原文:🦜️🏓 LangServe | 🦜️🔗 Langchain
LangServe
🚩 We will be releasing a hosted version of LangServe for one-click deployments of LangChain applications. Sign up here to get on the waitlist.
Overview
LangServe helps developers deploy LangChain runnables and chains as a REST API.
This library is integrated with FastAPI and uses pydantic for data validation.
In addition, it provides a client that can be used to call into runnables deployed on a server. A javascript client is available in LangChainJS.
Features
- Input and Output schemas automatically inferred from your LangChain object, and enforced on every API call, with rich error messages
- API docs page with JSONSchema and Swagger (insert example link)
- Efficient
/invoke,/batchand/streamendpoints with support for many concurrent requests on a single server /stream_logendpoint for streaming all (or some) intermediate steps from your chain/agent- Playground page at
/playgroundwith streaming output and intermediate steps - Built-in (optional) tracing to LangSmith, just add your API key (see Instructions])
- All built with battle-tested open-source Python libraries like FastAPI, Pydantic, uvloop and asyncio.
- Use the client SDK to call a LangServe server as if it was a Runnable running locally (or call the HTTP API directly)
- LangServe Hub
Limitations
- Client callbacks are not yet supported for events that originate on the server
- OpenAPI docs will not be generated when using Pydantic V2. Fast API does not support mixing pydantic v1 and v2 namespaces. See section below for more details.
Hosted LangServe
We will be releasing a hosted version of LangServe for one-click deployments of LangChain applications. Sign up here to get on the waitlist.
Security
- Vulnerability in Versions 0.0.13 - 0.0.15 -- playground endpoint allows accessing arbitrary files on server. Resolved in 0.0.16.
Installation
For both client and server:
pip install "langserve[all]"
or pip install "langserve[client]" for client code, and pip install "langserve[server]" for server code.
LangChain CLI 🛠️
Use the LangChain CLI to bootstrap a LangServe project quickly.
To use the langchain CLI make sure that you have a recent version of langchain-cli installed. You can install it with pip install -U langchain-cli.
langchain app new ../path/to/directory
Examples
Get your LangServe instance started quickly with LangChain Templates.
For more examples, see the templates index or the examples directory.
Server
Here's a server that deploys an OpenAI chat model, an Anthropic chat model, and a chain that uses the Anthropic model to tell a joke about a topic.
#!/usr/bin/env python
from fastapi import FastAPI
from langchain.prompts import ChatPromptTemplate
from langchain.chat_models import ChatAnthropic, ChatOpenAI
from langserve import add_routesapp = FastAPI(title="LangChain Server",version="1.0",description="A simple api server using Langchain's Runnable interfaces",
)add_routes(app,ChatOpenAI(),path="/openai",
)add_routes(app,ChatAnthropic(),path="/anthropic",
)model = ChatAnthropic()
prompt = ChatPromptTemplate.from_template("tell me a joke about {topic}")
add_routes(app,prompt | model,path="/joke",
)if __name__ == "__main__":import uvicornuvicorn.run(app, host="localhost", port=8000)
Docs
If you've deployed the server above, you can view the generated OpenAPI docs using:
⚠️ If using pydantic v2, docs will not be generated for invoke/batch/stream/stream_log. See Pydantic section below for more details.
curl localhost:8000/docs
make sure to add the /docs suffix.
⚠️ Index page
/is not defined by design, socurl localhost:8000or visiting the URL will return a 404. If you want content at/define an endpoint@app.get("/").
Client
Python SDK
from langchain.schema import SystemMessage, HumanMessage
from langchain.prompts import ChatPromptTemplate
from langchain.schema.runnable import RunnableMap
from langserve import RemoteRunnableopenai = RemoteRunnable("http://localhost:8000/openai/")
anthropic = RemoteRunnable("http://localhost:8000/anthropic/")
joke_chain = RemoteRunnable("http://localhost:8000/joke/")joke_chain.invoke({"topic": "parrots"})# or async
await joke_chain.ainvoke({"topic": "parrots"})prompt = [SystemMessage(content='Act like either a cat or a parrot.'),HumanMessage(content='Hello!')
]# Supports astream
async for msg in anthropic.astream(prompt):print(msg, end="", flush=True)prompt = ChatPromptTemplate.from_messages([("system", "Tell me a long story about {topic}")]
)# Can define custom chains
chain = prompt | RunnableMap({"openai": openai,"anthropic": anthropic,
})chain.batch([{ "topic": "parrots" }, { "topic": "cats" }])
In TypeScript (requires LangChain.js version 0.0.166 or later):
import { RemoteRunnable } from "langchain/runnables/remote";const chain = new RemoteRunnable({url: `http://localhost:8000/joke/`,
});
const result = await chain.invoke({topic: "cats",
});
Python using requests:
import requests
response = requests.post("http://localhost:8000/joke/invoke/",json={'input': {'topic': 'cats'}}
)
response.json()
You can also use curl:
curl --location --request POST 'http://localhost:8000/joke/invoke/' \--header 'Content-Type: application/json' \--data-raw '{"input": {"topic": "cats"}}'
Endpoints
The following code:
...
add_routes(app,runnable,path="/my_runnable",
)
adds of these endpoints to the server:
POST /my_runnable/invoke- invoke the runnable on a single inputPOST /my_runnable/batch- invoke the runnable on a batch of inputsPOST /my_runnable/stream- invoke on a single input and stream the outputPOST /my_runnable/stream_log- invoke on a single input and stream the output, including output of intermediate steps as it's generatedGET /my_runnable/input_schema- json schema for input to the runnableGET /my_runnable/output_schema- json schema for output of the runnableGET /my_runnable/config_schema- json schema for config of the runnable
These endpoints match the LangChain Expression Language interface -- please reference this documentation for more details.
Playground
You can find a playground page for your runnable at /my_runnable/playground. This exposes a simple UI to configure and invoke your runnable with streaming output and intermediate steps.

