
目录
前言:
一:双链表的定义
编辑 二:双向链表的实现
2.1:链表的构造
2.2:创建头节点
2.3:创建节点
2.4:链表的尾插
2.5:链表的打印
2.6:链表的尾删
2.7:链表的头插
2.8:链表的头删
2.9:链表的查找
2.10:在目标位置前面插入
2.11:删除目标位置结点
2.12:链表的销毁
总代码:
test.c
List.c
List.h
前言:
双链表的引入是因为单链表要访问某个结点的前驱结点时,只能从头开始遍历,访问后驱结点的复杂度为O(1),访问前驱结点的复杂度为O(n)。为了克服上述缺点,引入了双链表。
双链表的引进,对于链表的操作有了极大的遍历;
一:双链表的定义
链表由单向的链变成了双向链。
双向链表(double linked list)是在单链表的每个结点中再设置一个指向其前驱结点的指针域。
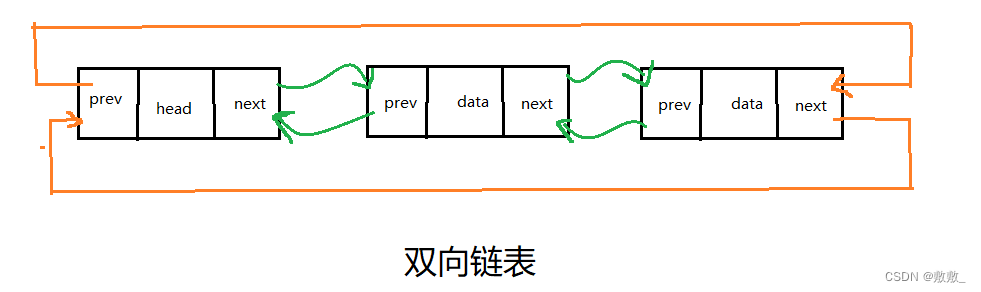 二:双向链表的实现
二:双向链表的实现
2.1:链表的构造
包含了一个数据域,两个指针域(指向前后驱节点)
// 带头+双向+循环链表增删查改实现
typedef int LTDataType;
typedef struct ListNode
{LTDataType data; //数据struct ListNode* next; //下一个指针域struct ListNode* prev; //上一个指针域
}ListNode;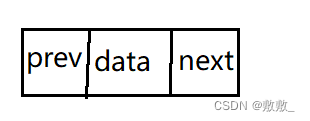
2.2:创建头节点
双向链表一般都是带头节点的,在链表中,带了头节点对于链表分割这一问题有了简单化;
动态开辟出一块空间,前后指针都指向自己;
//初始化链表头头节点
ListNode* ListInit()
{ListNode* phead = (ListNode*)malloc(sizeof(ListNode));assert(phead);phead->data = -1;phead->next = phead;phead->prev = phead;return phead;
}2.3:创建节点
这里置NULL,和单链表的置NULL,是一样的意思,对后续的操作提供便利;
// 创建返回链表的结点.
ListNode* ListCreate(LTDataType x)
{ListNode* newnode = (ListNode*)malloc(sizeof(ListNode));assert(newnode);newnode->data = x;newnode->next = NULL;newnode->prev = NULL;return newnode;
}2.4:链表的尾插
单链表的尾插还需要考虑是否存在第一个节点,这里直接插入即可;
注意操作顺序
// 双向链表尾插
void ListPushBack(ListNode* phead, LTDataType x)
{assert(phead);ListNode* newnode = ListCreate(x);struct ListNode* tail = phead->prev;// phead tail newnode//newnode->prev = phead->prev;//newnode->next = phead;//phead->prev->next = newnode;//phead->prev = newnode;//注意前后顺序newnode->prev = tail;tail->next = newnode;newnode->next = phead;phead->prev = newnode;}
2.5:链表的打印
这里的关键就是从哪里开始?如何判断结束(因为是循环)?
