强连通分量,不能再加任何一个点了,再加一个点就不是强连通了
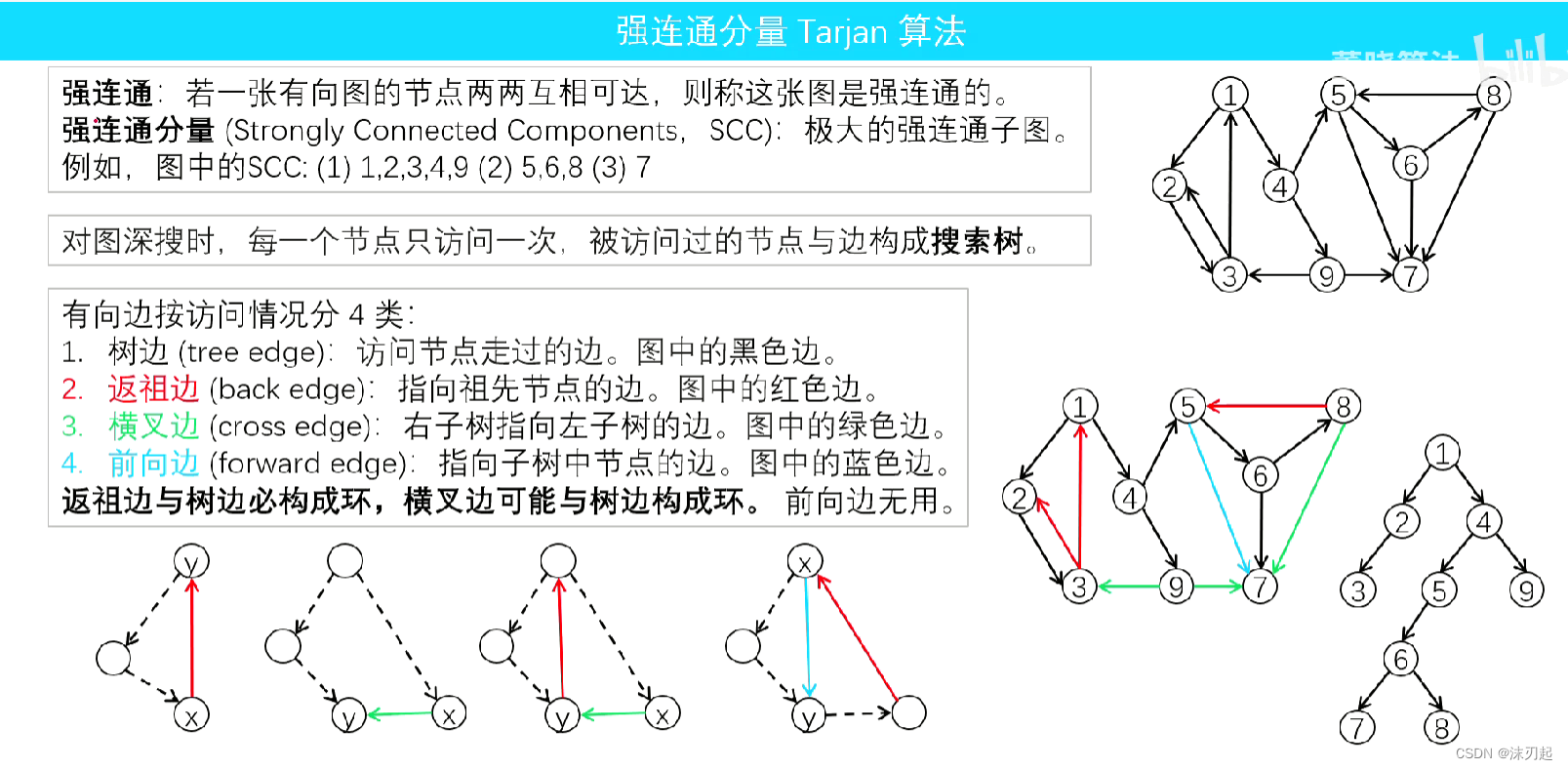

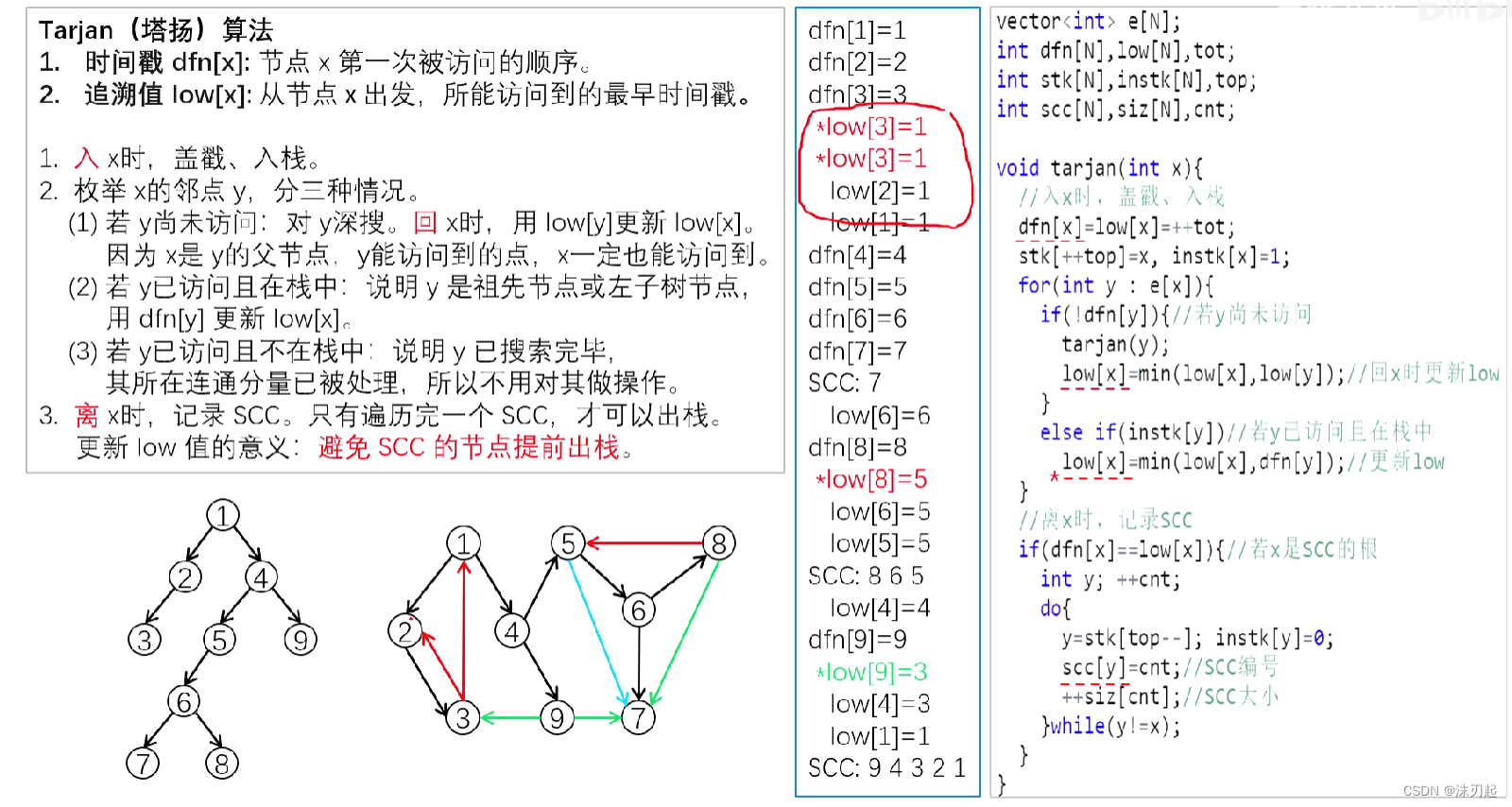
vector<int>e[N];
int dfn[N],low[N],tot;
bool instk[N];
int scc[N],siz[N],cnt;
void tarjan(int x){//入x时,盖戳,入栈dfn[x]=low[x]=++tot;q.push(x);instk[x]=true;for(auto y:e[x]){if(!dfn[y]){//若y尚未访问tarjan(y);low[x]=min(low[x],low[y]);//回x时更新low}else if(instk[y]){//若y已被访问且在栈中low[x]=min(low[x],dfn[y]);//更新low}}//离x时,记录SCCif(dfn[x]==low[x]){//若x是SCC的根int y;cnt++;do{y=q.top();q.pop();instk[y]=false;scc[y]=cnt;//SCC编号siz[cnt]++;//SCC大小}while(y!=x);}
}[USACO06JAN] The Cow Prom S - 洛谷
AC代码:
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
#define endl '\n'
#define int long long
using namespace std;
const int N=1e4+10;
int dfn[N],low[N],tot;
bool instk[N];
int siz[N],cnt;
stack<int>q;
vector<vector<int>>e(N);
int n,m;
void tarjan(int x){dfn[x]=low[x]=++tot;q.push(x);instk[x]=true;for(auto v:e[x]){if(!dfn[v]){tarjan(v);low[x]=min(low[x],low[v]);}else if(instk[v]){low[x]=min(low[x],dfn[v]);}}if(dfn[x]==low[x]){int y;cnt++;do{y=q.top();q.pop();instk[y]=false;siz[cnt]++;}while(y!=x);}
}
void solve() {cin>>n>>m;while(m--){int a,b;cin>>a>>b;e[a].push_back(b);}for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){if(!dfn[i]) tarjan(i);}int ans=0;for(int i=1;i<=cnt;i++){if(siz[i]>1) ans++;}cout<<ans<<endl;
