#include<stdio.h>struct Student{int age;float score;char sex;};main(){struct Student st={25,88,'M'};printf("%d\n",st.age); struct Student *pst=&st;pst->age=100;printf("%d\n",st.age);printf("%d",pst->age); }
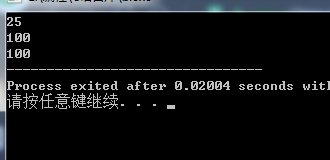
构造结构体并且输出,方式不同。指针or st.XXX
*pst=&st;
pst->age
看了很多->这个符号,一直不懂什么意思,现在终于算有点了解了。
定义指针变量后,可以直接用地址指向它的成员变量。




)

)


)

)






)