Widgets
The playground supports widgets and can be used to test your runnable with different inputs.
In addition, for configurable runnables, the playground will allow you to configure the runnable and share a link with the configuration:
Sharing

Legacy Chains
LangServe works with both Runnables (constructed via LangChain Expression Language) and legacy chains (inheriting from Chain). However, some of the input schemas for legacy chains may be incomplete/incorrect, leading to errors. This can be fixed by updating the input_schema property of those chains in LangChain. If you encounter any errors, please open an issue on THIS repo, and we will work to address it.
Deployment
Deploy to GCP
You can deploy to GCP Cloud Run using the following command:
gcloud run deploy [your-service-name] --source . --port 8001 --allow-unauthenticated --region us-central1 --set-env-vars=OPENAI_API_KEY=your_key
Pydantic
LangServe provides support for Pydantic 2 with some limitations.
- OpenAPI docs will not be generated for invoke/batch/stream/stream_log when using Pydantic V2. Fast API does not support [mixing pydantic v1 and v2 namespaces].
- LangChain uses the v1 namespace in Pydantic v2. Please read the following guidelines to ensure compatibility with LangChain
Except for these limitations, we expect the API endpoints, the playground and any other features to work as expected.
Advanced
Handling Authentication
If you need to add authentication to your server, please reference FastAPI's security documentation and middleware documentation.
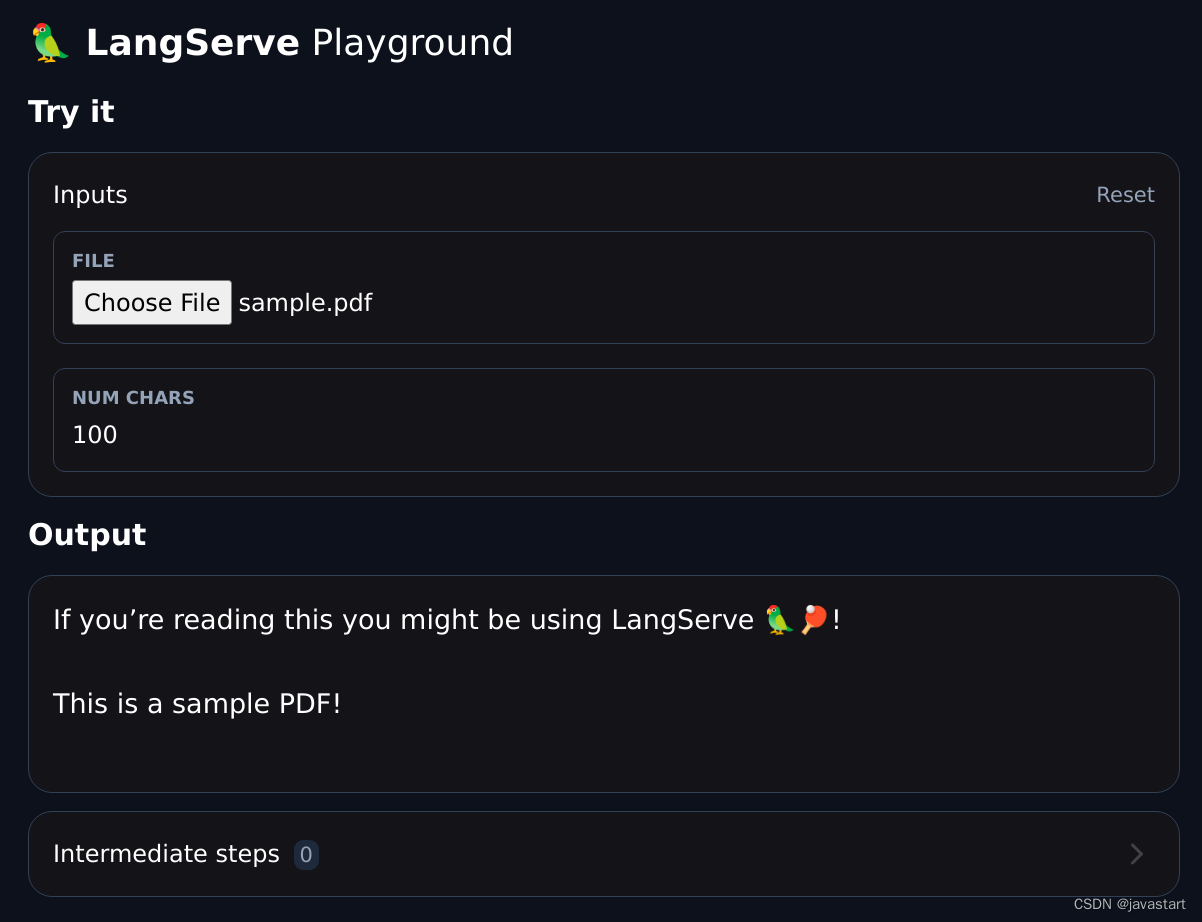
Files
LLM applications often deal with files. There are different architectures that can be made to implement file processing; at a high level:
- The file may be uploaded to the server via a dedicated endpoint and processed using a separate endpoint
- The file may be uploaded by either value (bytes of file) or reference (e.g., s3 url to file content)
- The processing endpoint may be blocking or non-blocking
- If significant processing is required, the processing may be offloaded to a dedicated process pool
You should determine what is the appropriate architecture for your application.
Currently, to upload files by value to a runnable, use base64 encoding for the file (multipart/form-data is not supported yet).
Here's an example that shows how to use base64 encoding to send a file to a remote runnable.
Remember, you can always upload files by reference (e.g., s3 url) or upload them as multipart/form-data to a dedicated endpoint.
Custom Input and Output Types
Input and Output types are defined on all runnables.
You can access them via the input_schema and output_schema properties.
LangServe uses these types for validation and documentation.
If you want to override the default inferred types, you can use the with_types method.
