一、this

- 手写call

//1、定义myCall方法
//3、接收剩余参数并返回结果
Function.prototype.myCall = function (thisArg, ...arg) {// console.log(thisArg); //person对象// console.log(this); //func方法//2、设置this并调用原函数//下面三行代码有个缺陷就是如果person上有属性f,这里会把原有的f覆盖掉,可以用symbol规避该问题// thisArg.f = this;// let result = thisArg.f(...arg)// delete thisArg.f//4、使用symbol调优let key = Symbol("key");thisArg[key] = this;let result = thisArg[key](...arg)delete thisArg[key]// console.log(arg);return result
}
let person = { name: "张三" }
function func(a,b) {console.log(this); //person对象console.log(a,b); //1 2return a + b;
}
let result = func.myCall(person, 1,2)
console.log(result); //3
- 手写applay
/**
* 1、定义myApply方法论
* 2、设置this并调用原函数
* 3、接收参数并返回结果
* **/
Function.prototype.myApply = function (thisArg, args) {const key = Symbol("key");thisArg[key] = this;let result = thisArg[key](...args)delete thisArg[key]return result
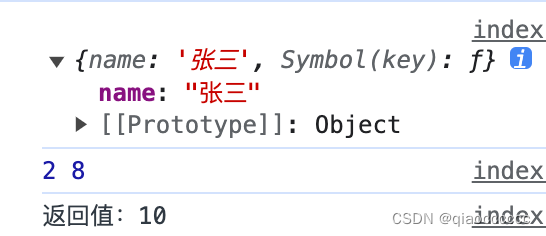
}const person = { name: "张三" }
