最近项目原因,要在uboot中增加内核验校和内核损坏修复功能,所以需要回头看看uboot。这次选择了uboot2015来进行分析
uboot是明远睿智提供的。
下载地址 链接:https://pan.baidu.com/s/13SuRii3WTqvFTNIsSS9GAg 密码:65zz
环境:ubuntu16
主控:imx6q
1、start.s arch\arm\cpu\armv7\start.S
因为我们这款cpu指令集是armv7的所以选择这个目录下的start.s,如果不知道自己该看那个目录下的start.s,可以用如下方法
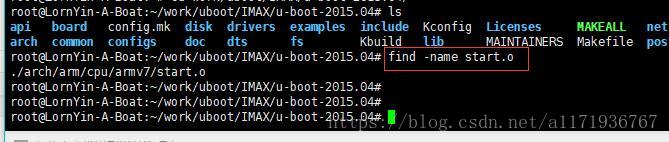
先编译uboot,编译成功后,执行 find -name start.0 即可看见start文件所在目录
然后我们来看看代码,我对代码进行了删减,我们目的在于流程分析,就不分析具体每句话了
reset:/* Allow the board to save important registers */b save_boot_params
save_boot_params_ret:/** disable interrupts (FIQ and IRQ), also set the cpu to SVC32 mode,* except if in HYP mode already*/。。。。。。。。/** Setup vector:* (OMAP4 spl TEXT_BASE is not 32 byte aligned.* Continue to use ROM code vector only in OMAP4 spl)*/
#if !(defined(CONFIG_OMAP44XX) && defined(CONFIG_SPL_BUILD))/* Set V=0 in CP15 SCTLR register - for VBAR to point to vector */。。。。。。。。。/* Set vector address in CP15 VBAR register */。。。。。。。。。
#endif/* the mask ROM code should have PLL and others stable */
#ifndef CONFIG_SKIP_LOWLEVEL_INITbl cpu_init_cp15bl cpu_init_crit
#endifbl _main //进入_mainarch\arm\lib\crt0.S _main在这个文件里
ENTRY(_main)/** Set up initial C runtime environment and call board_init_f(0).*/#if defined(CONFIG_SPL_BUILD) && defined(CONFIG_SPL_STACK)ldr sp, =(CONFIG_SPL_STACK)
#elseldr sp, =(CONFIG_SYS_INIT_SP_ADDR)
#endif。。。。。。。
clr_gd:。。。。。。。
#if defined(CONFIG_SYS_MALLOC_F_LEN)sub sp, sp, #CONFIG_SYS_MALLOC_F_LENstr sp, [r9, #GD_MALLOC_BASE]
#endif/* mov r0, #0 not needed due to above code */bl board_init_f /*这个函数把uboot拷贝到ram*/#if ! defined(CONFIG_SPL_BUILD)/** Set up intermediate environment (new sp and gd) and call* relocate_code(addr_moni). Trick here is that we'll return* 'here' but relocated.*/。。。。。。b relocate_code
here:
/** now relocate vectors*/bl relocate_vectors/* Set up final (full) environment */bl c_runtime_cpu_setup /* we still call old routine here */
#endif
#if !defined(CONFIG_SPL_BUILD) || defined(CONFIG_SPL_FRAMEWORK)
# ifdef CONFIG_SPL_BUILD/* Use a DRAM stack for the rest of SPL, if requested */bl spl_relocate_stack_gdcmp r0, #0movne sp, r0
# endifldr r0, =__bss_start /* this is auto-relocated! */#ifdef CONFIG_USE_ARCH_MEMSETldr r3, =__bss_end /* this is auto-relocated! */mov r1, #0x00000000 /* prepare zero to clear BSS */subs r2, r3, r0 /* r2 = memset len */bl memset
#elseldr r1, =__bss_end /* this is auto-relocated! */mov r2, #0x00000000 /* prepare zero to clear BSS */clbss_l:cmp r0, r1 /* while not at end of BSS */strlo r2, [r0] /* clear 32-bit BSS word */addlo r0, r0, #4 /* move to next */blo clbss_l
#endif#if ! defined(CONFIG_SPL_BUILD)bl coloured_LED_initbl red_led_on
#endif/* call board_init_r(gd_t *id, ulong dest_addr) */mov r0, r9 /* gd_t */ldr r1, [r9, #GD_RELOCADDR] /* dest_addr *//* call board_init_r */ldr pc, =board_init_r /* this is auto-relocated! *//* we should not return here. */
#endifENDPROC(_main)然后调用了 board_init_r 函数
common\board_r.c
void board_init_r(gd_t *new_gd, ulong dest_addr)
{
#ifdef CONFIG_NEEDS_MANUAL_RELOCint i;
#endif#ifdef CONFIG_AVR32mmu_init_r(dest_addr);
#endif#if !defined(CONFIG_X86) && !defined(CONFIG_ARM) && !defined(CONFIG_ARM64)gd = new_gd;
#endif#ifdef CONFIG_NEEDS_MANUAL_RELOCfor (i = 0; i < ARRAY_SIZE(init_sequence_r); i++)init_sequence_r[i] += gd->reloc_off;
