一、Spring AOP基础概念
1、基础概念
- 连接点(Join point):能够被拦截的地方,Spring AOP
是基于动态代理的,所以是方法拦截的,每个成员方法都可以称之为连接点; - 切点(Poincut):每个方法都可以称之为连接点,我们具体定位到某一个方法就成为切点;
- 增强/通知(Advice):表示添加到切点的一段逻辑代码,并定位连接点的方位信息,简单来说就定义了是干什么的,具体是在哪干;
- 织入(Weaving):将增强/通知添加到目标类的具体连接点上的过程;
- 引入/引介(Introduction):允许我们向现有的类添加新方法或属性,是一种特殊的增强;
- 切面(Aspect):切面由切点和增强/通知组成,它既包括了横切逻辑的定义、也包括了连接点的定义。
五种通知的分类:
- 前置通知(Before Advice):在目标方法被调用前调用通知功能;
- 后置通知(After Advice):在目标方法被调用之后调用通知功能;
- 返回通知(After-returning):在目标方法成功执行之后调用通知功能;
- 异常通知(After-throwing):在目标方法抛出异常之后调用通知功能;
- 环绕通知(Around):把整个目标方法包裹起来,在被调用前和调用之后分别调用通知功能。
2、 Spring中AOP的实现
2.1 实现方式
Spring 提供了很多的实现AOP的方式:Spring 接口方式,schema配置方式和注解的方式.
如果使用接口方式引入AOP, 就是用JDK提供的动态代理来实现.
如果没有使用接口的方式引入. 那么就是使用CGLIB来实现的
研究使用接口方式实现AOP, 目的是为了更好地理解spring使用动态代理实现AOP的两种方
2.2 AspectJ
Spring提供了对AspectJ的支持, 但只提供了部分功能的支持: 即AspectJ的切点解析(表达式)和匹配
我们在写切面的时候,经常使用到的@Aspect, @Before, @Pointcut, @After, @AfterReturning, @AfterThrowing等就是AspectJ提供的.
AspectJ很好用, 效率也很高. 那么为什么Spring不使用AspectJ全套的东西呢? 尤其是AspectJ的静态织入.
AspectJ的特点
-
AspectJ属于静态织入. 他是通过修改代码实现的. 它的织入时机有三种
(a) 、Compile-time weaving: 编译期织入. 例如: 类A使用AspectJ增加了一个属性. 类B引用了类A, 这个场景就需要在编译期的时候进行织入, 否则类B就没有办法编译, 会报错.
(b)、 Post-compile weaving: 编译后织入.也就是已经生成了.class文件了, 或者是都已经达成jar包了. 这个时候, 如果我们需要增强, 就要使用到编译后织入
( c)、Loading-time weaving: 指的是在加载类的时候进行织入. -
AspectJ实现了对AOP变成完全的解决方案. 他提供了很多Spring AOP所不能实现的功能
-
由于AspectJ是在实际代码运行前就完成了织入, 因此可以认为他生成的类是没有额外运行开销的.
-
扩展: 这里为什么没有使用到AspectJ的静态织入呢? 因为如果引入静态织入, 需要使用AspectJ自己的解析器. AspectJ文件是以aj后缀结尾的文件, 这个文件Spring是没有办法, 因此要使用AspectJ自己的解析器进行解析. 这样就增加了Spring的成本.
三、 AOP的配置方式
上面说了Spring AOP和AspectJ. 也说道了AspectJ定义了很多注解, 比如: @Aspect, @Pointcut, @Before, @After等等. 但是, 我们使用Spring AOP是使用纯java代码写的. 也就是说他完全属于Spring, 和AspectJ没有什么关系. Spring只是沿用了AspectJ中的概念. 包括AspectJ提供的jar包的注解. 但是, 并不依赖于AspectJ的功能.
第一种: 基于接口方式的配置. 在Spring1.2版本, 提供的是完全基于接口方式实现的
第二种: 基于schema-based配置. 在spring2.0以后使用了xml的方式来配置.
第三种: 基于注解@Aspect的方式. 这种方式是最简单, 方便的. 这里虽然叫做AspectJ, 但实际上和AspectJ一点关系也没有.
因为我们在平时工作中主要使用的是注解的方式配置AOP, 而注解的方式主要是基于第一种接口的方式实现的. 所以, 我们会重点研究第一种和第三种配置方式.
二、AOP中的Spring案列
1、示例代码
@Data
@Service
public class CarService {public void action() {System.out.println("行驶中");}
}@Aspect
@Component
public class MyAspect {@Pointcut("execution(* com.test.CarService.action())")private void myPointCut() {}@Before("myPointCut()")public void myBefore() {System.out.println("加油");}@AfterReturning(value = "myPointCut()")public void myAfterReturning() {System.out.println("停车");}
}public class MyTest {public static void main(String[] args) {ApplicationContext context= new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext("com.test");CarService carService = (CarService) context.getBean("carService");carService.action();}
}
2、输出结果
加油
行驶中
停车
三、Spring AOP执行原理
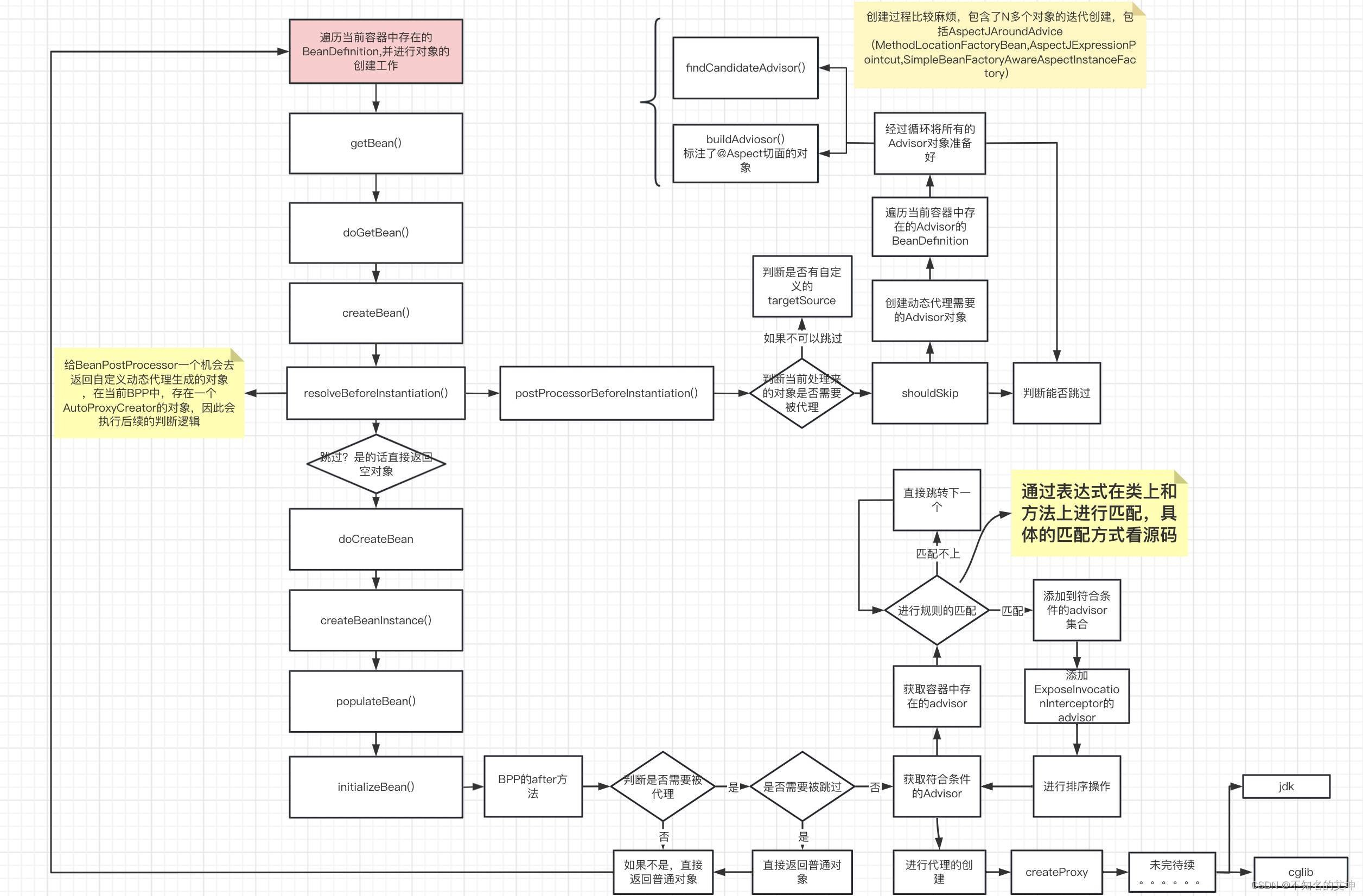
Spring中的AOP其实和ioc没有必要的关系了,aop主要有3步。
前置处理 在创建bean之前提前准备一些AOP需要用到的对象
在创建bean的后置初始化中进行代理对象的生成
进行方法的调用
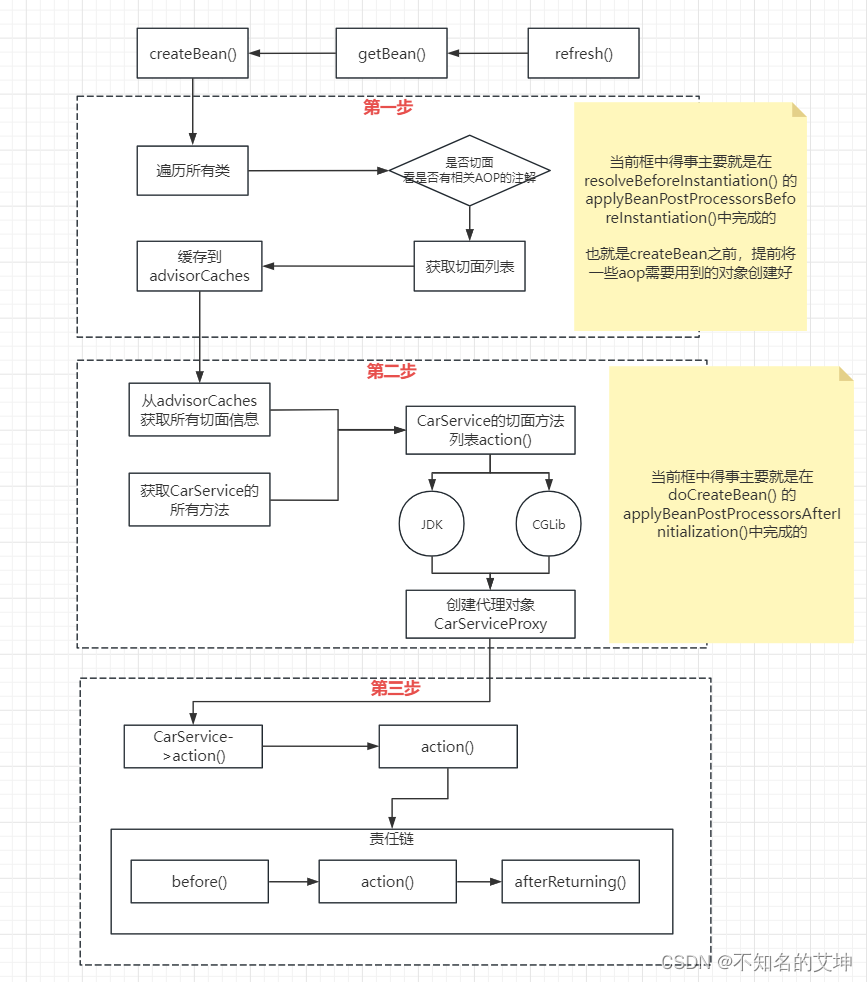
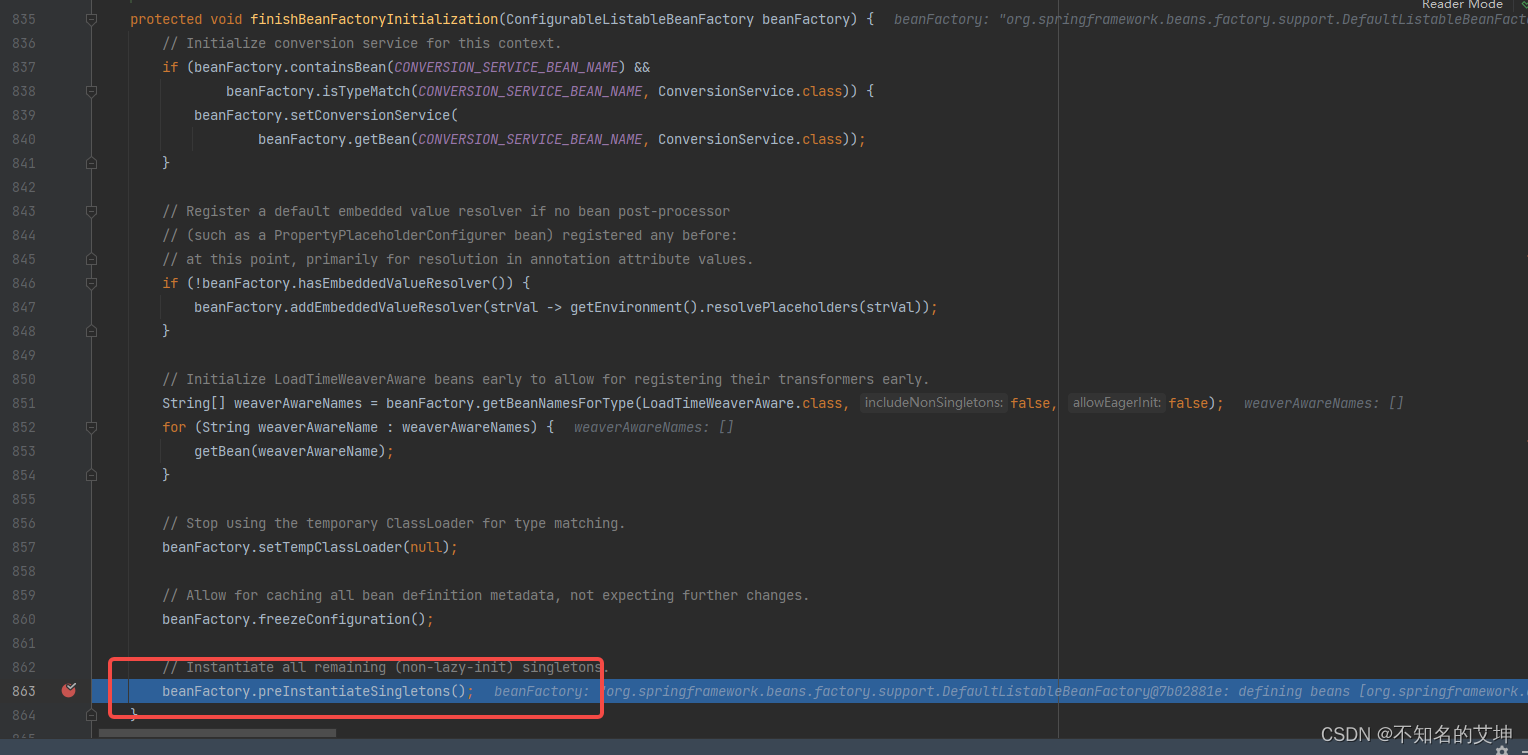
第一步、AOP前置环节
1、resolveBeforeInstantiation()
省略ioc中讲过,debug看起
其他的bean都跳过 直接看CarService类
进入前置处理环节
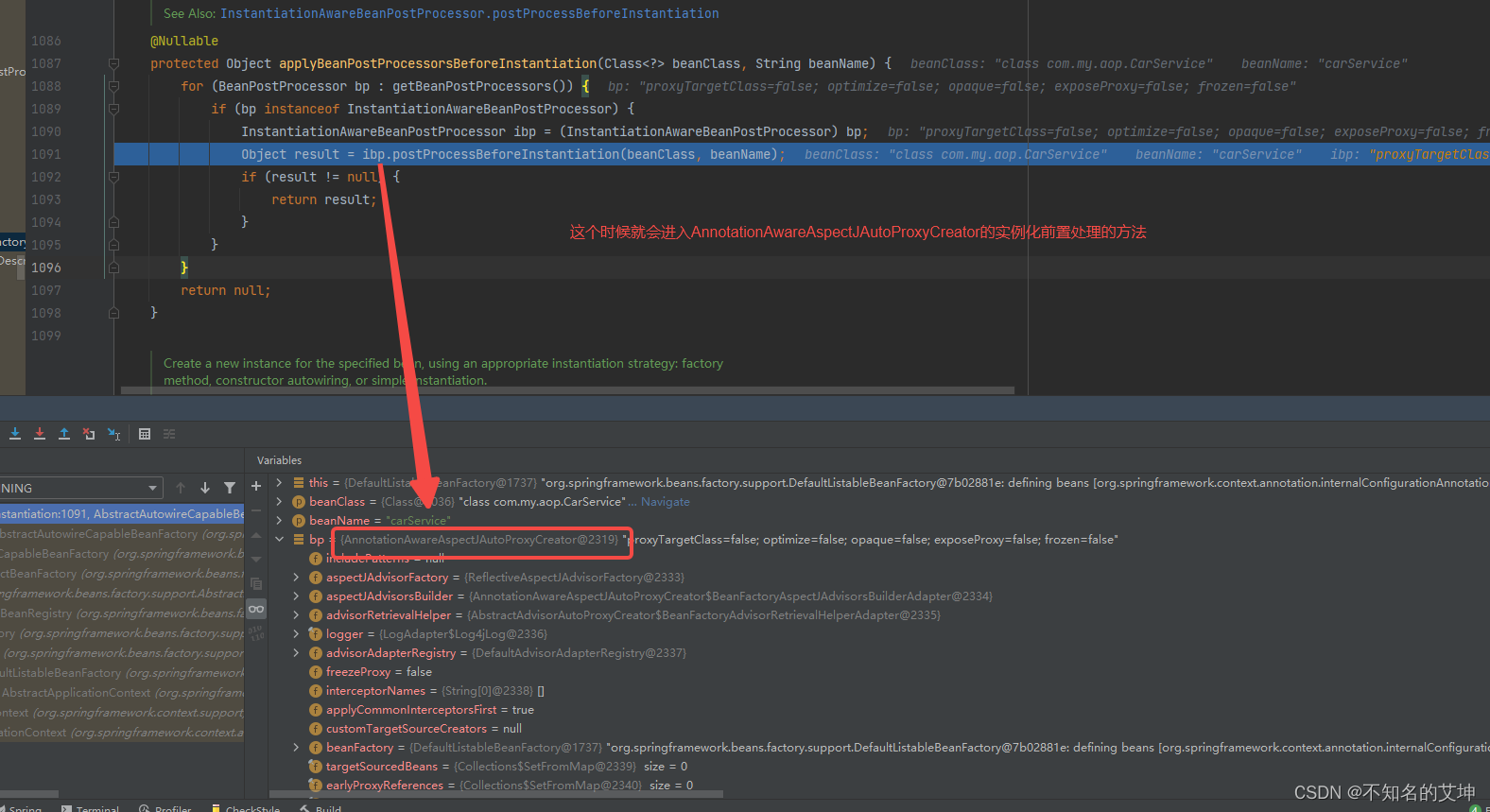
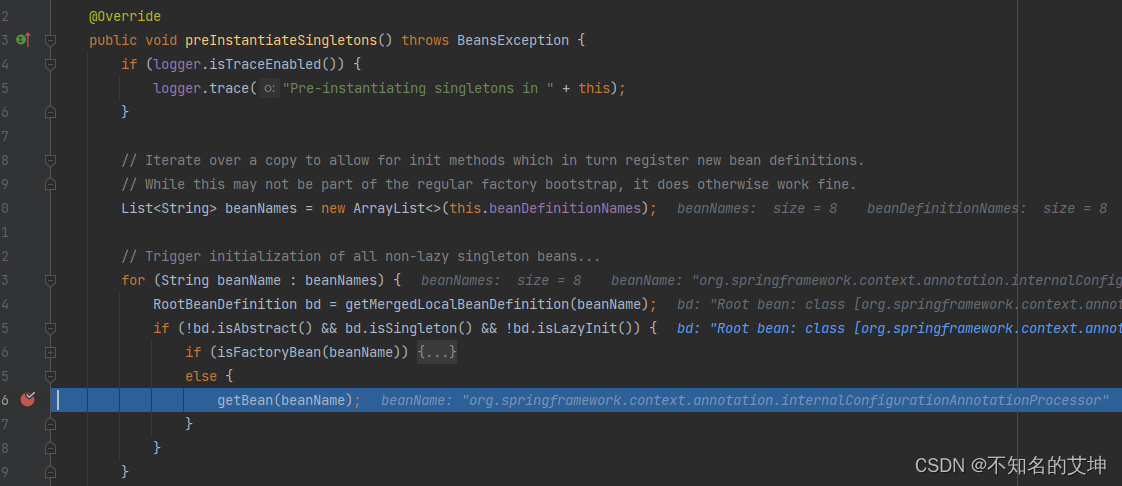
2、AbstractAutoProxyCreator#postProcessBeforeInstantiation()
resolveBeforeInstantiation方法进去就会调到AbstractAutoProxyCreator的postProcessBeforeInstantiation方法
/*** 在创建Bean的流程中还没调用构造器来实例化Bean的时候进行调用(实例化前后)* AOP解析切面以及事务解析事务注解都是在这里完成的* @param beanClass 当前正在创建的Bean的Class对象* @param beanName beanName* @return* @throws BeansException*/@Overridepublic Object postProcessBeforeInstantiation(Class<?> beanClass, String beanName) throws BeansException {//构建我们的缓存keyObject cacheKey = getCacheKey(beanClass, beanName);if (!StringUtils.hasLength(beanName) || !this.targetSourcedBeans.contains(beanName)) {//如果被解析过直接返回if (this.advisedBeans.containsKey(cacheKey)) {return null;}/*** 判断是不是基础的Bean(Advice、PointCut、Advisor、AopInfrastructureBean)是就直接跳过* 判断是不是应该跳过 (AOP解析直接解析出我们的切面信息(并且把我们的切面信息进行缓存),而事务在这里是不会解析的)*/if (isInfrastructureClass(beanClass) || shouldSkip(beanClass, beanName)) {this.advisedBeans.put(cacheKey, Boolean.FALSE);return null;}}TargetSource targetSource = getCustomTargetSource(beanClass, beanName);if (targetSource != null) {if (StringUtils.hasLength(beanName)) {this.targetSourcedBeans.add(beanName);}Object[] specificInterceptors = getAdvicesAndAdvisorsForBean(beanClass, beanName, targetSource);Object proxy = createProxy(beanClass, beanName, specificInterceptors, targetSource);this.proxyTypes.put(cacheKey, proxy.getClass());return proxy;}return null;}
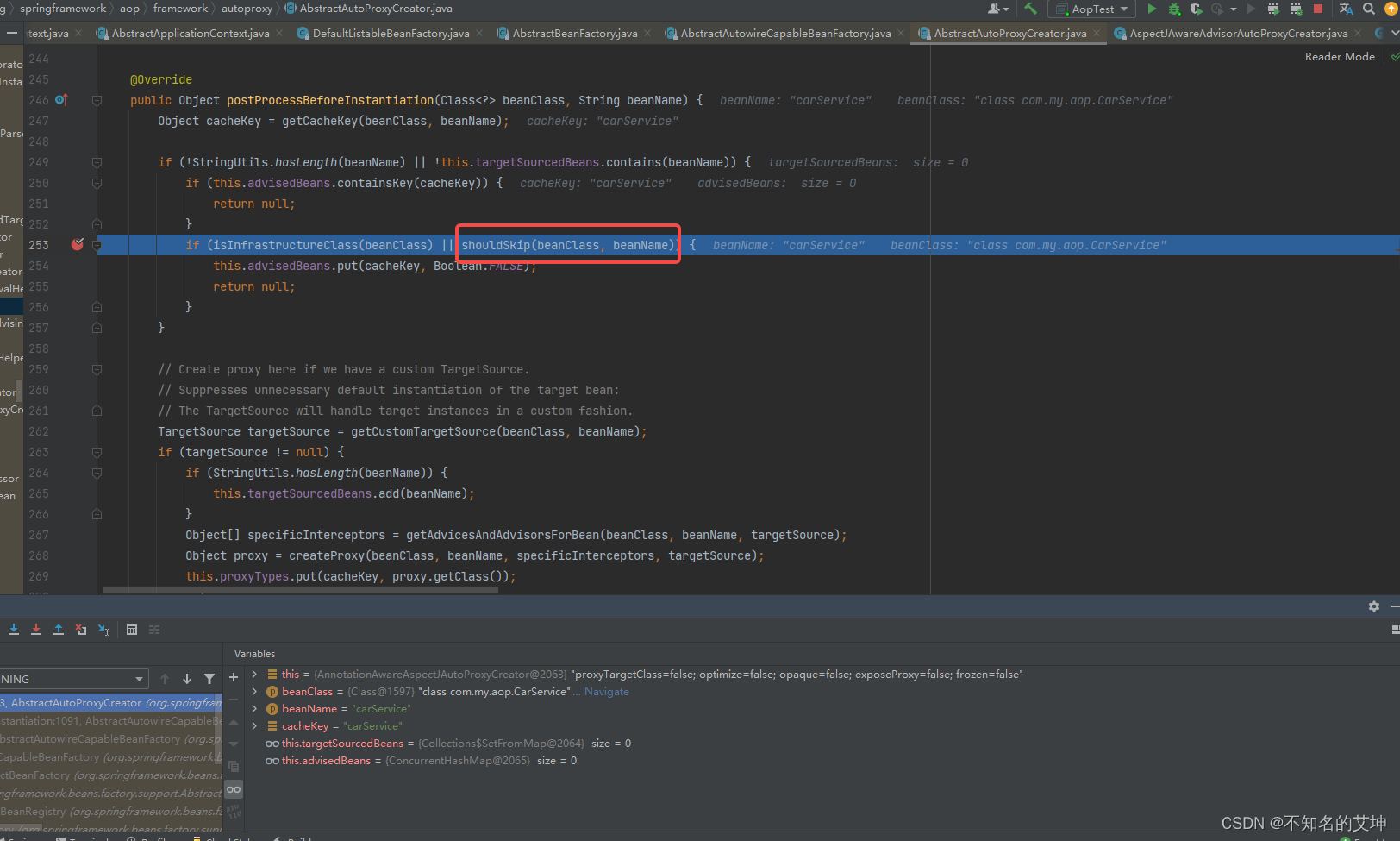
3、shouldSkip()
这一步很重要,会找出所有的切面
protected boolean shouldSkip(Class<?> beanClass, String beanName) {/*** 找到候选的Advisors(通知者或者增强器对象)*/List<Advisor> candidateAdvisors = findCandidateAdvisors();for (Advisor advisor : candidateAdvisors) {if (advisor instanceof AspectJPointcutAdvisor &&((AspectJPointcutAdvisor) advisor).getAspectName().equals(beanName)) {return true;}}return super.shouldSkip(beanClass, beanName);}
