1前言
日常开发中,难免遇到一些并发的场景,为了保证接口执行的一致性,通常采用加锁的方式,因为服务是分布式部署模式,本地锁Reentrantlock和Synchnorized这些就先放到一边了,Redis的setnx锁存在无法抱保证原子性的问题就暂时搁且到一边,直接上大招Redisson也是我最近开发项目中基本都在用的缓存,并且也都是用它的分布式锁机制。
2Redisson分布式锁常规使用
关于Redisson的一些基本概念,本章就不做太详细的说明了,有兴趣的小伙伴可以自己去了解下,主要说下加锁的常规使用,Redisson分布式锁是基于Redis的Rlock锁,实现了JavaJUC包下的Lock接口。
Lock
public void getLock(){//获取锁RLock lock = redisson.getLock("Lxlxxx_Lock");try {// 2.加锁lock.lock();} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.getStackTrace();} finally {// 3.解锁lock.unlock();System.out.println("Finally,释放锁成功");}
getLock获取锁,lock.lock进行加锁,会出现的问题就是lock拿不到锁一直等待,会进入阻塞状态,显然这样是不好的。
TryLock
返回boolean类型,和Reentrantlock的tryLock是一个意思,尝试获取锁,获取到就返回true,获取失败就返回false,不会使获不到锁的线程一直处于等待状态,返回false可以继续执行下面的业务逻辑,当然Ression锁内部也涉及到watchDog看门狗机制,主要作用就是给快过期的锁进行续期,主要用途就是使拿到锁的有限时间让业务执行完,再进行锁释放。
RLock lock = redisson.getLock(name);
try {if (lock.tryLock(2, 10, TimeUnit.SECONDS)) {//执行业务逻辑} else {System.out.println("已存在");}
} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
//判断当前线程持有的锁是不是处于锁定状态,锁定状态再进行释放if (this.redissonLock.isHeldByCurrentThread(lockName)) {this.redissonLock.unlock(lockName);}
}
3自定义注解实现锁机制
@Documented
@Inherited
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Target({ElementType.METHOD})
public @interface DistributedLock {String key() default "";int leaseTime() default 10;boolean autoRelease() default true;String errorDesc() default "系统正常处理,请稍后提交";int waitTime() default 1;
}
切面类实现
@Aspect
@Component
public class DistributedLockHandler {private static final Logger log = LoggerFactory.getLogger(DistributedLockHandler.class);@AutowiredRedissonLock redissonLock;public DistributedLockHandler() {}@Around("@annotation(distributedLock)")public Object around(ProceedingJoinPoint joinPoint, DistributedLock distributedLock) throws Throwable {String lockName = this.getRedisKey(joinPoint, distributedLock);int leaseTime = distributedLock.leaseTime();String errorDesc = distributedLock.errorDesc();int waitTime = distributedLock.waitTime();Object var8;try {boolean lock = this.redissonLock.tryLock(lockName, (long)leaseTime, (long)waitTime);if (!lock) {throw new RuntimeException(errorDesc);}var8 = joinPoint.proceed();} catch (Throwable var12) {log.error("执行业务方法异常", var12);throw var12;} finally {if (this.redissonLock.isHeldByCurrentThread(lockName)) {this.redissonLock.unlock(lockName);}}return var8;}/*** 获取加锁的key* @param joinPoint* @param distributedLock* @return*/private String getRedisKey(ProceedingJoinPoint joinPoint, DistributedLock distributedLock) {String key = distributedLock.key();Object[] parameterValues = joinPoint.getArgs();MethodSignature signature = (MethodSignature)joinPoint.getSignature();Method method = signature.getMethod();DefaultParameterNameDiscoverer nameDiscoverer = new DefaultParameterNameDiscoverer();String[] parameterNames = nameDiscoverer.getParameterNames(method);if (StringUtils.isEmpty(key)) {if (parameterNames != null && parameterNames.length > 0) {StringBuffer sb = new StringBuffer();int i = 0;for(int len = parameterNames.length; i < len; ++i) {sb.append(parameterNames[i]).append(" = ").append(parameterValues[i]);}key = sb.toString();} else {key = "redissionLock";}return key;} else {SpelExpressionParser parser = new SpelExpressionParser();Expression expression = parser.parseExpression(key);if (parameterNames != null && parameterNames.length != 0) {EvaluationContext evaluationContext = new StandardEvaluationContext();for(int i = 0; i < parameterNames.length; ++i) {evaluationContext.setVariable(parameterNames[i], parameterValues[i]);}try {Object expressionValue = expression.getValue(evaluationContext);return expressionValue != null && !"".equals(expressionValue.toString()) ? expressionValue.toString() : key;} catch (Exception var13) {return key;}} else {return key;}}}
}
具体使用
 方法头加自定义注解,key参数代表需要加锁的key,errorDesc获取锁失败提示报错信息。
方法头加自定义注解,key参数代表需要加锁的key,errorDesc获取锁失败提示报错信息。
这边我将项目通过修改端口启动了两个服务,分别是8460和8461
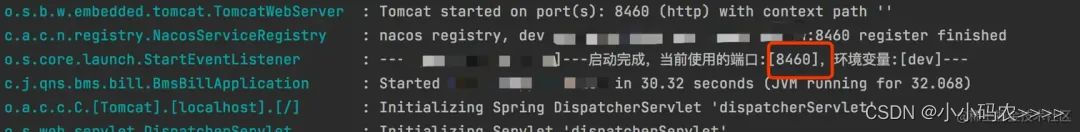
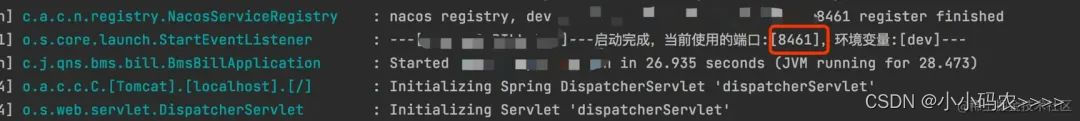
通过postman调用这两个服务,模拟两个服务同时获取一把锁的场景,其中一个服务拿到锁,另外一个服务获取锁失败。