#endifif (initcall_run_list(init_sequence_r)) //只是一个函数指针的数组,里面包含了一系列初始化函数hang();/* NOTREACHED - run_main_loop() does not return */hang();
}我们来看看这个init_sequence_r 为了更加清晰的看到他的流程,我删减了一部分代码
init_fnc_t init_sequence_r[] = {initr_trace,initr_reloc,/* TODO: could x86/PPC have this also perhaps? */
#ifdef CONFIG_ARMinitr_caches,
#endifinitr_reloc_global_data,。。。。。。。board_init, /* Setup chipselects */
#endif/** TODO: printing of the clock inforamtion of the board is now* implemented as part of bdinfo command. Currently only support for* davinci SOC's is added. Remove this check once all the board* implement this.*/。。。。。。。。INIT_FUNC_WATCHDOG_RESET
#ifdef CONFIG_SYS_DELAYED_ICACHEinitr_icache_enable,
#endif
#if defined(CONFIG_PCI) && defined(CONFIG_SYS_EARLY_PCI_INIT)/** Do early PCI configuration _before_ the flash gets initialised,* because PCU ressources are crucial for flash access on some boards.*/initr_pci,
#endif。。。。。。。
#ifdef CONFIG_ARCH_MISC_INITarch_misc_init, /* miscellaneous arch-dependent init */
#endif
#ifdef CONFIG_MISC_INIT_Rmisc_init_r, /* miscellaneous platform-dependent init */
#endifINIT_FUNC_WATCHDOG_RESET。。。。。。。
#if defined(CONFIG_X86) || defined(CONFIG_MICROBLAZE) || defined(CONFIG_AVR32) \|| defined(CONFIG_M68K)timer_init, /* initialize timer */
#endifINIT_FUNC_WATCHDOG_RESET/** Some parts can be only initialized if all others (like* Interrupts) are up and running (i.e. the PC-style ISA* keyboard).*/last_stage_init,
#endif
#ifdef CONFIG_CMD_BEDBUGINIT_FUNC_WATCHDOG_RESETinitr_bedbug,
#endif
#if defined(CONFIG_PRAM) || defined(CONFIG_LOGBUFFER)initr_mem,
#endif
#ifdef CONFIG_PS2KBDinitr_kbd,
#endif
#ifdef CONFIG_FSL_FASTBOOTinitr_check_fastboot,
#endifrun_main_loop,
};
这里满足宏条件的函数都会被执行,最后一个执行的函数是run_main_loop,我继续追踪下去,这个函数 还是在这个文件中board_r.c
static int run_main_loop(void)
{
#ifdef CONFIG_SANDBOXsandbox_main_loop_init();
#endif/* main_loop() can return to retry autoboot, if so just run it again */for (;;) //死循环main_loop();return 0;
}可以看见,这里是单向的,调用了run_main_loop就不会返回了,我们继续看看main_loop();
common\main.c
/* We come here after U-Boot is initialised and ready to process commands */
void main_loop(void)
{const char *s;。。。。。。。。。puts("#test!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!\n");modem_init();
#ifdef CONFIG_VERSION_VARIABLEsetenv("ver", version_string); /* set version variable */
#endif /* CONFIG_VERSION_VARIABLE */cli_init();run_preboot_environment_command();#if defined(CONFIG_UPDATE_TFTP)update_tftp(0UL);
#endif /* CONFIG_UPDATE_TFTP */s = bootdelay_process(); //uboot读秒,等待用户按键if (cli_process_fdt(&s))cli_secure_boot_cmd(s);printf("flag2");autoboot_command(s); //用户没有按键,执行环境参数命令cli_loop();
}我们 继续进入到 autoboot_command(s);
void autoboot_command(const char *s)
{debug("### main_loop: bootcmd=\"%s\"\n", s ? s : "<UNDEFINED>");if (stored_bootdelay != -1 && s && !abortboot(stored_bootdelay)) {
#if defined(CONFIG_AUTOBOOT_KEYED) && !defined(CONFIG_AUTOBOOT_KEYED_CTRLC)int prev = disable_ctrlc(1); /* disable Control C checking */
#endifrun_command_list(s, -1, 0); //传递过来的命令流s会在这里被解析执行#if defined(CONFIG_AUTOBOOT_KEYED) && !defined(CONFIG_AUTOBOOT_KEYED_CTRLC)disable_ctrlc(prev); /* restore Control C checking */