function func(a,b) {console.log(this);console.log(a,b);return a + b
}let res = func.myApply(person, [2,8]);
console.log("返回值:"+res);
- 手写bind方法
/**
* 手写bind方法
* 1、定义myBind方法
* 2、返回绑定this的心函数
* 3、合并绑定和新传入的参数
* **/
Function.prototype.myBind = function (thisArg, ...args) {console.log(this);//因为下面bingDunc要作为方法执行,所以这里要返回一个方法return (...reargs) => {//改变this的指向并返回数据return this.call(thisArg, ...args, ...reargs)}
}const person = { name: "张三" }
function func(a,b,c,d) {console.log(this);console.log(a,b,c,d);return a + b + c + d
}
const bindFunc = func.myBind(person, 1,2)
const res = bindFunc(3,4)
console.log("返回值:", res);
二、class
- 基本使用
class Person {constructor(name) {this.name = name}sayHi(){console.log("我的名字是"+this.name);}
}
let p = new Person("张三")
p.sayHi()//我的名字是张三
- class继承

注:
1)子类有自己额外的属性是,需要在 constructor 里调用 super 方法,参数要传父类所需要的参数
2)当父类、子类有同名方法时,子类优先父类
class Person {// nameconstructor(name) {this.name = name}sayHi(){console.log("我的名字是"+this.name);}}class Student extends Person {constructor(name, age) {super(name)this.age = age}sayHi(){console.log("Student--我的名字是"+this.name);}sayHello() {console.log(`Student--我的名字是${this.name},我今年${this.age}岁`);}}let s = new Student("张三", 18)s.sayHi()//Student--我的名字是张三s.sayHello()//Student--我的名字是张三,我今年18岁
- 静态属性、方法和私有属性、方法

/*** 静态属性* 定义时:用 static 开头* 使用时:通过类访问,无法通过实例去使用* 私有属性* 定义时:以 # 开头* 使用时:以 # 开头,和定义的名字相同,只能在类的内部使用,无法通过实例调用* 注:chrome 的控制台中,可以直接访问私有属性和方法(便于调试)t.prInfo / t.prMethod()* **/class Test {static stInfo = "静态属性"static stMethod() {console.log("静态方法");}#prInfo = "私有属性"#prMethod() {console.log("私有方法");}testPr() {console.log(this.#prInfo);console.log(this.#prMethod());}}Test.stMethod()console.log(Test.stInfo);let t = new Test()t.testPr()
三、继承

//组合式继承:借用构造函数,原型链
//寄生:父类的原型中有子类的构造函数//父类function Person(name) {this.name = name}Person.prototype.sayHi = function () {console.log(`你好,我叫${this.name}`);}//寄生组合式继承核心代码//通过构造函数继承属性function