我们可以从头结点的下一个开始打印,当遇到头结点即是结束;
// 双向链表打印
void ListPrint(ListNode* phead)
{assert(phead);struct ListNode* cur = phead->next;printf("哨兵位<=>");while (cur != phead){printf("%d<=>", cur->data);cur = cur->next;}printf("\n");
}
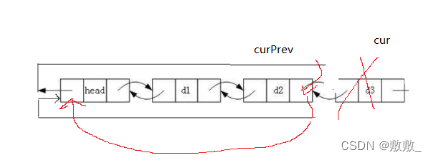
2.6:链表的尾删
要多一个断言判断:如果只有一个头指针就不用操作了;
保存尾结点的前驱,释放尾结点即可
// 双向链表尾删
void ListPopBack(ListNode* phead)
{assert(phead);assert(phead->next != phead); //只有头指针不删struct ListNode* cur = phead->prev;struct ListNode* curPrev = cur->prev; //尾节点的上一个phead->prev = curPrev;curPrev->next = phead;free(cur);cur = NULL;
} 
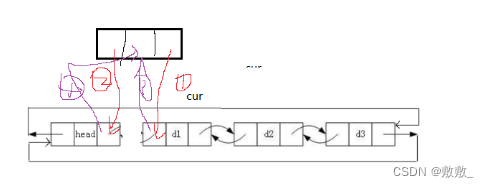
2.7:链表的头插
和尾插操作相似,定义头节点的下一个结点,进行链接即可;
注意顺序;
// 双向链表头插
void ListPushFront(ListNode* phead, LTDataType x)
{assert(phead);ListNode* newnode = ListCreate(x);struct ListNode* cur = phead->next;newnode->next = cur; cur->prev = newnode;newnode->prev = phead;phead->next = newnode;
} 
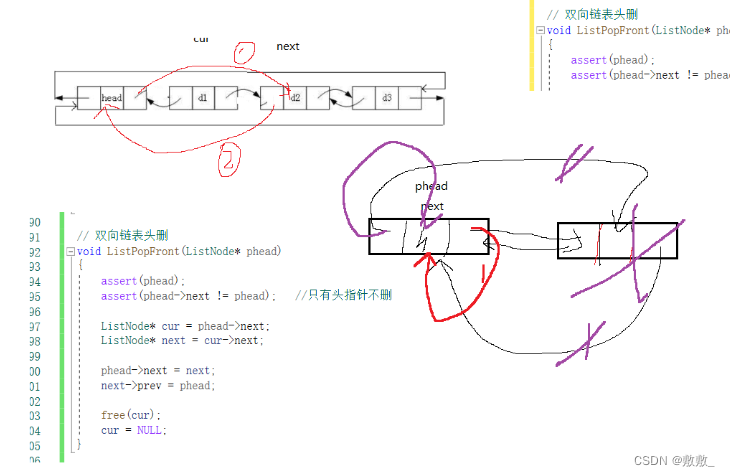
2.8:链表的头删
删除操作一般都需要判断一下是否只有头节点。判断双向链表的条件是:phead->next != phead;
// 双向链表头删
void ListPopFront(ListNode* phead)
{assert(phead);assert(phead->next != phead); //只有头指针不删ListNode* cur = phead->next;ListNode* next = cur->next;phead->next = next;next->prev = phead;free(cur);cur = NULL;
}
2.9:链表的查找
找到该结点后,返回的是指针,而不是数据,返回该指针位置,方便后续操作
// 双向链表查找
ListNode* ListFind(ListNode* phead, LTDataType x)
{assert(phead);ListNode* cur = phead->next;while (cur != phead){if (cur->data == x)return cur;cur = cur->next;}return NULL;
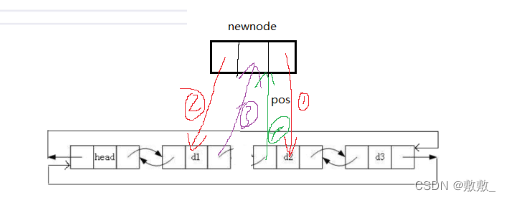
}2.10:在目标位置前面插入
// 双向链表在pos的前面进行插入
void ListInsert(ListNode* pos, LTDataType x)
{assert(pos); //检查pos位置是否有效ListNode* newnode = ListCreate(x);newnode->next = pos; //将newnode节点next prev 链接前后节点newnode->prev = pos->prev;pos->prev->next = newnode;pos->prev = newnode;
}
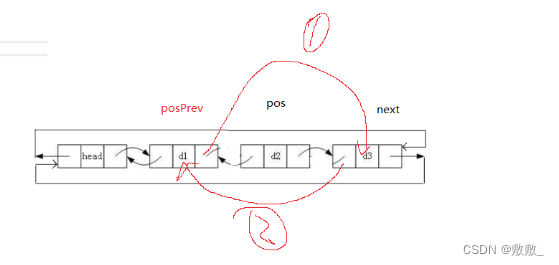
2.11:删除目标位置结点
// 双向链表删除pos位置的节点
void ListErase(ListNode* pos)
{assert(pos);ListNode* posPrev = pos->prev;ListNode* next = pos->next;posPrev->next = next;next->prev = posPrev;free(pos);pos = NULL;
} 
2.12:链表的销毁
// 双向链表销毁
void ListDestory(ListNode* phead)
{assert(phead);ListNode* cur = phead->prev;while (cur != phead) //将除了头结点的都销毁{ListNode* curPrev = cur->prev;free(cur);cur = curPrev;}free(phead); //再释放头结点//phead = NULL;
}总代码:
test.c
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 1
#include"List.h"void test1()
{ListNode* plist = NULL;plist = ListInit();ListPushBack(plist, 1);ListPushBack(plist, 2);ListPushBack(plist, 3);ListPushBack(plist, 4);ListPrint(plist);ListPopBack(plist);ListPrint(plist);ListPopBack(plist);ListPrint(plist);ListPopBack(plist);ListPrint(plist);ListPopBack(plist);ListPrint(plist);}void test2()
{ListNode* plist = NULL;plist = ListInit();ListPrint(plist);//ͷListPushFront(plist, 6);ListPrint(plist);//ͷɾListPopFront(plist);ListPrint(plist);}void test3()
{ListNode* plist = NULL;plist = ListInit();ListPushBack(plist, 1);ListPushBack(plist, 2);ListPushBack(plist, 3);ListPushBack(plist, 4);ListPrint(plist);//βɾListPopBack(plist);ListPopBack(plist);ListPopBack(plist);ListNode* pos = ListFind(plist,1);ListInsert(pos, 666);ListPrint(plist);ListErase(pos);ListPrint(plist);ListDestory(plist);
}
int main()
{//test1();//test2();test3();return 0;
}List.c
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 1
#include"List.h"//初始化链表头头节点
ListNode* ListInit()
{ListNode* phead = (ListNode*)malloc(sizeof(ListNode));assert(phead);phead->data = -1;phead->next = phead;phead->prev = phead;return phead;
}// 创建返回链表的头结点.