#endif}#ifdef CONFIG_MENUKEYif (menukey == CONFIG_MENUKEY) {s = getenv("menucmd");if (s)run_command_list(s, -1, 0);}
#endif /* CONFIG_MENUKEY */
}对于命令的解析执行,我们追踪 run_command_list(s, -1, 0);来分析分析
int run_command_list(const char *cmd, int len, int flag)
{int need_buff = 1;char *buff = (char *)cmd; /* cast away const */int rcode = 0;if (len == -1) {len = strlen(cmd);
#ifdef CONFIG_SYS_HUSH_PARSER/* hush will never change our string */need_buff = 0;
#else/* the built-in parser will change our string if it sees \n */need_buff = strchr(cmd, '\n') != NULL;
#endif}if (need_buff) {buff = malloc(len + 1);if (!buff)return 1;memcpy(buff, cmd, len);buff[len] = '\0';}
#ifdef CONFIG_SYS_HUSH_PARSERrcode = parse_string_outer(buff, FLAG_PARSE_SEMICOLON);
#else。。。。。。。。。
#endifreturn rcode;
}继续追踪parse_string_outer(buff, FLAG_PARSE_SEMICOLON);
#ifndef __U_BOOT__
static int parse_string_outer(const char *s, int flag)
#else
int parse_string_outer(const char *s, int flag)
#endif /* __U_BOOT__ */
{struct in_str input;
#ifdef __U_BOOT__char *p = NULL;int rcode;if (!s)return 1;if (!*s)return 0;if (!(p = strchr(s, '\n')) || *++p) {p = xmalloc(strlen(s) + 2);strcpy(p, s);strcat(p, "\n");setup_string_in_str(&input, p);rcode = parse_stream_outer(&input, flag);free(p);return rcode;} else {
#endifsetup_string_in_str(&input, s);return parse_stream_outer(&input, flag);
#ifdef __U_BOOT__}
#endif
}这里主要是对命令流进行了分割、执行。我们再继续追踪 parse_stream_outer(&input, flag);
/* most recursion does not come through here, the exeception is* from builtin_source() */
static int parse_stream_outer(struct in_str *inp, int flag)
{struct p_context ctx;o_string temp=NULL_O_STRING;int rcode;
#ifdef __U_BOOT__int code = 1;
#endifdo {ctx.type = flag;initialize_context(&ctx);update_ifs_map();if (!(flag & FLAG_PARSE_SEMICOLON) || (flag & FLAG_REPARSING)) mapset((uchar *)";$&|", 0);inp->promptmode=1;rcode = parse_stream(&temp, &ctx, inp,flag & FLAG_CONT_ON_NEWLINE ? -1 : '\n');
#ifdef __U_BOOT__if (rcode == 1) flag_repeat = 0;
#endifif (rcode != 1 && ctx.old_flag != 0) {syntax();
#ifdef __U_BOOT__flag_repeat = 0;
#endif}if (rcode != 1 && ctx.old_flag == 0) {done_word(&temp, &ctx);done_pipe(&ctx,PIPE_SEQ);
#ifndef __U_BOOT__run_list(ctx.list_head); //执行命令
#else。。。。。。。。
#endif} else {if (ctx.old_flag != 0) {free(ctx.stack);b_reset(&temp);}
#ifdef __U_BOOT__if (inp->__promptme == 0) printf("<INTERRUPT>\n");inp->__promptme = 1;
#endiftemp.nonnull = 0;temp.quote = 0;inp->p = NULL;free_pipe_list(ctx.list_head,0);}b_free(&temp);/* loop on syntax errors, return on EOF */} while (rcode != -1 && !(flag & FLAG_EXIT_FROM_LOOP) &&(inp->peek != static_peek || b_peek(inp)));
#ifndef __U_BOOT__return 0;
#elsereturn (code != 0) ? 1 : 0;
#endif /* __U_BOOT__ */
}追踪run_list(ctx.list_head);
/* Select which version we will use */
static int run_list(struct pipe *pi)
{int rcode=0;
#ifndef __U_BOOT__if (fake_mode==0) {
#endifrcode = run_list_real(pi);
#ifndef __U_BOOT__}
#endif/* free_pipe_list has the side effect of clearing memory* In the long run that function can be merged with run_list_real,* but doing that now would hobble the debugging effort. */free_pipe_list(pi,0);
return rcode;
}追踪 run_list_real(pi);
static int run_list_real(struct pipe *pi)