}
signed main() {ios::sync_with_stdio(false);cin.tie(0);cout.tie(0);int t=1;
// cin>>t;while(t--) {solve();}return 0;
}Trajan SCC缩点

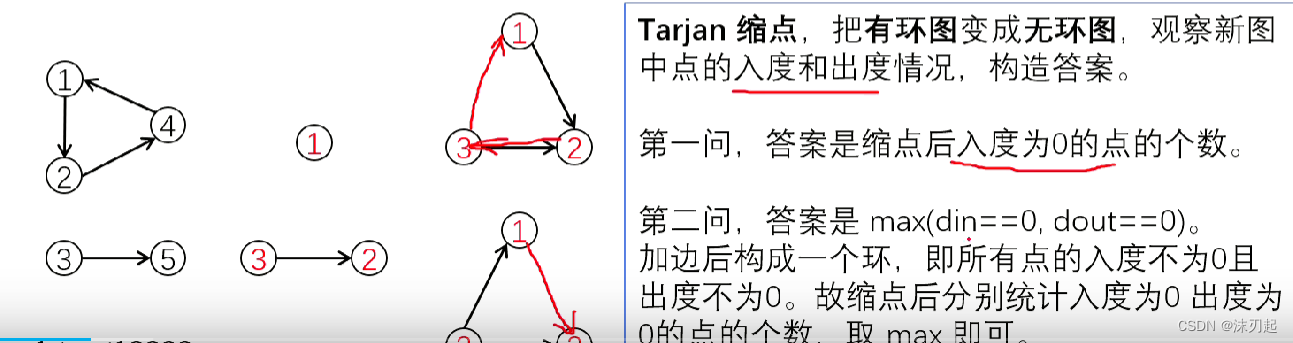
我们加边的时候让出度为0的点指向入度为0的点,那么只要max(din,dout)即可
AC代码:
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
#define endl '\n'
#define int long long
using namespace std;
const int N=1e4+10;
int dfn[N],low[N],tot;
bool instk[N];
int scc[N],cnt;
int din[N],dout[N];//SCC的入度,出度
int n;
vector<vector<int>>e(N);
stack<int>q;
void tarjan(int x){dfn[x]=low[x]=++tot;q.push(x);instk[x]=true;for(auto v:e[x]){if(!dfn[v]){tarjan(v);low[x]=min(low[x],low[v]);}else if(instk[v]){low[x]=min(low[x],dfn[v]);}}if(dfn[x]==low[x]){int y;cnt++;do{y=q.top();q.pop();instk[y]=false;scc[y]=cnt;}while(y!=x);}
}
void solve() {cin>>n;for(int i=1,a;i<=n;i++){cin>>a;while(a){e[i].push_back(a);cin>>a;}}for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){if(!dfn[i]) tarjan(i);//一些点可能走不到,即图不连通}for(int x=1;x<=n;x++){//枚举n个点for(int y:e[x]){//枚举点x的邻边,x指向yif(scc[x]!=scc[y]){//如果x和y所在的强连通分量不一样,即不在同一个强连通分量之内din[scc[y]]++;//y所在的强连通分量的入度++dout[scc[x]]++;//x所在的强连通分量的出度++}}}int a=0,b=0;for(int i=1;i<=cnt;i++){if(!din[i]) a++;//a表示缩点后入度为0的个数if(!dout[i]) b++;//b表示缩点后出度为0的个数}cout<<a<<endl;if(cnt==1) cout<<0<<endl;//特判,如果只有一个强连通分量,那么就不用加边了else cout<<max(a,b)<<endl;