ListNode* ListCreate(LTDataType x)
{ListNode* newnode = (ListNode*)malloc(sizeof(ListNode));assert(newnode);newnode->data = x;newnode->next = NULL;newnode->prev = NULL;return newnode;
}// 双向链表尾插
void ListPushBack(ListNode* phead, LTDataType x)
{assert(phead);ListNode* newnode = ListCreate(x);struct ListNode* tail = phead->prev;// phead tail newnode//newnode->prev = phead->prev;//newnode->next = phead;//phead->prev->next = newnode;//phead->prev = newnode;//注意前后顺序newnode->prev = tail;tail->next = newnode;newnode->next = phead;phead->prev = newnode;}// 双向链表打印
void ListPrint(ListNode* phead)
{assert(phead);struct ListNode* cur = phead->next;printf("哨兵位<=>");while (cur != phead){printf("%d<=>", cur->data);cur = cur->next;}printf("\n");
}// 双向链表尾删
void ListPopBack(ListNode* phead)
{assert(phead);assert(phead->next != phead); //只有头指针不删struct ListNode* cur = phead->prev;struct ListNode* curPrev = cur->prev; //尾节点的上一个phead->prev = curPrev;curPrev->next = phead;free(cur);cur = NULL;
}// 双向链表头插
void ListPushFront(ListNode* phead, LTDataType x)
{assert(phead);ListNode* newnode = ListCreate(x);struct ListNode* cur = phead->next;newnode->next = cur; cur->prev = newnode;newnode->prev = phead;phead->next = newnode;
}// 双向链表头删
void ListPopFront(ListNode* phead)
{assert(phead);assert(phead->next != phead); //只有头指针不删ListNode* cur = phead->next;ListNode* next = cur->next;phead->next = next;next->prev = phead;free(cur);cur = NULL;
}// 双向链表查找
ListNode* ListFind(ListNode* phead, LTDataType x)
{assert(phead);ListNode* cur = phead->next;while (cur != phead){if (cur->data == x)return cur;cur = cur->next;}return NULL;
}// 双向链表在pos的前面进行插入
void ListInsert(ListNode* pos, LTDataType x)
{assert(pos); //检查pos位置是否有效ListNode* newnode = ListCreate(x);newnode->next = pos; //将newnode节点next prev 链接前后节点newnode->prev = pos->prev;pos->prev->next = newnode;pos->prev = newnode;
}// 双向链表删除pos位置的节点
void ListErase(ListNode* pos)
{assert(pos);ListNode* posPrev = pos->prev;ListNode* next = pos->next;posPrev->next = next;next->prev = posPrev;free(pos);pos = NULL;
}// 双向链表销毁
void ListDestory(ListNode* phead)
{assert(phead);ListNode* cur = phead->prev;while (cur != phead) //将除了头节点的都销毁{ListNode* curPrev = cur->prev;free(cur);cur = curPrev;}free(phead);//phead = NULL;
}List.h
#pragma once
#include<stdio.h>
#include<assert.h>
#include<stdlib.h>// 带头+双向+循环链表增删查改实现
typedef int LTDataType;
typedef struct ListNode
{LTDataType data; //数据struct ListNode* next; //下一个指针域struct ListNode* prev; //上一个指针域
}ListNode;// 创建返回链表的头结点.
ListNode* ListCreate(LTDataType x);//初始化链表头头节点
ListNode* ListInit();// 双向链表尾插
void ListPushBack(ListNode* pHead, LTDataType x);// 双向链表打印
void ListPrint(ListNode* pHead);// 双向链表尾删
void ListPopBack(ListNode* pHead);// 双向链表头插
void ListPushFront(ListNode* pHead, LTDataType x);// 双向链表头删
void ListPopFront(ListNode* pHead);// 双向链表查找
ListNode* ListFind(ListNode* pHead, LTDataType x);// 双向链表在pos的前面进行插入
void ListInsert(ListNode* pos, LTDataType x);// 双向链表删除pos位置的节点
void ListErase(ListNode* pos);// 双向链表销毁
void ListDestory(ListNode* pHead);以上就是我对【数据结构|双向链表|增删改查】的介绍,不足之处,还望指点。



![[计算机网络]网络层概述](http://pic.xiahunao.cn/[计算机网络]网络层概述)


【第13章 层次式架构设计理论与实践(P466~495)-思维导图】)

)









作为查询条件)