{char *save_name = NULL;char **list = NULL;char **save_list = NULL;struct pipe *rpipe;int flag_rep = 0;
#ifndef __U_BOOT__int save_num_progs;
#endifint rcode=0, flag_skip=1;int flag_restore = 0;int if_code=0, next_if_code=0; /* need double-buffer to handle elif */reserved_style rmode, skip_more_in_this_rmode=RES_XXXX;/* check syntax for "for" */for (rpipe = pi; rpipe; rpipe = rpipe->next) {if ((rpipe->r_mode == RES_IN ||rpipe->r_mode == RES_FOR) &&(rpipe->next == NULL)) {syntax();
#ifdef __U_BOOT__flag_repeat = 0;
#endifreturn 1;}if ((rpipe->r_mode == RES_IN &&(rpipe->next->r_mode == RES_IN &&rpipe->next->progs->argv != NULL))||(rpipe->r_mode == RES_FOR &&rpipe->next->r_mode != RES_IN)) {syntax();
#ifdef __U_BOOT__flag_repeat = 0;
#endifreturn 1;}}for (; pi; pi = (flag_restore != 0) ? rpipe : pi->next) {if (pi->r_mode == RES_WHILE || pi->r_mode == RES_UNTIL ||pi->r_mode == RES_FOR) {
#ifdef __U_BOOT__。。。。。。。。。。
#endif。。。。。。。。。。
#ifndef __U_BOOT__pi->progs->glob_result.gl_pathv[0] =pi->progs->argv[0];
#endifcontinue;} else {/* insert new value from list for variable */if (pi->progs->argv[0])free(pi->progs->argv[0]);pi->progs->argv[0] = *list++;
#ifndef __U_BOOT__pi->progs->glob_result.gl_pathv[0] =pi->progs->argv[0];
#endif}}if (rmode == RES_IN) continue;if (rmode == RES_DO) {if (!flag_rep) continue;}if (rmode == RES_DONE) {if (flag_rep) {flag_restore = 1;} else {rpipe = NULL;}}if (pi->num_progs == 0) continue;
#ifndef __U_BOOT__save_num_progs = pi->num_progs; /* save number of programs */
#endifrcode = run_pipe_real(pi); //执行debug_printf("run_pipe_real returned %d\n",rcode);
#ifndef __U_BOOT__if (rcode!=-1) {/* We only ran a builtin: rcode was set by the return value* of run_pipe_real(), and we don't need to wait for anything. */} else if (pi->followup==PIPE_BG) {/* XXX check bash's behavior with nontrivial pipes *//* XXX compute jobid *//* XXX what does bash do with attempts to background builtins? */insert_bg_job(pi);rcode = EXIT_SUCCESS;} else {。。。。。。。} else {rcode = checkjobs(pi);}debug_printf("checkjobs returned %d\n",rcode);}last_return_code=rcode;
#elseif (rcode < -1) {last_return_code = -rcode - 2;return -2; /* exit */}last_return_code=(rcode == 0) ? 0 : 1;
#endif
#ifndef __U_BOOT__pi->num_progs = save_num_progs; /* restore number of programs */
#endifif ( rmode == RES_IF || rmode == RES_ELIF )next_if_code=rcode; /* can be overwritten a number of times */if (rmode == RES_WHILE)flag_rep = !last_return_code;if (rmode == RES_UNTIL)flag_rep = last_return_code;if ( (rcode==EXIT_SUCCESS && pi->followup==PIPE_OR) ||(rcode!=EXIT_SUCCESS && pi->followup==PIPE_AND) )skip_more_in_this_rmode=rmode;
#ifndef __U_BOOT__checkjobs(NULL);
#endif}return rcode;
}追踪 rcode = run_pipe_real(pi);
/* run_pipe_real() starts all the jobs, but doesn't wait for anything* to finish. See checkjobs().** return code is normally -1, when the caller has to wait for children* to finish to determine the exit status of the pipe. If the pipe* is a simple builtin command, however, the action is done by the* time run_pipe_real returns, and the exit code is provided as the* return value.** The input of the pipe is always stdin, the output is always* stdout. The outpipe[] mechanism in BusyBox-0.48 lash is bogus,* because it tries to avoid running the command substitution in* subshell, when that is in fact necessary. The subshell process* now has its stdout directed to the input of the appropriate pipe,* so this routine is noticeably simpler.*/