}
signed main() {ios::sync_with_stdio(false);cin.tie(0);cout.tie(0);int t=1;
// cin>>t;while(t--) {solve();}return 0;
}[USACO03FALL / HAOI2006] 受欢迎的牛 G - 洛谷
 AC代码:
AC代码:
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
#define endl '\n'
#define int long long
using namespace std;
const int N=1e4+10;
int dfn[N],low[N],tot;
bool instk[N];
int scc[N],siz[N];
int cnt;
int dout[N];
vector<vector<int>>e(N);
stack<int>q;
int n,m;
void tarjan(int x){dfn[x]=low[x]=++tot;q.push(x);instk[x]=true;for(auto v:e[x]){if(!dfn[v]){tarjan(v);low[x]=min(low[x],low[v]);}else if(instk[v]){low[x]=min(low[x],dfn[v]);}}if(dfn[x]==low[x]){int y;cnt++;do{y=q.top();q.pop();instk[y]=false;scc[y]=cnt;siz[cnt]++;}while(y!=x);}
}
void solve() {cin>>n>>m;for(int i=0;i<m;i++){int a,b;cin>>a>>b;e[a].push_back(b);}for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){if(!dfn[i]) tarjan(i);}for(int x=1;x<=n;x++){for(auto y:e[x]){if(scc[x]!=scc[y]){dout[scc[x]]++;}}}int sum=0;int cnt1=0;for(int i=1;i<=cnt;i++){if(dout[i]==0){sum=siz[i];cnt1++;}}if(cnt1>1) sum=0;cout<<sum<<endl;
}
signed main() {ios::sync_with_stdio(false);cin.tie(0);cout.tie(0);int t=1;
// cin>>t;while(t--) {solve();}return 0;
}【模板】缩点 - 洛谷
先缩点转化成一个无环图
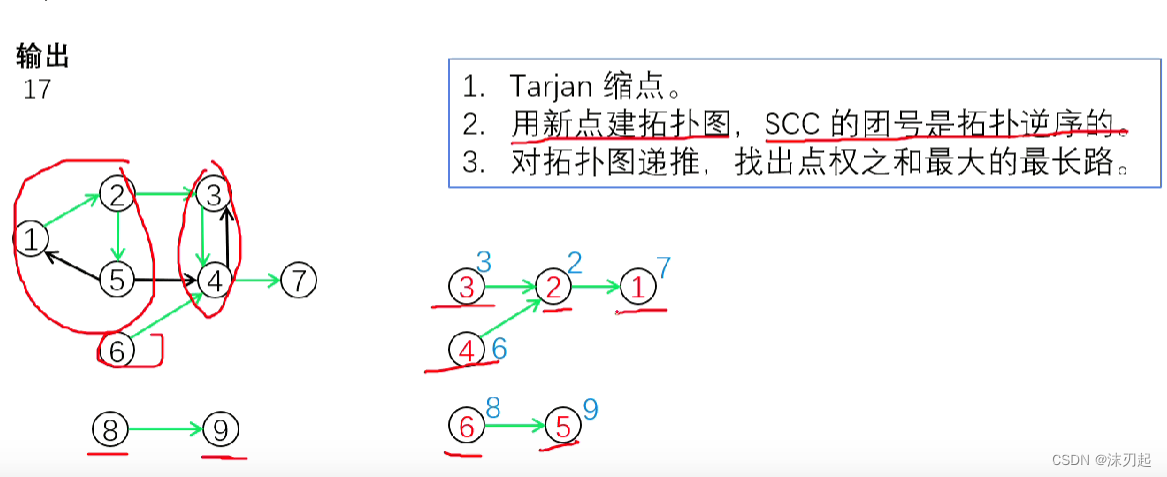