Here's a toy example to illustrate the idea:
from typing import Anyfrom fastapi import FastAPI
from langchain.schema.runnable import RunnableLambdaapp = FastAPI()def func(x: Any) -> int:"""Mistyped function that should accept an int but accepts anything."""return x + 1runnable = RunnableLambda(func).with_types(input_schema=int,
)add_routes(app, runnable)
Custom User Types
Inherit from CustomUserType if you want the data to de-serialize into a pydantic model rather than the equivalent dict representation.
At the moment, this type only works server side and is used to specify desired decoding behavior. If inheriting from this type the server will keep the decoded type as a pydantic model instead of converting it into a dict.
from fastapi import FastAPI
from langchain.schema.runnable import RunnableLambdafrom langserve import add_routes
from langserve.schema import CustomUserTypeapp = FastAPI()class Foo(CustomUserType):bar: intdef func(foo: Foo) -> int:"""Sample function that expects a Foo type which is a pydantic model"""assert isinstance(foo, Foo)return foo.bar# Note that the input and output type are automatically inferred!
# You do not need to specify them.
# runnable = RunnableLambda(func).with_types( # <-- Not needed in this case
# input_schema=Foo,
# output_schema=int,
#
add_routes(app, RunnableLambda(func), path="/foo")
Playground Widgets
The playground allows you to define custom widgets for your runnable from the backend.
- A widget is specified at the field level and shipped as part of the JSON schema of the input type
- A widget must contain a key called
typewith the value being one of a well known list of widgets - Other widget keys will be associated with values that describe paths in a JSON object
General schema:
type JsonPath = number | string | (number | string)[];
type NameSpacedPath = { title: string; path: JsonPath }; // Using title to mimick json schema, but can use namespace
type OneOfPath = { oneOf: JsonPath[] };type Widget = {type: string // Some well known type (e.g., base64file, chat etc.)[key: string]: JsonPath | NameSpacedPath | OneOfPath;
};
File Upload Widget
Allows creation of a file upload input in the UI playground for files that are uploaded as base64 encoded strings. Here's the full example.
Snippet:
try:from pydantic.v1 import Field
except ImportError:from pydantic import Fieldfrom langserve import CustomUserType# ATTENTION: Inherit from CustomUserType instead of BaseModel otherwise
# the server will decode it into a dict instead of a pydantic model.
class FileProcessingRequest(CustomUserType):"""Request including a base64 encoded file."""# The extra field is used to specify a widget for the playground UI.file: str = Field(..., extra={"widget": {"type": "base64file"}})num_chars: int = 100Example widget:

——基于jrtplib实现tcp被动和主动发流)




 D. Absolute Beauty)


)
和递减运算符(--))








