一、Github地址:
https://github.com/duwei1996/wc
二、PSP2.1表格
| PSP2.1 | PSP阶段 | 预估耗时 (分钟) | 实际耗时 (分钟) |
| Planning | 计划 | 30 | 30 |
| · Estimate | · 估计这个任务需要多少时间 | 30 | 30 |
| Development | 开发 | 540 | 900 |
| · Analysis | · 需求分析 (包括学习新技术) | 60 | 120 |
| · Design Spec | · 生成设计文档 | 0 | 0 |
| · Design Review | · 设计复审 (和同事审核设计文档) | 0 | 0 |
| · Coding Standard | · 代码规范 (为目前的开发制定合适的规范) | 60 | 120 |
| · Design | · 具体设计 | 60 | 60 |
| · Coding | · 具体编码 | 240 | 360 |
| · Code Review | · 代码复审 | 60 | 120 |
| · Test | · 测试(自我测试,修改代码,提交修改) | 60 | 60 |
| Reporting | 报告 | 90 | 120 |
| · Test Report | · 测试报告 | 30 | 45 |
| · Size Measurement | · 计算工作量 | 30 | 30 |
| · Postmortem & Process Improvement Plan | · 事后总结, 并提出过程改进计划 | 30 | 45 |
| 合计 | 700 | 1050 |
三、设计思路
1.程序设计两个主要方法baseFunction()和extendFunction(),分别用于实现基本功能和扩展功能
2.设计辅助方法如countChar()、countLine()等供上面两个方法调用
3.根据接收的命令参数,判断执行相应的操作
四、主要代码
1.main函数
从输入参数获取要处理的文件, 并对文件做基本功能和扩展功能的处理
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{ File file = new File(args[args.length-1]); baseFunction(args,file);extendFunction(args,file);
}
2.baseFunction函数和baseCount函数
调用baseCount方法,根据参数,输出相应结果
public static void baseFunction(String[] strings, File file)throws IOException{if (file == null || !file.exists())throw new FileNotFoundException(file + ",文件不存在!");baseCount(file);List<String> list = Arrays.asList(strings);if (list.contains("-c")){//countChar()System.out.println(file.getName() + "," + result1); } if (list.contains("-w")&& !list.contains("-e")){ //countWord() System.out.println(file.getName() + "," + result2); } if (list.contains("-l")){ //counLine() System.out.println(file.getName() + "," + result3); } if (list.contains("-o")){ String content = new String(file.getName() + "\r\n" + result1 + "\r\n" + result2 + "\r\n" + result3); Path outPath = Paths.get("output.txt"); File output = new File(outPath.toString()); Files.write(outPath,content.getBytes()); } } baseCount方法用于读取文件内容,并计算字符、单词和行数
public static void baseCount(File file) throws IOException{BufferedReader br = helper(file);String s = null;while ((s = br.readLine()) != null){s = br.readLine();countChar(s);countWord(s);countLine(s);}}
3.extendFunction函数和extendCount函数
调用baseCount方法,根据参数,输出相应结果
public static void extendFunction(String[] strings,File file)throws IOException{extendCount(file);List<String> list = Arrays.asList(strings);if (list.contains("-s")){//recFile(file);}if (list.contains("-a")){System.out.println(file.getName() +",代码行 / 空行 / 注释行:" + codeLineNum + "/" + blankLineNum + "/" + annotationLineNum); } if (list.contains("-w")&&list.contains("-e")){ baseCount(file); String s1 = list.get(list.indexOf("-w")+1); String s2 = list.get(list.indexOf("-e")+1); File file1 = new File(s1); File file2 = new File(s2); int sameNum = stopList(file1,file2); System.out.println(file.getName() +",单词数:" + (wordNum - sameNum)); } } extendCount方法
public static void extendCount(File file) throws IOException{exCountLine(file);recFile(file);} exCountLine方法
public static void exCountLine(File file) throws IOException {if (file == null || !file.exists())throw new FileNotFoundException(file + ",文件不存在!");//fileCount ++; // 文件数累加if (file.isDirectory()) {recFile(file);} else {BufferedReader bufr = null; try { // 将指定路径的文件与字符流绑定 bufr = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(new FileInputStream(file))); } catch (FileNotFoundException e) { throw new FileNotFoundException(file + ",文件不存在!" + e); } // 定义匹配每一行的正则匹配器 Pattern annotationLinePattern = Pattern.compile("((//)|(/\\*+)|((^\\s)*\\*)|((^\\s)*\\*+/))+", Pattern.MULTILINE + Pattern.DOTALL); // 注释匹配器(匹配单行、多行、文档注释) Pattern blankLinePattern = Pattern.compile("^\\s*$"); // 空白行匹配器(匹配回车、tab键、空格) Pattern codeLinePattern = Pattern.compile("(?!import|package).+;\\s*(((//)|(/\\*+)).*)*", Pattern.MULTILINE + Pattern.DOTALL); // 代码行匹配器(以分号结束为一行有效语句,但不包括import和package语句) // 遍历文件中的每一行,并根据正则匹配的结果记录每一行匹配的结果 String line = null; try { while ((line = bufr.readLine()) != null) { if (annotationLinePattern.matcher(line).find()) { annotationLineNum++; } if (blankLinePattern.matcher(line).find()) { blankLineNum++; } if (codeLinePattern.matcher(line).matches()) { codeLineNum++; } } } catch (IOException e) { throw new RuntimeException("读取文件失败!" + e); } finally { try { bufr.close(); // 关闭文件输入流并释放系统资源 } catch (IOException e) { throw new RuntimeException("关闭文件输入流失败!"); } } } } recFile函数,实现递归处理文件夹
public static void recFile(File file) throws IOException{File[] files = file.listFiles(new FileFilter() {public boolean accept(File pathname) {return pathname.getName().endsWith(".c") || pathname.isDirectory();}});for (File target : files) {extendCount(target);}} stopList函数,实现禁用单词计数;
public static int stopList(File file1,File file2) throws IOException{String[] strings1 = word(file1);String[] strings2 = word(file2);return same(strings1,strings2);}public static String[] word(File file) throws IOException{BufferedReader br = helper(file); String s = null; String[] content = null; while ((s=br.readLine())!=null){ s = br.readLine(); String a = ","; s.replaceAll(a," "); content = s.split(" "); } return content; } public static int same(String[] a,String[] b){ ArrayList<String> same = new ArrayList<String>(); ArrayList<String> temp = new ArrayList<String>(); for (int i = 0; i < a.length; i++) { temp.add(a[i]); //把数组a中的元素放到Set中,可以去除重复的元素 } for (int j = 0; j < b.length; j++) { //把数组b中的元素添加到temp中 //如果temp中已存在相同的元素,则temp.add(b[j])返回false if(!temp.add(b[j])) same.add(b[j]); } return same.size(); }
五、测试
1.基本功能
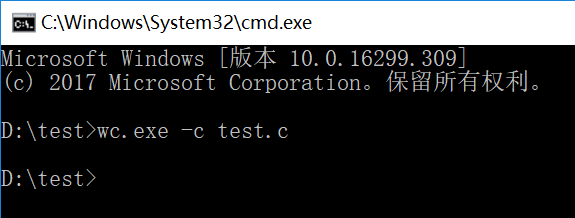
wc.exe -c file.c //返回文件 file.c 的字符数 wc.exe -w file.c //返回文件 file.c 的单词总数 wc.exe -l file.c //返回文件 file.c 的总行数 wc.exe -o outputFile.txt //将结果输出到指定文件outputFile.txt
测试文本
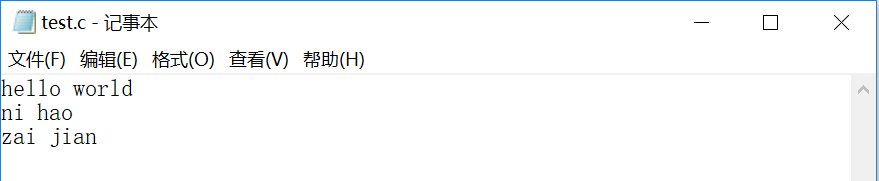
命令与结果


