一、需求背景
比如我们需要对系统的部分接口进行token验证,防止对外的接口裸奔。所以,在调用这类接口前,先校验token的合法性,进而得到登录用户的userId/role/authority/tenantId等信息;再进一步对比当前用户是否有权限调用该接口。
但是,不是所有的接口都需要token校验,我们应该按需配置,能够支持排除掉无需token校验的接口。
本文的重点是讲述,如果让业务方开启token校验,不会涉及到如何去做权限及接口配置等方面。
因为,接口配置,我们是建议放在api网关层(不应该放在具体的微服务里),而实际生产中,不同的业务会有不同的api网关。
二、目标
- 接口支持token校验与否的开关控制
- 编写一个自定义注解
- 对业务方透明,简单易用
三、总体设计
- 建议的方案
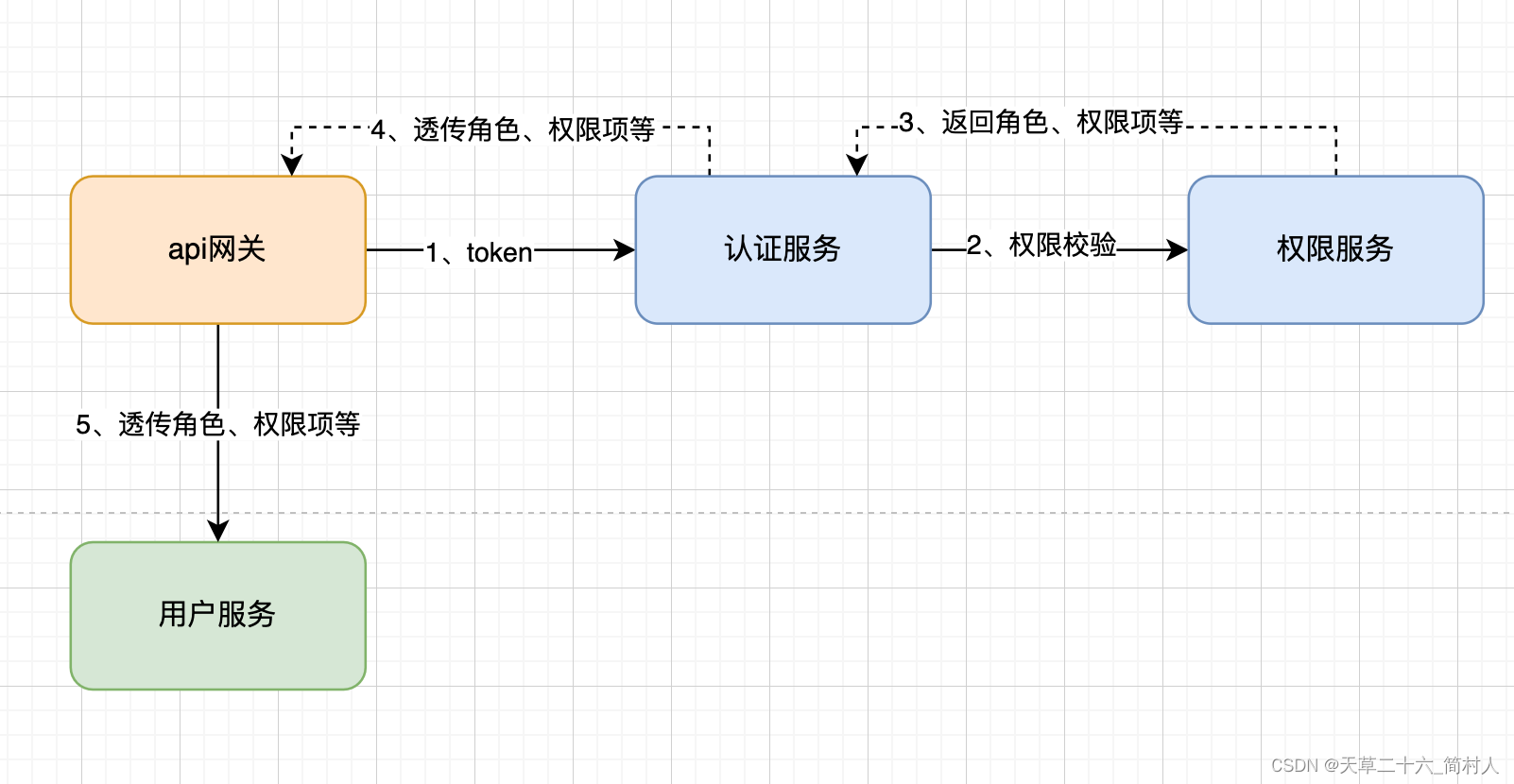
- 本文所说的方案
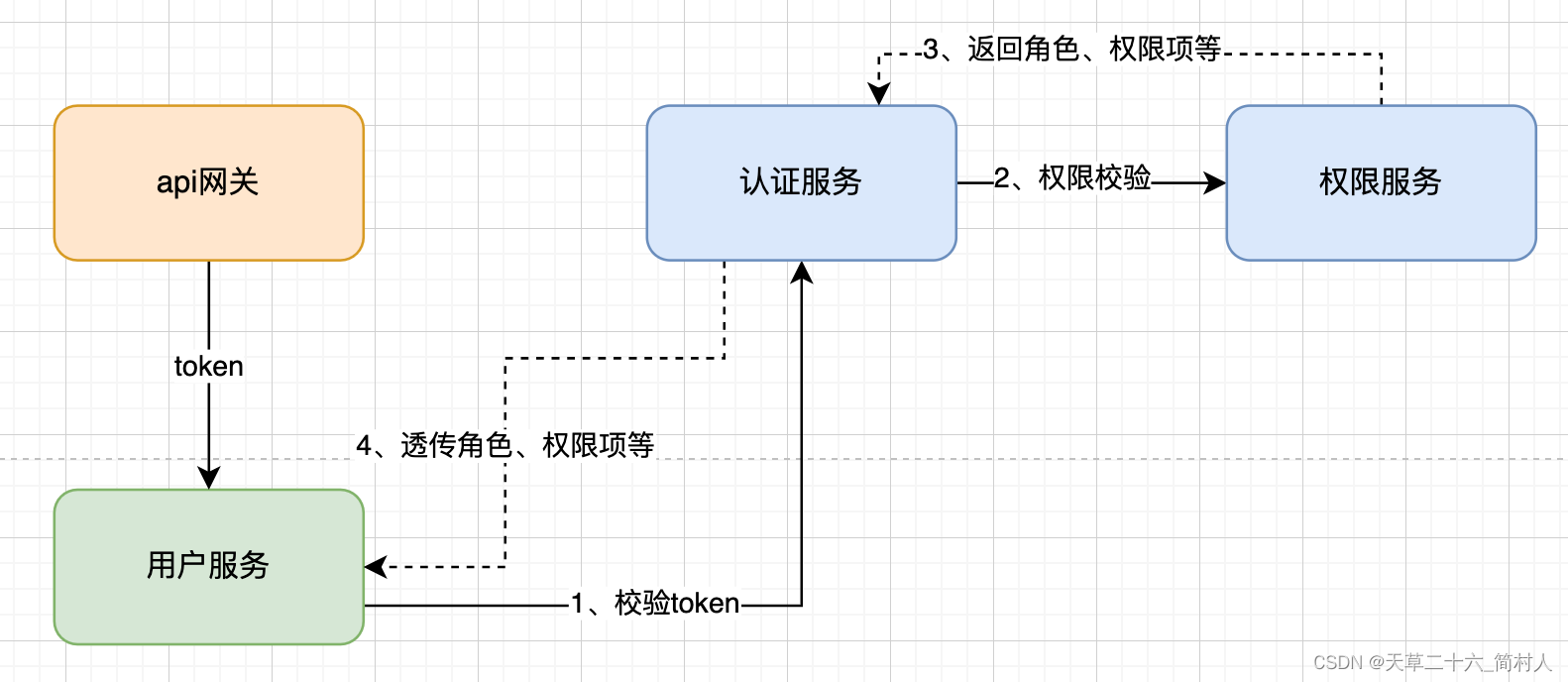
四、注解的定义
- EnableJwtAuth.java
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Import;import java.lang.annotation.*;@Target(ElementType.TYPE)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
@Inherited
@Import({EnableJwtAuthImportSelector.class})
public @interface EnableJwtAuth {}
- 增加开关
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.condition.ConditionalOnProperty;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Import;import java.lang.annotation.*;@Target(ElementType.TYPE)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
@Inherited
@Import({EnableJwtAuthImportSelector.class})
@ConditionalOnProperty(name = "spring.jwt.enabled", havingValue = "true", matchIfMissing = true)
public @interface EnableJwtAuth {}
- EnableJwtAuthImportSelector.java
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.gson.GsonAutoConfiguration;
import org.springframework.context.EnvironmentAware;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.ImportSelector;
import org.springframework.core.annotation.AnnotationAttributes;
import org.springframework.core.env.Environment;
import org.springframework.core.type.AnnotationMetadata;
import org.springframework.util.Assert;import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;// 实现接口EnvironmentAware和ImportSelector