可以看到端口8460服务先拿到锁,8461服务tryLock获取锁失败,实现了加锁逻辑。
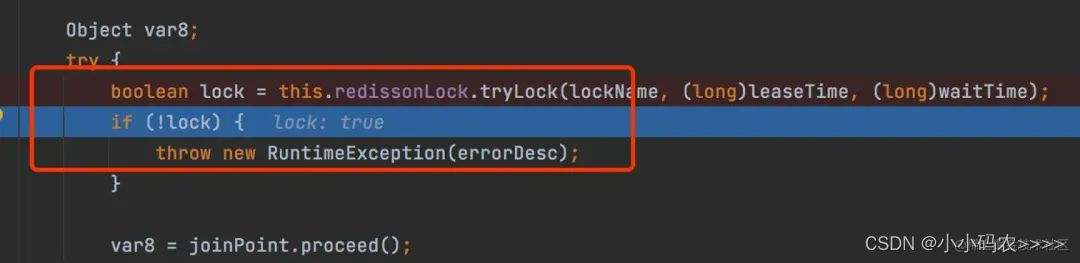
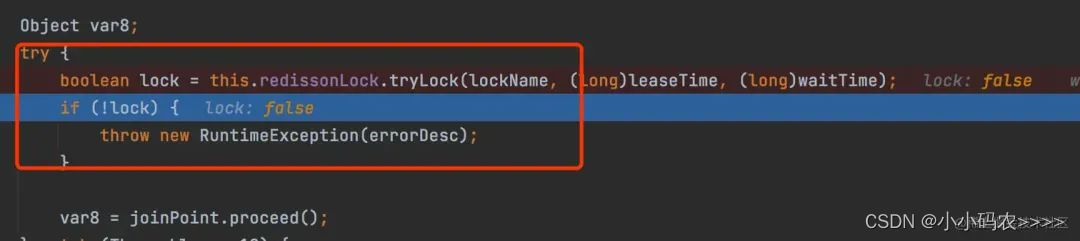
4总结
分布式锁的使用场景还是需要多注意下,根据业务场景来,并发量不大的情况下,其实没有必要加,可能在移动端操作比较频繁的情况下需要注意并发,目前我做的b端项目,通过简单接口幂等性操作就可以避免重复提交,切勿不要盲目加锁,多少会影响一些性能。


![[PHP]关联和操作MySQL数据库然后将数据库部署到ECS](http://pic.xiahunao.cn/[PHP]关联和操作MySQL数据库然后将数据库部署到ECS)


)









)



