本文参考以下博文:
Linux内核4.14版本——drm框架分析(4)——crtc分析
特此致谢!
1. 简介
CRTC实际上可以拆分为CRT+C。CRT的中文意思是阴极摄像管,就是当初老电视上普遍使用的显像管(老电视之所以都很厚,就是因为它的缘故)。而后边那个C,代表Controller即控制器(一说是Context即上下文)。

CRTC主要用于显示控制,如对于显示时序、分辨率、刷新率等的控制,还要承担将framebuffer(帧缓冲)内容送显、更新framebuffer等任务。
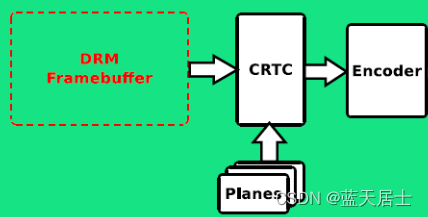
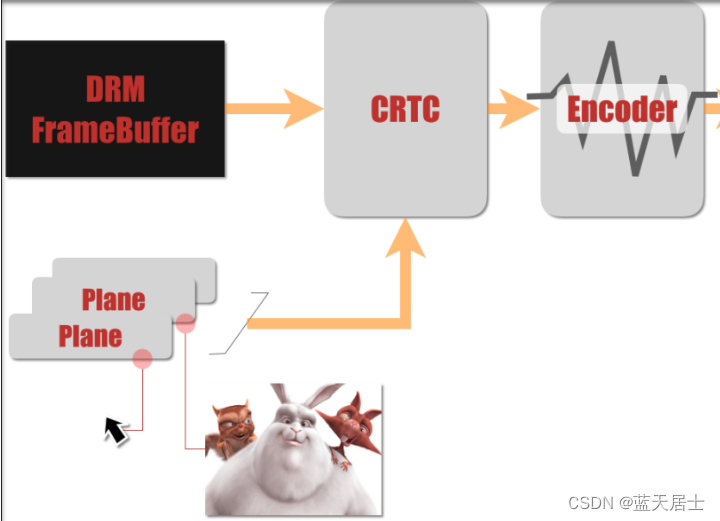
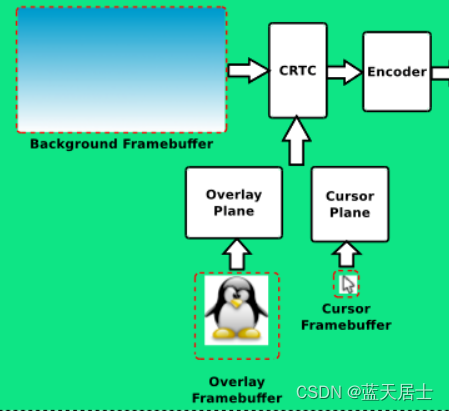
CRTC对内连接framebuffer地址,对外连接encoder。扫描framebuffer上的内容,叠加上 planes的内容,最后传给encoder。
CRTC在系统中的位置和作用如下所示:
2. 核心结构
在Linux内核的DRM中,CRTC对应的核心结构体为:struct drm_crtc。该结构体在include/drm/drm_crtc.h中定义,代码如下(Linux内核版本:6.1):
/*** struct drm_crtc - central CRTC control structure** Each CRTC may have one or more connectors associated with it. This structure* allows the CRTC to be controlled.*/
struct drm_crtc {/** @dev: parent DRM device */struct drm_device *dev;/** @port: OF node used by drm_of_find_possible_crtcs(). */struct device_node *port;/*** @head:** List of all CRTCs on @dev, linked from &drm_mode_config.crtc_list.* Invariant over the lifetime of @dev and therefore does not need* locking.*/struct list_head head;/** @name: human readable name, can be overwritten by the driver */char *name;/*** @mutex:** This provides a read lock for the overall CRTC state (mode, dpms* state, ...) and a write lock for everything which can be update* without a full modeset (fb, cursor data, CRTC properties ...). A full* modeset also need to grab &drm_mode_config.connection_mutex.** For atomic drivers specifically this protects @state.*/struct drm_modeset_lock mutex;/** @base: base KMS object for ID tracking etc. */struct drm_mode_object base;/*** @primary:* Primary plane for this CRTC. Note that this is only* relevant for legacy IOCTL, it specifies the plane implicitly used by* the SETCRTC and PAGE_FLIP IOCTLs. It does not have any significance* beyond that.*/struct drm_plane *primary;/*** @cursor:* Cursor plane for this CRTC. Note that this is only relevant for* legacy IOCTL, it specifies the plane implicitly used by the SETCURSOR* and SETCURSOR2 IOCTLs. It does not have any significance* beyond that.*/struct drm_plane *cursor;/*** @index: Position inside the mode_config.list, can be used as an array* index. It is invariant over the lifetime of the CRTC.*/unsigned index;/*** @cursor_x: Current x position of the cursor, used for universal* cursor planes because the SETCURSOR IOCTL only can update the* framebuffer without supplying the coordinates. Drivers should not use* this directly, atomic drivers should look at &drm_plane_state.crtc_x* of the cursor plane instead.*/int cursor_x;/*** @cursor_y: Current y position of the cursor, used for universal* cursor planes because the SETCURSOR IOCTL only can update the* framebuffer without supplying the coordinates. Drivers should not use* this directly, atomic drivers should look at &drm_plane_state.crtc_y* of the cursor plane instead.*/int cursor_y;/*** @enabled:** Is this CRTC enabled? Should only be used by legacy drivers, atomic* drivers should instead consult &drm_crtc_state.enable and* &drm_crtc_state.active. Atomic drivers can update this by calling* drm_atomic_helper_update_legacy_modeset_state().*/bool enabled;/*** @mode:** Current mode timings. Should only be used by legacy drivers, atomic* drivers should instead consult &drm_crtc_state.mode. Atomic drivers* can update this by calling* drm_atomic_helper_update_legacy_modeset_state().*/struct drm_display_mode mode;/*** @hwmode:** Programmed mode in hw, after adjustments for encoders, crtc, panel* scaling etc. Should only be used by legacy drivers, for high* precision vblank timestamps in* drm_crtc_vblank_helper_get_vblank_timestamp().** Note that atomic drivers should not use this, but instead use* &drm_crtc_state.adjusted_mode. And for high-precision timestamps* drm_crtc_vblank_helper_get_vblank_timestamp() used* &drm_vblank_crtc.hwmode,* which is filled out by calling drm_calc_timestamping_constants().*/struct drm_display_mode hwmode;/*** @x:* x position on screen. Should only be used by legacy drivers, atomic* drivers should look at &drm_plane_state.crtc_x of the primary plane* instead. Updated by calling* drm_atomic_helper_update_legacy_modeset_state().