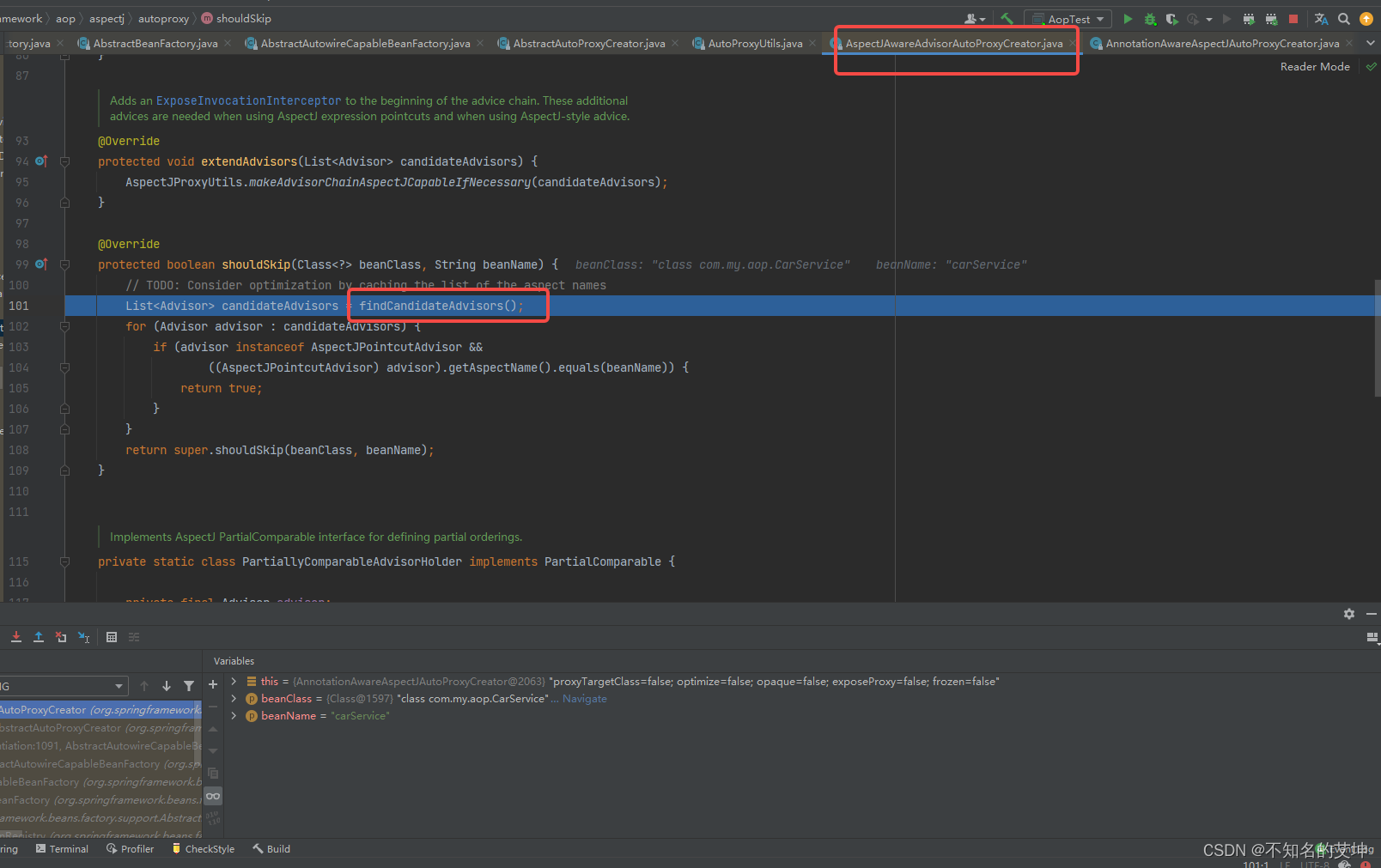
4、findCandidateAdvisors()
获取切面相关得信息,重点方法开始
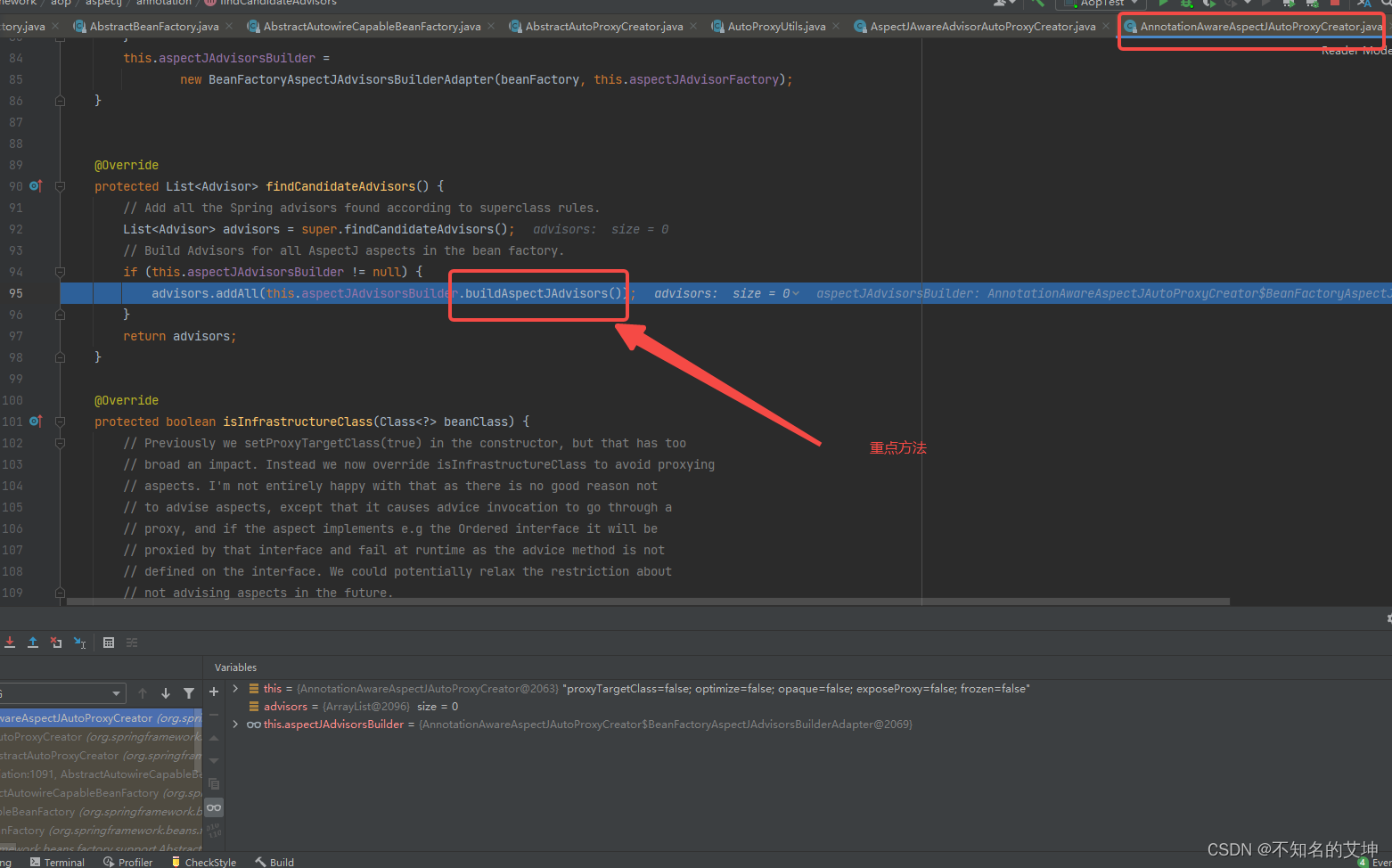
@Overrideprotected List<Advisor> findCandidateAdvisors() {//找出事务相关的advisorList<Advisor> advisors = super.findCandidateAdvisors();//找出Aspect相关的信息之后封装为一个advisorif (this.aspectJAdvisorsBuilder != null) {advisors.addAll(this.aspectJAdvisorsBuilder.buildAspectJAdvisors());}//返回我们所有的通知return advisors;}
4.1 findCandidateAdvisors()
protected List<Advisor> findCandidateAdvisors() {Assert.state(this.advisorRetrievalHelper != null, "No BeanFactoryAdvisorRetrievalHelper available");/*** 通过通知者检测帮助类来帮助我们找到通知**/return this.advisorRetrievalHelper.findAdvisorBeans();}
4.2 buildAspectJAdvisors()
遍历所有的类, 判断是否切面;
是切面才会进入后面逻辑;
获取每个 Aspect 的切面列表;
保存 Aspect 的切面列表到缓存 advisorsCache 中。
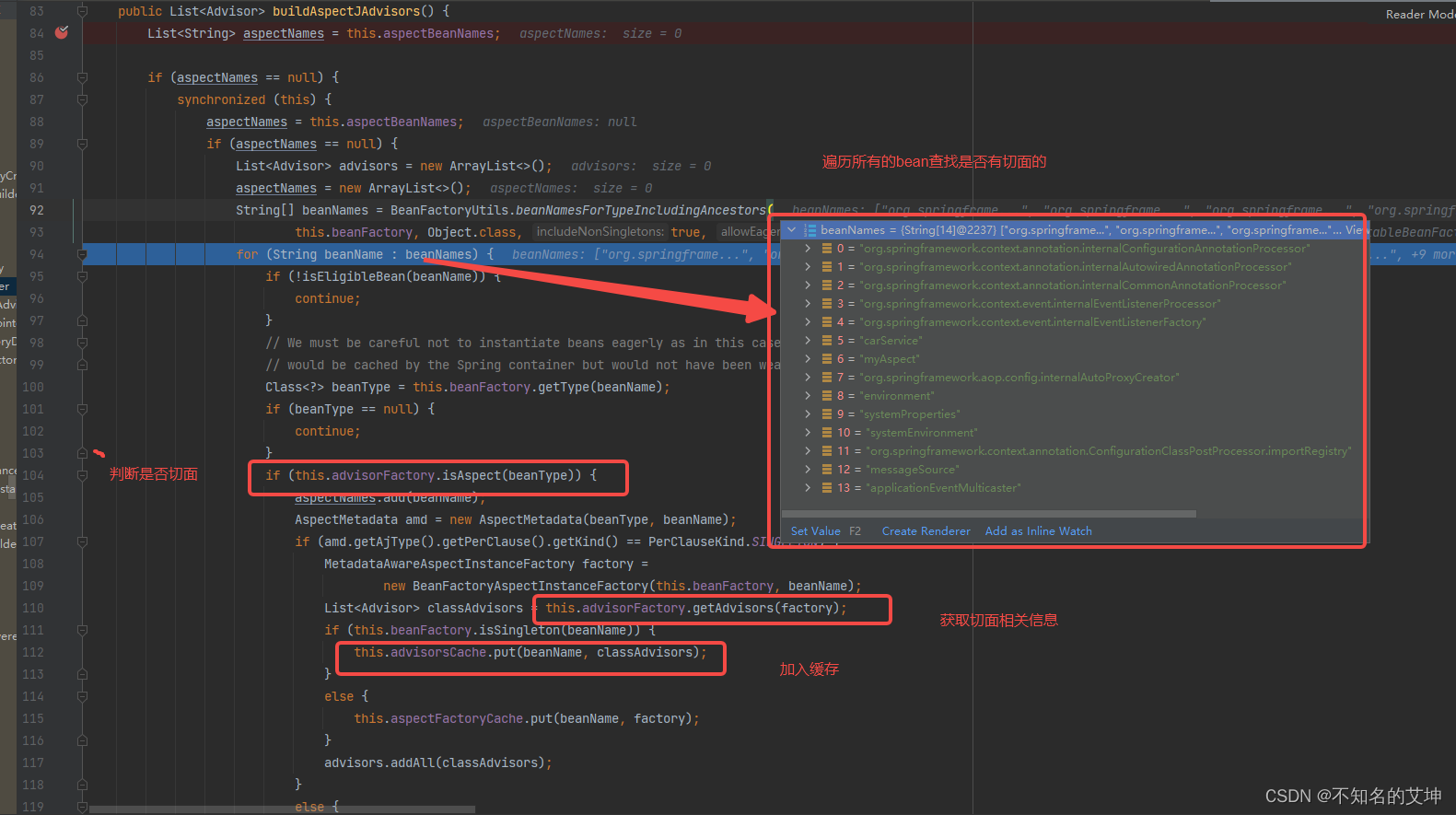
/*** 寻找Aspect注解的面向对象,然后解析他的方法,通过注解来生成对应的通知器Advisor** Look for AspectJ-annotated aspect beans in the current bean factory,* and return to a list of Spring AOP Advisors representing them.* <p>Creates a Spring Advisor for each AspectJ advice method.* @return the list of {@link org.springframework.aop.Advisor} beans* @see #isEligibleBean*/public List<Advisor> buildAspectJAdvisors() {// 获取切面名字列表List<String> aspectNames = this.aspectBeanNames;// 缓存字段aspectNames没有值,注意实例化第一个单实例bean的时候就会触发解析切面if (aspectNames == null) {// 双重检查synchronized (this) {aspectNames = this.aspectBeanNames;if (aspectNames == null) {// 用于保存所有解析出来的Advisors集合对象List<Advisor> advisors = new ArrayList<>();// 用于保存切面的名称的集合aspectNames = new ArrayList<>();/*** AOP功能中在这里传入的是Object对象,代表去容器中获取到所有的组件的名称,然后再* 进行遍历,这个过程是十分的消耗性能的,所以说Spring会再这里加入了保存切面信息的缓存。* 但是事务功能不一样,事务模块的功能是直接去容器中获取Advisor类型的,选择范围小,且不消耗性能。* 所以Spring在事务模块中没有加入缓存来保存我们的事务相关的advisor*/String[] beanNames = BeanFactoryUtils.beanNamesForTypeIncludingAncestors(this.beanFactory, Object.class, true, false);// 遍历我们从IOC容器中获取处的所有Bean的名称for (String beanName : beanNames) {// 判断当前bean是否为子类定制的需要过滤的beanif (!isEligibleBean(beanName)) {continue;}// We must be careful not to instantiate beans eagerly as in this case they// would be cached by the Spring container but would not have been weaved.// 通过beanName去容器中获取到对应class对象Class<?> beanType = this.beanFactory.getType(beanName, false);if (beanType == null) {continue;}// 判断当前bean是否使用了@Aspect注解进行标注if (this.advisorFactory.isAspect(beanType)) {aspectNames.add(beanName);// 对于使用了@Aspect注解标注的bean,将其封装为一个AspectMetadata类型。// 这里在封装的过程中会解析@Aspect注解上的参数指定的切面类型,如perthis// 和pertarget等。这些被解析的注解都会被封装到其perClausePointcut属性中AspectMetadata amd = new AspectMetadata(beanType, beanName);// 判断@Aspect注解中标注的是否为singleton类型,默认的切面类都是singleton类型if (amd.getAjType().getPerClause().getKind() == PerClauseKind.SINGLETON) {// 将BeanFactory和当前bean封装为MetadataAwareAspect-// InstanceFactory对象,这里会再次将@Aspect注解中的参数都封装// 为一个AspectMetadata,并且保存在该factory中MetadataAwareAspectInstanceFactory factory =new BeanFactoryAspectInstanceFactory(this.beanFactory, beanName);// 通过封装的bean获取其Advice,如@Before,@After等等,并且将这些// Advice都解析并且封装为一个个的AdvisorList<Advisor> classAdvisors = this.advisorFactory.getAdvisors(factory);// 如果切面类是singleton类型,则将解析得到的Advisor进行缓存,// 否则将当前的factory进行缓存,以便再次获取时可以通过factory直接获取if (this.beanFactory.isSingleton(beanName)) {this.advisorsCache.put(beanName, classAdvisors);}else {this.aspectFactoryCache.put(beanName, factory);}advisors.addAll(classAdvisors);}else {// Per target or per this.// 如果@Aspect注解标注的是perthis和pertarget类型,说明当前切面// 不可能是单例的,因而这里判断其如果是单例的则抛出异常if (this.beanFactory.isSingleton(beanName)) {throw new IllegalArgumentException("Bean with name '" + beanName +"' is a singleton, but aspect instantiation model is not singleton");}// 将当前BeanFactory和切面bean封装为一个多例类型的FactoryMetadataAwareAspectInstanceFactory factory =new PrototypeAspectInstanceFactory(this.beanFactory, beanName);// 对当前bean和factory进行缓存this.aspectFactoryCache.put(beanName, factory);advisors.addAll(this.advisorFactory.getAdvisors(factory));}}}this.aspectBeanNames = aspectNames;return advisors;}}}if (aspectNames.isEmpty()) {return Collections.emptyList();}// 通过所有的aspectNames在缓存中获取切面对应的Advisor,这里如果是单例的,则直接从advisorsCache// 获取,如果是多例类型的,则通过MetadataAwareAspectInstanceFactory立即生成一个List<Advisor> advisors = new ArrayList<>();for (String aspectName : aspectNames) {List<Advisor> cachedAdvisors = this.advisorsCache.get(aspectName);// 如果是单例的Advisor bean,则直接添加到返回值列表中if (cachedAdvisors != null) {advisors.addAll(cachedAdvisors);}else {// 如果是多例的Advisor bean,则通过MetadataAwareAspectInstanceFactory生成MetadataAwareAspectInstanceFactory factory = this.aspectFactoryCache.get(aspectName);advisors.addAll(this.advisorFactory.getAdvisors(factory));}}return advisors;}
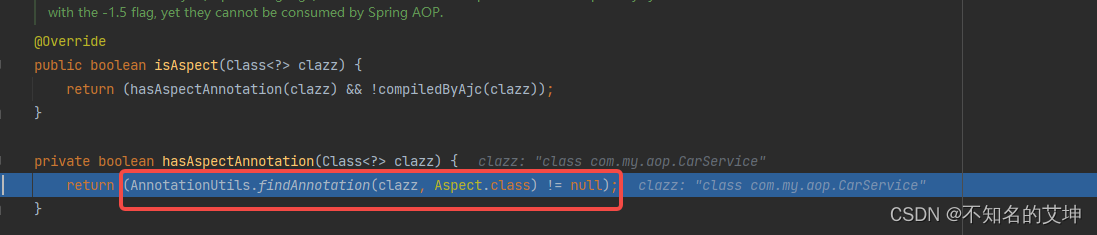
4.2.0 isAspect()
判断是否切面就看是否有@Aspect注解修饰
4.2.1 getAdvisors()
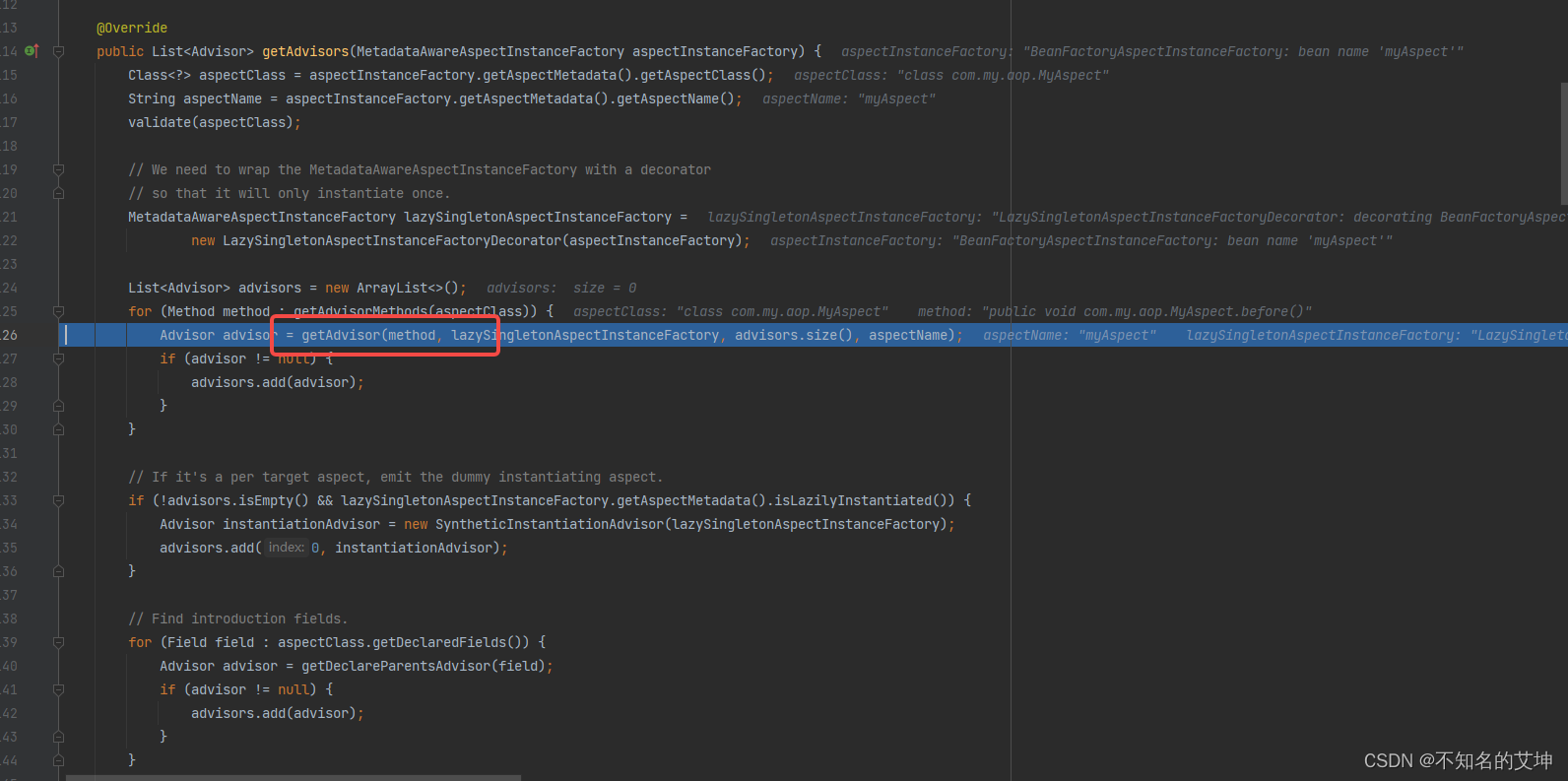