static int run_pipe_real(struct pipe *pi)
{int i;
#ifndef __U_BOOT__int nextin, nextout;int pipefds[2]; /* pipefds[0] is for reading */struct child_prog *child;struct built_in_command *x;char *p;
# if __GNUC__/* Avoid longjmp clobbering */(void) &i;(void) &nextin;(void) &nextout;(void) &child;
# endif
#elseint nextin;int flag = do_repeat ? CMD_FLAG_REPEAT : 0;struct child_prog *child;char *p;
# if __GNUC__/* Avoid longjmp clobbering */(void) &i;(void) &nextin;(void) &child;
# endif
#endif /* __U_BOOT__ */nextin = 0;
#ifndef __U_BOOT__pi->pgrp = -1;
#endif/* Check if this is a simple builtin (not part of a pipe).* Builtins within pipes have to fork anyway, and are handled in* pseudo_exec. "echo foo | read bar" doesn't work on bash, either.*/if (pi->num_progs == 1) child = & (pi->progs[0]);
#ifndef __U_BOOT__。。。。。。。
#elseif (pi->num_progs == 1 && child->group) {int rcode;debug_printf("non-subshell grouping\n");rcode = run_list_real(child->group);
#endif
return rcode;} else if (pi->num_progs == 1 && pi->progs[0].argv != NULL) {for (i=0; is_assignment(child->argv[i]); i++) { /* nothing */ }if (i!=0 && child->argv[i]==NULL) {/* assignments, but no command: set the local environment */for (i=0; child->argv[i]!=NULL; i++) {/* Ok, this case is tricky. We have to decide if this is a* local variable, or an already exported variable. If it is* already exported, we have to export the new value. If it is* not exported, we need only set this as a local variable.* This junk is all to decide whether or not to export this* variable. */int export_me=0;char *name, *value;name = xstrdup(child->argv[i]);debug_printf("Local environment set: %s\n", name);value = strchr(name, '=');if (value)*value=0;
#ifndef __U_BOOT__if ( get_local_var(name)) {export_me=1;}
#endiffree(name);p = insert_var_value(child->argv[i]);set_local_var(p, export_me);if (p != child->argv[i]) free(p);}
return EXIT_SUCCESS; /* don't worry about errors in set_local_var() yet */}for (i = 0; is_assignment(child->argv[i]); i++) {p = insert_var_value(child->argv[i]);
#ifndef __U_BOOT__putenv(strdup(p));
#elseset_local_var(p, 0);
#endifif (p != child->argv[i]) {child->sp--;free(p);}}if (child->sp) {char * str = NULL;str = make_string(child->argv + i,child->argv_nonnull + i);parse_string_outer(str, FLAG_EXIT_FROM_LOOP | FLAG_REPARSING);free(str);
return last_return_code;}
#ifndef __U_BOOT__。。。。。。。。
#else/* check ";", because ,example , argv consist from* "help;flinfo" must not execute*/if (strchr(child->argv[i], ';')) {printf("Unknown command '%s' - try 'help' or use ""'run' command\n", child->argv[i]);
return -1;}/* Process the command */
return cmd_process(flag, child->argc, child->argv,&flag_repeat, NULL);
#endif}追踪 cmd_process(flag, child->argc, child->argv, &flag_repeat, NULL);
enum command_ret_t cmd_process(int flag, int argc, char * const argv[],int *repeatable, ulong *ticks)