*/int x;/*** @y:* y position on screen. Should only be used by legacy drivers, atomic* drivers should look at &drm_plane_state.crtc_y of the primary plane* instead. Updated by calling* drm_atomic_helper_update_legacy_modeset_state().*/int y;/** @funcs: CRTC control functions */const struct drm_crtc_funcs *funcs;/*** @gamma_size: Size of legacy gamma ramp reported to userspace. Set up* by calling drm_mode_crtc_set_gamma_size().** Note that atomic drivers need to instead use* &drm_crtc_state.gamma_lut. See drm_crtc_enable_color_mgmt().*/uint32_t gamma_size;/*** @gamma_store: Gamma ramp values used by the legacy SETGAMMA and* GETGAMMA IOCTls. Set up by calling drm_mode_crtc_set_gamma_size().** Note that atomic drivers need to instead use* &drm_crtc_state.gamma_lut. See drm_crtc_enable_color_mgmt().*/uint16_t *gamma_store;/** @helper_private: mid-layer private data */const struct drm_crtc_helper_funcs *helper_private;/** @properties: property tracking for this CRTC */struct drm_object_properties properties;/*** @scaling_filter_property: property to apply a particular filter while* scaling.*/struct drm_property *scaling_filter_property;/*** @state:** Current atomic state for this CRTC.** This is protected by @mutex. Note that nonblocking atomic commits* access the current CRTC state without taking locks. Either by going* through the &struct drm_atomic_state pointers, see* for_each_oldnew_crtc_in_state(), for_each_old_crtc_in_state() and* for_each_new_crtc_in_state(). Or through careful ordering of atomic* commit operations as implemented in the atomic helpers, see* &struct drm_crtc_commit.*/struct drm_crtc_state *state;/*** @commit_list:** List of &drm_crtc_commit structures tracking pending commits.* Protected by @commit_lock. This list holds its own full reference,* as does the ongoing commit.** "Note that the commit for a state change is also tracked in* &drm_crtc_state.commit. For accessing the immediately preceding* commit in an atomic update it is recommended to just use that* pointer in the old CRTC state, since accessing that doesn't need* any locking or list-walking. @commit_list should only be used to* stall for framebuffer cleanup that's signalled through* &drm_crtc_commit.cleanup_done."*/struct list_head commit_list;/*** @commit_lock:** Spinlock to protect @commit_list.*/spinlock_t commit_lock;/*** @debugfs_entry:** Debugfs directory for this CRTC.*/struct dentry *debugfs_entry;/*** @crc:** Configuration settings of CRC capture.*/struct drm_crtc_crc crc;/*** @fence_context:** timeline context used for fence operations.*/unsigned int fence_context;/*** @fence_lock:** spinlock to protect the fences in the fence_context.*/spinlock_t fence_lock;/*** @fence_seqno:** Seqno variable used as monotonic counter for the fences* created on the CRTC's timeline.*/unsigned long fence_seqno;/*** @timeline_name:** The name of the CRTC's fence timeline.*/char timeline_name[32];/*** @self_refresh_data: Holds the state for the self refresh helpers** Initialized via drm_self_refresh_helper_init().*/struct drm_self_refresh_data *self_refresh_data;
};3. drm_crtc结构释义
(0)总述
/*** struct drm_crtc - central CRTC control structure** Each CRTC may have one or more connectors associated with it. This structure* allows the CRTC to be controlled.*/struct drm_crtc —— 核心的DRM CRTC控制结构。
每个CRTC可以有一个或多个与其相关的连接器。这种结构允许控制CRTC。
(1)struct drm_device *dev
/** @dev: parent DRM device */struct drm_device *dev;父DRM设备。
(2)struct device_node *port
/** @port: OF node used by drm_of_find_possible_crtcs(). */struct device_node *port;由drm_of_find_possible_crtcs()使用的OF结点。
(3)struct list_head head
/*** @head:** List of all CRTCs on @dev, linked from &drm_mode_config.crtc_list.* Invariant over the lifetime of @dev and therefore does not need* locking.*/struct list_head head;
@dev上所有crtc的列表,链接自&drm_mode_config.crtc_List。
在@dev的生命周期内保持不变,因此不需要锁定。
(4)char *name
/** @name: human readable name, can be overwritten by the driver */char *name;人类可读的名称(名字),可以被驱动程序覆盖。
drm_crtc结构的其余成员将在下一篇文章中继续深入释义。
)



)