@Overridepublic List<Advisor> getAdvisors(MetadataAwareAspectInstanceFactory aspectInstanceFactory) {//获取我们的标记为Aspect的类Class<?> aspectClass = aspectInstanceFactory.getAspectMetadata().getAspectClass();//获取我们的切面类的名称String aspectName = aspectInstanceFactory.getAspectMetadata().getAspectName();//校验我们的切面类validate(aspectClass);//我们使用的是包装模式来包装我们的MetadataAwareAspectInstanceFactory构建为MetadataAwareAspectInstanceFactoryMetadataAwareAspectInstanceFactory lazySingletonAspectInstanceFactory =new LazySingletonAspectInstanceFactoryDecorator(aspectInstanceFactory);List<Advisor> advisors = new ArrayList<>();//获取到切面类中的所有方法,但是该方法不会解析到标注了@PointCut注解的方法for (Method method : getAdvisorMethods(aspectClass)) {//循环解析我们切面中的方法Advisor advisor = getAdvisor(method, lazySingletonAspectInstanceFactory, advisors.size(), aspectName);if (advisor != null) {advisors.add(advisor);}}if (!advisors.isEmpty() && lazySingletonAspectInstanceFactory.getAspectMetadata().isLazilyInstantiated()) {Advisor instantiationAdvisor = new SyntheticInstantiationAdvisor(lazySingletonAspectInstanceFactory);advisors.add(0, instantiationAdvisor);}for (Field field : aspectClass.getDeclaredFields()) {Advisor advisor = getDeclareParentsAdvisor(field);if (advisor != null) {advisors.add(advisor);}}return advisors;}
a、getAdvisorMethods(Class<?> aspectClass)
获取切面上的通知方法,并按照规则排序,getAdvisorMethods(aspectClass):
排序规则;Around.class, Before.class, After.class, AfterReturning.class, AfterThrowing.class
private List<Method> getAdvisorMethods(Class<?> aspectClass) {final List<Method> methods = new ArrayList<>();ReflectionUtils.doWithMethods(aspectClass, method -> {if (AnnotationUtils.getAnnotation(method, Pointcut.class) == null) {methods.add(method);}});methods.sort(METHOD_COMPARATOR);return methods;}//排序规则
public class ReflectiveAspectJAdvisorFactory extends AbstractAspectJAdvisorFactory implements Serializable {private static final Comparator<Method> METHOD_COMPARATOR;static {Comparator<Method> adviceKindComparator = new ConvertingComparator<>(new InstanceComparator<>(Around.class, Before.class, After.class, AfterReturning.class, AfterThrowing.class),(Converter<Method, Annotation>) method -> {AspectJAnnotation<?> annotation =AbstractAspectJAdvisorFactory.findAspectJAnnotationOnMethod(method);return (annotation != null ? annotation.getAnnotation() : null);});Comparator<Method> methodNameComparator = new ConvertingComparator<>(Method::getName);METHOD_COMPARATOR = adviceKindComparator.thenComparing(methodNameComparator);}b、getAdvisor(method, lazySingletonAspectInstanceFactory, advisors.size(), aspectName)
public Advisor getAdvisor(Method candidateAdviceMethod, MetadataAwareAspectInstanceFactory aspectInstanceFactory,int declarationOrderInAspect, String aspectName) {validate(aspectInstanceFactory.getAspectMetadata().getAspectClass());//切面的方法上构建切点表达式AspectJExpressionPointcut expressionPointcut = getPointcut(candidateAdviceMethod, aspectInstanceFactory.getAspectMetadata().getAspectClass());if (expressionPointcut == null) {return null;}//实例化我们的切面通知对象return new InstantiationModelAwarePointcutAdvisorImpl(expressionPointcut, candidateAdviceMethod,this, aspectInstanceFactory, declarationOrderInAspect, aspectName);}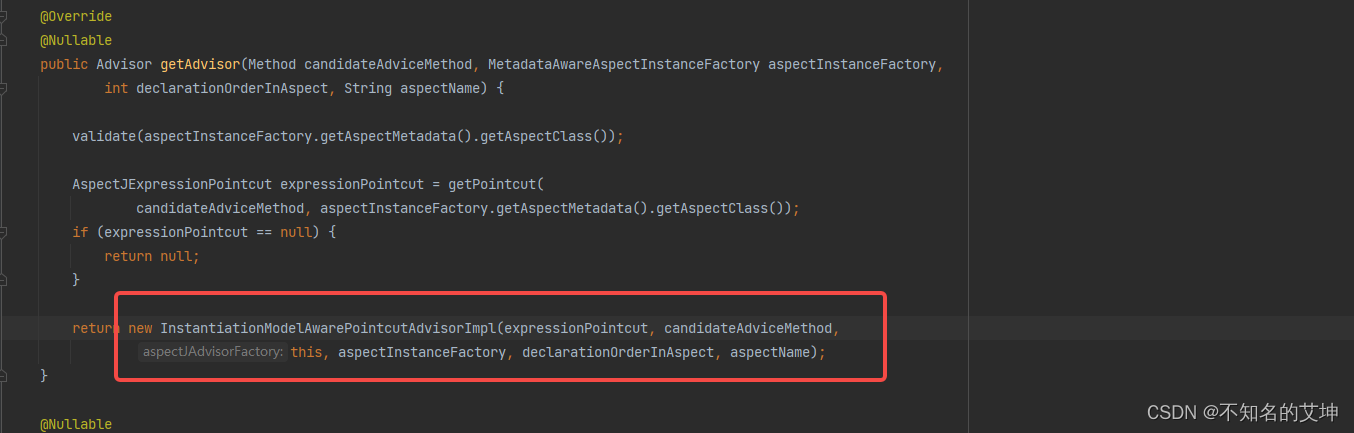
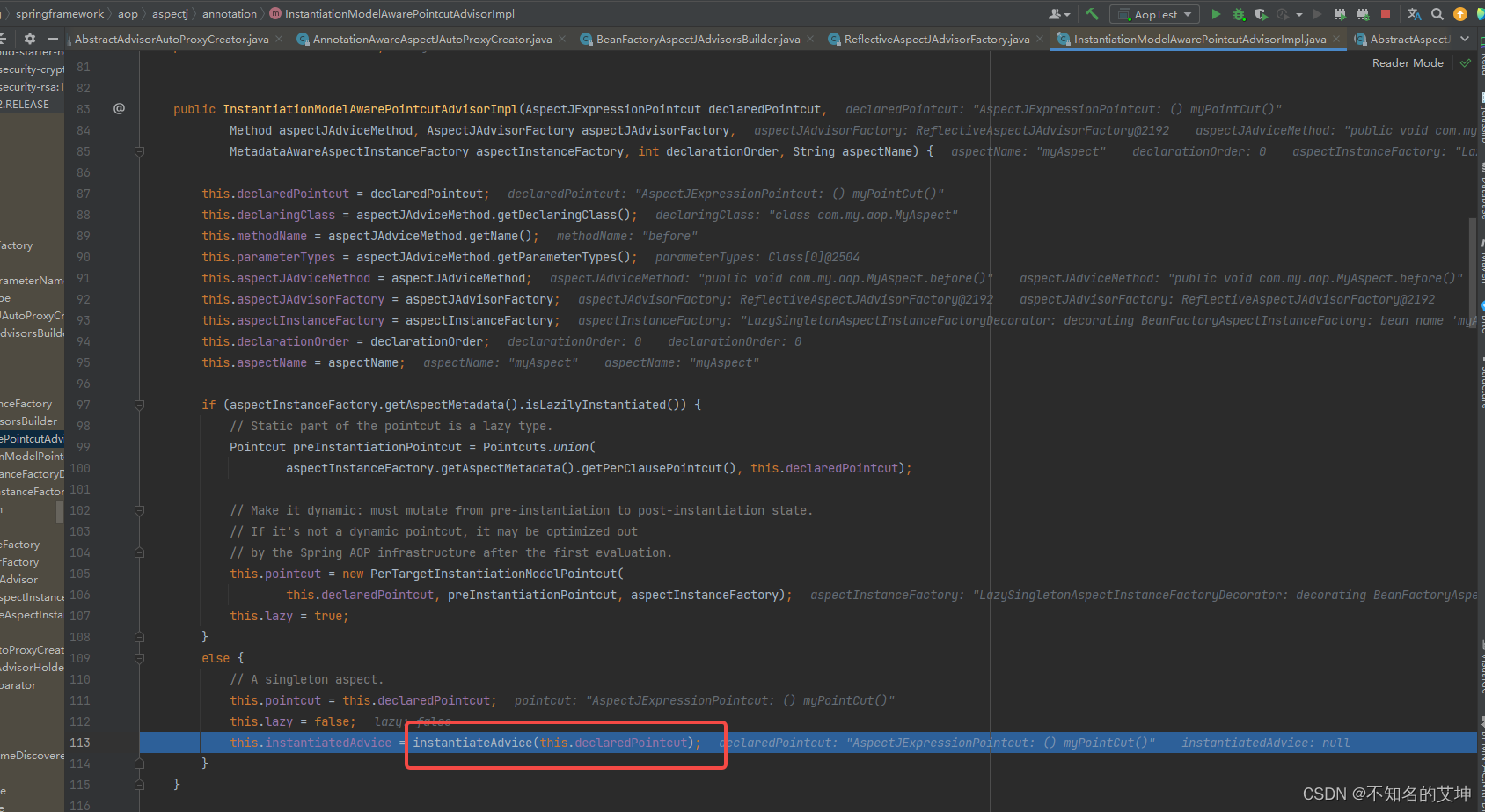
c、InstantiationModelAwarePointcutAdvisorImpl()
实例化切面通知对象
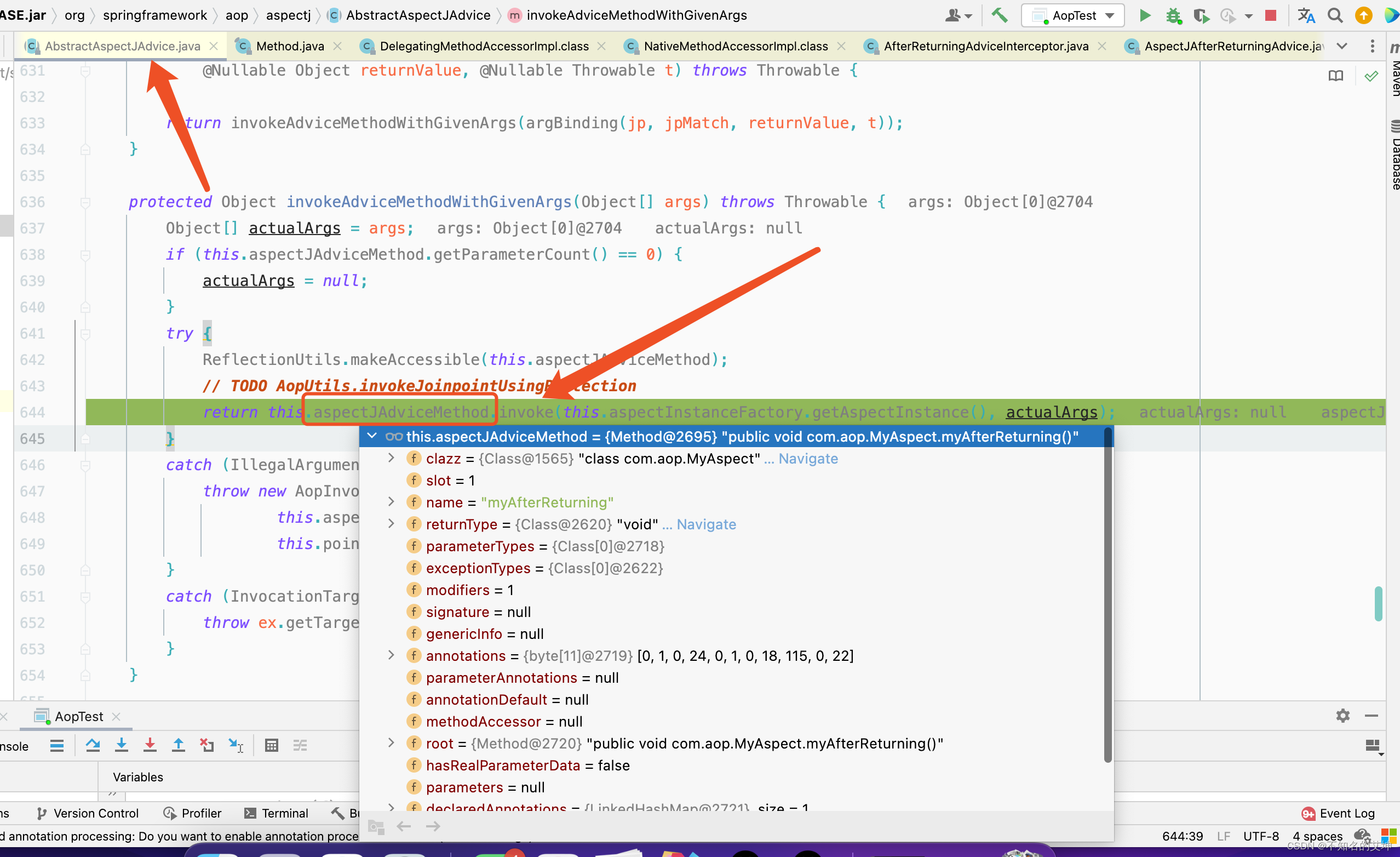
public InstantiationModelAwarePointcutAdvisorImpl(AspectJExpressionPointcut declaredPointcut,Method aspectJAdviceMethod, AspectJAdvisorFactory aspectJAdvisorFactory,MetadataAwareAspectInstanceFactory aspectInstanceFactory, int declarationOrder, String aspectName) {//当前的切点表达式this.declaredPointcut = declaredPointcut;//切面的class对象this.declaringClass = aspectJAdviceMethod.getDeclaringClass();//切面方法的名称this.methodName = aspectJAdviceMethod.getName();//切面方法的参数类型this.parameterTypes = aspectJAdviceMethod.getParameterTypes();//切面方法对象this.aspectJAdviceMethod = aspectJAdviceMethod;//aspectj的通知工厂this.aspectJAdvisorFactory = aspectJAdvisorFactory;//aspect的实例工厂this.aspectInstanceFactory = aspectInstanceFactory;//切面的顺序this.declarationOrder = declarationOrder;//切面的名称this.aspectName = aspectName;/*** 判断当前的切面对象是否需要延时加载*/if (aspectInstanceFactory.getAspectMetadata().isLazilyInstantiated()) {// Static part of the pointcut is a lazy type.Pointcut preInstantiationPointcut = Pointcuts.union(aspectInstanceFactory.getAspectMetadata().getPerClausePointcut(), this.declaredPointcut);// Make it dynamic: must mutate from pre-instantiation to post-instantiation state.// If it's not a dynamic pointcut, it may be optimized out// by the Spring AOP infrastructure after the first evaluation.this.pointcut = new PerTargetInstantiationModelPointcut(this.declaredPointcut, preInstantiationPointcut, aspectInstanceFactory);this.lazy = true;}else {// A singleton aspect.this.pointcut = this.declaredPointcut;this.lazy = false;//将切面中的通知构造为advice通知对象this.instantiatedAdvice = instantiateAdvice(this.declaredPointcut);}}
d、instantiateAdvice()
将切面中的通知构造为advice通知对象
