两点需要注意的.
第一是在构造函数声明时,会同时创建一个该构造函数的原型对象,而该原型对象是继承自Object的原型对象
// 声明一个构造函数Rectengle
function Rectangle(length, width) {this.length = length;this.width = width;
}// 即:看见function 后面函数名是大写,一般认为其是一个构造函数,同时函数都会有一个prototype属性
// Rectangle.prototype的[[Prototype]]属性默认指向Object.prototype属性.
// 即:Rectangle.prototype.__proto__ === Object.prototype// 打印出来看看,,
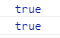
console.log(Rectangle.prototype.__proto__ === Object.prototype);
console.log(Object.prototype.isPrototypeOf(Rectangle));
第二点是,使用new操作符,如 p = new P();
等号左侧会有一个[[Prototype]]属性(浏览器中可以使用__proto__读取),指向P.prototype
// 于是,可以尝试将左侧的p改为一个自定义的构造函数,如下:// 自定义Rectangle构造函数
function Rectangle(length, width) {this.length = length;this.width = width;
}// 给Rectangle的原型添加一个getArea()方法
Recangle.prototype.getArea = function() {return this.length* this.width;
}// Square构造函数
function Square(size) {this.length = size;this.width = size;
}// Square继承Rectangle(实际上是是Square的原型对象指向构造函数Rectangle)
Square.prototype = new Rectangle();var sq1 = new Square(2);
console.log(sq1.getArea()); // 4// 执行sq1.getArea()方法时,JavaScript引擎实际上是按如下方式工作的:
// 首先在sq1中寻找getArea(),未找到
// 在顺着sq1的[[Prototype]]属性,找到sq1的原型Square.prototype,并在原型中查找,未找到
// 数着Square.prototype的[[Prototype]]属性找到其原型Rectangle.prototype,找到了..执行getArea()方法
所以继承的实质就是让,A的原型对象(A.prototype)成为另一个构造函数的实例,
就可以在A的实例中使用父元素的方法和属性了
参考《JavaScript面向对象精要》P72~P73


![[树形dp] Jzoj P1046 寻宝之旅](http://pic.xiahunao.cn/[树形dp] Jzoj P1046 寻宝之旅)

二)













)