public final class EnableJwtAuthImportSelector implements ImportSelector, EnvironmentAware {private Environment environment;protected Environment getEnvironment() {return this.environment;}@Overridepublic void setEnvironment(Environment environment) {this.environment = environment;}// 读取配置项spring.jwt.enabled的值,默认是开启jwt校验protected boolean isEnabled() {return getEnvironment().getProperty("spring.jwt.enabled", Boolean.class, Boolean.TRUE);}@Overridepublic final String[] selectImports(AnnotationMetadata importingClassMetadata) {if (!isEnabled()) {return new String[0];}Class<EnableJwtAuth> annoType = EnableJwtAuth.class;Map<String, Object> annotationAttributes = importingClassMetadata.getAnnotationAttributes(annoType.getName(), false);AnnotationAttributes attributes = AnnotationAttributes.fromMap(annotationAttributes);Assert.notNull(attributes, String.format("@%s is not present on importing class '%s' as expected",annoType.getSimpleName(), importingClassMetadata.getClassName()));// 实例化两个类List<String> classNames = new ArrayList<>(2);classNames.add(GsonAutoConfiguration.class.getName());// JwtAuthConfiguration是我们自定义的类classNames.add(JwtAuthConfiguration.class.getName());return classNames.toArray(new String[0]);}}
- JwtAuthConfiguration.java
此类中定义你所需要的java类。
另外一点,如果你需要对接口uri进行过滤,也需要在这里进行校验。
@Beanpublic JwtAuthenticationProvider jwtAuthenticationManager() {return new JwtAuthenticationProvider();}
- JwtAuthenticationProvider.java
import org.slf4j.Logger;
import org.slf4j.LoggerFactory;
import org.springframework.security.authentication.AuthenticationCredentialsNotFoundException;
import org.springframework.security.authentication.AuthenticationProvider;
import org.springframework.security.core.Authentication;
