文献速递:生成对抗网络医学影像中的应用——基于CycleGAN的图像到图像转换,用于逼真的外科手术训练模型
本周给大家分享文献的主题是生成对抗网络(Generative adversarial networks, GANs)在医学影像中的应用。文献的研究内容包括同模态影像生成、跨模态影像生成、GAN在分类和分割方面的应用等。生成对抗网络与其他方法相比展示出了优越的数据生成能力,使它们在医学图像应用中广受欢迎。这些特性引起了医学成像领域研究人员的浓厚兴趣,导致这些技术在各种传统和新颖应用中迅速实施,如图像重建、分割、检测、分类和跨模态合成。
01
文献速递介绍
外科手术训练对于发展技能和灵巧性至关重要。为了获得必要的经验,外科医生需要数千小时的实践。在内窥镜微创手术中,任务更加具有挑战性。为了避免仅与真实病人进行训练,外科医生通常在离体器官、虚拟模拟器或物理训练幻影上发展他们的技能。物理训练幻影为缝合和使用真实仪器操作提供了出色的触觉反馈和组织特性,并且易于获得。此外,它们可以为特定病人解剖定制,并为期望的程序进行优化 。在不同的范围内,外科训练幻影甚至可以用于开发额外的外科应用,如自动外科阶段识别。然而,它们缺乏生命力和不现实的外观,并不反映外科场景的复杂环境 。正如 Engelhardt 等人 所提出的,超现实主义是一种新的增强现实范式,旨在通过将手术过程中的域内模式映射到在这些外科模拟器训练期间捕获的视频流上,解决物理幻影中缺乏现实感的问题。通过生成模型,可以实现从一幅图像到另一幅图像的特征映射。这些生成模型存在不同的方法和概念,即应用变分自编码器(VAE)或生成对抗网络(GANs)。近年来,GANs 在图像合成和图像到图像转换 (I2I) 方面表现出了巨大的潜力 。
最近,已经开发了具有不同架构的几种 GAN 模型,这些架构高度依赖于用作输入的信息类型。对于这种每个域的图像都是未配对的特定域适应任务,CycleGAN 模型已显示出有希望的结果。 本工作的目标是从未配对的合成训练幻影图像生成逼真的二尖瓣术中图像。我们旨在使用 CycleGAN 生成模型实现成功的 I2I 转换,并进行以下实验:
- 研究最合适的训练损失函数;
- 建立训练和图像质量度量标准,以实现客观和定量的结果评估;
- 评估输入变异性对模型性能的影响。
Title
题目
CycleGAN-Based Image to Image Translation for Realistic SurgicalTraining Phantoms
基于CycleGAN的图像到图像转换,用于逼真的外科手术训练模型
Abstract
摘要
Training in surgery is essential for surgeons to develop skill and dexterity. Physical training phantoms provide excellent haptic feedback and tissue properties for stitching and operating with authentic instruments and are easily available. However, they lack realistic traits and fail to reflect the complex environment of a surgical scene. Generative Adversarial Networks can be used for image-to-image translation,addressing the lack of realism in physical phantoms, by mapping patterns from the intraoperative domain onto the video stream captured during training with these surgical simulators. This work aims to achieve a successful I2I translation, from intra
operatory mitral valve surgery images onto a surgical simulator,using the CycleGAN model. Different experiments are performed - comparing the Mean Square Error Loss with the Binary Cross Entropy Loss; validating the Fréchet Inception Distance as a training and image quality metric; and studying the impact of input variability on the model performance.Differences between .
MSE and BCE are modest, with MSE being marginally more robust. The FID score proves to be very useful in identifying the best training epochs for the CycleGAN I2I translation architecture. Carefully selecting the input images**can have a great impact in the end results. Using less style variability and input images with good feature details and clearly defined characteristics enables the network to achieve better results.