private Advice instantiateAdvice(AspectJExpressionPointcut pointcut) {Advice advice = this.aspectJAdvisorFactory.getAdvice(this.aspectJAdviceMethod, pointcut,this.aspectInstanceFactory, this.declarationOrder, this.aspectName);return (advice != null ? advice : EMPTY_ADVICE);}
e、instantiateAdvice()#getAdvice()
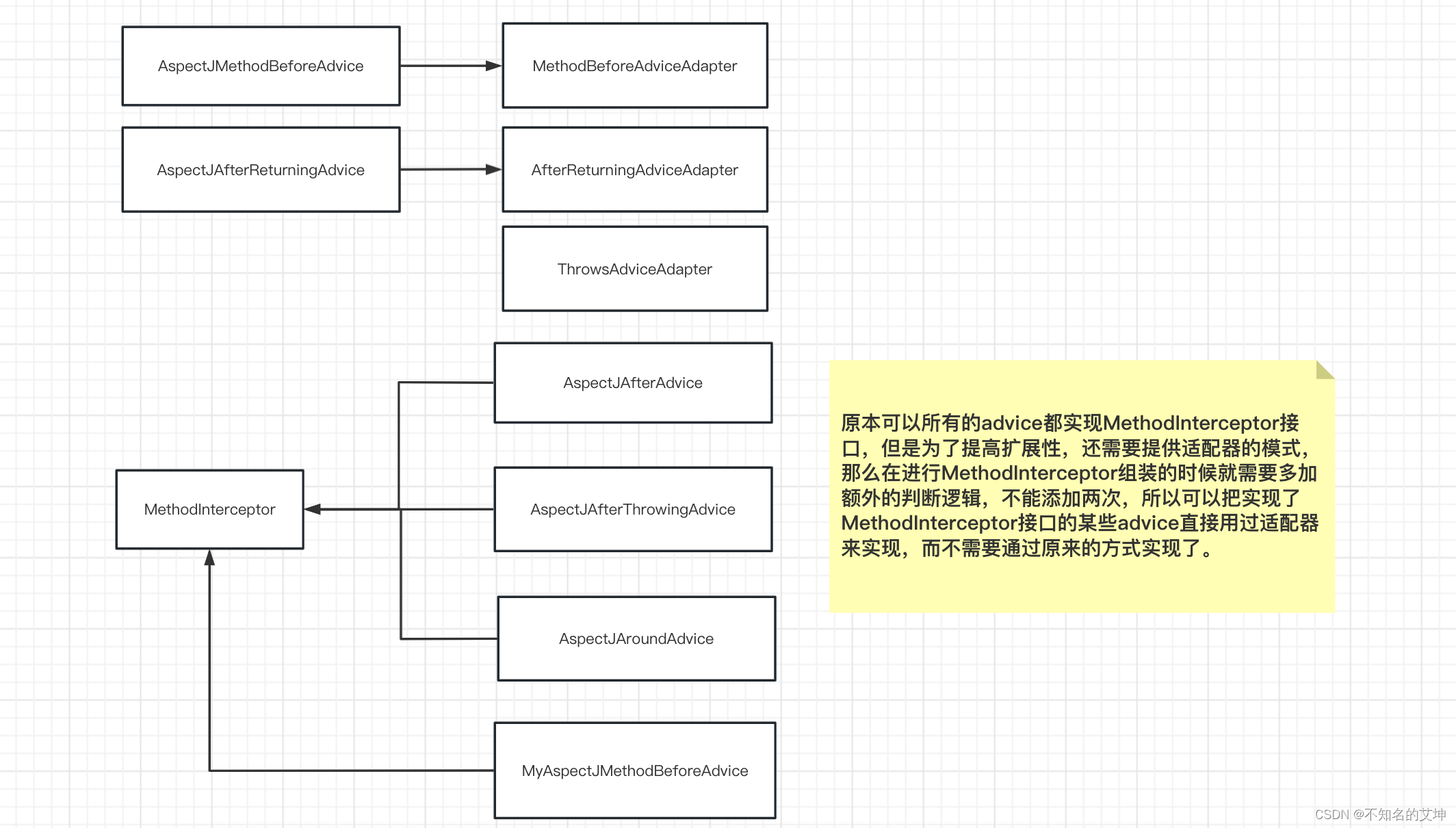
执行完这一步以后就是获取到了所有的advice,然后逐级返回。
是单例就加入this.advisorsCache.put(beanName, classAdvisors)
public Advice getAdvice(Method candidateAdviceMethod, AspectJExpressionPointcut expressionPointcut,MetadataAwareAspectInstanceFactory aspectInstanceFactory, int declarationOrder, String aspectName) {//获取我们的切面类的class对象Class<?> candidateAspectClass = aspectInstanceFactory.getAspectMetadata().getAspectClass();validate(candidateAspectClass);//获取切面方法上的注解AspectJAnnotation<?> aspectJAnnotation =AbstractAspectJAdvisorFactory.findAspectJAnnotationOnMethod(candidateAdviceMethod);//解析出来的注解信息是否为nullif (aspectJAnnotation == null) {return null;}//再次判断是否是切面对象if (!isAspect(candidateAspectClass)) {throw new AopConfigException("Advice must be declared inside an aspect type: " +"Offending method '" + candidateAdviceMethod + "' in class [" +candidateAspectClass.getName() + "]");}if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {logger.debug("Found AspectJ method: " + candidateAdviceMethod);}AbstractAspectJAdvice springAdvice;//判断标注在方法上的注解类型switch (aspectJAnnotation.getAnnotationType()) {//是PointCut注解 那么就抛出异常 因为在外面传递进来的方法已经排除了Pointcut的方法case AtPointcut:if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {logger.debug("Processing pointcut '" + candidateAdviceMethod.getName() + "'");}return null;//环绕通知 构建AspectJAroundAdvicecase AtAround:springAdvice = new AspectJAroundAdvice(candidateAdviceMethod, expressionPointcut, aspectInstanceFactory);break;//前置通知 构建AspectJMethodBeforeAdvicecase AtBefore:springAdvice = new AspectJMethodBeforeAdvice(candidateAdviceMethod, expressionPointcut, aspectInstanceFactory);break;//后置通知 AspectJAfterAdvicecase AtAfter:springAdvice = new AspectJAfterAdvice(candidateAdviceMethod, expressionPointcut, aspectInstanceFactory);break;//返回通知 AspectJAfterReturningAdvicecase AtAfterReturning:springAdvice = new AspectJAfterReturningAdvice(candidateAdviceMethod, expressionPointcut, aspectInstanceFactory);AfterReturning afterReturningAnnotation = (AfterReturning) aspectJAnnotation.getAnnotation();if (StringUtils.hasText(afterReturningAnnotation.returning())) {springAdvice.setReturningName(afterReturningAnnotation.returning());}break;//异常通知 AspectJAfterThrowingAdvicecase AtAfterThrowing:springAdvice = new AspectJAfterThrowingAdvice(candidateAdviceMethod, expressionPointcut, aspectInstanceFactory);AfterThrowing afterThrowingAnnotation = (AfterThrowing) aspectJAnnotation.getAnnotation();if (StringUtils.hasText(afterThrowingAnnotation.throwing())) {springAdvice.setThrowingName(afterThrowingAnnotation.throwing());}break;default:throw new UnsupportedOperationException("Unsupported advice type on method: " + candidateAdviceMethod);}//设置我们构建出来的通知对象的相关属性比如DeclarationOrder,在代理调用的时候,责任链顺序上会用到springAdvice.setAspectName(aspectName);springAdvice.setDeclarationOrder(declarationOrder);String[] argNames = this.parameterNameDiscoverer.getParameterNames(candidateAdviceMethod);if (argNames != null) {springAdvice.setArgumentNamesFromStringArray(argNames);}springAdvice.calculateArgumentBindings();return springAdvice;}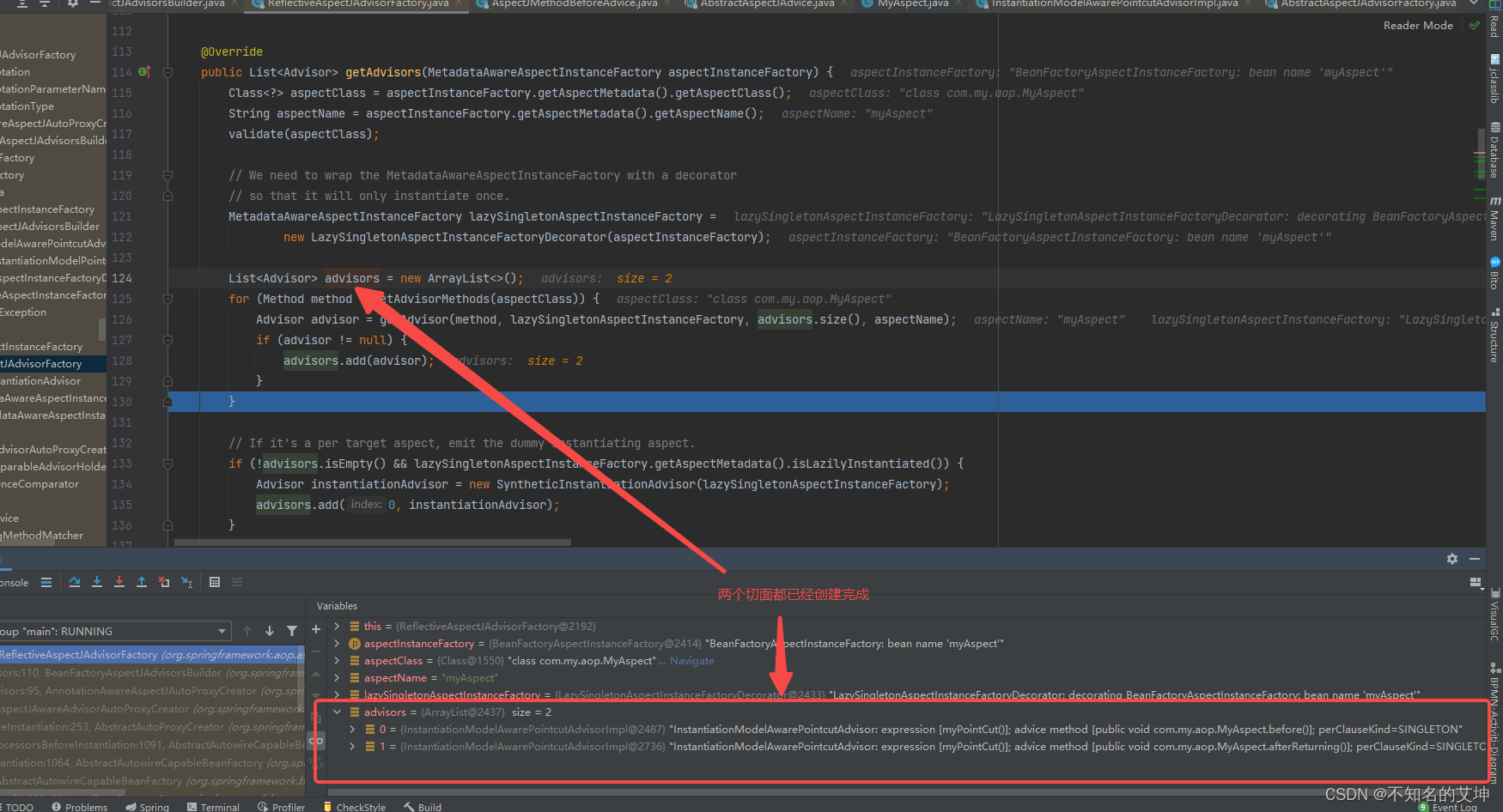
5、回到shouldSkip()
再上面经过逐级返回后,回到shouldSkip();
AbstractAutoProxyCreator.shouldSkip()方法中的List candidateAdvisors = findCandidateAdvisors();返回找到的候选的增强器,然后再调用父类的shouldSkip()返回false,就是不跳过的意思
执行完shouldSkip()返回到AbstractAutoProxyCreator.postProcessBeforeInstantiation的方法,至此postProcessBeforeInstantiation执行完成。
上面得准备工作已经做好以后就准备在后置环节进行代理对象得创建了
6、创建总结以及流程
1、哪些类需要进行相关的切入:
expression,pointcut
2、额外的逻辑处理,有几个通知消息或者说有哪些逻辑可以被执行
before,after,afterThrowing,afterReturing,around:advisor—》advice
3、额外的处理逻辑的类是哪个,也就是哪个切面
aspect
6.1 创建对象得顺序
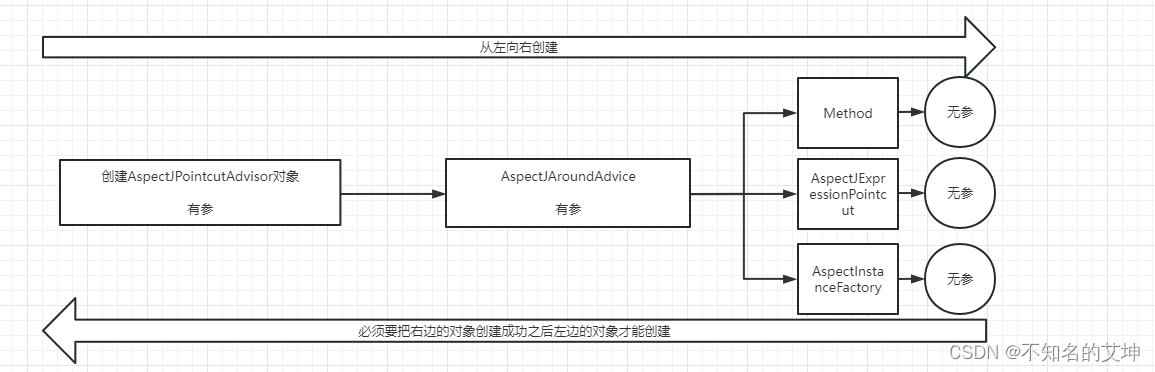
6.2 创建切面的几个常见对象
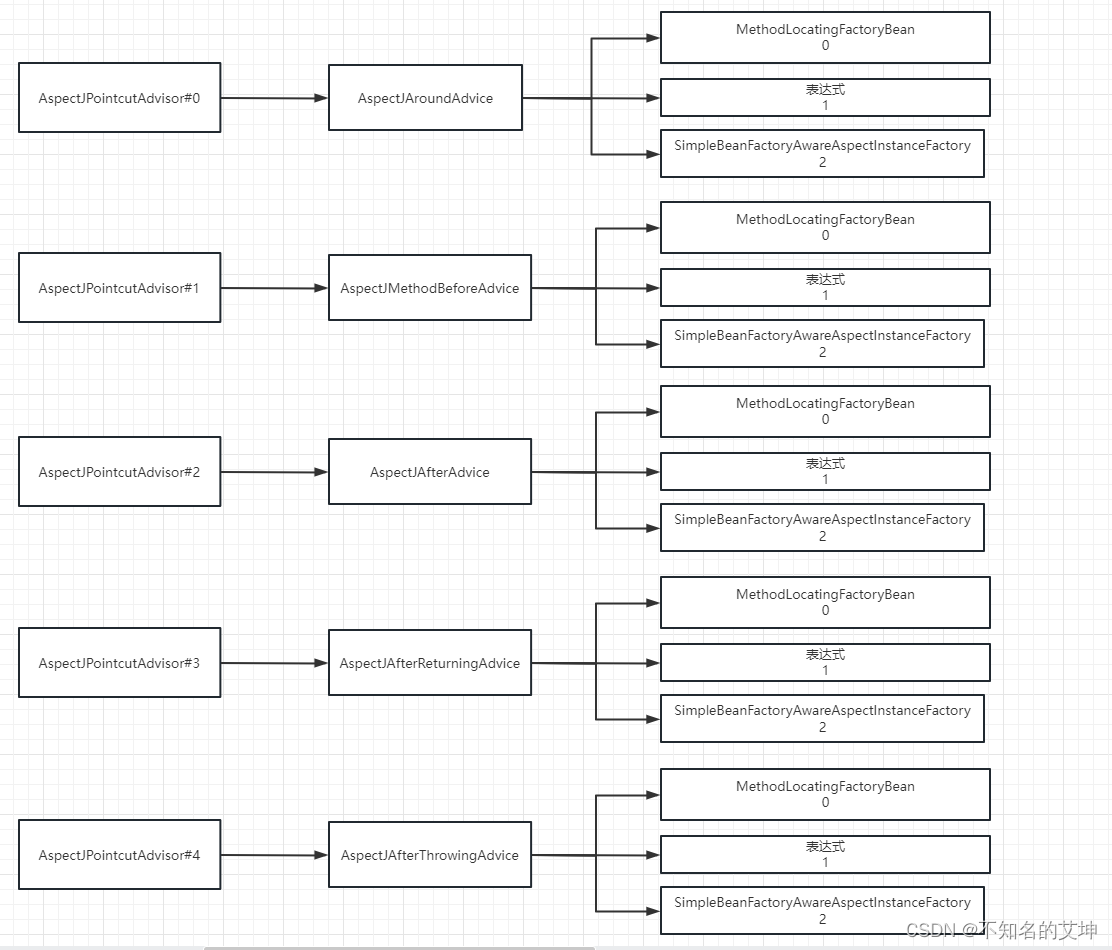
第二步、AOP后置环节创建代理对象
在上面执行完shouldSkip()返回到AbstractAutoProxyCreator.postProcessBeforeInstantiation的方法,至此postProcessBeforeInstantiation执行完成。
而AnnotationAwareAspectJAutoProxyCreator继承了AbstractAutoProxyCreator实现了Bean的后置处理器BeanPostProcessor接口:
该接口有2个方法:postProcessBeforeInitialization和postProcessAfterInitialization,其中在postProcessAfterInitialization方法主要就是通过前面创建的增强器来创建代理对象
0、从doCreateBean进入
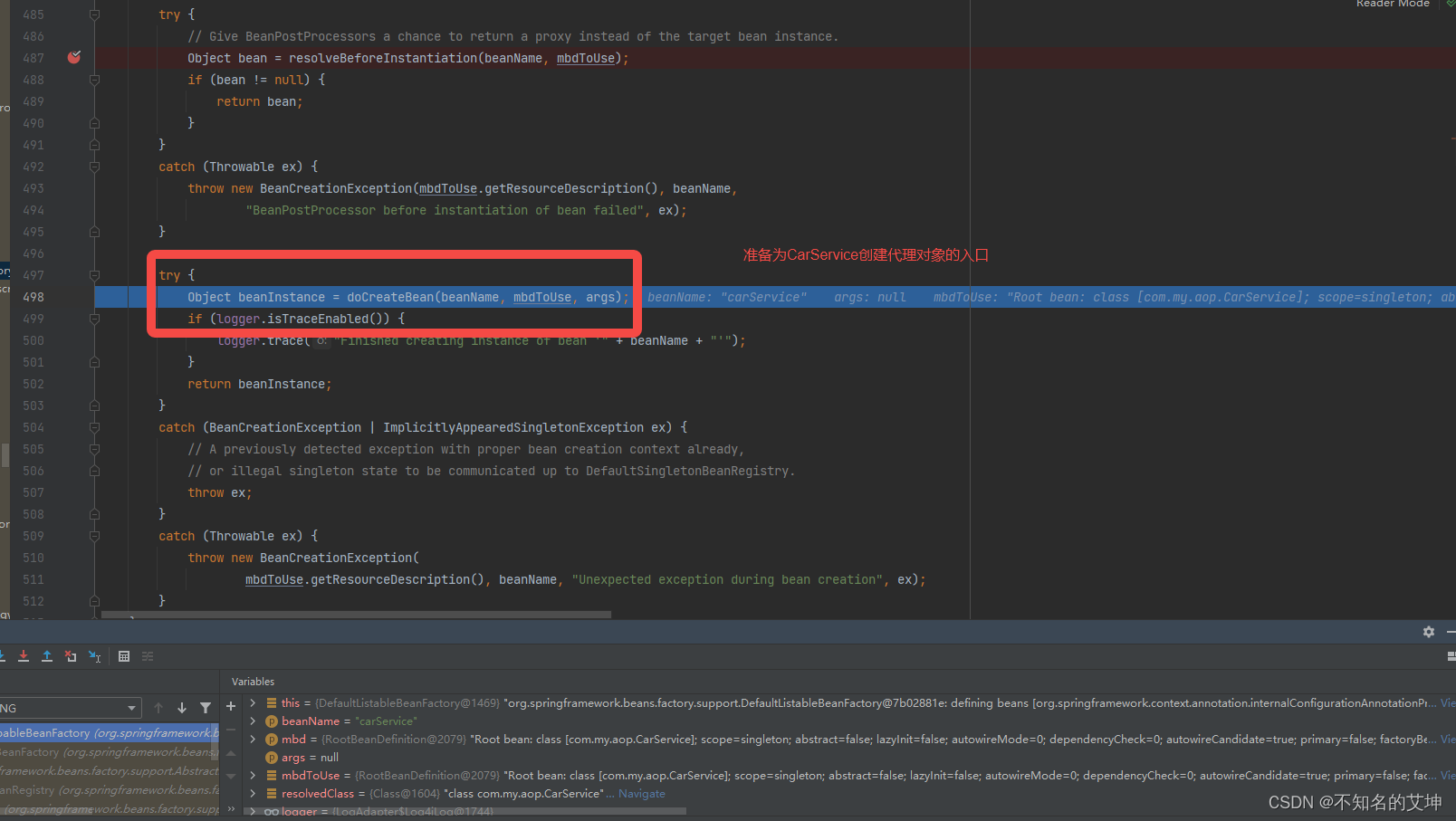
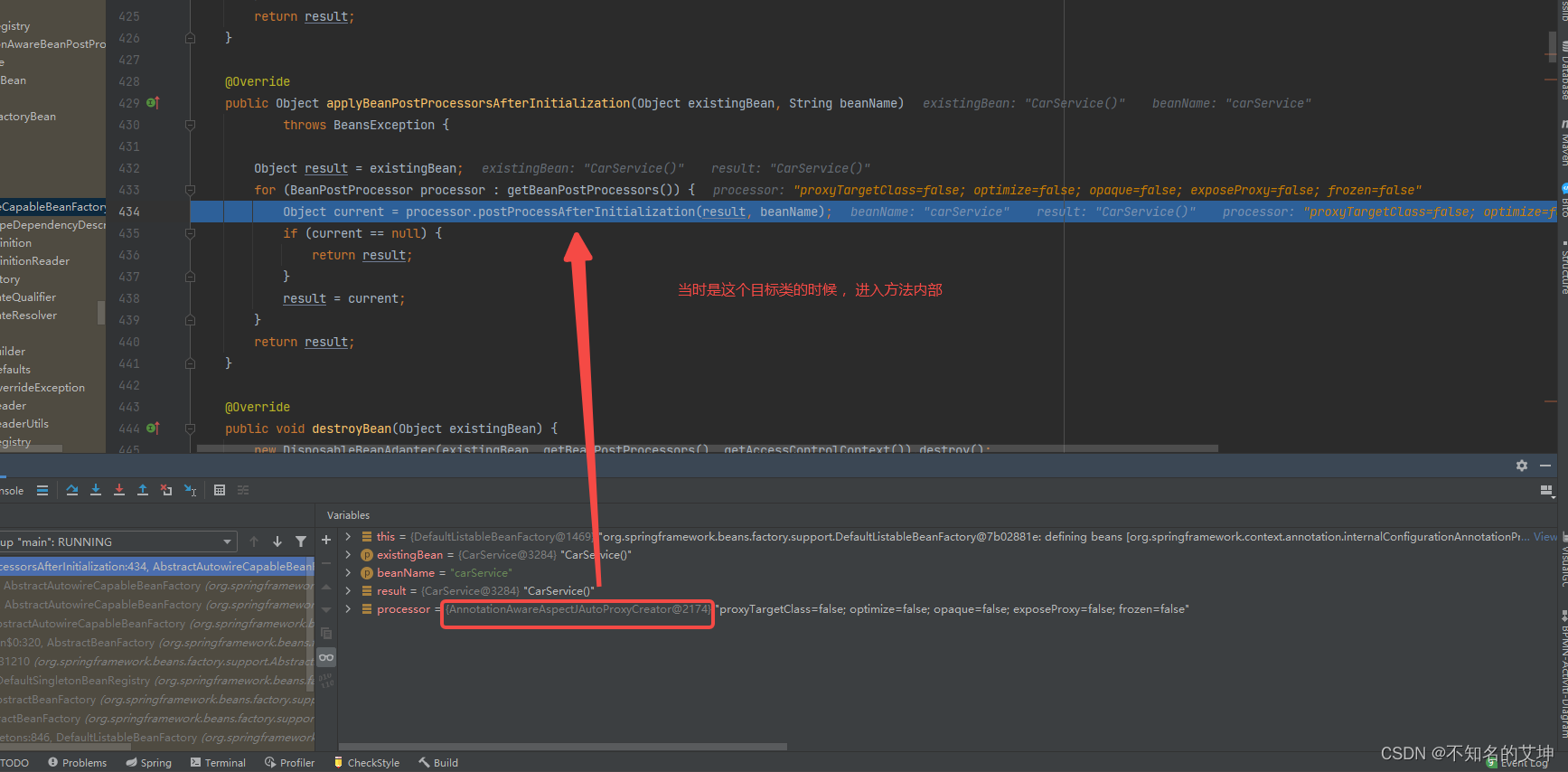
1、postProcessAfterInitialization()
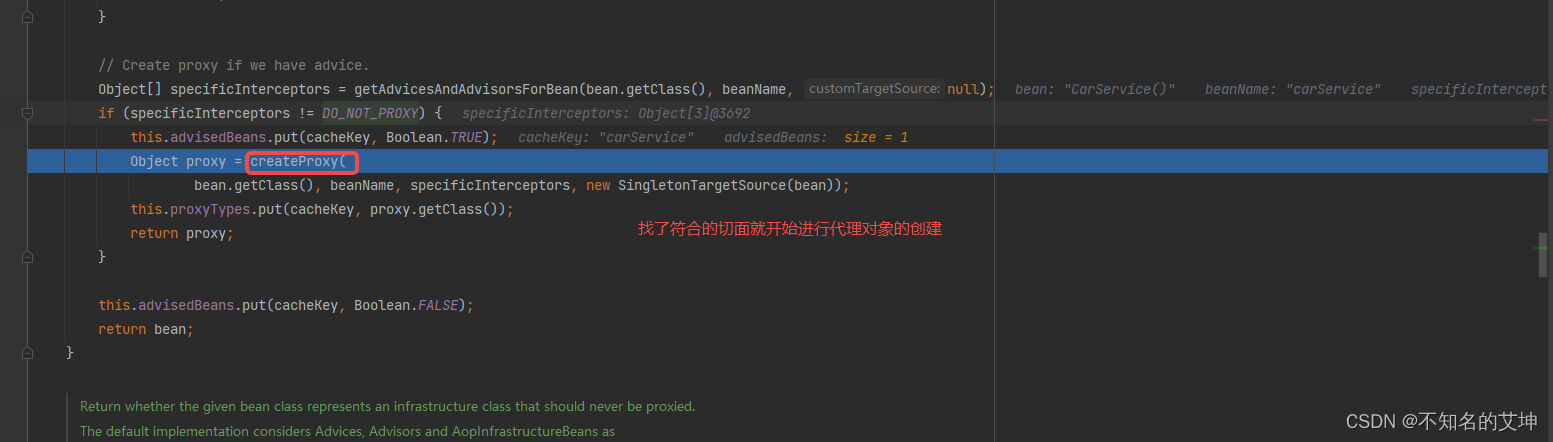
/*** 此处是真正创建aop代理的地方,在实例化之后,初始化之后就行处理* 首先查看是否在earlyProxyReferences里存在,如果有就说明处理过了,不存在就考虑是否要包装,也就是代理*/@Overridepublic Object postProcessAfterInitialization(@Nullable Object bean, String beanName) {if (bean != null) {// 获取当前bean的key:如果beanName不为空,则以beanName为key,如果为FactoryBean类型,// 前面还会添加&符号,如果beanName为空,则以当前bean对应的class为keyObject cacheKey = getCacheKey(bean.getClass(), beanName);// 判断当前bean是否正在被代理,如果正在被代理则不进行封装if (this.earlyProxyReferences.remove(cacheKey) != bean) {// 如果它需要被代理,则需要封装指定的beanreturn wrapIfNecessary(bean, beanName, cacheKey);}}return bean;}
