及在框架中注册服务。
清单文件
Import-Package: org.osgi.framework;version="1.3.0",com.chandana.hello.service导入捆绑软件后,您可以访问该服务。 重要的是只能通过bundle上下文访问服务。 您可以通过BundleContext.getService()方法获取实际的服务对象。
激活器类:
public class Activator implements BundleActivator {ServiceReference serviceReference; /** (non-Javadoc)* @see org.osgi.framework.BundleActivator#start(org.osgi.framework.BundleContext)*/public void start(BundleContext context) throws Exception {serviceReference= context.getServiceReference(HelloService.class.getName());HelloService helloService =(HelloService)context.getService(serviceReference);System.out.println(helloService.helloMethods());}/** (non-Javadoc)* @see org.osgi.framework.BundleActivator#stop(org.osgi.framework.BundleContext)*/public void stop(BundleContext context) throws Exception {context.ungetService(serviceReference);}
}context.getServiceReference()方法返回HelloService OSGi服务引用,使用该服务引用可以访问实际的服务对象。
对于“运行此项目”,请单击“ 运行”->“运行配置” ,在OSGi Framework中,右键单击并创建新的“运行配置” 。 确保HelloService和HelloClient 。
问题 :
如果客户端访问服务时未启动服务,会发生什么情况?
如果您停止了该服务捆绑包,会发生什么?
代码仓库 :
http://code.google.com/p/osgi-world/source/browse/#svn/trunk/com.chandana.hello.HelloService
http://code.google.com/p/osgi-world/source/browse/#svn/trunk/com.chandana.hello.HelloClient
参考:来自JCG合作伙伴的 OSGi(Java模块化) 简介和OSGi – 2(OSGi服务)简介 Chandana Napagoda博客上的Chandana Napagoda 。
翻译自: https://www.javacodegeeks.com/2012/01/introduction-to-osgi-modular-java.html



)
)


![[HDU1232] 畅通工程 (并查集 or 连通分量)](http://pic.xiahunao.cn/[HDU1232] 畅通工程 (并查集 or 连通分量))
)






方法)


