GKE是 Google Cloud Platform 提供的托管 Kubernetes 服务,允许用户在 Google 的基础设施上部署、管理和扩展容器。本文介绍如何部署一个简单的springboot项目到GKE.
本文使用podman.
如果你用的是docker, 只需要把本文中所有命令中的podman替换成docker即可
- 非Helm部署方式
准备工作: 在springboot项目路径下,新增3个文件:deployment.yaml,service.yaml,Dockerfile:
结构如下:
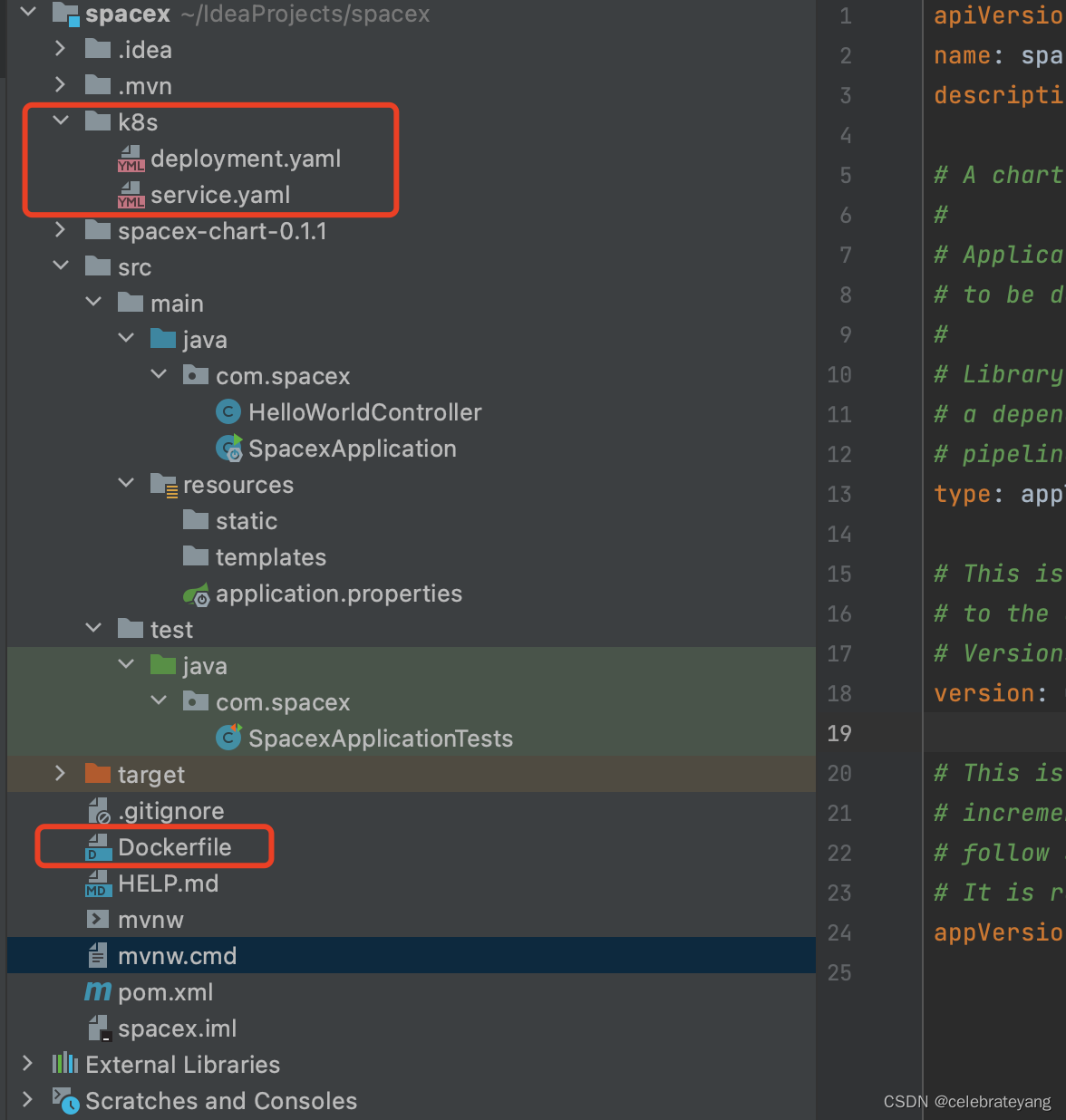
deployment.yaml, 注意文件里的image地址,由后续podman push image gcr.io后得到
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:name: springboot-app
spec:replicas: 1selector:matchLabels:app: springboot-apptemplate:metadata:labels:app: springboot-appspec:containers:- name: springboot-appimage: gcr.io/xxxx/yyyy/springboot-app@sha256:3725a57f9cd0b6fb63eb91e49c2305a6b684abd129f3f075838a80b54472455cports:- containerPort: 8080
service.yaml
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:name: springboot-app-service
spec:type: LoadBalancerselector:app: springboot-appports:- protocol: TCPport: 80targetPort: 8080
Dockerfile
# 使用Amazon Corretto 17作为构建环境
FROM amazoncorretto:17 as build
WORKDIR /workspace/app# 复制Maven Wrapper和其他构建文件
COPY mvnw .