import org.springframework.util.StringUtils;/*** 依赖spring security 权限框架** @author xxx*/
public class JwtAuthenticationProvider implements AuthenticationProvider {private static final Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(JwtAuthenticationProvider.class);@Overridepublic boolean supports(Class<?> authentication) {return JwtAuthenticationToken.class.isAssignableFrom(authentication);}@Overridepublic Authentication authenticate(Authentication authenticationToken) {final String authToken = (String) authenticationToken.getCredentials();if (StringUtils.isEmpty(authToken)) {throw new AuthenticationCredentialsNotFoundException(MessageDefs.TOKEN_MISSING);}// 调用认证服务进行token校验,示意图见上面的总体设计// 下面是伪代码,自定义类JwtUser用于包装用户信息JwtUser userDetails = tokenVerifyClient.verify(authToken);// 取出需要的字段,传递给TransmittedUserInfo透传对象TransmittedUserInfo userInfo = new TransmittedUserInfo(userDetails);XxTransmittableThreadLocal<TransmittedUserInfo> xxTransmittableThreadLocal = (XxTransmittableThreadLocal<TransmittedUserInfo>) ApplicationContextProvider.getApplicationContext().getBean("xxTransmittableThreadLocal");xhTransmittableThreadLocal.set(userInfo);// 校验成功return new JwtAuthenticationToken(userDetails.getId(), null, userDetails.getAuthorities());}}
五、自定义注解的使用

六、说在最后的话
自定义注解,本身比较简单,这里使用了@Import注解,故不需要再在META-INF/spring.factories增加org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.EnableAutoConfiguration配置类。
我这里想要补充说明的是,文章里的权限校验,只是一种实现方案。
更建议你在api网关中实现token的校验。
那么,java服务中,需要做哪些工作呢?
把api网关传过来的字段,很好地传承并透传至下游服务。
还有一个重要的工作就是,取出当前服务上下文中的数据,做以下工作:
- 用户ID是否和token一致,防止token被冒用
- 接口的权限(判断当前用户是否能够访问该接口)
- 取出当前用户的角色、租户ID、用户ID、学校ID等关键字段,保存到数据库,并输出打印日志。





![[开发|java] java 将json转化java对象](http://pic.xiahunao.cn/[开发|java] java 将json转化java对象)










--- 0.96寸OLED液晶屏模块11)