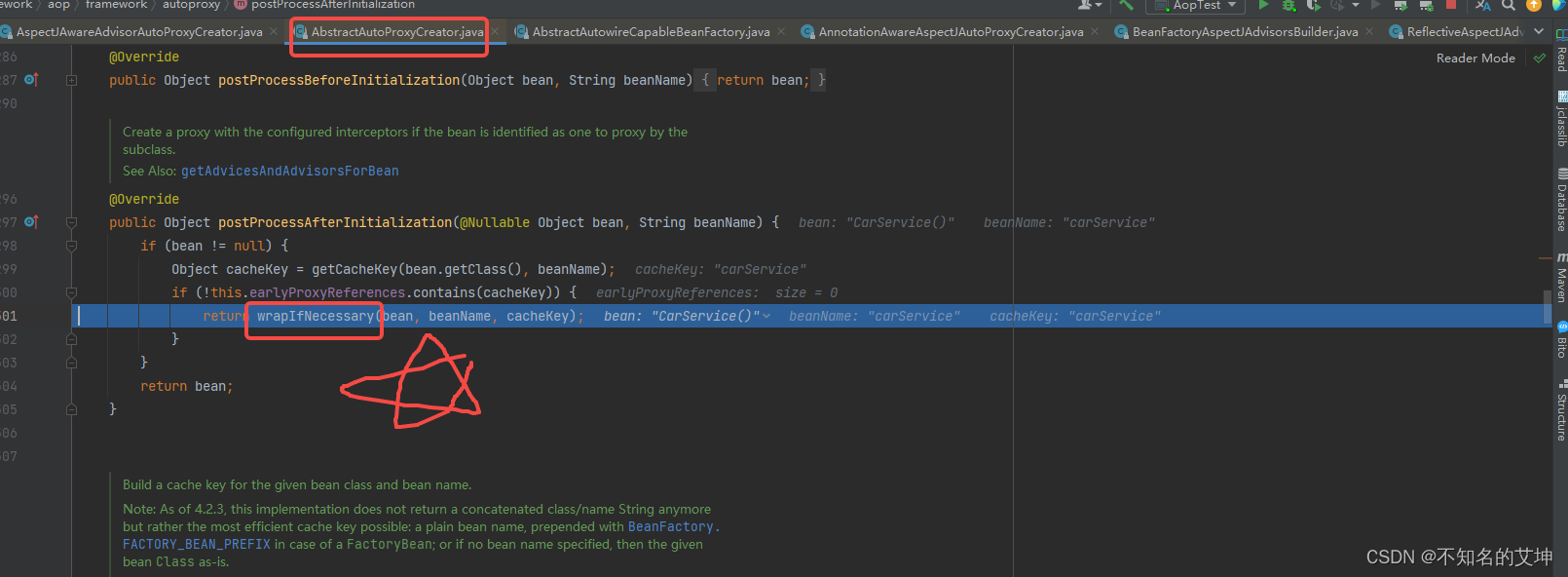
2、wrapIfNecessary() 重点开始
/*** 先判断是否已经处理过,是否需要跳过,跳过的话直接就放进advisedBeans里,表示不进行代理,如果这个bean处理过了,获取通知拦截器,然后开始进行代理** Wrap the given bean if necessary, i.e. if it is eligible for being proxied.* @param bean the raw bean instance* @param beanName the name of the bean* @param cacheKey the cache key for metadata access* @return a proxy wrapping the bean, or the raw bean instance as-is*/protected Object wrapIfNecessary(Object bean, String beanName, Object cacheKey) {// 如果已经处理过,直接返回if (StringUtils.hasLength(beanName) && this.targetSourcedBeans.contains(beanName)) {return bean;}// 这里advisedBeans缓存了已经进行了代理的bean,如果缓存中存在,则可以直接返回if (Boolean.FALSE.equals(this.advisedBeans.get(cacheKey))) {return bean;}// 这里isInfrastructureClass()用于判断当前bean是否为Spring系统自带的bean,自带的bean是// 不用进行代理的;shouldSkip()则用于判断当前bean是否应该被略过if (isInfrastructureClass(bean.getClass()) || shouldSkip(bean.getClass(), beanName)) {// 对当前bean进行缓存this.advisedBeans.put(cacheKey, Boolean.FALSE);return bean;}// Create proxy if we have advice.// 获取当前bean的Advices和AdvisorsObject[] specificInterceptors = getAdvicesAndAdvisorsForBean(bean.getClass(), beanName, null);// 对当前bean的代理状态进行缓存if (specificInterceptors != DO_NOT_PROXY) {// 对当前bean的代理状态进行缓存this.advisedBeans.put(cacheKey, Boolean.TRUE);// 根据获取到的Advices和Advisors为当前bean生成代理对象Object proxy = createProxy(bean.getClass(), beanName, specificInterceptors, new SingletonTargetSource(bean));// 缓存生成的代理bean的类型,并且返回生成的代理beanthis.proxyTypes.put(cacheKey, proxy.getClass());return proxy;}this.advisedBeans.put(cacheKey, Boolean.FALSE);return bean;}
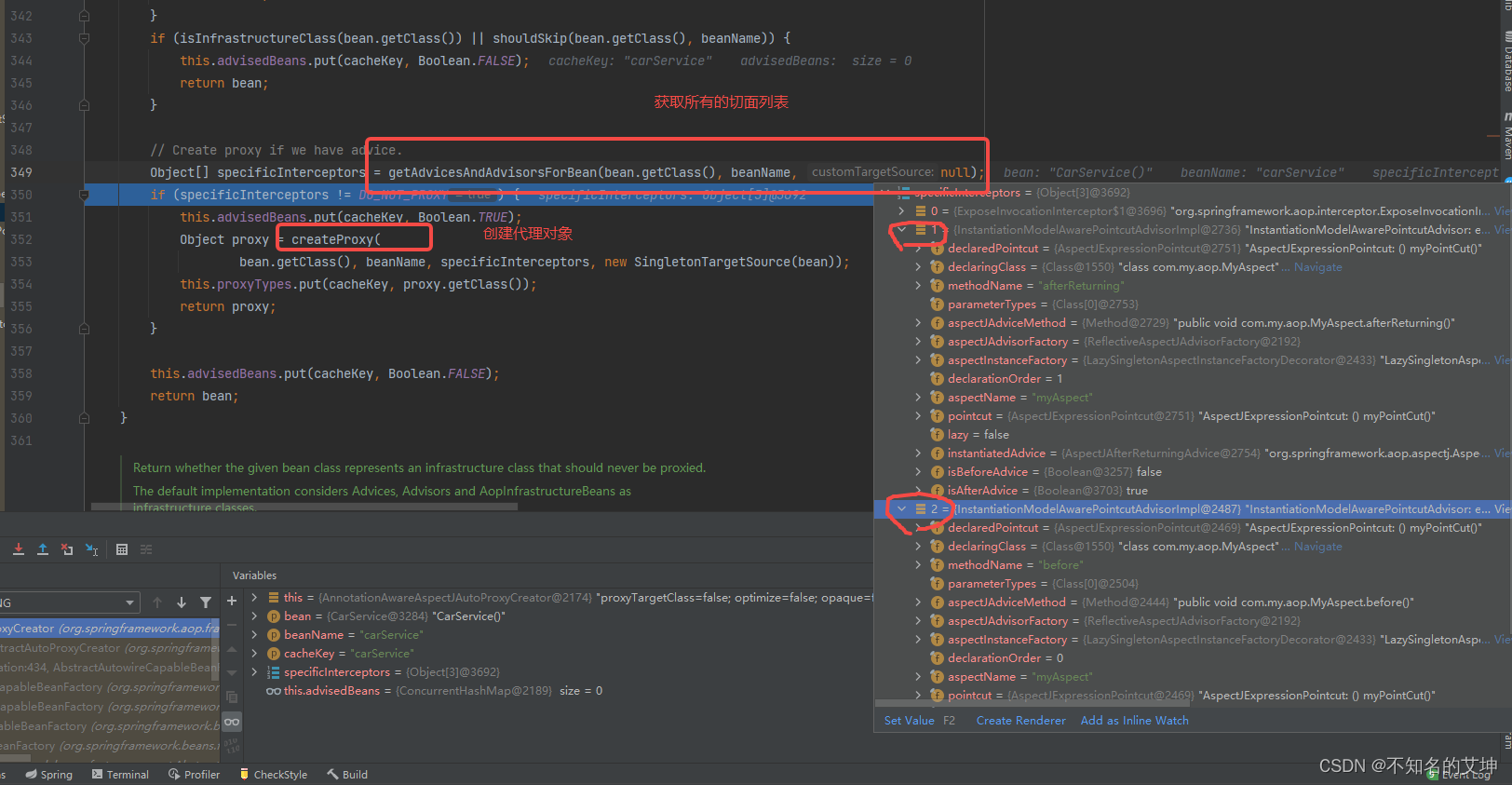
2.1、getAdvicesAndAdvisorsForBean()
获取匹配的通知方法,这时候就是直接从缓存中获取的,因为在上面的前置环节已经处理过了。
/*** 检查前面切面解析是否有通知器advisors创建,有就返回,没有就是null* @param beanClass the class of the bean to advise* @param beanName the name of the bean* @param targetSource* @return*/@Override@Nullableprotected Object[] getAdvicesAndAdvisorsForBean(Class<?> beanClass, String beanName, @Nullable TargetSource targetSource) {// 找合适的增强器对象List<Advisor> advisors = findEligibleAdvisors(beanClass, beanName);// 若为空表示没找到if (advisors.isEmpty()) {return DO_NOT_PROXY;}return advisors.toArray();}
2.1.1、findEligibleAdvisors(beanClass, beanName)
跟进到找合适的增强器对象方法
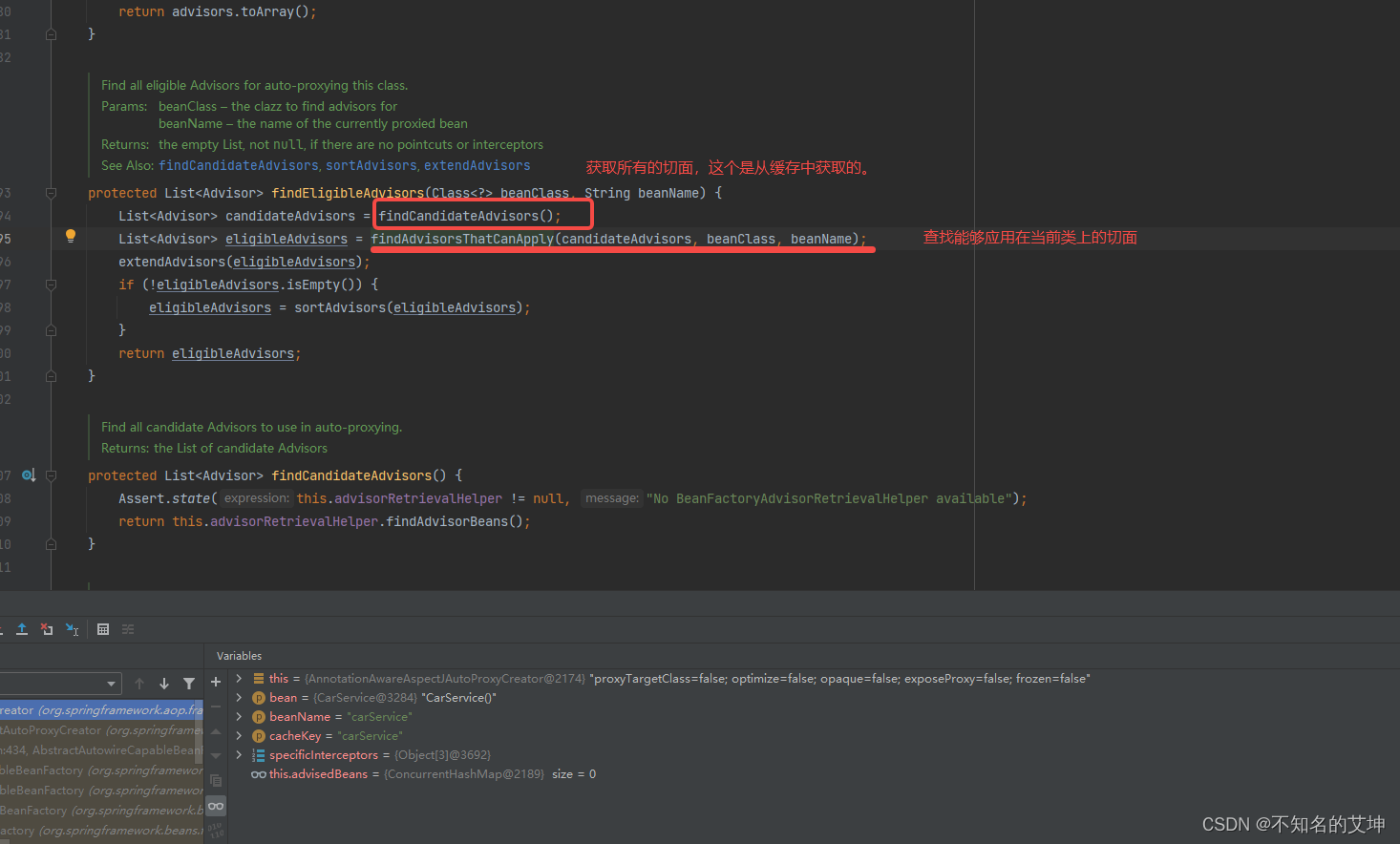
/*** 找到所有符合条件的通知对于自动代理的类** Find all eligible Advisors for auto-proxying this class.* @param beanClass the clazz to find advisors for* @param beanName the name of the currently proxied bean* @return the empty List, not {@code null},* if there are no pointcuts or interceptors* @see #findCandidateAdvisors* @see #sortAdvisors* @see #extendAdvisors*/protected List<Advisor> findEligibleAdvisors(Class<?> beanClass, String beanName) {// 将当前系统中所有的切面类的切面逻辑进行封装,从而得到目标AdvisorList<Advisor> candidateAdvisors = findCandidateAdvisors();// 对获取到的所有Advisor进行判断,看其切面定义是否可以应用到当前bean,从而得到最终需要应用的AdvisorList<Advisor> eligibleAdvisors = findAdvisorsThatCanApply(candidateAdvisors, beanClass, beanName);// 提供的hook方法,用于对目标Advisor进行扩展extendAdvisors(eligibleAdvisors);if (!eligibleAdvisors.isEmpty()) {// 对需要代理的Advisor按照一定的规则进行排序eligibleAdvisors = sortAdvisors(eligibleAdvisors);}return eligibleAdvisors;}2.1.2、findAdvisorsThatCanApply(candidateAdvisors, beanClass, beanName)
1、跟进到判断找到的通知能不能作用到当前的类上方法,
2、跟进到从候选的通知器中找到合适正在创建的实例对象的通知器方法
3、跟进到是否能用方法
4、如果该方法返回true就表示匹配,就添加到合适的集合eligibleAdvisors中,遍历完所有的候选增强器后
5、返回到AbstractAdvisorAutoProxyCreator.findEligibleAdvisors方法中,然后扩展增强器,如果合适的增强器列表不是空的就排序
6、返回到AbstractAdvisorAutoProxyCreator.getAdvicesAndAdvisorsForBean,如果空就表示不需要代理,不为空就表示需要代理。
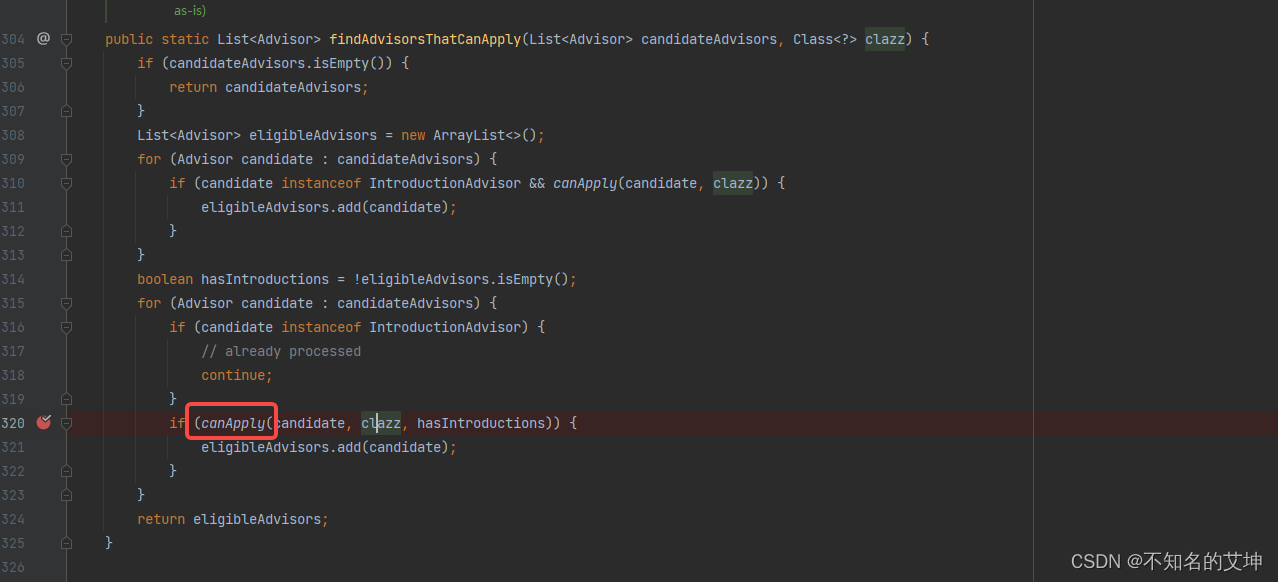
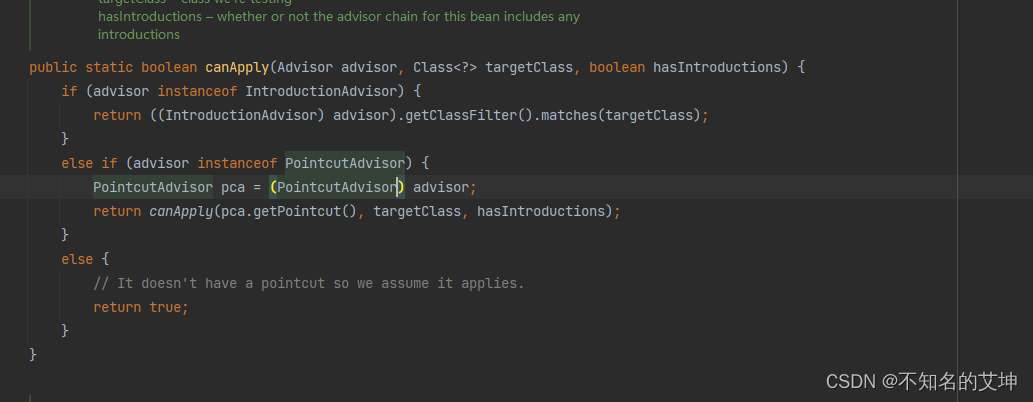
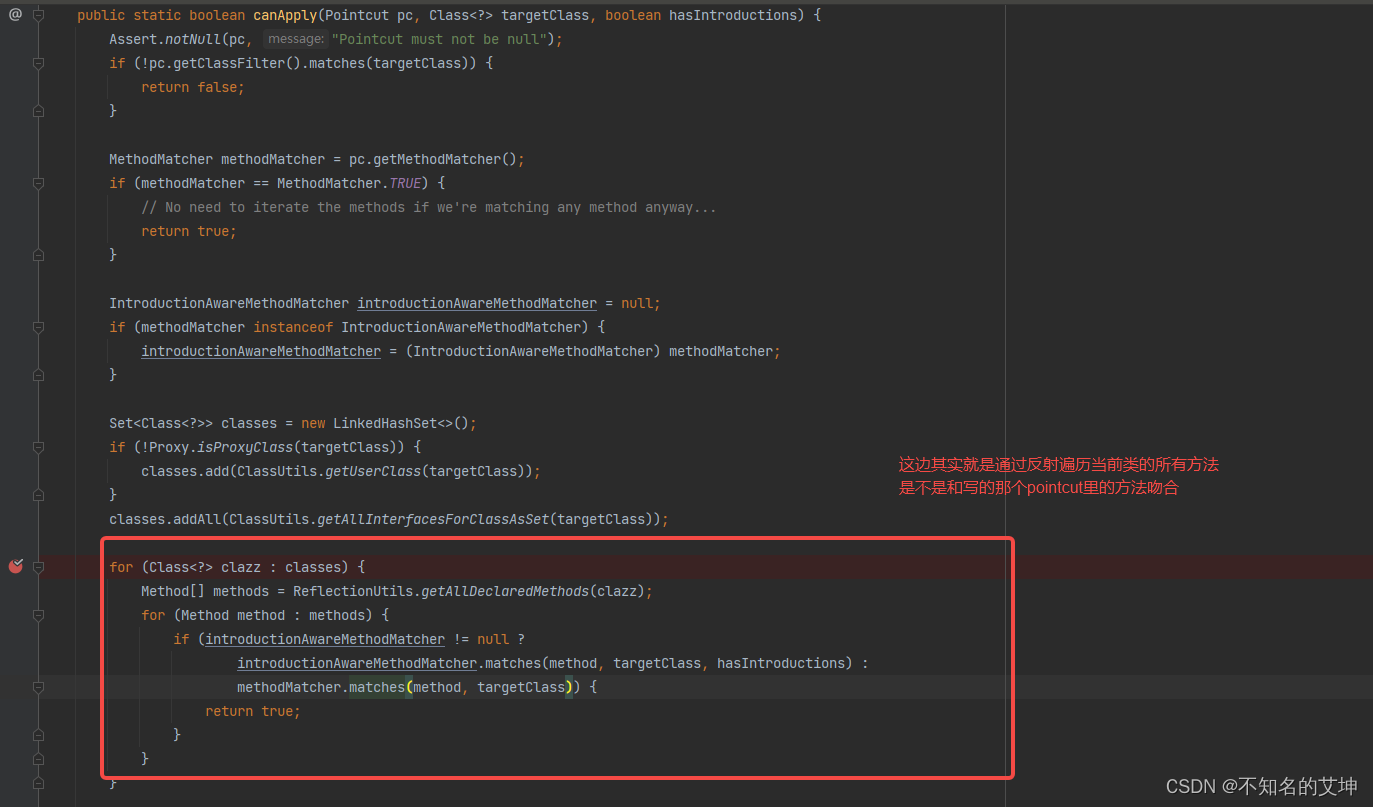
protected List<Advisor> findAdvisorsThatCanApply(List<Advisor> candidateAdvisors, Class<?> beanClass, String beanName) {ProxyCreationContext.setCurrentProxiedBeanName(beanName);try {//从候选的通知器中找到合适正在创建的实例对象的通知器return AopUtils.findAdvisorsThatCanApply(candidateAdvisors, beanClass);}finally {ProxyCreationContext.setCurrentProxiedBeanName(null);}}public static List<Advisor> findAdvisorsThatCanApply(List<Advisor> candidateAdvisors, Class<?> clazz) {//若候选的增强器集合为空 直接返回if (candidateAdvisors.isEmpty()) {return candidateAdvisors;}//定义一个合适的增强器集合对象List<Advisor> eligibleAdvisors = new ArrayList<>();//循环我们候选的增强器对象for (Advisor candidate : candidateAdvisors) {//判断我们的增强器对象是不是实现了IntroductionAdvisor (很明显我们事务的没有实现 所以不会走下面的逻辑)if (candidate instanceof IntroductionAdvisor && canApply(candidate, clazz)) {eligibleAdvisors.add(candidate);}}//不为空boolean hasIntroductions = !eligibleAdvisors.isEmpty();for (Advisor candidate : candidateAdvisors) {//判断我们的增强器对象是不是实现了IntroductionAdvisor (很明显我们事务的没有实现 所以不会走下面的逻辑)if (candidate instanceof IntroductionAdvisor) {//在上面已经处理过 ,不需要处理continue;}/*** 真正的判断增强器是否合适当前类型*/if (canApply(candidate, clazz, hasIntroductions)) {eligibleAdvisors.add(candidate);}}return eligibleAdvisors;}public static boolean canApply(Advisor advisor, Class<?