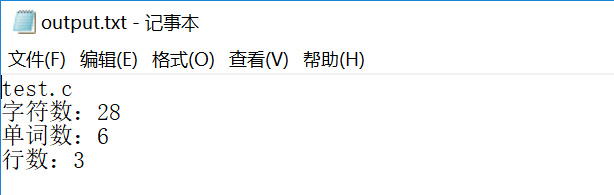
2.扩展功能
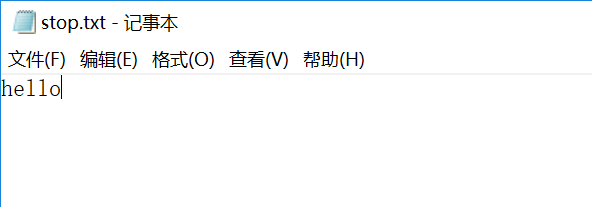
wc.exe -s //递归处理目录下符合条件的文件 wc.exe -a file.c //返回更复杂的数据(代码行 / 空行 / 注释行) wc.exe -e stopList.txt // 停用词表,统计文件单词总数时,不统计该表中的单词
禁用列表
命令与结果
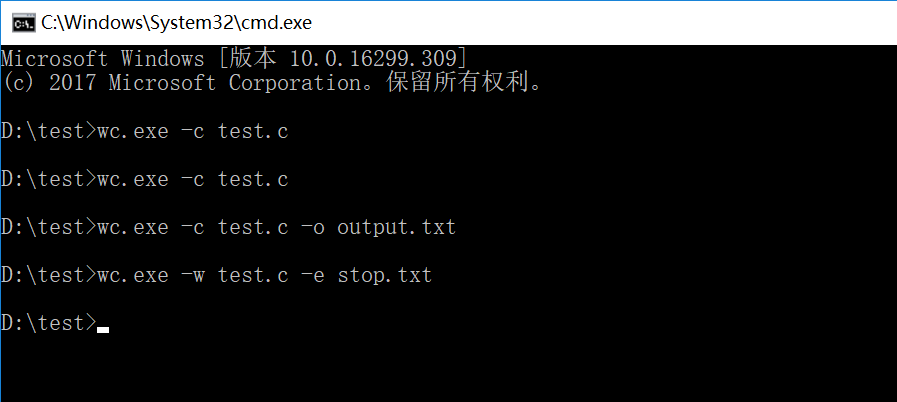

注:另外两个功能尚未实现
六、体会
通过编程,更深地体会到需求设计的重要性;通过测试,更加了解需求与产品之间的差别,以及测试的必要性和重要性。
七、参考文献
http://www.cnblogs.com/ningjing-zhiyuan/p/8563562.html







:新元素之video,audio,meter,datalist,keygen,output)









![[UE4]集合:TSet容器](http://pic.xiahunao.cn/[UE4]集合:TSet容器)