{enum command_ret_t rc = CMD_RET_SUCCESS;cmd_tbl_t *cmdtp;/* Look up command in command table */cmdtp = find_cmd(argv[0]);if (cmdtp == NULL) {printf("Unknown command '%s' - try 'help'\n", argv[0]);return 1;}/* found - check max args */if (argc > cmdtp->maxargs)rc = CMD_RET_USAGE;#if defined(CONFIG_CMD_BOOTD)/* avoid "bootd" recursion */else if (cmdtp->cmd == do_bootd) {if (flag & CMD_FLAG_BOOTD) {puts("'bootd' recursion detected\n");rc = CMD_RET_FAILURE;} else {flag |= CMD_FLAG_BOOTD;}}
#endif/* If OK so far, then do the command */if (!rc) {if (ticks)*ticks = get_timer(0);rc = cmd_call(cmdtp, flag, argc, argv);if (ticks)*ticks = get_timer(*ticks);*repeatable &= cmdtp->repeatable;}if (rc == CMD_RET_USAGE)rc = cmd_usage(cmdtp);return rc;
}命令最终在这里被执行,以上一系列过程 将收到的指令通过一系列字符处理然后加入一个执行列表,然后执行这个列表。这些命令的的具体实现大家可以 执行 find -name ./common/cmd*.c
这些文件里定义了命令的具体实现。
比如我们mmc read xx xx命令,在common\cmd_mmc.c :842中,大家可以具体去看看,其实读秒过后的,系统自动执行了一系列环境变量()中保存的命令,执行命令这一套的通用的,只是命令的来源不一样,一个是用户输入的,一个是从环境命令中读取的。我们可以做个实验,在parse_string_outer函数中添加如下代码
#ifndef __U_BOOT__
static int parse_string_outer(const char *s, int flag)
#else
int parse_string_outer(const char *s, int flag)
#endif /* __U_BOOT__ */
{struct in_str input;
#ifdef __U_BOOT__char *p = NULL;int rcode;if (!s)return 1;if (!*s)return 0;if (!(p = strchr(s, '\n')) || *++p) {p = xmalloc(strlen(s) + 2)printf("#stream =%s \n", s); //yinstrcpy(p, s);strcat(p, "\n");printf("#hush\n"); //yinsetup_string_in_str(&input, p);rcode = parse_stream_outer(&input, flag);free(p);return rcode;} else {
#endifsetup_string_in_str(&input, s);return parse_stream_outer(&input, flag);
#ifdef __U_BOOT__}
#endif
}然后编译,烧写,启动,观察输出信息
U-Boot 2015.04 (Mar 16 2018 - 18:45:12)CPU: Freescale i.MX6Q rev1.5 at 792 MHz
CPU: Temperature 35 C
Reset cause: POR
Board: MYZR i.MX6 Evaluation Kit
Model: MY-IMX6-EK314-6Q-1G
I2C: ready
DRAM: 1 GiB
MMC: FSL_SDHC: 0, FSL_SDHC: 1
SF: Detected SST25VF016B with page size 256 Bytes, erase size 4 KiB, total 2 MiB
*** Warning - bad CRC, using default environmentNo panel detected: default to Hannstar-XGA
Display: Hannstar-XGA (1024x600)
In: serial
Out: serial
Err: serial
Net: using phy at 5
FEC [PRIME]
#test!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!
Normal Boot
flag1
flag2Hit any key to stop autoboot: 0
#run start
stream = mmc dev ${mmcdev}; if run loadimage; then run mmcboot; else run netboot; fi;
#hush
switch to partitions #0, OK
mmc1(part 0) is current device
stream = fatload mmc ${mmcdev}:${mmcpart} ${loadaddr} ${image_file}
#hush
reading zImage-myimx6
5602432 bytes read in 157 ms (34 MiB/s)
stream = echo Booting from mmc ...; run mmcargs; if run loadfdt; then bootz ${loadaddr} - ${fdt_addr}; else echo WARN: Cannot boot from mmc; fi;
#hush
Booting from mmc ...
stream = run set_disp; setenv bootargs console=${console},${baudrate} ${smp} cma=320M root=${mmcroot} ${disp_args}
#hush
stream = setenv disp_args ${display}
#hush
stream = fatload mmc ${mmcdev}:${mmcpart} ${fdt_addr} ${fdt_file}
#hush
reading myimx6ek314-6q.dtb
42887 bytes read in 18 ms (2.3 MiB/s)
Kernel image @ 0x12000000 [ 0x000000 - 0x557c80 ]
## Flattened Device Tree blob at 18000000Booting using the fdt blob at 0x18000000Using Device Tree in place at 18000000, end 1800d786Starting kernel ...分析到这里想必大家都有了自己想法,剩下的就交给你们去探索了,这里仅仅是个抛砖引玉,做个粗浅的分析,感谢您耐着性子读到这里,哈哈哈~~
lornyin 2018/3/17
)



、开启新内核)






--习题及答案技术总结.docx)



)