> targetClass, boolean hasIntroductions) {//判断我们的增强器是否是IntroductionAdvisorif (advisor instanceof IntroductionAdvisor) {return ((IntroductionAdvisor) advisor).getClassFilter().matches(targetClass);}//判断我们事务的增强器BeanFactoryTransactionAttributeSourceAdvisor是否实现了PointcutAdvisorelse if (advisor instanceof PointcutAdvisor) {//转为PointcutAdvisor类型PointcutAdvisor pca = (PointcutAdvisor) advisor;//找到真正能用的增强器return canApply(pca.getPointcut(), targetClass, hasIntroductions);}else {// It doesn't have a pointcut so we assume it applies.return true;}}public static boolean canApply(Pointcut pc, Class<?> targetClass, boolean hasIntroductions) {Assert.notNull(pc, "Pointcut must not be null");if (!pc.getClassFilter().matches(targetClass)) {return false;}/*** 通过切点获取到一个方法匹配器对象*/MethodMatcher methodMatcher = pc.getMethodMatcher();if (methodMatcher == MethodMatcher.TRUE) {// No need to iterate the methods if we're matching any method anyway...return true;}//判断匹配器是不是IntroductionAwareMethodMatcherIntroductionAwareMethodMatcher introductionAwareMethodMatcher = null;if (methodMatcher instanceof IntroductionAwareMethodMatcher) {introductionAwareMethodMatcher = (IntroductionAwareMethodMatcher) methodMatcher;}//创建一个集合用于保存targetClass的class对象Set<Class<?>> classes = new LinkedHashSet<>();//判断当前class是不是代理的class对象if (!Proxy.isProxyClass(targetClass)) {//加入到集合中去classes.add(ClassUtils.getUserClass(targetClass));}//获取到targetClass所实现的接口的class对象,然后加入到集合中classes.addAll(ClassUtils.getAllInterfacesForClassAsSet(targetClass));//循环所有的class对象for (Class<?> clazz : classes) {//通过class获取到所有的方法Method[] methods = ReflectionUtils.getAllDeclaredMethods(clazz);//循环我们的方法for (Method method : methods) {//通过methodMatcher.matches来匹配我们的方法if (introductionAwareMethodMatcher != null ?introductionAwareMethodMatcher.matches(method, targetClass, hasIntroductions) ://通过方法匹配器进行匹配methodMatcher.matches(method, targetClass)) {return true;}}}return false;}2.1.3、回到getAdvicesAndAdvisorsForBean()
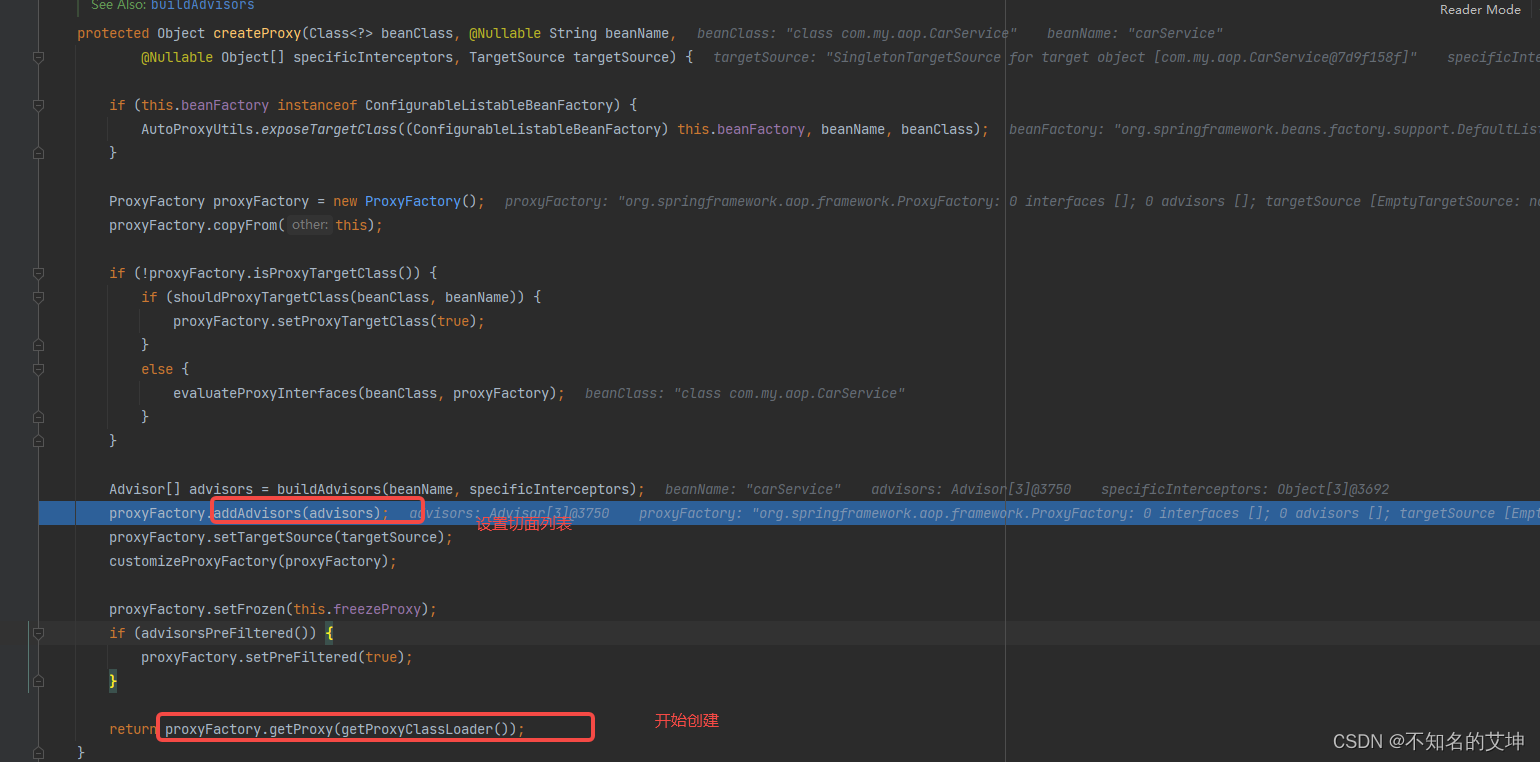
2.2 createProxy()
真正创建代理对象
/*** 进行代理工厂的创建,然后判断是否需要设置proxyTargetClass,以便于后面决定是不是要进行jdk动态代理还是cglib的动态代理* 然后把通知器advisors包装下,加入到代理工厂,获取代理对象** Create an AOP proxy for the given bean.* @param beanClass the class of the bean* @param beanName the name of the bean* @param specificInterceptors the set of interceptors that is* specific to this bean (may be empty, but not null)* @param targetSource the TargetSource for the proxy,* already pre-configured to access the bean* @return the AOP proxy for the bean* @see #buildAdvisors*/protected Object createProxy(Class<?> beanClass, @Nullable String beanName,@Nullable Object[] specificInterceptors, TargetSource targetSource) {// 给bean定义设置暴露属性if (this.beanFactory instanceof ConfigurableListableBeanFactory) {AutoProxyUtils.exposeTargetClass((ConfigurableListableBeanFactory) this.beanFactory, beanName, beanClass);}// 创建代理工厂ProxyFactory proxyFactory = new ProxyFactory();// 获取当前类中相关属性proxyFactory.copyFrom(this);// 决定对于给定的bean是否应该使用targetClass而不是他的接口代理,检查proxyTargetClass设置以及preserverTargetClass属性if (!proxyFactory.isProxyTargetClass()) {// 判断是 使用jdk动态代理 还是cglib代理if (shouldProxyTargetClass(beanClass, beanName)) {proxyFactory.setProxyTargetClass(true);}else {// 添加代理接口evaluateProxyInterfaces(beanClass, proxyFactory);}}// 构建增强器Advisor[] advisors = buildAdvisors(beanName, specificInterceptors);proxyFactory.addAdvisors(advisors);// 设置到要代理的类proxyFactory.setTargetSource(targetSource);// 定制代理customizeProxyFactory(proxyFactory);// 控制代理工程被配置之后,是否还允许修改通知,默认值是falseproxyFactory.setFrozen(this.freezeProxy);if (advisorsPreFiltered()) {proxyFactory.setPreFiltered(true);}// 真正创建代理对象return proxyFactory.getProxy(getProxyClassLoader());}public Object getProxy(@Nullable ClassLoader classLoader) {// createAopProxy() 用来创建我们的代理工厂return createAopProxy().getProxy(classLoader);}
2.2.1 createAopProxy()
开始进行代理对象的创建
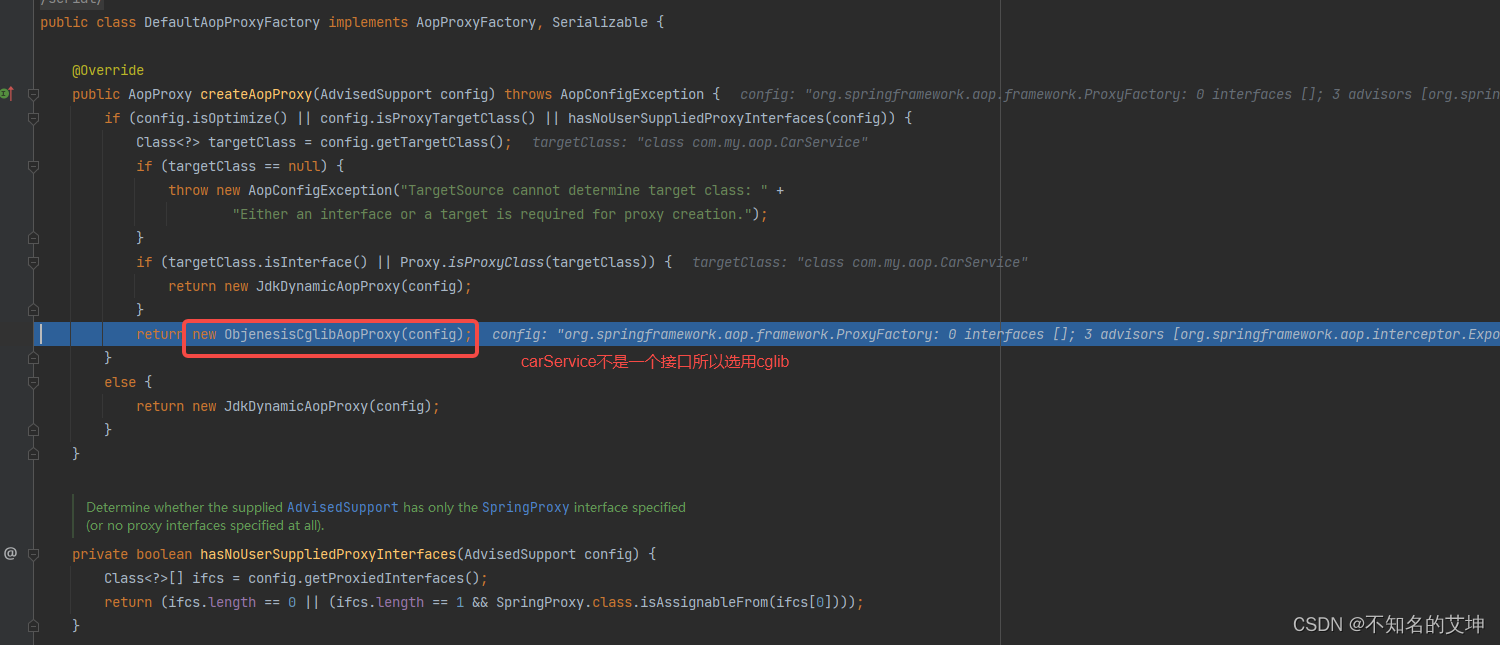
/*** 真正的创建代理,判断一些列条件,有自定义的接口的就会创建jdk代理,否则就是cglib* @param config the AOP configuration in the form of an* AdvisedSupport object* @return* @throws AopConfigException*/@Overridepublic AopProxy createAopProxy(AdvisedSupport config) throws AopConfigException {// 这段代码用来判断选择哪种创建代理对象的方式// config.isOptimize() 是否对代理类的生成使用策略优化 其作用是和isProxyTargetClass是一样的 默认为false// config.isProxyTargetClass() 是否使用Cglib的方式创建代理对象 默认为false// hasNoUserSuppliedProxyInterfaces目标类是否有接口存在 且只有一个接口的时候接口类型不是SpringProxy类型if (config.isOptimize() || config.isProxyTargetClass() || hasNoUserSuppliedProxyInterfaces(config)) {// 上面的三个方法有一个为true的话,则进入到这里// 从AdvisedSupport中获取目标类 类对象Class<?> targetClass = config.getTargetClass();if (targetClass == null) {throw new AopConfigException("TargetSource cannot determine target class: " +"Either an interface or a target is required for proxy creation.");}// 判断目标类是否是接口 如果目标类是接口的话,则还是使用JDK的方式生成代理对象// 如果目标类是Proxy类型 则还是使用JDK的方式生成代理对象if (targetClass.isInterface() || Proxy.isProxyClass(targetClass)) {return new JdkDynamicAopProxy(config);}// 配置了使用Cglib进行动态代理或者目标类没有接口,那么使用Cglib的方式创建代理对象return new ObjenesisCglibAopProxy(config);}else {// 使用JDK的提供的代理方式生成代理对象return new JdkDynamicAopProxy(config);}}