Clinical Relevance— This work further contributes for the domain of realistic surgical training, successfully generating fake intra operatory images from a surgical simulator of thecardiac mitral valve.
外科手术训练对于外科医生培养技能和灵巧性至关重要。物理训练模型提供了极佳的触感反馈和缝合以及使用真实器械操作的组织特性,并且容易获得。然而,它们缺乏逼真的特质,无法反映外科手术现场的复杂环境。生成对抗网络可用于图像到图像的转换,通过将术中领域的模式映射到在这些外科模拟器训练期间捕获的视频流中,解决物理模型缺乏现实感的问题。这项工作旨在使用CycleGAN模型实现从术中二尖瓣手术图像到外科模拟器的成功I2I(Image-to-Image)转换。进行了不同的实验 - 比较均方误差损失与二元交叉熵损失;验证Fréchet Inception Distance作为训练和图像质量指标;以及研究输入变异性对模型性能的影响。
MSE和BCE之间的差异较小,MSE略微更加稳健。FID得分在确定CycleGAN I2I转换架构的最佳训练时期方面非常有用。仔细选择输入图像可以对最终结果产生很大影响。使用风格变异性较小且输入图像具有良好特征细节和清晰定义的特征可以使网络取得更好的结果。
临床相关性 - 这项工作为逼真的外科手术训练领域做出了进一步的贡献,成功地从心脏二尖瓣的外科模拟器生成了虚假的术中图像。
Methods
方法
A. Image to Image translation using CycleGAN The goal of I2I is to convert an input image from a source domain A to a target domain B. Ideally the extrinsic target style (domain specific features) should be transferred withoutaltering the inherent physical content of the source domain.
A. 使用 CycleGAN 进行图像到图像的转换 图像到图像转换的目标是将输入图像从源域 A 转换到目标域 B。理想情况下,应该转换外在的目标风格(特定于域的特征),而不改变源域的固有物理内容。
Results
结果
Figure 3 displays some of the results obtained with the previously described experiments. Three frames from the validation data set were selected based on the presence of specific attributes, such as surgical instruments in a large area of the image, suture wires with different colors and clear contact points with the phantom and, finally, a frame in which the surgical wires overlap with the surgical instrument. The image shows the best and worst FID results for both MSE and BCE losses, from all training epochs.
The final experiment results, comparing the performance of the GAN with one single surgical style input, are shown in Figure 4. The same frames were used in order to enable a better
comparison with the experiments with 3 surgical styles. Again, the best and worst FID results for both MSE and BCE losses, from all training epochs, are displayed.
图3展示了之前描述实验中获得的一些结果。根据特定属性的存在,从验证数据集中选择了三个帧,例如手术工具占据大面积的图像、不同颜色的缝合线和与幻影明显接触的点,以及手术线与手术工具重叠的一个帧。该图像显示了MSE和BCE损失下的所有训练周期中最佳和最差的FID结果。
最终实验结果,比较了仅使用单一手术风格输入的GAN的性能,在图4中展示。为了更好地与使用3种手术风格的实验进行比较,使用了相同的帧。同样,展示了MSE和BCE损失下的所有训练周期中最佳和最差的FID结果。
Conclusions
结论
MSE Loss is more stable than BCE Loss as, usually, better results are achieved, in a fewer number of epochs. The FID score proves be very useful in identifying the best training epochs for the CycleGAN I2I translation architecture. Carefully selecting the input images can cause a big impact on the end results. Images can be from multiple domains, however using images, with good feature details and clearly defined characteristics, enables the network to achieve better results. Not using sets of images that feature specific instruments, that do not appear in the simulator domain, further potentiates the network performance.