Student(name) {Person.call(this, name)}//通过原型链继承方法//复制Person的原型链,并将construct改为Studentlet prototype = Object.create(Person.prototype, {//没有该配置的话,Person的construct是Studentconstructor: {value: Student}})//将创建的原型链赋值给子类的原型Student.prototype = prototypelet s = new Student("张三")s.sayHi()console.log(s);let p = new Person("李四")console.log(p);

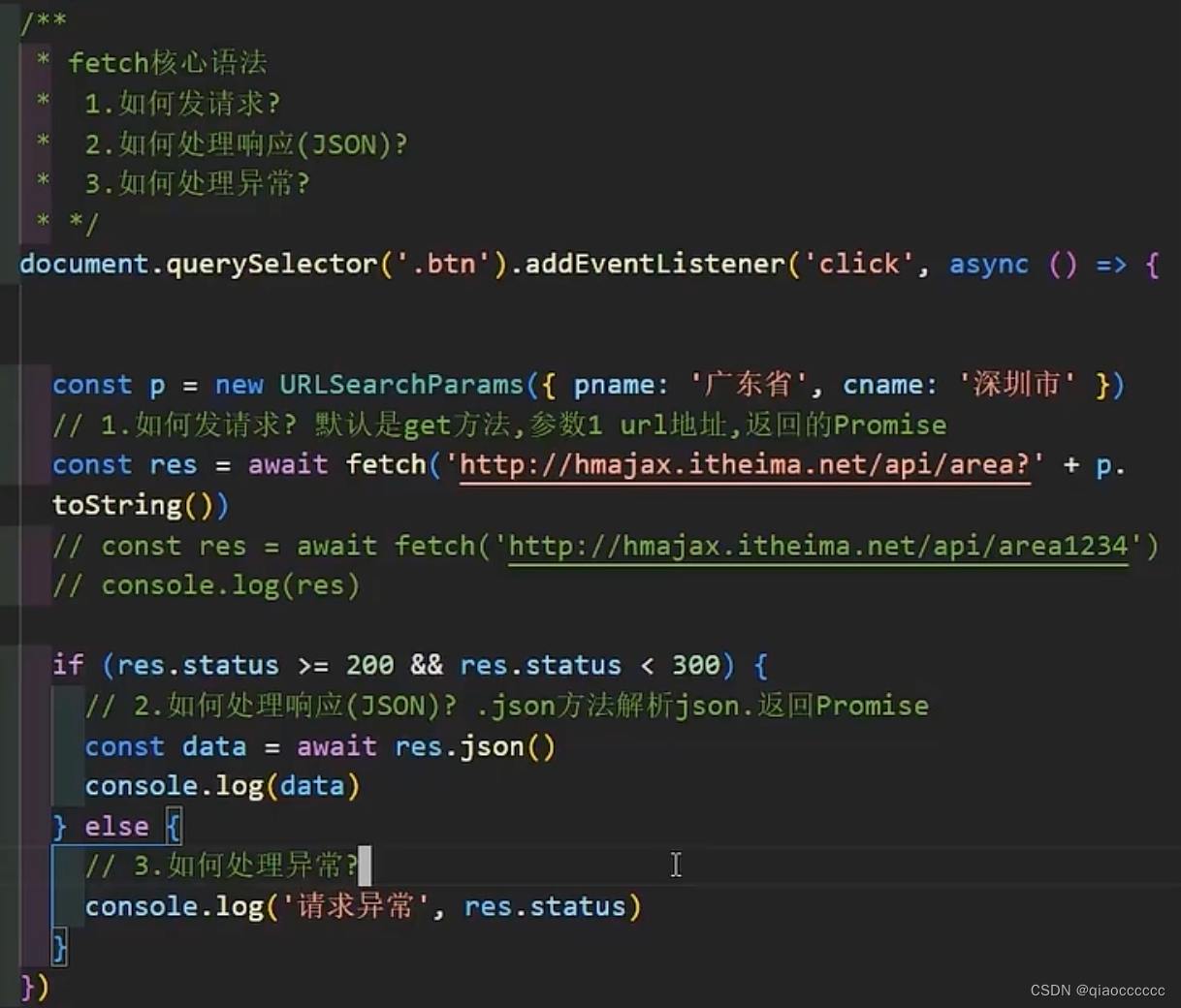
四、fetch

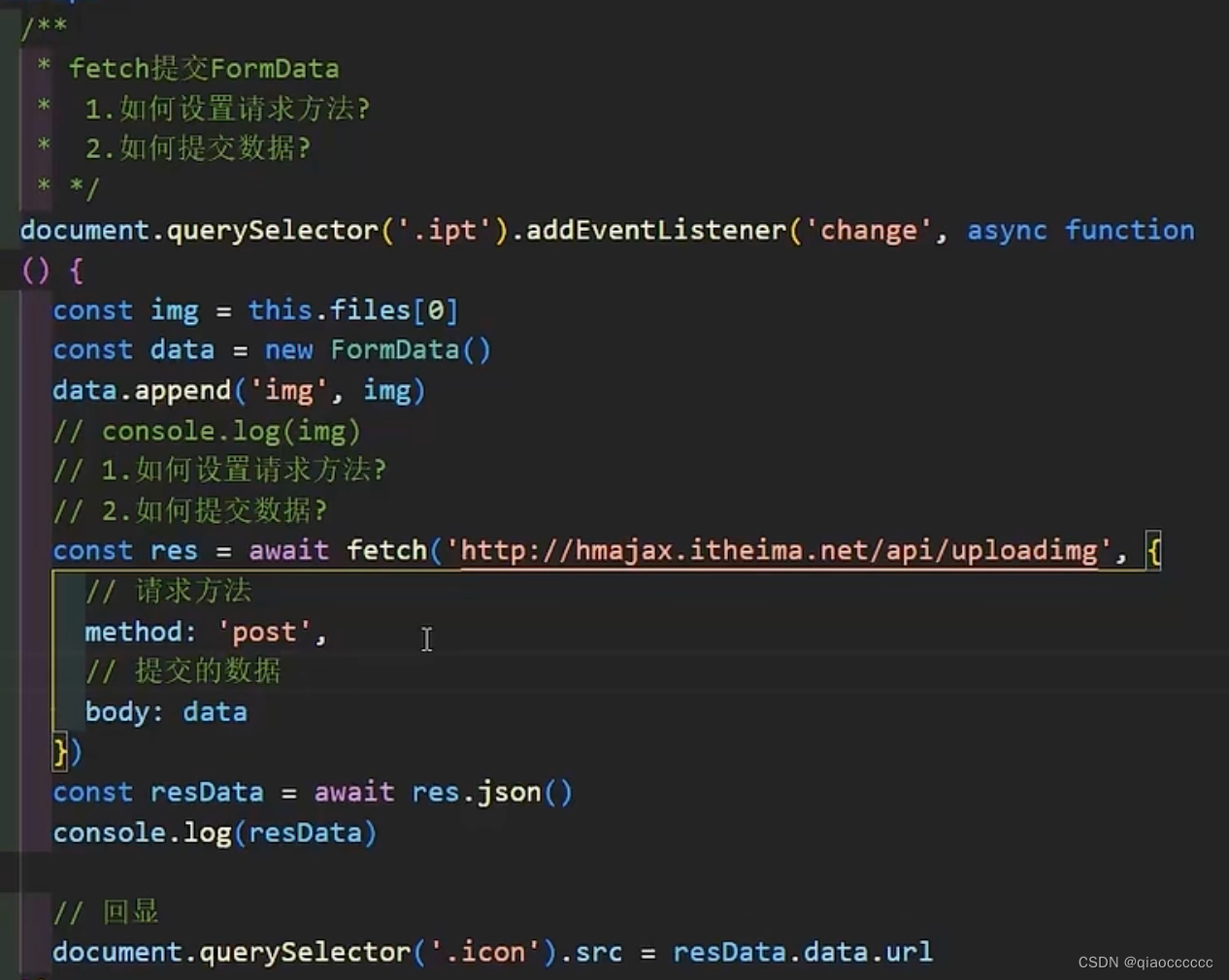
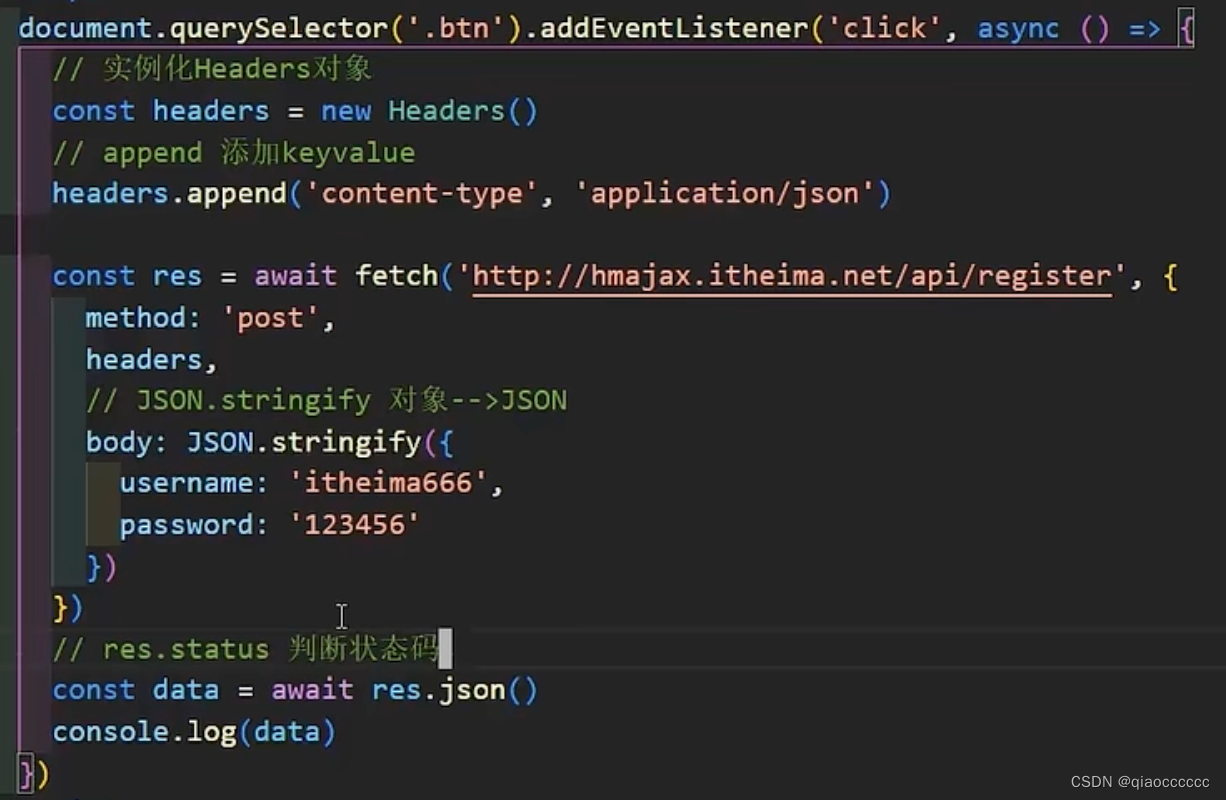
五、Generator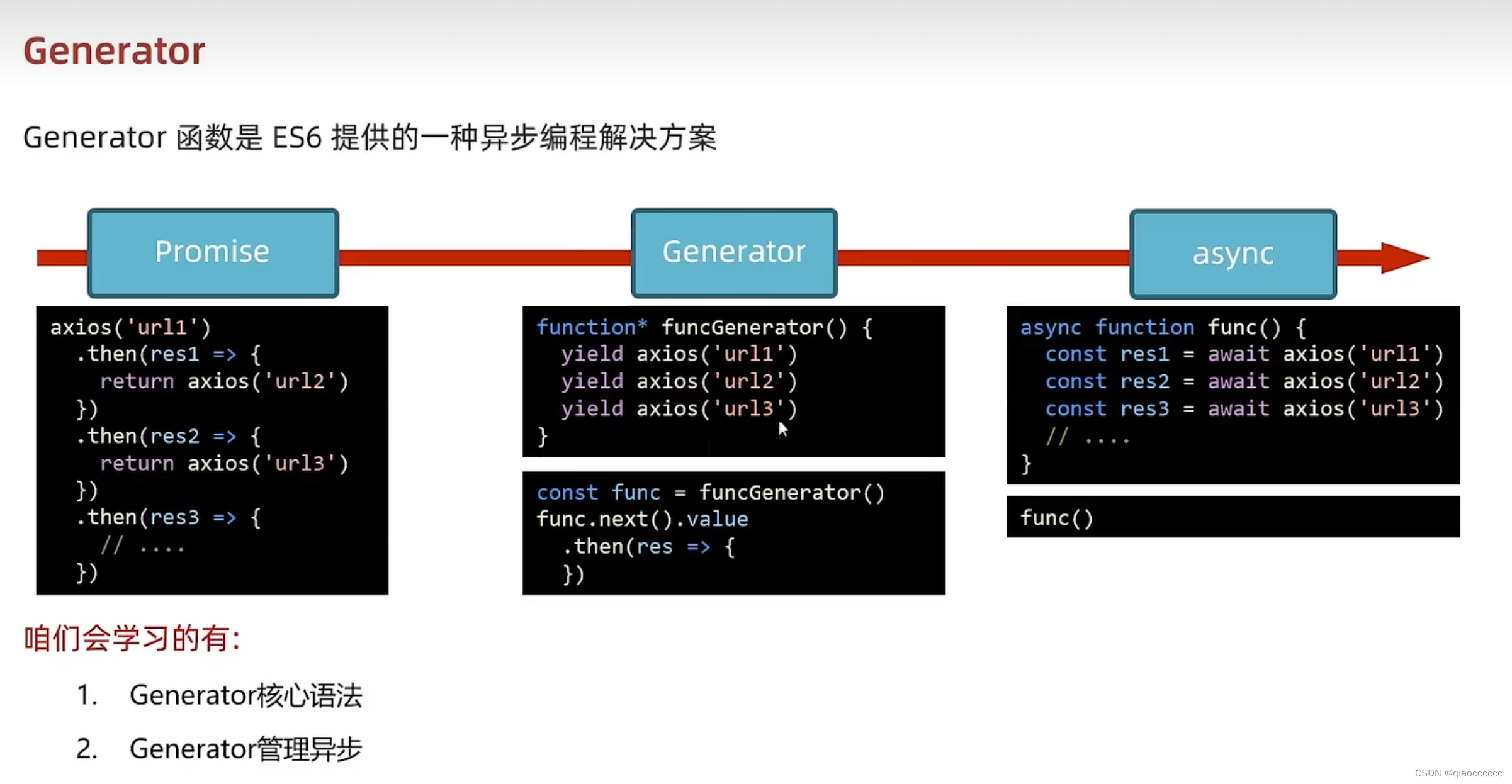

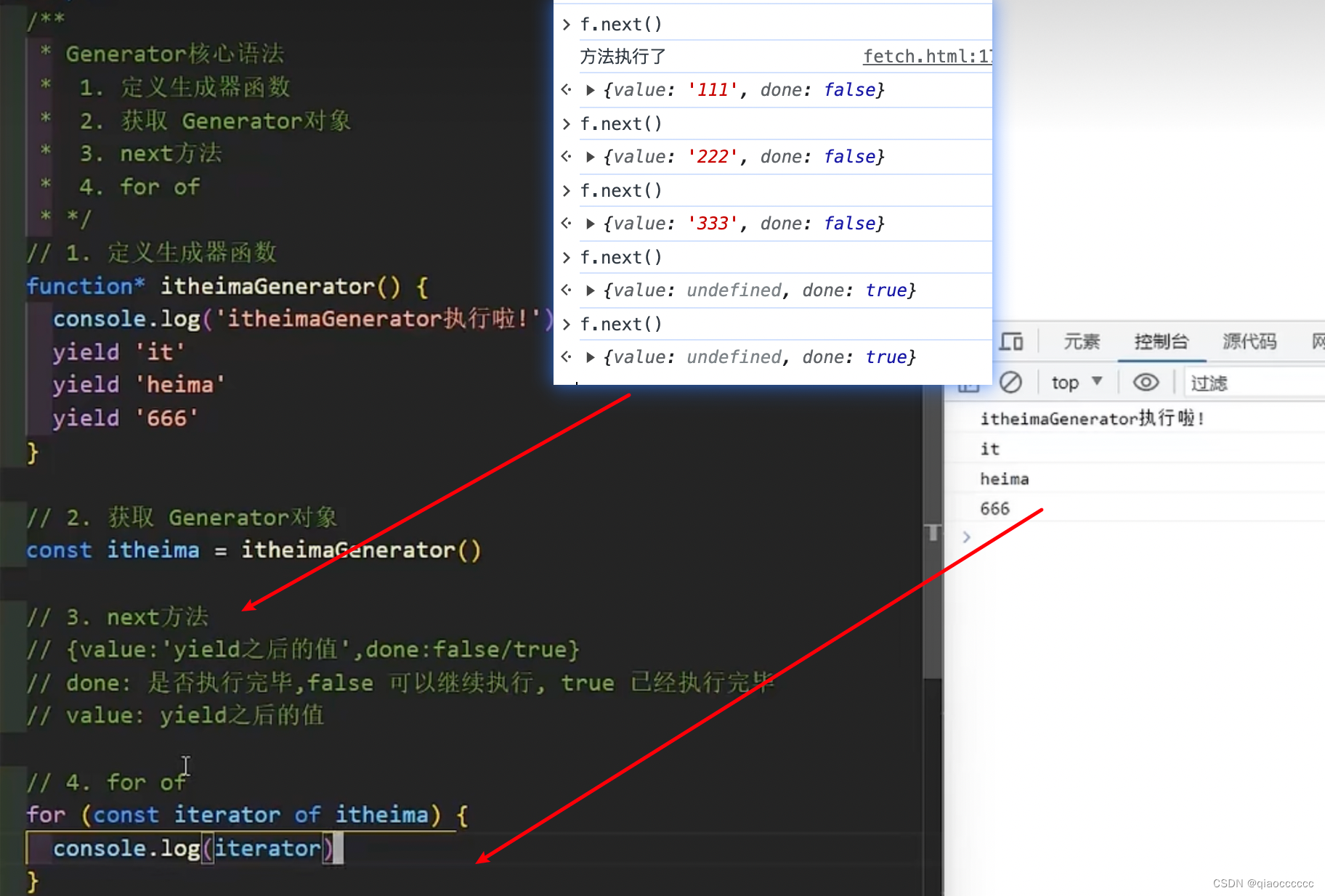
六、手写Promise
- promise 基本
//1、定义类
class MyPromise {//2、添加构造函数constructor(func) {//3、定义resolve、rejectlet resolve = (res) => {console.log(res);}let reject = (res) => {console.log(res);}//4、执行回调函数func(resolve, reject)}
}const p = new MyPromise((resolve,reject) => {resolve("成功了");// reject("失败了");
})
- 处理promise的状态和原因
const PENDING = "pending"
const FULFILLED = "fulfilled"