2.2.2 getProxy()cglib的代理对象
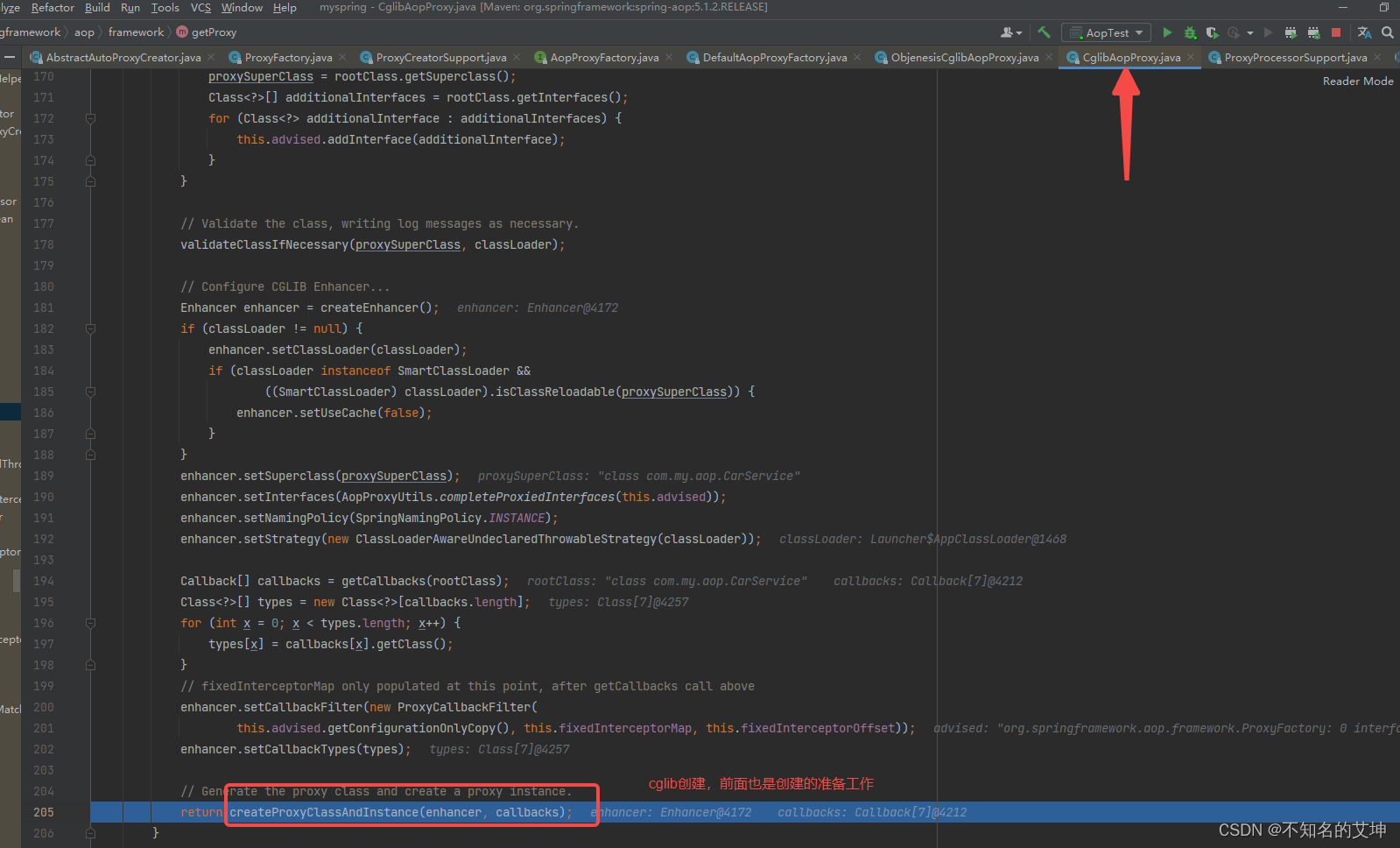
/*** 获取cglib的代理对象* @param classLoader the class loader to create the proxy with* (or {@code null} for the low-level proxy facility's default)* @return*/@Overridepublic Object getProxy(@Nullable ClassLoader classLoader) {if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {logger.trace("Creating CGLIB proxy: " + this.advised.getTargetSource());}try {// 从advised中获取ioc容器中配置的target对象Class<?> rootClass = this.advised.getTargetClass();Assert.state(rootClass != null, "Target class must be available for creating a CGLIB proxy");Class<?> proxySuperClass = rootClass;//如果目标对象已经是CGLIB 生成代理对象(就是比较类名称中有 $$ 字符串),那么就取目标对象的父类作为目标对象的类if (rootClass.getName().contains(ClassUtils.CGLIB_CLASS_SEPARATOR)) {proxySuperClass = rootClass.getSuperclass();// 获取原始父类的接口Class<?>[] additionalInterfaces = rootClass.getInterfaces();for (Class<?> additionalInterface : additionalInterfaces) {this.advised.addInterface(additionalInterface);}}// Validate the class, writing log messages as necessary.// 打印出不能代理的方法名,CGLIB 是使用继承实现的,所以final , static 的方法不能被增强validateClassIfNecessary(proxySuperClass, classLoader);// Configure CGLIB Enhancer...// 创建及配置EnhancerEnhancer enhancer = createEnhancer();if (classLoader != null) {enhancer.setClassLoader(classLoader);if (classLoader instanceof SmartClassLoader &&((SmartClassLoader) classLoader).isClassReloadable(proxySuperClass)) {enhancer.setUseCache(false);}}// 配置超类,代理类实现的接口,回调方法等enhancer.setSuperclass(proxySuperClass);enhancer.setInterfaces(AopProxyUtils.completeProxiedInterfaces(this.advised));enhancer.setNamingPolicy(SpringNamingPolicy.INSTANCE);enhancer.setStrategy(new ClassLoaderAwareGeneratorStrategy(classLoader));// 获取callbacksCallback[] callbacks = getCallbacks(rootClass);Class<?>[] types = new Class<?>[callbacks.length];for (int x = 0; x < types.length; x++) {types[x] = callbacks[x].getClass();}// fixedInterceptorMap only populated at this point, after getCallbacks call aboveenhancer.setCallbackFilter(new ProxyCallbackFilter(this.advised.getConfigurationOnlyCopy(), this.fixedInterceptorMap, this.fixedInterceptorOffset));enhancer.setCallbackTypes(types);// Generate the proxy class and create a proxy instance.// 通过 Enhancer 生成代理对象,并设置回调return createProxyClassAndInstance(enhancer, callbacks);}catch (CodeGenerationException | IllegalArgumentException ex) {throw new AopConfigException("Could not generate CGLIB subclass of " + this.advised.getTargetClass() +": Common causes of this problem include using a final class or a non-visible class",ex);}catch (Throwable ex) {// TargetSource.getTarget() failedthrow new AopConfigException("Unexpected AOP exception", ex);}}
2.2.3 getProxy()jdk的代理对象
@Overridepublic Object getProxy(@Nullable ClassLoader classLoader) {if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {logger.trace("Creating JDK dynamic proxy: " + this.advised.getTargetSource());}// 获取AdvisedSupport类型对象的所有接口Class<?>[] proxiedInterfaces = AopProxyUtils.completeProxiedInterfaces(this.advised, true);// 接口是否定义了equals和hashcode方法,正常是没有的findDefinedEqualsAndHashCodeMethods(proxiedInterfaces);// 创建代理对象 this是JdkDynamicAopProxy// JdkDynamicAopProxy同时实现了InvocationHandler接口// 这里我们生成的代理对象可以向上造型为任意proxiedInterfaces中的类型return Proxy.newProxyInstance(classLoader, proxiedInterfaces, this);}
2.3 AnnotationAwareAspectJAutoProxyCreator创建动态代理完成
第三步、AOP代理类方法调用invoke()
在前置环节和后置环节都准备好后,当业务代码是涉及到进行方法的调用的时候
以CglibAopProxy为例
1、调用入口
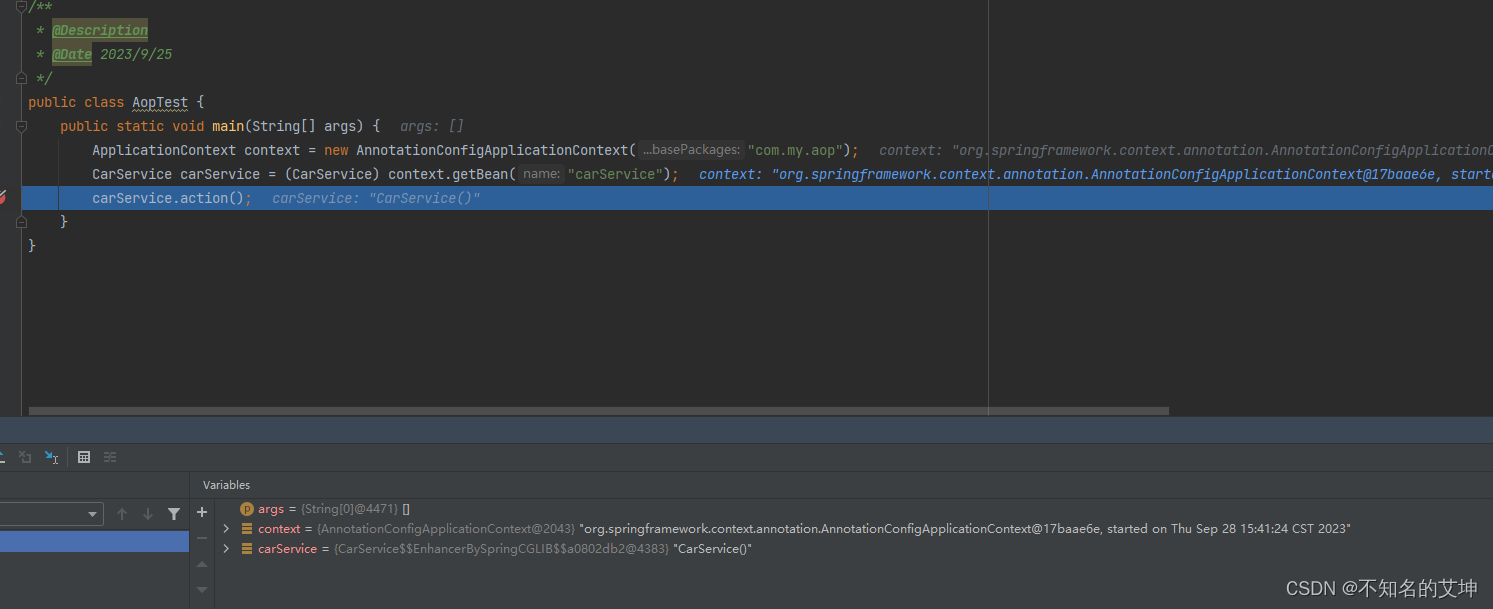
public static void main(String[] args) {ApplicationContext context = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext("com.test");CarService carService = (CarService) context.getBean("carService");carService.action();}
2、CglibAopProxy#intercept()
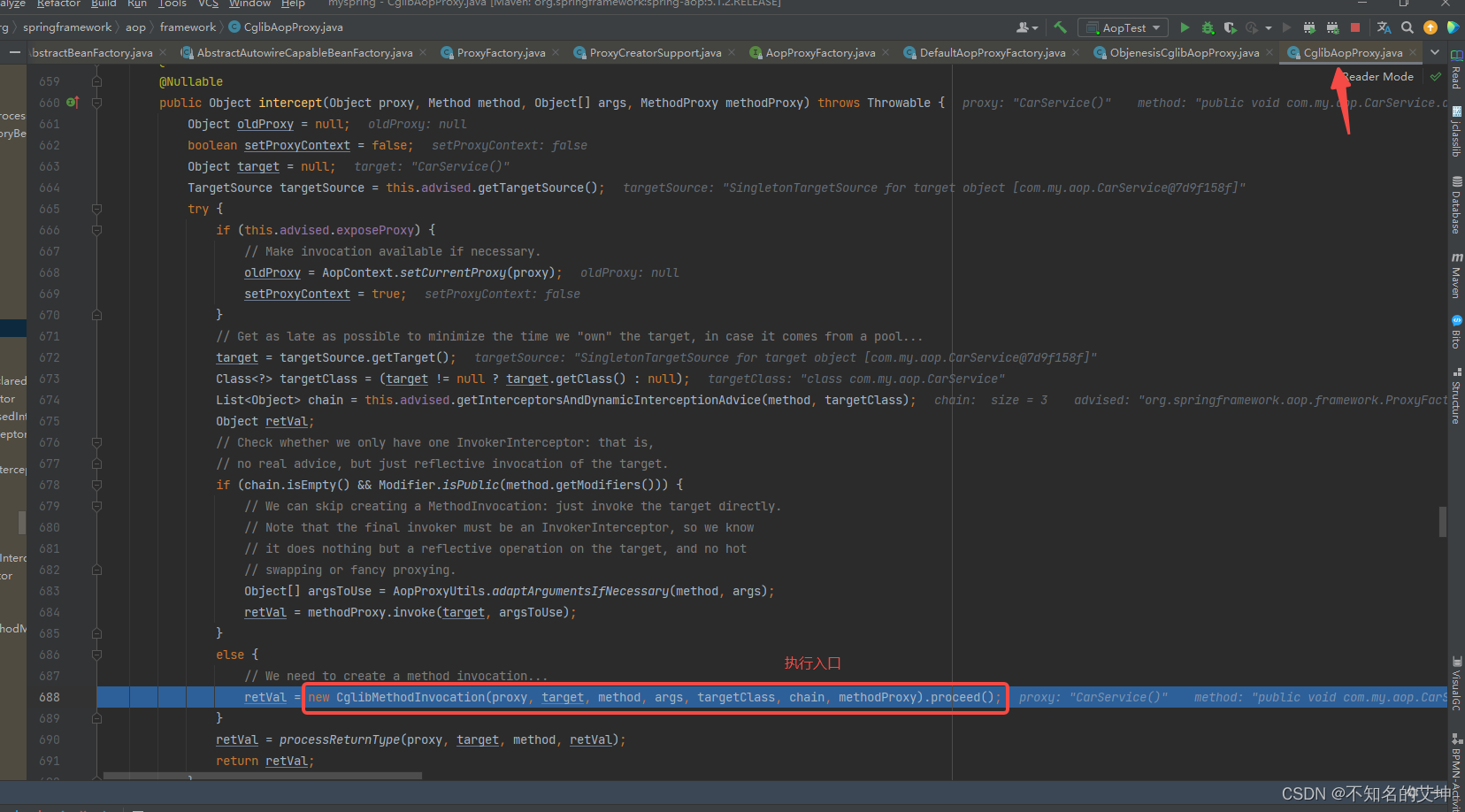
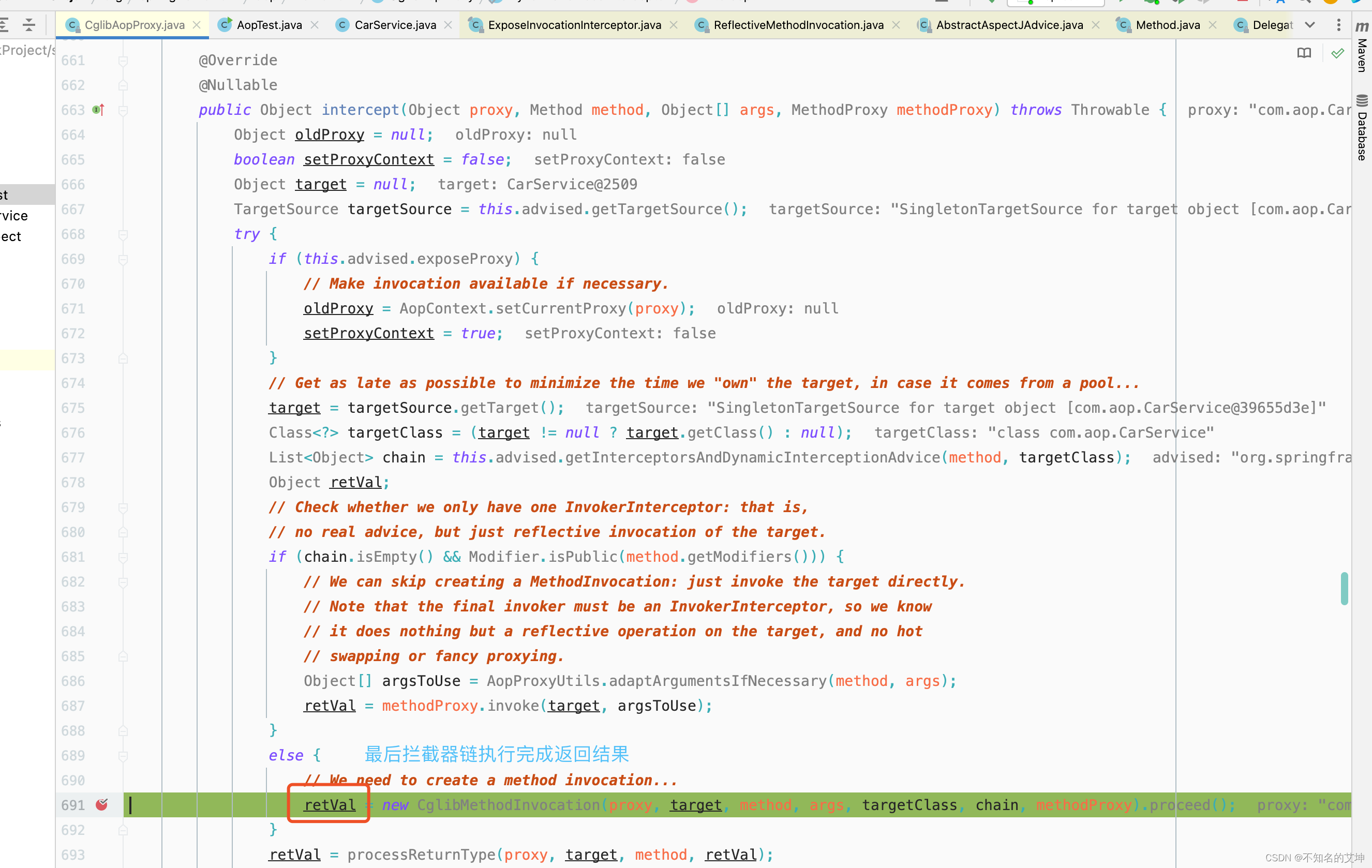
public Object intercept(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args, MethodProxy methodProxy) throws Throwable {Object oldProxy = null;boolean setProxyContext = false;Object target = null;TargetSource targetSource = this.advised.getTargetSource();try {if (this.advised.exposeProxy) {// Make invocation available if necessary.oldProxy = AopContext.setCurrentProxy(proxy);setProxyContext = true;}// Get as late as possible to minimize the time we "own" the target, in case it comes from a pool...target = targetSource.getTarget();Class<?> targetClass = (target != null ? target.getClass() : null);// 从advised中获取配置好的AOP通知List<Object> chain = this.advised.getInterceptorsAndDynamicInterceptionAdvice(method, targetClass);Object retVal;// Check whether we only have one InvokerInterceptor: that is,// no real advice, but just reflective invocation of the target.