团号逆序是拓扑序,因为我们给强连通分量标号的时候是从1开始标的,于是团号小的在拓扑序的末端,这样从大到小枚举团号即为拓扑序,保证是线性的,这样dp的话才能满足无后效性
AC代码:
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
#define endl '\n'
#define int long long
using namespace std;
const int N=1e4+10;
int dfn[N],low[N],tot;
bool instk[N];
int scc[N],cnt;
int w[N],nw[N];
int n,m;
vector<vector<int>>e(N),ne(N);
stack<int>q;
int dp[N];
void tarjan(int x){dfn[x]=low[x]=++tot;q.push(x);instk[x]=true;for(auto v:e[x]){if(!dfn[v]){tarjan(v);low[x]=min(low[x],low[v]);}else if(instk[v]){low[x]=min(low[x],dfn[v]);}}if(dfn[x]==low[x]){int y;cnt++;do{y=q.top();q.pop();instk[y]=false;scc[y]=cnt;}while(y!=x);}
}
void solve() {cin>>n>>m;for(int i=1;i<=n;i++) cin>>w[i];for(int i=0;i<m;i++){int a,b;cin>>a>>b;e[a].push_back(b);}for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){if(!dfn[i]) tarjan(i);}for(int x=1;x<=n;x++){nw[scc[x]]+=w[x];//新点的权值for(int y:e[x]){if(scc[x]!=scc[y]){ne[scc[x]].push_back(scc[y]);}}}//缩点后建拓扑图for(int x=cnt;x>=1;x--){if(dp[x]==0){//若x为路的起点dp[x]=nw[x];}for(auto y:ne[x]){dp[y]=max(dp[y],dp[x]+nw[y]);}}int ans=0;for(int i=1;i<=cnt;i++) ans=max(ans,dp[i]);//可能图不连通,有多个强连通分量cout<<ans<<endl;
}
signed main() {ios::sync_with_stdio(false);cin.tie(0);cout.tie(0);int t=1;
// cin>>t;while(t--) {solve();}return 0;
}











)
))

)