COPY .mvn .mvn
COPY pom.xml .
COPY src src# 使用Maven Wrapper进行构建,跳过测试
RUN ./mvnw install -DskipTests# 使用Amazon Corretto 17作为生产环境
FROM amazoncorretto:17
VOLUME /tmp
ARG JAR_FILE=/workspace/app/target/*.jar
COPY --from=build ${JAR_FILE} app.jar
ENTRYPOINT ["java","-jar","/app.jar"]
podman build -t gcr.io/xxxx/yyyy/springboot-app:v1 .
podman push gcr.io/xxxx/yyyy/springboot-app:v1
会生成如下路径
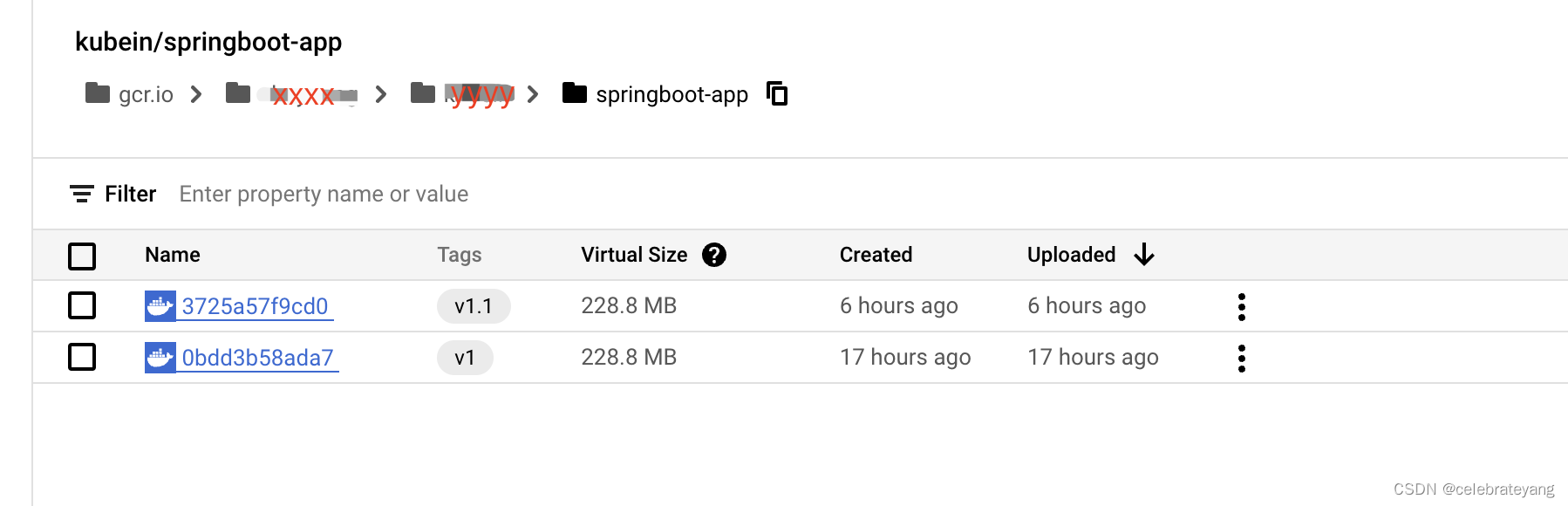
kubectl apply -f deployment.yaml -n infra --使用这个命令之前,先修改一下image的地址。
kubectl apply -f service.yaml -n infra
ok啦,此时你应该可以访问你的应用了。
- Helm部署方式
a. helm create spacex-chart -n infra
生成的chart目录结构如下:
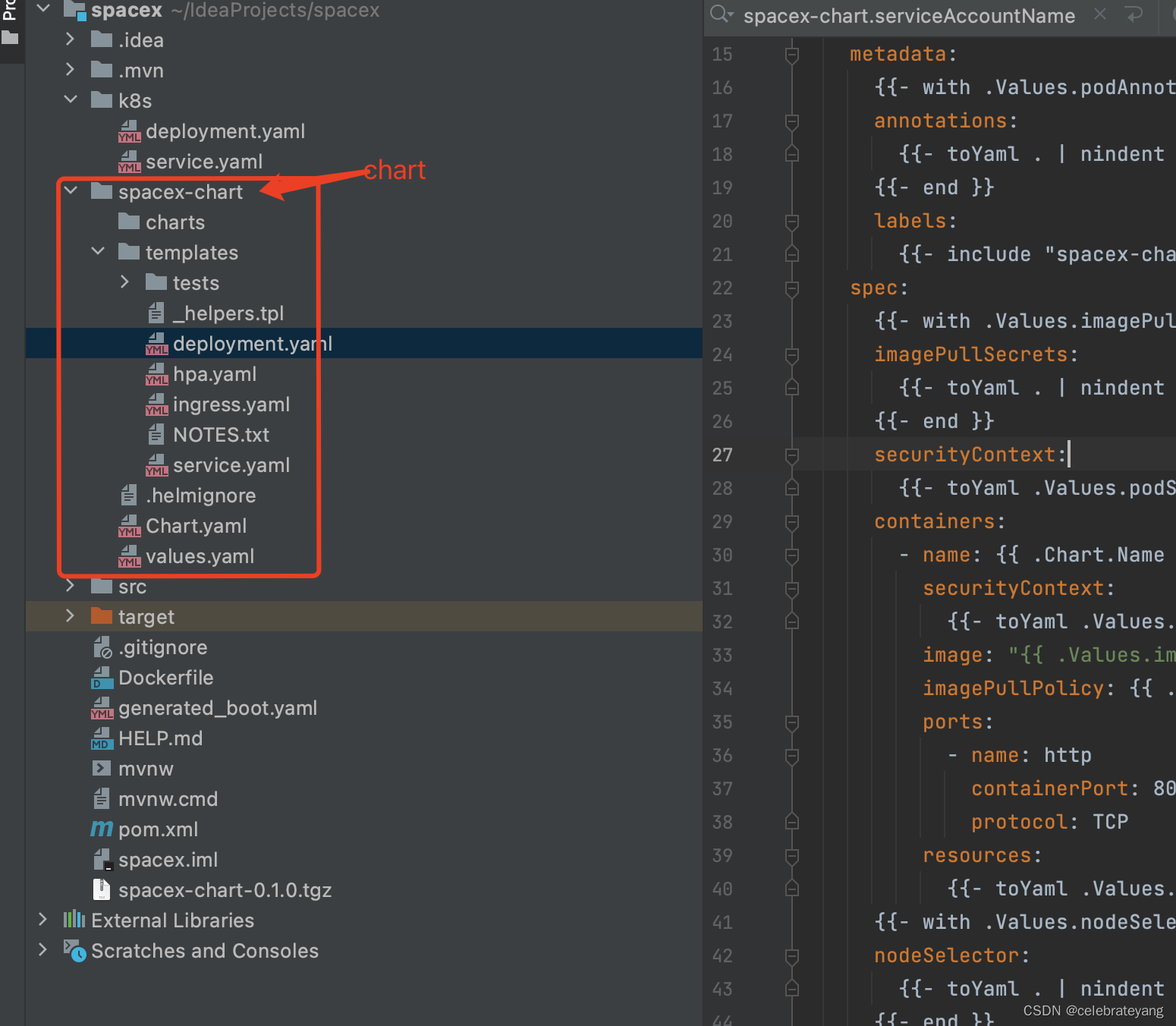
关于values的优先级:
命令行参数或自定义 values.yaml > 集群中存储的值 > Chart 的默认 values.yaml
可以用这个命令查看生成的k8s组件是否符合你的预期。
helm template spacex-chart ./spacex-chart
--values=./spacex-chart/values.yaml > generated_boot.yaml
b. 修改一些文件,修改过的文件如下: 另外还移除了service-account等一些不必要的文件
values.yaml
# Default values for spacex-chart.
# This is a YAML-formatted file.
# Declare variables to be passed into your templates.replicaCount: 1image:repository: gcr.io/ebay-mag/kubein/springboot-apppullPolicy: IfNotPresent# Overrides the image tag whose default is the chart appVersion.tag: "v1.1"imagePullSecrets: []
nameOverride: ""
fullnameOverride: ""service:type: LoadBalancerport: 80targetPort: 8080ingress:enabled: falseclassName: ""annotations: {}# kubernetes.io/ingress.class: nginx# kubernetes.io/tls-acme: "true"hosts:- host: chart-example.localpaths:- path: /pathType: ImplementationSpecifictls: []# - secretName: chart-example-tls# hosts:# - chart-example.localresources: {}# We usually recommend not to specify default resources and to leave this as a conscious# choice for the user. This also increases chances charts run on environments with little# resources, such as Minikube. If you do want to specify resources, uncomment the following# lines, adjust them as necessary, and remove the curly braces after 'resources:'.# limits:# cpu: 100m# memory: 128Mi# requests:# cpu: 100m# memory: 128Miautoscaling:enabled: falseminReplicas: 1maxReplicas: 2targetCPUUtilizationPercentage: 80# targetMemoryUtilizationPercentage: 80nodeSelector: {}tolerations: []affinity: {}
deployment.yaml
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:name: {{ include "spacex-chart.fullname" . }}labels:{{- include "spacex-chart.labels" . | nindent 4 }}
spec:{{- if not .Values.autoscaling.enabled }}replicas: {{ .Values.replicaCount }}{{- end }}selector:matchLabels:{{- include "spacex-chart.selectorLabels" . | nindent 6 }}template:metadata:{{- with .Values.podAnnotations }}annotations:{{- toYaml . | nindent 8 }}{{- end }}labels:{{- include "spacex-chart.selectorLabels" . | nindent 8 }}spec:{{- with .Values.imagePullSecrets }}imagePullSecrets:{{- toYaml . | nindent 8 }}{{- end }}securityContext:{{- toYaml .Values.podSecurityContext | nindent 8 }}containers:- name: {{ .Chart.Name }}securityContext:{{- toYaml .Values.securityContext | nindent 12 }}image: "{{ .Values.image.repository }}:{{ .Values.image.tag | default .Chart.AppVersion }}"imagePullPolicy: {{ .Values.image.pullPolicy }}ports:- name: httpcontainerPort: 80protocol: TCPresources:{{- toYaml .Values.resources | nindent 12 }}{{- with .Values.nodeSelector }}nodeSelector:{{- toYaml . | nindent 8 }}{{- end }}{{- with .Values.affinity }}affinity:{{- toYaml . | nindent 8 }}{{- end }}{{- with .Values.tolerations }}tolerations:{{- toYaml . | nindent 8 }}{{- end }}
service.yaml
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:name: {{ include "spacex-chart.fullname" . }}labels:{{- include "spacex-chart.labels" . | nindent 4 }}
spec:type: {{ .Values.service.type }}ports:- port: {{ .Values.service.port }}targetPort: {{ .Values.service.targetPort }}protocol: TCPname: httpselector:{{- include "spacex-chart.selectorLabels" . | nindent 4 }}
c. 安装 helm install boot-chart-release-001 spacex-chart -n infra
命令解释 helm install [release-name] [chart-name] -n infra,此时我们用helm ls可以查看安装chart后的一些对应关系

ok, 此时应用已经部署到GKE中了,你可以通过ip访问你的应用了。Happy Helming!
安装完后,如果发现需要修改values.yaml里面的值.在修改完values.yaml文件后,用如下命令更新。
helm upgrade boot-chart-release-001 spacex-chart -f spacex-chart/values.yaml -n infra
查看更新后的值
helm get values boot-chart-release-001 -n infra
![LeetCode [中等]二叉树的右视图(层序](http://pic.xiahunao.cn/LeetCode [中等]二叉树的右视图(层序)









)


:函数模板的匹配原则,类模板的实例化)