const REJECTED = "rejected"
class MyPromise{//1、添加状态state = PENDING//2、添加原因result = undefinedconstructor(func) {//3、调整resolve、reject//4、状态不可逆//改状态:pending-》fulfilled//记录原因const resolve = (res) => {if(this.state === PENDING) {this.state = FULFILLEDthis.result = res}}//改状态:pending-》rejected//记录原因const reject = (res) => {if(this.state === PENDING) {this.state = REJECTEDthis.result = res}}func(resolve, reject)}
}const p = new MyPromise((resolve,reject) => {resolve("成功了");// reject("失败了");
})
- then
const PENDING = "pending"
const FULFILLED = "fulfilled"
const REJECTED = "rejected"
class MyPromise{//1.1、添加状态state = PENDING//1.2、添加原因result = undefinedconstructor(func) {//1.3、调整resolve、reject//1.4、状态不可逆//改状态:pending-》fulfilled//记录原因const resolve = (res) => {if(this.state === PENDING) {this.state = FULFILLEDthis.result = res}}//改状态:pending-》rejected//记录原因const reject = (res) => {if(this.state === PENDING) {this.state = REJECTEDthis.result = res}}func(resolve, reject)}then(onFulfilled, onRejected) {//2.1、参数判断(参考文档)onFulfilled = typeof onFulfilled === "function" ? onFulfilled : x => xonRejected = typeof onRejected === "function" ? onRejected : x => {throw err}//2.2、执行成功、失败的回调if(this.state === FULFILLED) {onFulfilled(this.result)} else if(this.state === REJECTED) {onRejected(this.result)}}
}const p = new MyPromise((resolve,reject) => {resolve("成功了");// reject("失败了");
})
p.then(res => {console.log("成功回调:",res);
}, res => {console.log("失败回调:",res);
})
- then 的异步及多次调用
const PENDING = "pending"
const FULFILLED = "fulfilled"
const REJECTED = "rejected"
class MyPromise{state = PENDINGresult = undefined//1、定义实例私有属性(只有实例可以访问)#handlers = [] //里面放then的成功、失败方法[{onFulfilled,onRejected}...]constructor(func) {const resolve = (res) => {if(this.state === PENDING) {this.state = FULFILLEDthis.result = res//3、调用成功回调this.#handlers.forEach(( {onFulfilled} )=> {onFulfilled(this.result)})}}const reject = (res) => {if(this.state === PENDING) {this.state = REJECTEDthis.result = res//4、调用失败回调this.#handlers.forEach(( {onRejected} )=> {onRejected(this.result)})}}func(resolve, reject)}then(onFulfilled, onRejected) {onFulfilled = typeof onFulfilled === "function" ? onFulfilled : x => xonRejected = typeof onRejected === "function" ? onRejected : x => {throw err}if(this.state === FULFILLED) {onFulfilled(this.result)} else if(this.state === REJECTED) {onRejected(this.result)} else if (this.state === PENDING) {//2、保存回调函数//如果是异步,。then这里的状态就是Pendingthis.#handlers.push({ onFulfilled, onRejected })}}
}const p = new MyPromise((resolve,reject) => {setTimeout(() => {resolve("成功了");// reject("失败了");},2000)
})
p.then(res => {console.log("成功回调111:",res);
}, res => {console.log("失败回调111:",res);
})
p.then(res => {console.log("成功回调222:",res);
}, res => {console.log("失败回调222:",res);
})





)



)
)



)

)
Pytorch快速搭建神经网络模型实现气温预测回归(代码+详细注解))