与BCE损失相比,MSE损失更稳定,通常在较少的训练周期内就能达到更好的结果。FID得分在识别CycleGAN图像到图像(I2I)翻译架构的最佳训练周期方面证明非常有用。仔细选择输入图像可以对最终结果产生重大影响。图像可以来自多个领域,但使用具有良好特征细节和清晰定义特性的图像,可以使网络获得更好的结果。不使用特定仪器的图像集,这些仪器在模拟器领域中不出现,进一步增强了网络性能。
Figure
图
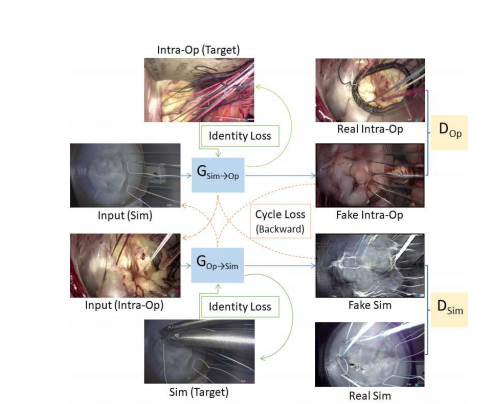
Figure 1 - CycleGAN architecture. The Generator network path is represented in blue and the Discriminator in yellow. Cycle loss is schematized in orange, with a backward flow. The identity loss input is shown in green.
图1 - CycleGAN架构。生成器网络路径用蓝色表示,判别器用黄色表示。循环损失用橙色示意,带有反向流动。身份损失输入用绿色显示。
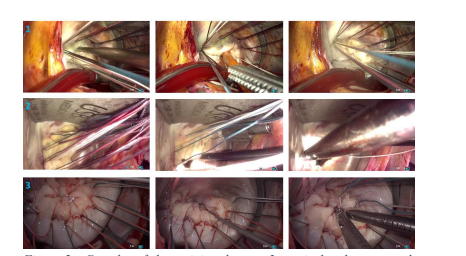
Figure 2 - Samples of the training dataset. 3 surgical styles are used,numbered 1 to 3 from top to bottom.
图2 - 训练数据集的样本。使用了3种手术风格,从上到下编号为1至3。
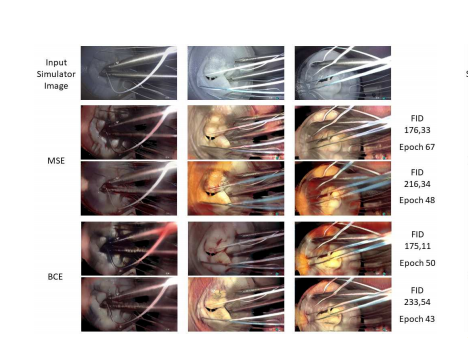
Figure 3 - Selection of images to show the obtained results for both losses.Top row: original phantom image. 2nd and 3rd rows: best and worst FIDscores for MSE, respectively. 4th and 5th rows: best and worst FID scores for BCE, respectively.
图3 - 选择图像以显示两种损失所获得的结果。
顶部行:原始幻影图像。第2和第3行:分别为MSE的最佳和最差FID得分。第4和第5行:分别为BCE的最佳和最差FID得分。
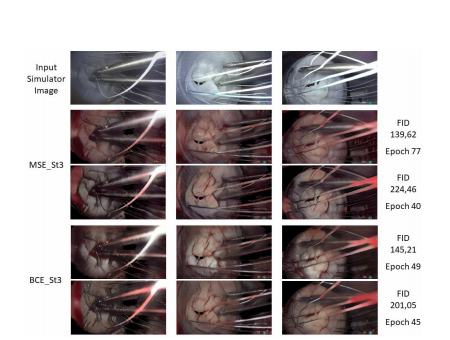
Figure 4 - Selection of images to show the obtained results using only surgical style 3 as input. Top row: original phantom image. 2nd and 3rd
rows: best and worst FID scores for MSE, respectively. 4th and 5th rows: best and worst FID scores for BCE, respectively.*
图4 - 选择图像以显示仅使用手术风格3作为输入获得的结果。


.)

)










工具,太实用了!)



