记录一下算法题的学习7
二叉树的最大深度
题目:给定一个二叉树 root ,返回其最大深度。
二叉树的 最大深度 是指从根节点到最远叶子节点的最长路径上的节点数。

输入:root = [3,9,20,null,null,15,7] 输出:3
示例分析:
这里根节点为3,叶子节点是什么呢?---->是指没有子节点的节点,记录从根节点到最远叶子节点的最长路径上的节点数,那么就是3-20-15,或者3-20-7,一共是3个节点数
怎么体现呢?
深度优先搜索代码展示:
class Solution {public int maxDepth(TreeNode root) {//首先输入根节点为空的情况下,二叉树就不存在 if(root==null){return 0;}//判断输入根节点不为空,存在二叉树else{int leftDepth=maxDepth(root.left); //得到根节点root左子树的最长路径上的节点数int rightDepth=maxDepth(root.right);//得到根节点root右子树的最长路径上的节点数return Math.max(leftDepth,rightDepth)+1;//由题目可知,还需加上代表根节点的节点数1}}
}广度优先搜索代码展示:
这里进行回忆记录Queue?
- Queue是java中实现队列的接口,它总共有6个方法,我们一般只用其中3个就可以了。
- Queue的实现类有LinkedList和PriorityQueue。最常用的实现类是LinkedList。
| 方法 | 作用 | 区别 |
| add() | 压入元素(添加) | 相同:未超出容量,从队尾压入元素,返回压入的那个元素。 区别:在超出容量时,add()方法会对抛出异常,offer()返回false |
| offer() | 压入元素(添加) | |
| remove() | 弹出元素(删除) | 相同:容量大于0的时候,删除并返回队头被删除的那个元素。 区别:在容量为0的时候,remove()会抛出异常,poll()返回false |
| poll() | 弹出元素(删除) | |
| element() | 获取对头元素 | 相同:容量大于0的时候,都返回队头元素。但是不删除。 区别:容量为0的时候,element()会抛出异常,peek()返回null。 |
| peek() | 获取对头元素 |
class Solution {public int maxDepth(TreeNode root) {//首先输入根节点为空的情况下,二叉树就不存在 if(root==null){return 0;}Queue<TreeNode> queue=new LinkedList<>();//初始化队列queuequeue.offer(root);//将根节点加入队列中int result=0;//初始化结果while(!queue.isEmpty()){ //队列不为空的情况,即刚才加入的根节点!=nullint size=queue.size();//取出当前队列的长度while(size-->0){//取出相同数量的节点数进行遍历TreeNode node=queue.poll();if(node.left!=null){queue.offer(node.left);}if(node.right!=null){queue.offer(node.right);}}result++; }return result;}
}二叉树的最小深度
题目:给定一个二叉树,找出其最小深度。最小深度是从根节点到最近叶子节点的最短路径上的节点数量。
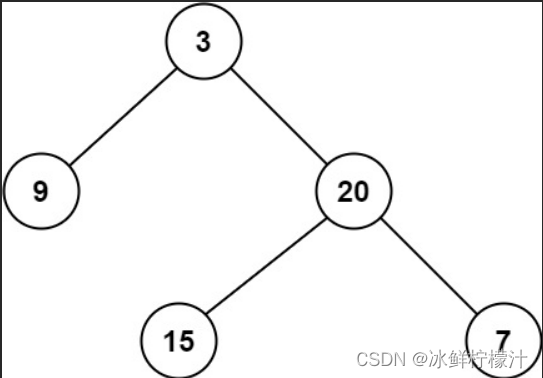
输入:root = [3,9,20,null,null,15,7] 输出:2
输入:root = [2,null,3,null,4,null,5,null,6] 输出:5
示例分析:
如果我们直接将二叉树的最大深度的代码,直接拿来用,就会报错,因为我们忽略了还有一种情况(左孩子和右孩子有一个为空的情况,但不确定是哪一个,我们返回leftDepth+rightDepth+1)在求二叉树的最小深度中。
深度优先搜索代码展示:
class Solution {public int minDepth(TreeNode root) {//首先输入根节点为空的情况下,二叉树就不存在 if(root==null){return 0;}//1.左孩子和右孩子都为空的情况,说明到达了叶子节点,直接返回1if(root.left == null && root.right == null){return 1;}int leftDepth=minDepth(root.left); //得到根节点root左子树的最短路径上的节点数int rightDepth=minDepth(root.right);//得到根节点root右子树的最短路径上的节点数//2.左孩子和右孩子有一个为空的情况,但不确定是哪一个,我们返回leftLength+rightLength+1if(root.left == null || root.right == null){return leftDepth+rightDepth+1;//3 左孩子和右孩子都不为空的情况,那就比较出两者之间更小的值,然后再加一,得到最小深度}else{return Math.min(leftDepth,rightDepth)+1;//由题目可知,还需加上代表根节点的节点数1} }
}
广度优先搜素代码展示:
class Solution {public int minDepth(TreeNode root) {//首先输入根节点为空的情况下,二叉树就不存在 if(root==null){return 0;}Queue<TreeNode> queue = new LinkedList<>();queue.offer(root);int result=1;while (!queue.isEmpty()) {int size=queue.size();for(int i=0;i<size;i++){TreeNode node =queue.poll();if (node.left == null && node.right == null) {return result;}if (node.left != null) {queue.offer(node.left);}if (node.right != null) {queue.offer(node.right);}}result++;}return result;}
}注意这里必须这样写
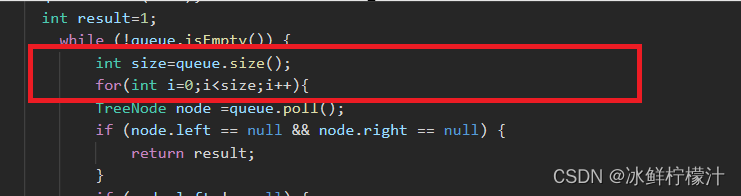
不能直接写成for(int i=0;i<queue.size();i++),因为queue.size()一直在变化,加入一个就变化一次,无法完成每次循环遍历每层内容,但是可以写成for(int i=queue.size()-1;i>=0;i--)。

)




)


 -Maven依赖管理,版本号管理,继承和聚合)







)
)