// 如果没有aop通知配置,那么直接调用target对象的调用方法if (chain.isEmpty() && Modifier.isPublic(method.getModifiers())) {// We can skip creating a MethodInvocation: just invoke the target directly.// Note that the final invoker must be an InvokerInterceptor, so we know// it does nothing but a reflective operation on the target, and no hot// swapping or fancy proxying.Object[] argsToUse = AopProxyUtils.adaptArgumentsIfNecessary(method, args);// 如果拦截器链为空则直接激活原方法retVal = methodProxy.invoke(target, argsToUse);}else {// We need to create a method invocation...// 通过cglibMethodInvocation来启动advice通知retVal = new CglibMethodInvocation(proxy, target, method, args, targetClass, chain, methodProxy).proceed();}retVal = processReturnType(proxy, target, method, retVal);return retVal;}finally {if (target != null && !targetSource.isStatic()) {targetSource.releaseTarget(target);}if (setProxyContext) {// Restore old proxy.AopContext.setCurrentProxy(oldProxy);}}}
3、CglibMethodInvocation#proceed()
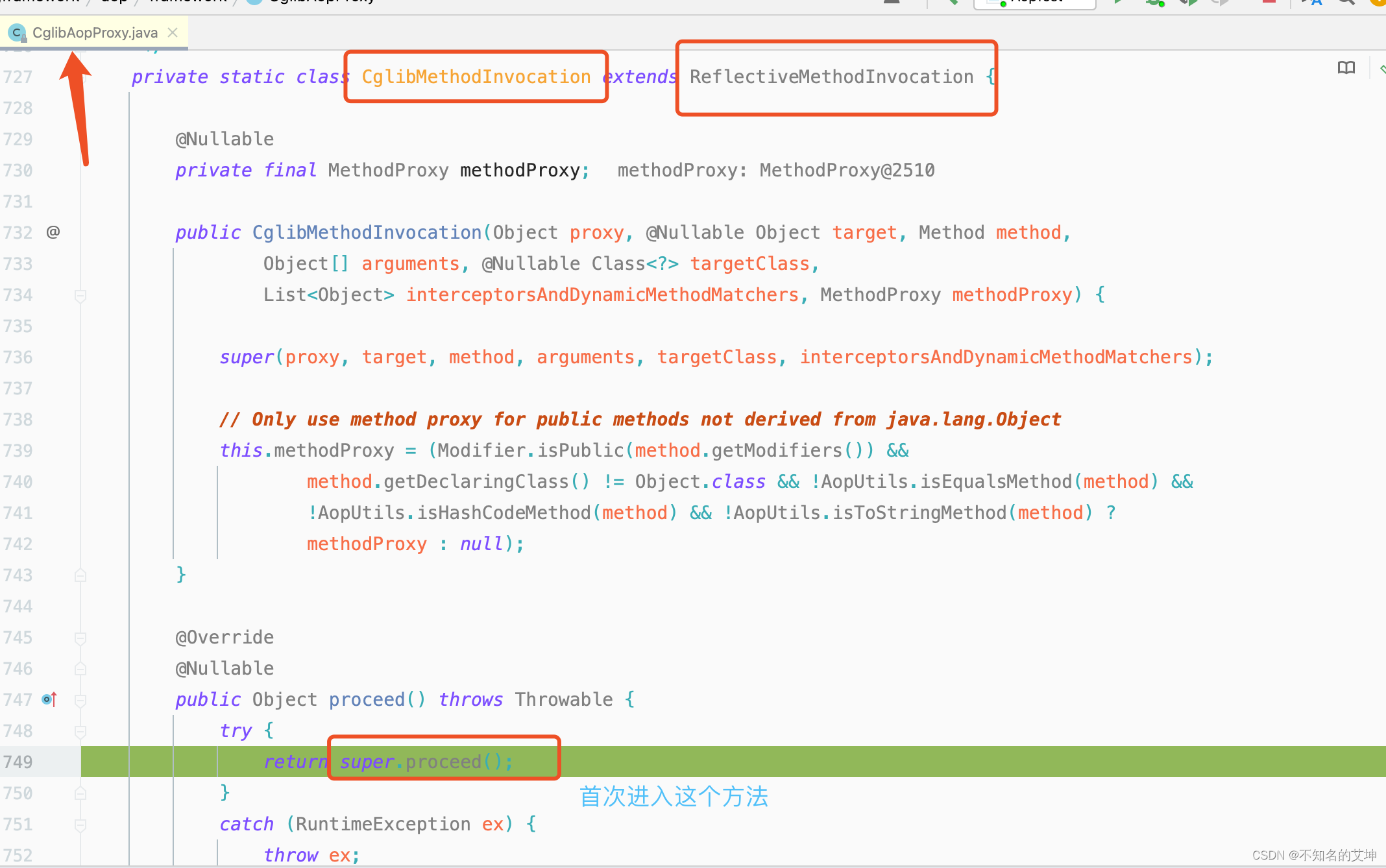
4、核心执行逻辑开始
1、递归:反复执行 CglibMethodInvocation 的 proceed();
2、结束递归条件:interceptorsAndDynamicMethodMatchers 数组中的对象,全部执行完毕;
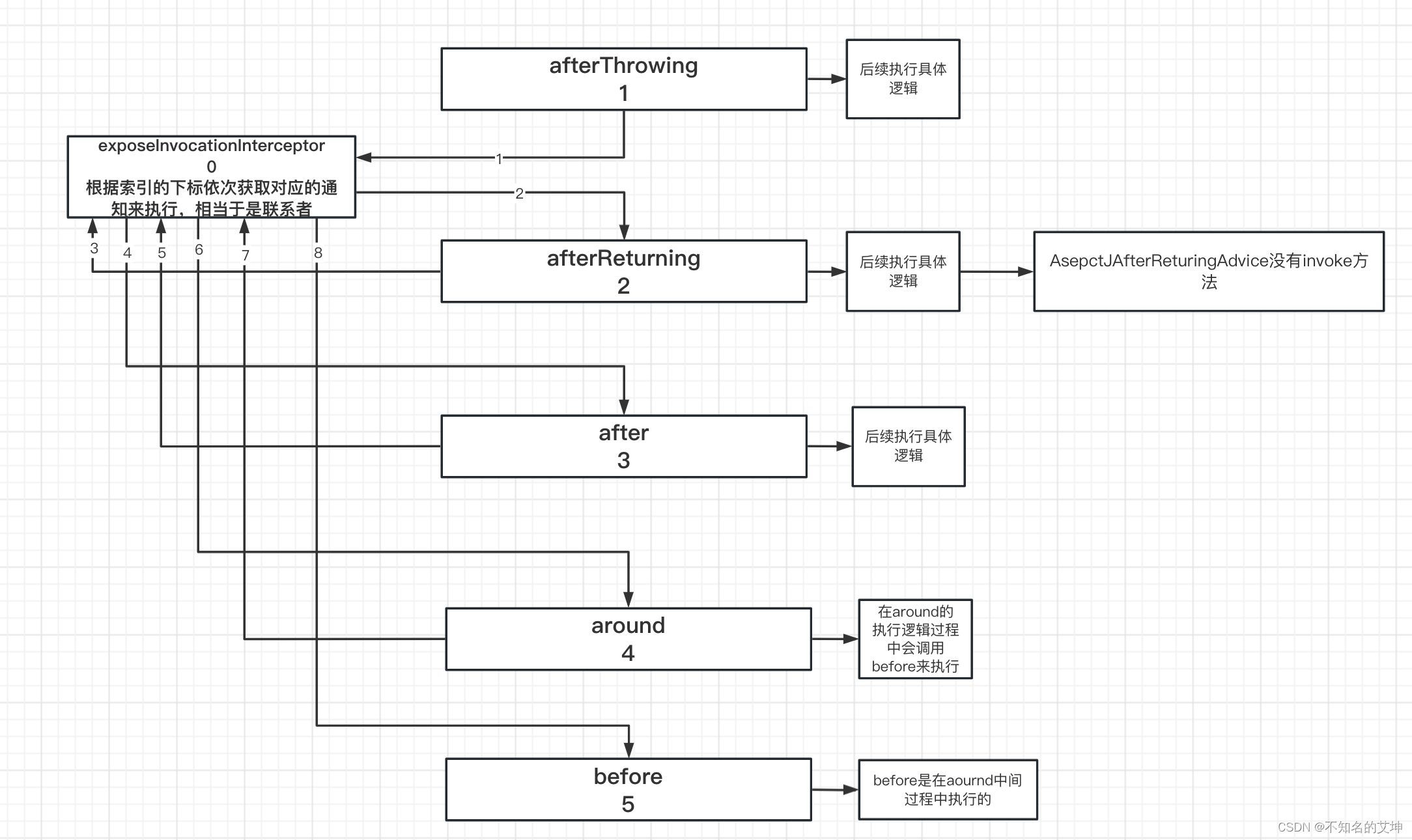
3、责任链:示例中的责任链,是个长度为 3 的数组,每次取其中一个数组对象,然后去执行对象的 invoke()
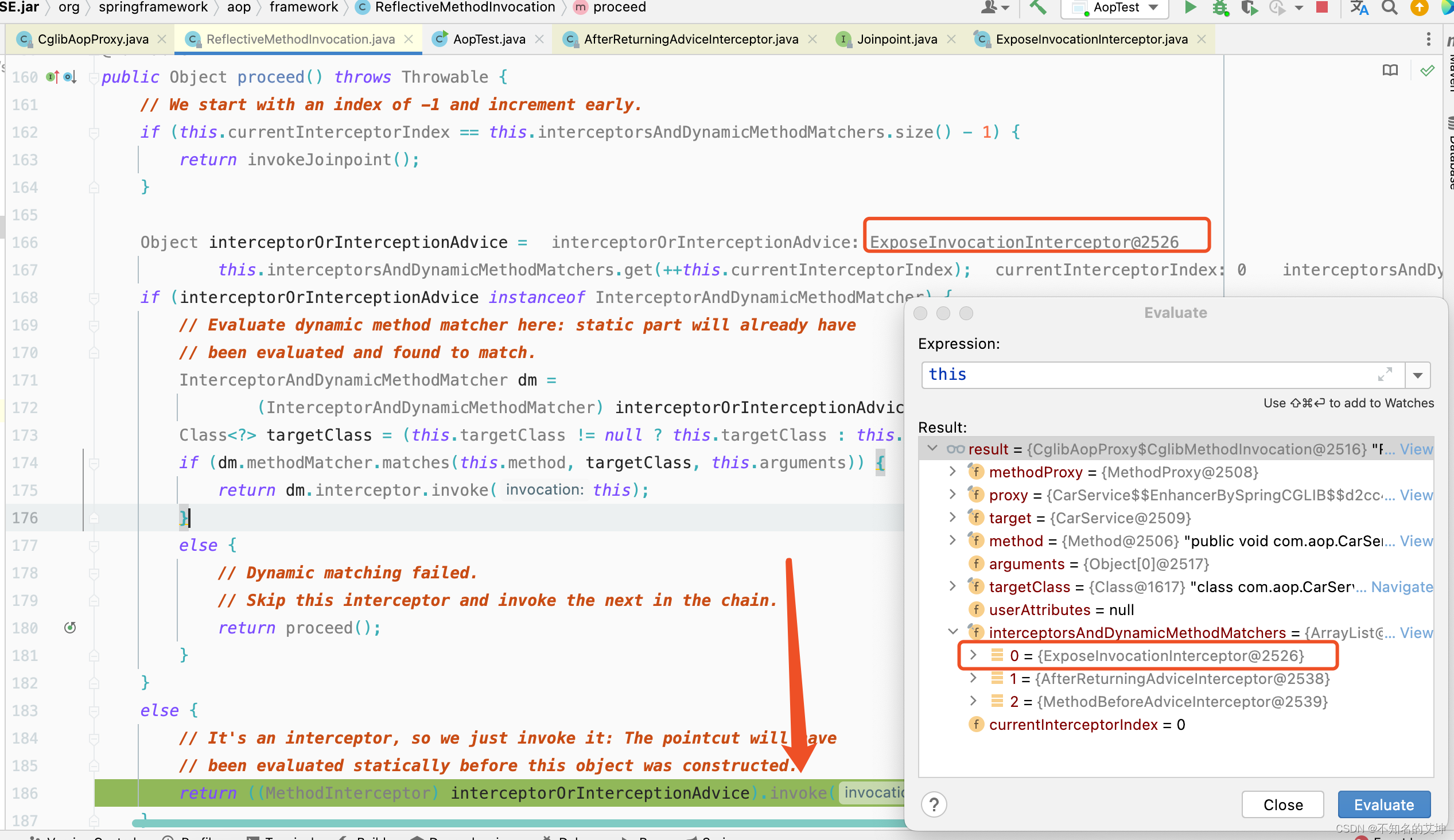
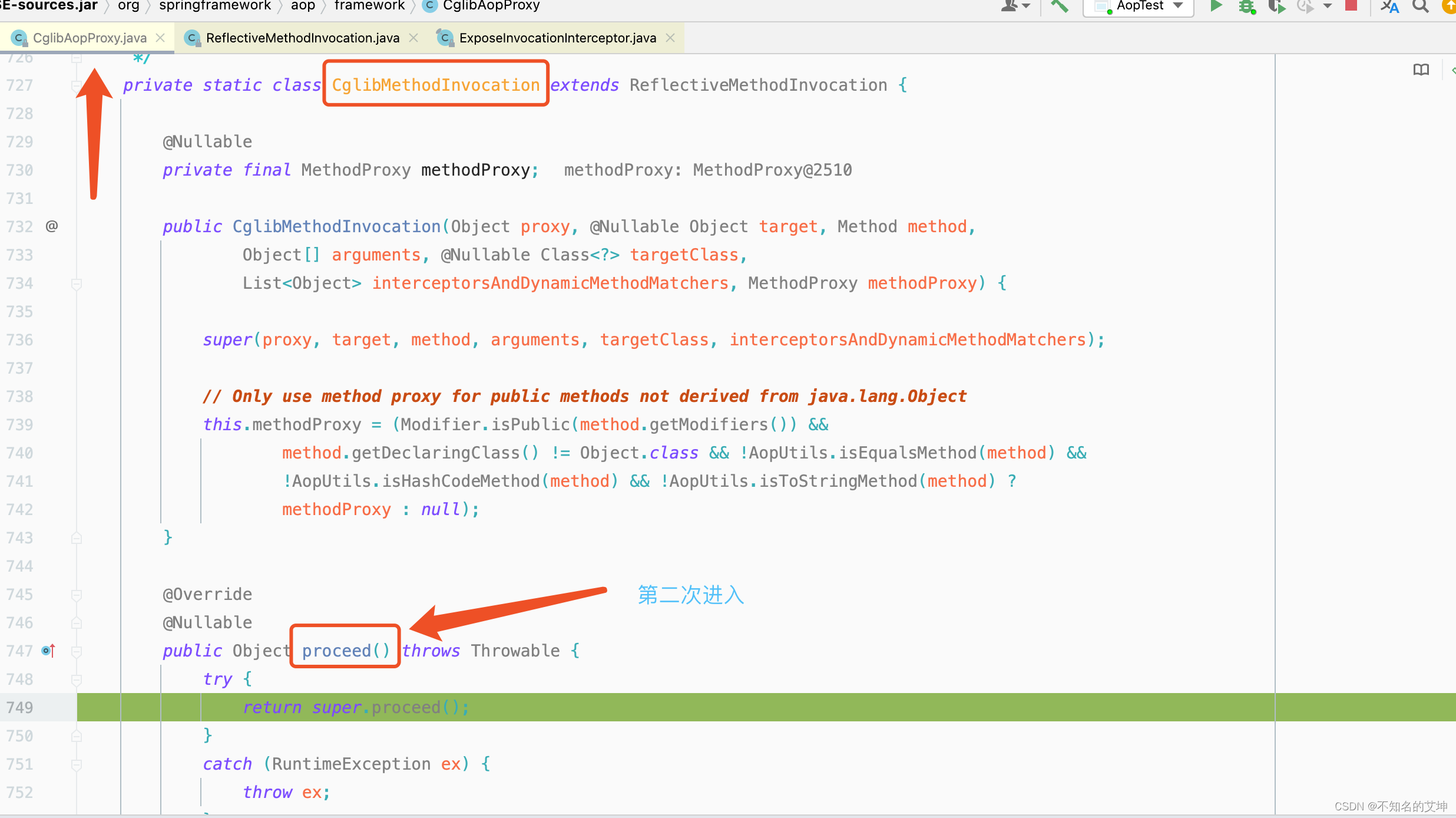
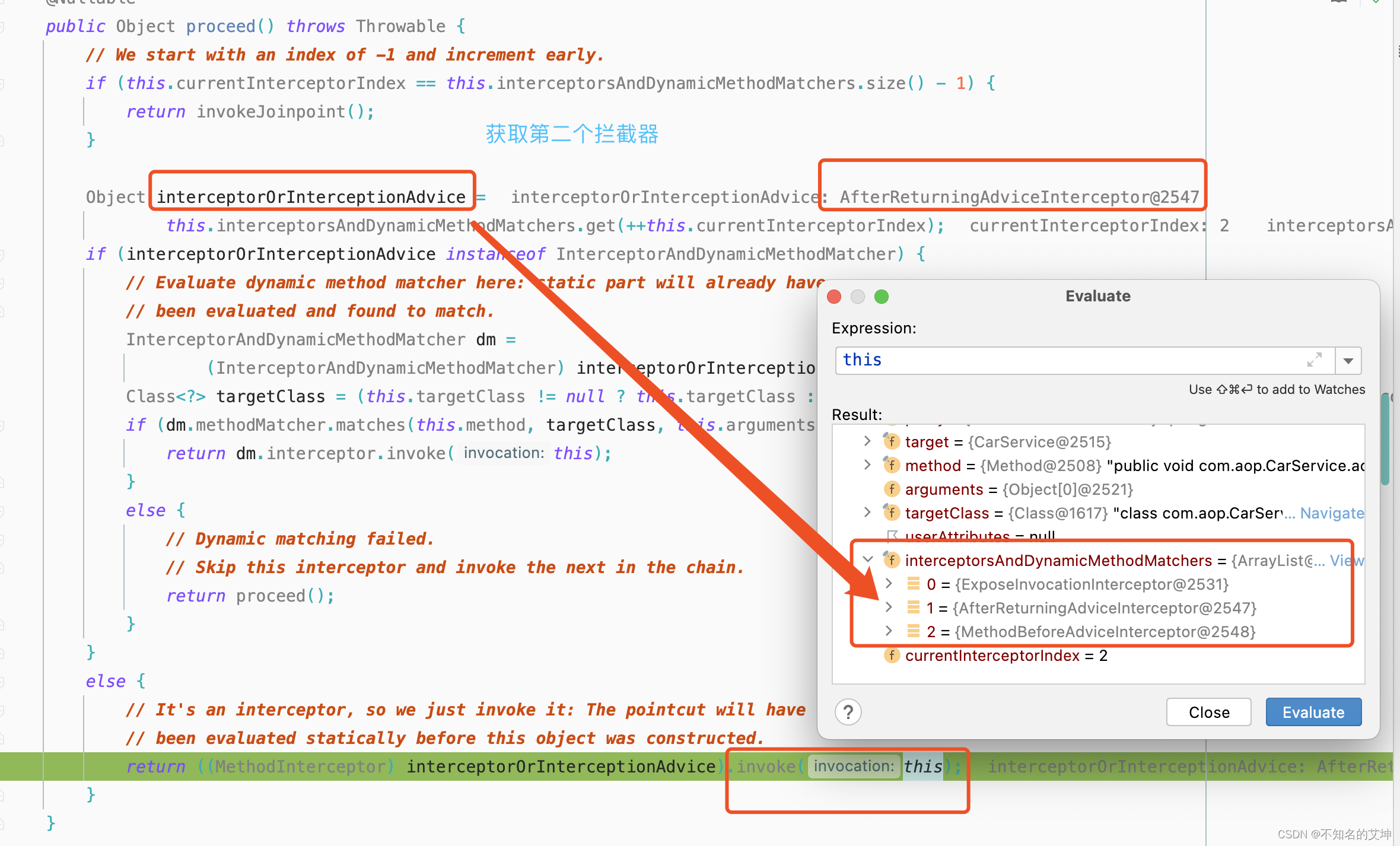
4.1 ExposeInvocationInterceptor执行第一个拦截器

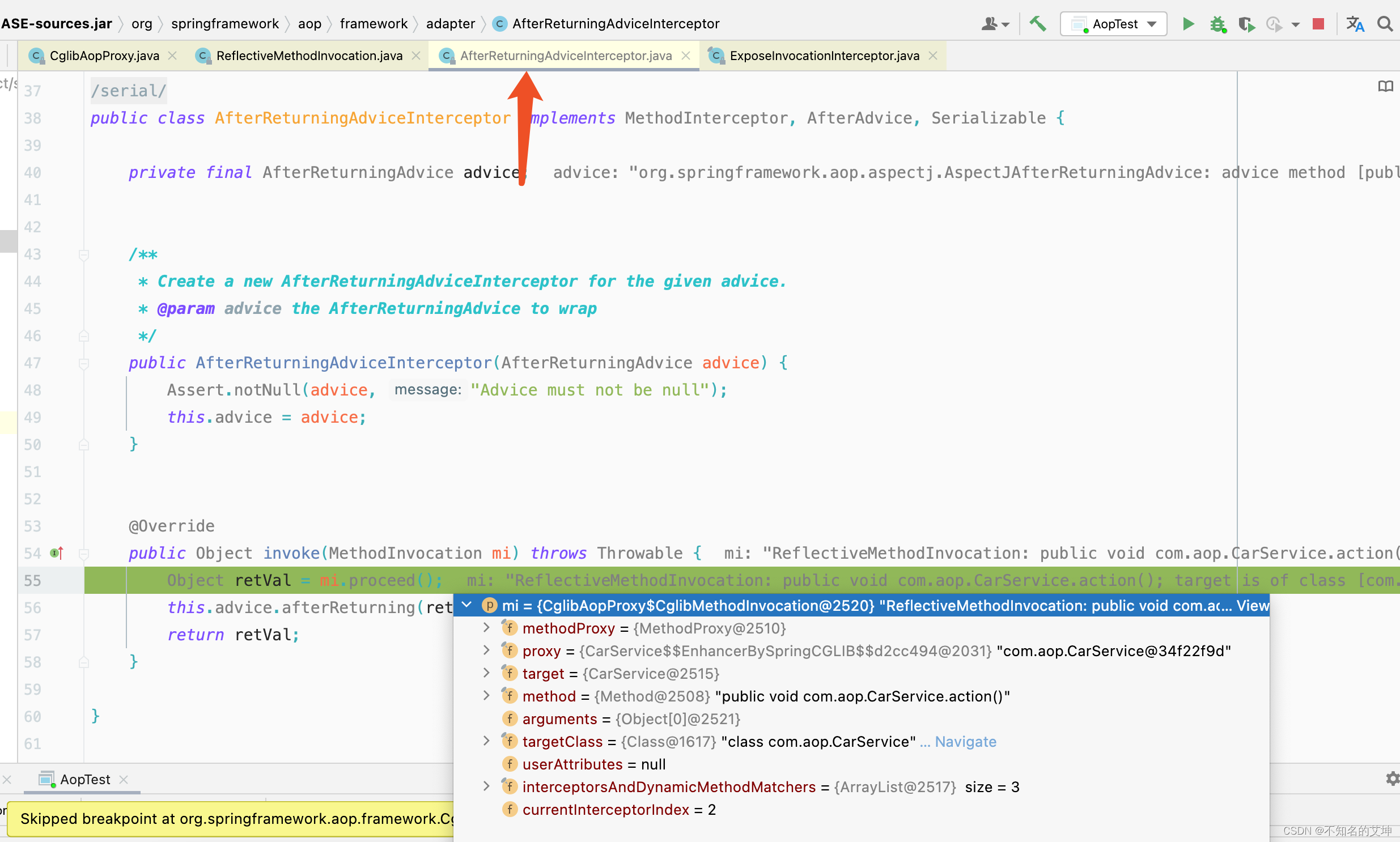
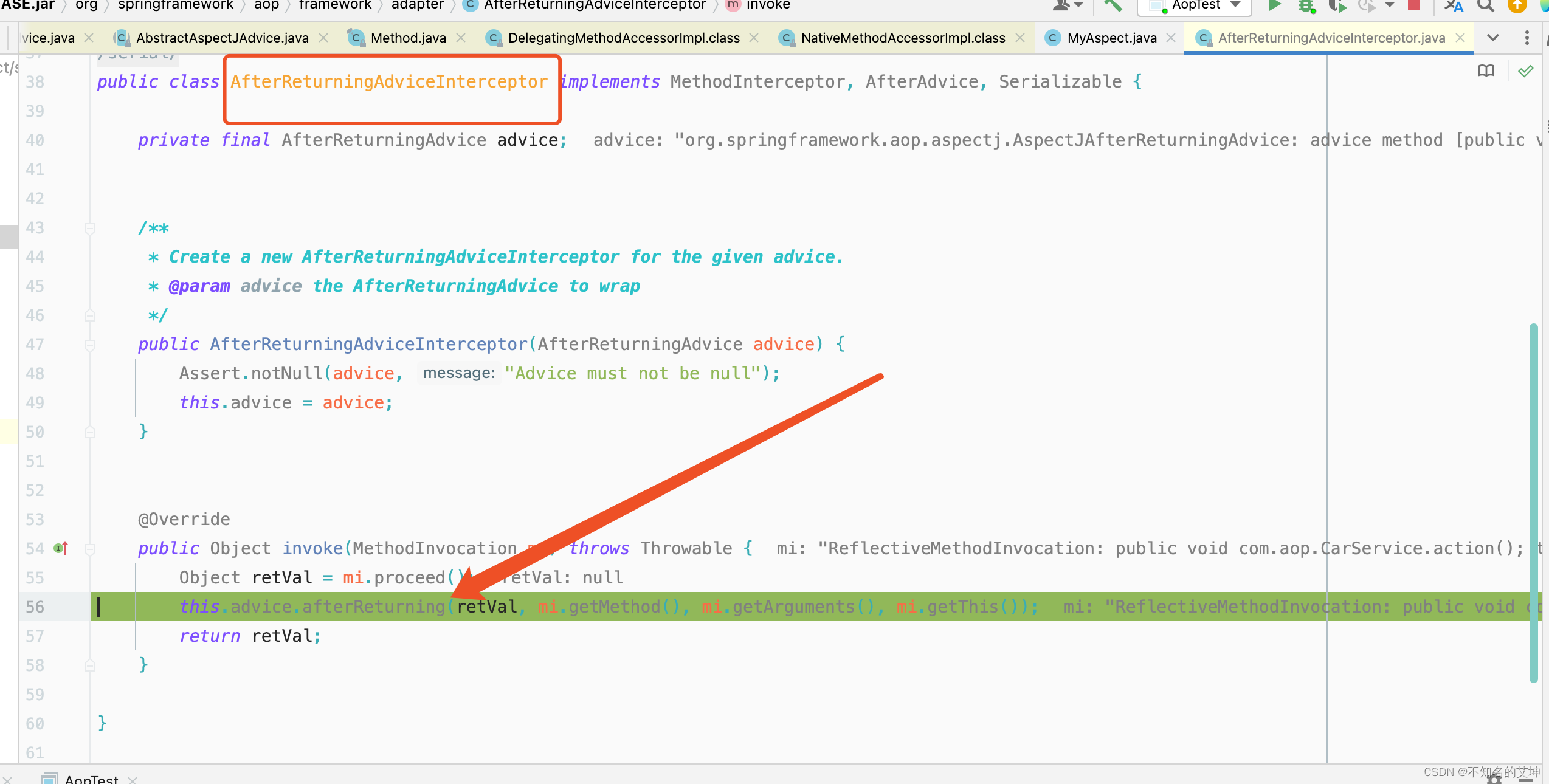
4.2 AfterReturningAdviceInterceptor执行第二个拦截器
> 在这个里面会继续调用下一个拦截器然后等下一拦截器执行完以后在执行当前拦截器的切面方法。这个拦截器的排序顺序在上面就已经描述过了
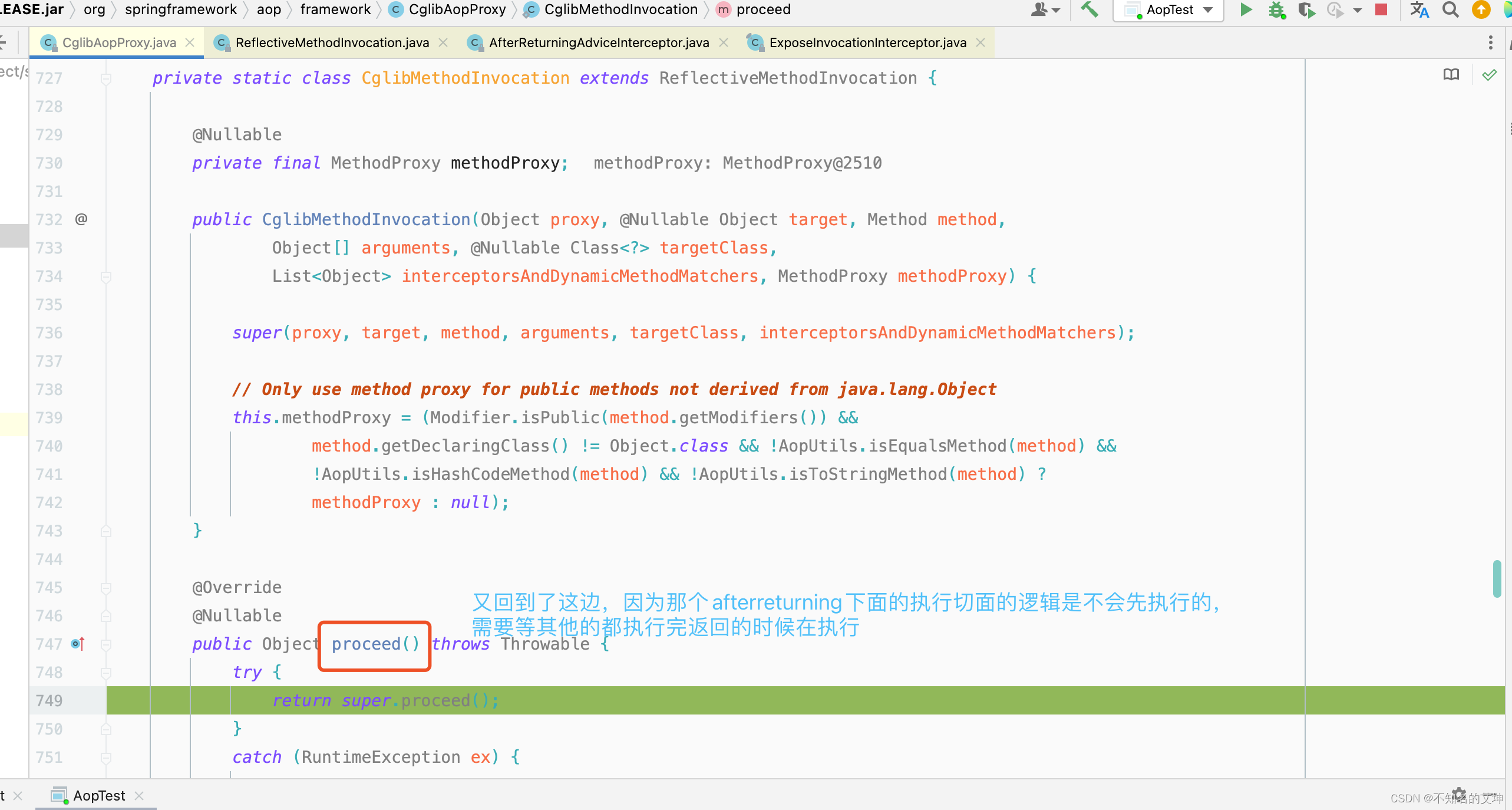
4.3 第三个拦截器MethodBeforeAdviceIntercept
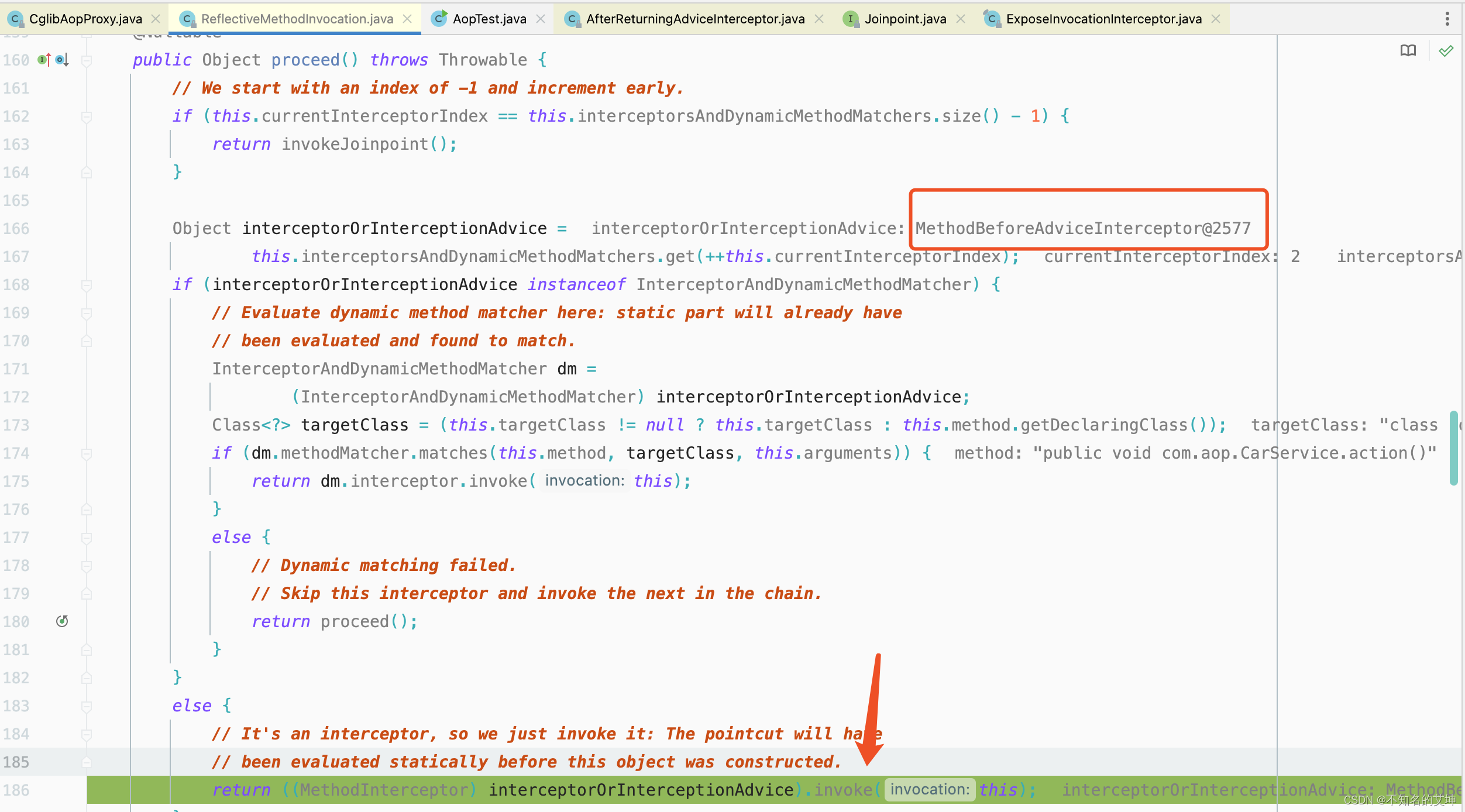
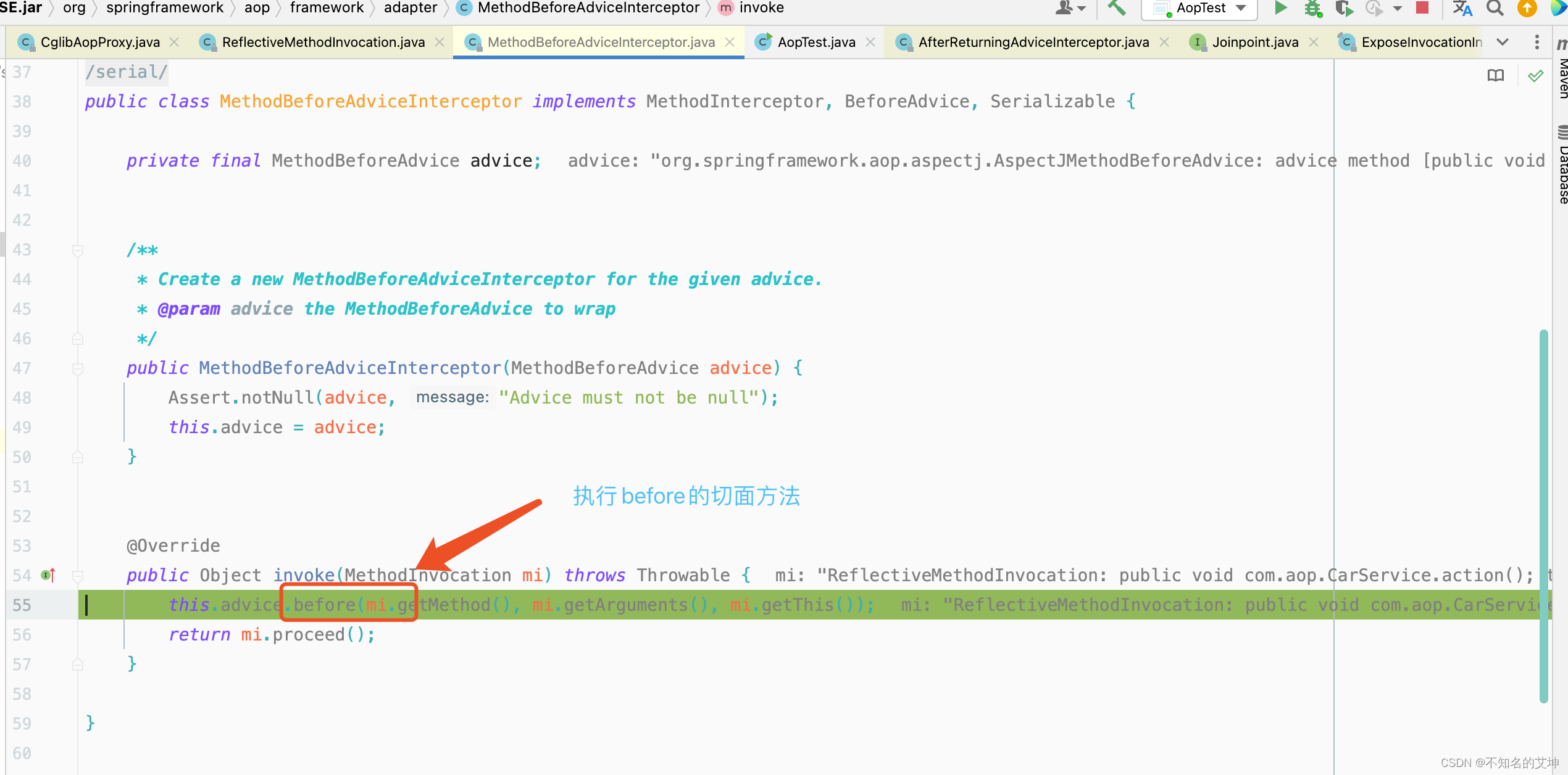
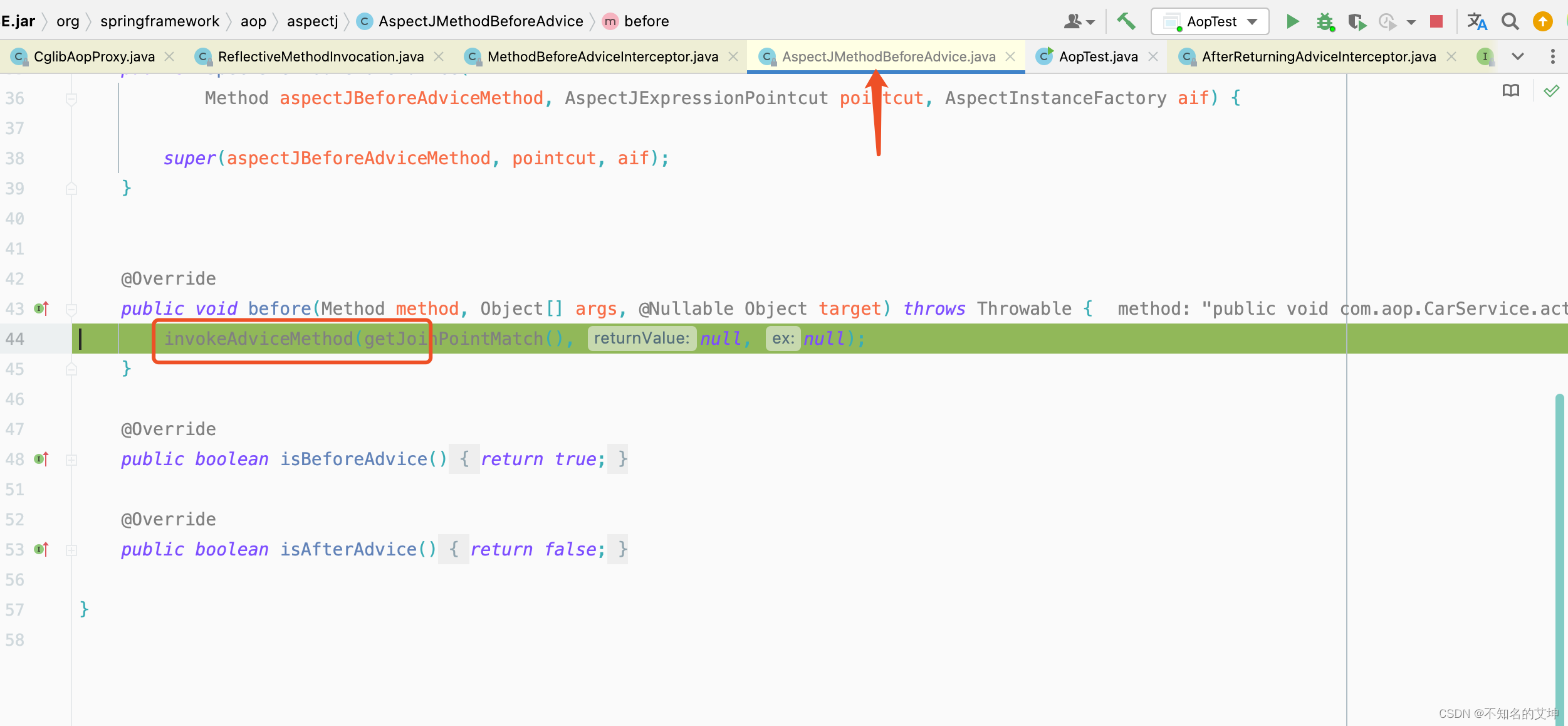
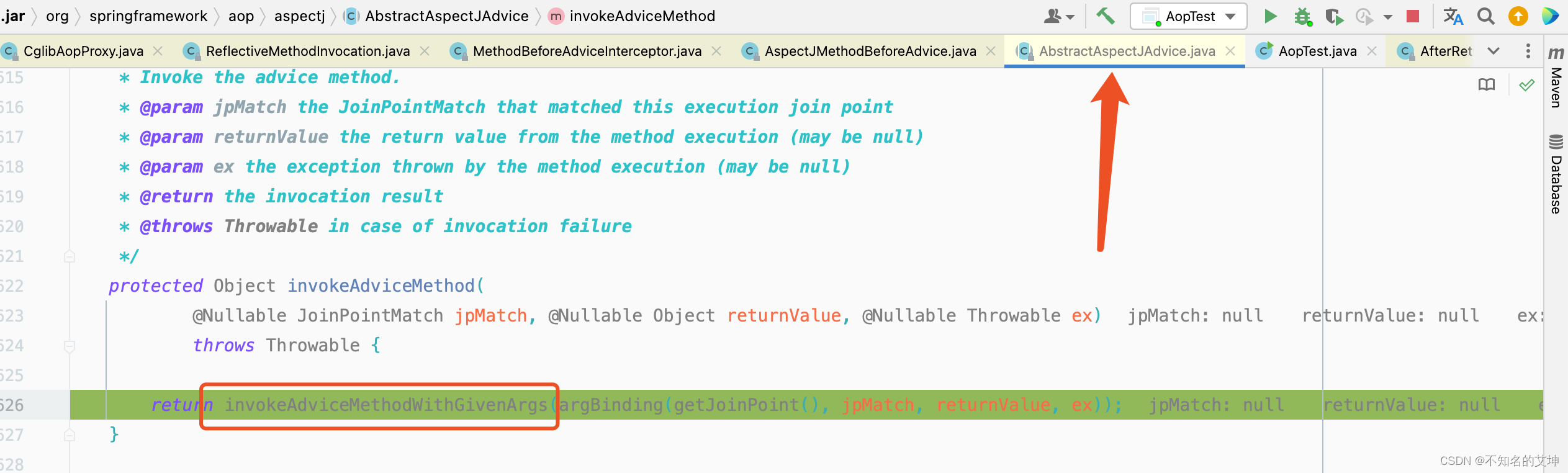
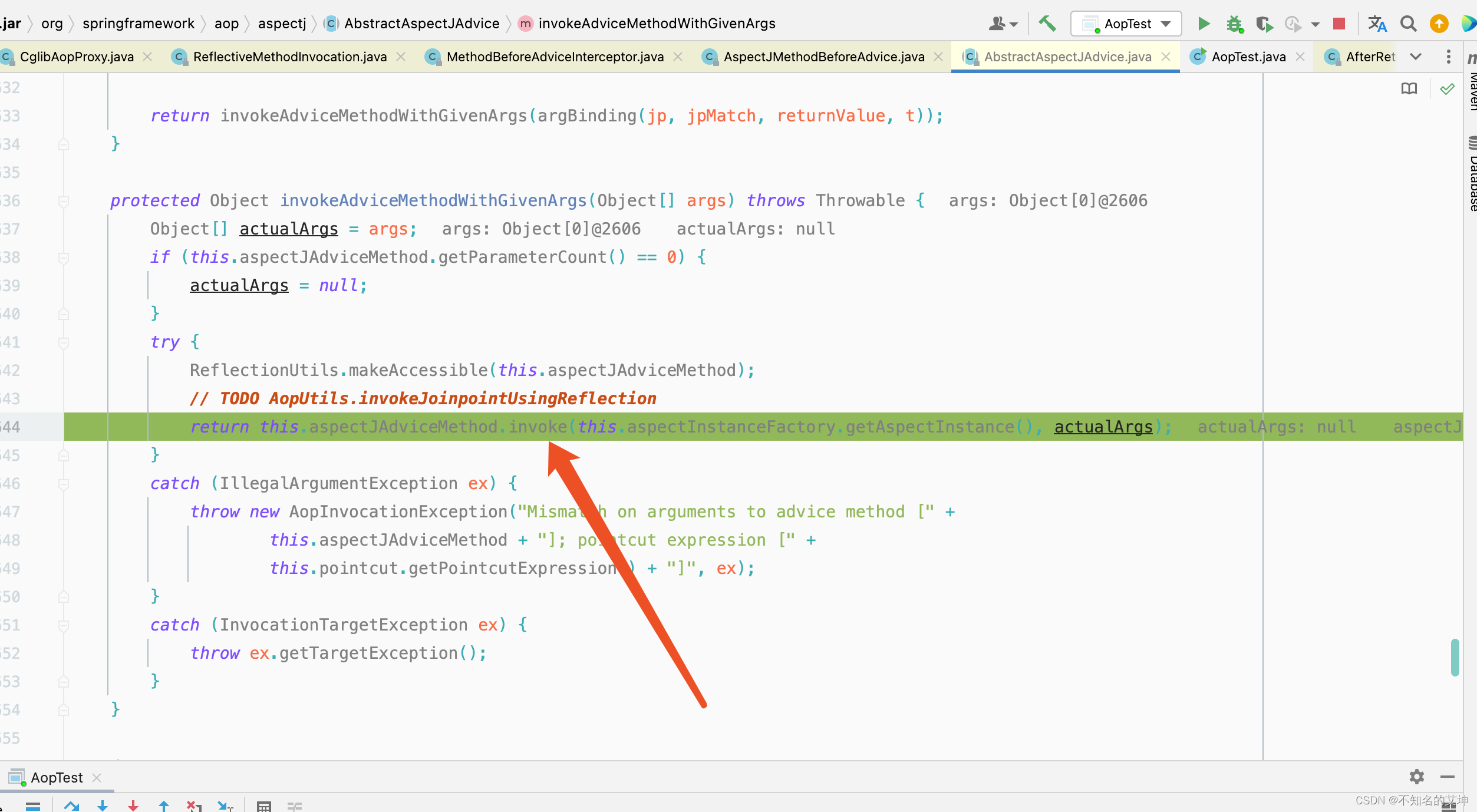


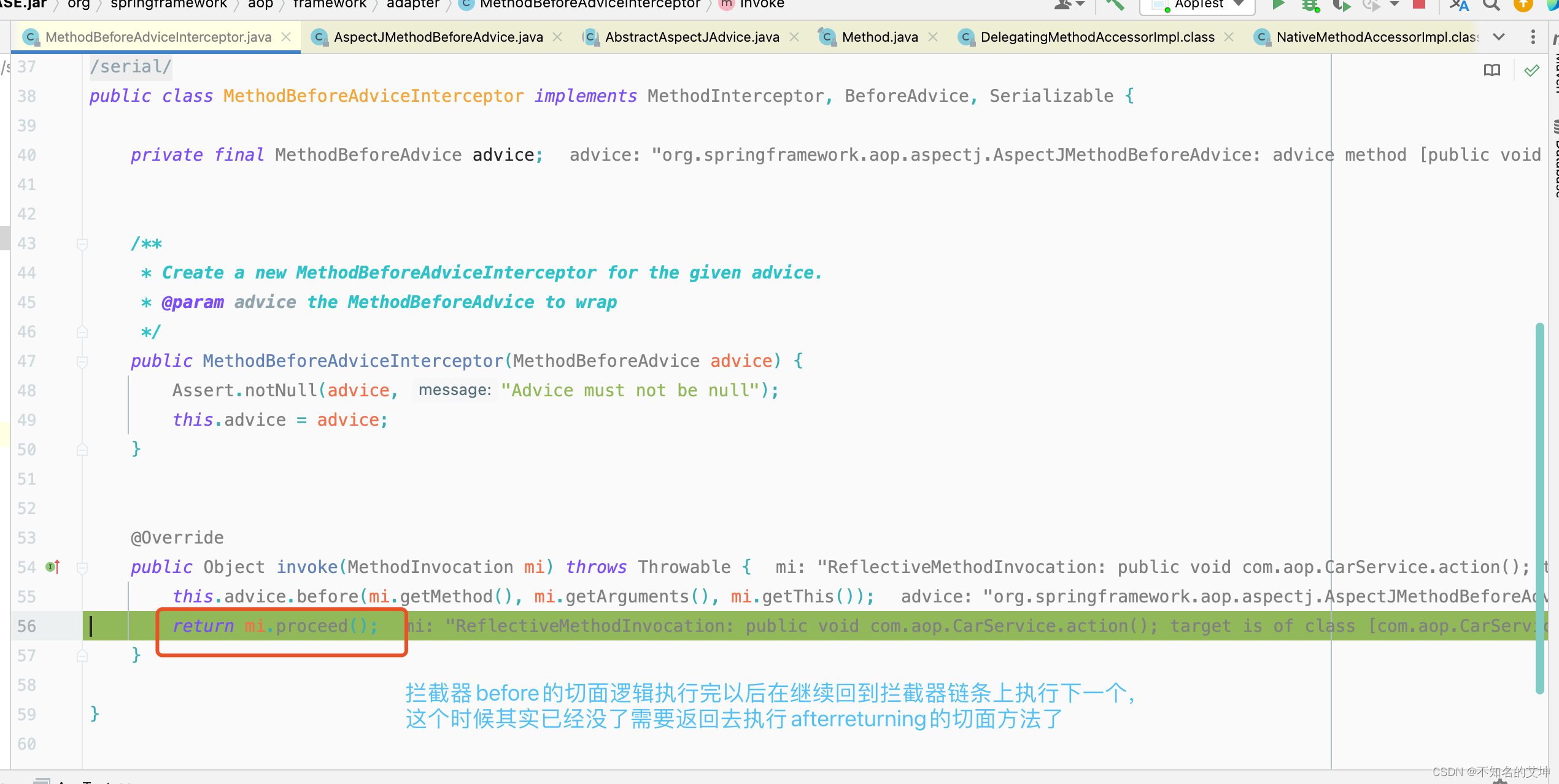
第三个拦截器before执行完以后回到第二个拦截器afterturning的调用处,进行afterturning切面的方法执行
5、CglibAopProxy#invoke()
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {Object oldProxy = null;boolean setProxyContext = false;//获取到我们的目标对象TargetSource targetSource = this.advised.targetSource;Object target = null;try {//若是equals方法不需要代理if (!this.equalsDefined && AopUtils.isEqualsMethod(method)) {// The target does not implement the equals(Object) method itself.return equals(args[0]);}//若是hashCode方法不需要代理else if (!this.hashCodeDefined && AopUtils.isHashCodeMethod(method)) {// The target does not implement the hashCode() method itself.return hashCode();}//若是DecoratingProxy也不要拦截器执行else if (method.getDeclaringClass() == DecoratingProxy.class) {// There is only getDecoratedClass() declared -> dispatch to proxy config.return AopProxyUtils.ultimateTargetClass(this.advised);}else if (!this.advised.opaque && method.getDeclaringClass().isInterface() &&method.getDeclaringClass().isAssignableFrom(Advised.class)) {// Service invocations on ProxyConfig with the proxy config...return AopUtils.invokeJoinpointUsingReflection(this.advised, method, args);}Object retVal;/*** 这个配置是暴露我们的代理对象到线程变量中,需要搭配@EnableAspectJAutoProxy(exposeProxy = true)一起使用* 比如在目标对象方法中再次获取代理对象可以使用这个AopContext.currentProxy()* 还有的就是事务方法调用事务方法的时候也是用到这个*/if (this.advised.exposeProxy) {//把我们的代理对象暴露到线程变量中oldProxy = AopContext.setCurrentProxy(proxy);setProxyContext = true;}//获取我们的目标对象target = targetSource.getTarget();//获取我们目标对象的classClass<?> targetClass = (target != null ? target.getClass() : null);//把aop的advisor转化为拦截器链List<Object> chain = this.advised.getInterceptorsAndDynamicInterceptionAdvice(method, targetClass);//如果拦截器链为空if (chain.isEmpty()) {//通过反射直接调用执行Object[] argsToUse = AopProxyUtils.adaptArgumentsIfNecessary(method, args);retVal = AopUtils.invokeJoinpointUsingReflection(target, method, argsToUse);}else {//创建一个方法调用对象MethodInvocation invocation =new ReflectiveMethodInvocation(proxy, target, method, args, targetClass, chain);//调用执行retVal = invocation.proceed();}// Massage return value if necessary.Class<?> returnType = method.getReturnType();if (retVal != null && retVal == target &&returnType != Object.class && returnType.isInstance(proxy) &&!RawTargetAccess.class.isAssignableFrom(method.getDeclaringClass())) {// Special case: it returned "this" and the return type of the method// is type-compatible. Note that we can't help if the target sets// a reference to itself in another returned object.retVal = proxy;}else if (retVal == null && returnType != Void.TYPE && returnType.isPrimitive()) {throw new AopInvocationException("Null return value from advice does not match primitive return type for: " + method);}return retVal;}finally {if (target != null && !targetSource.isStatic()) {// Must have come from TargetSource.targetSource.releaseTarget(target);}if (setProxyContext) {// Restore old proxy.AopContext.setCurrentProxy(oldProxy);}}}
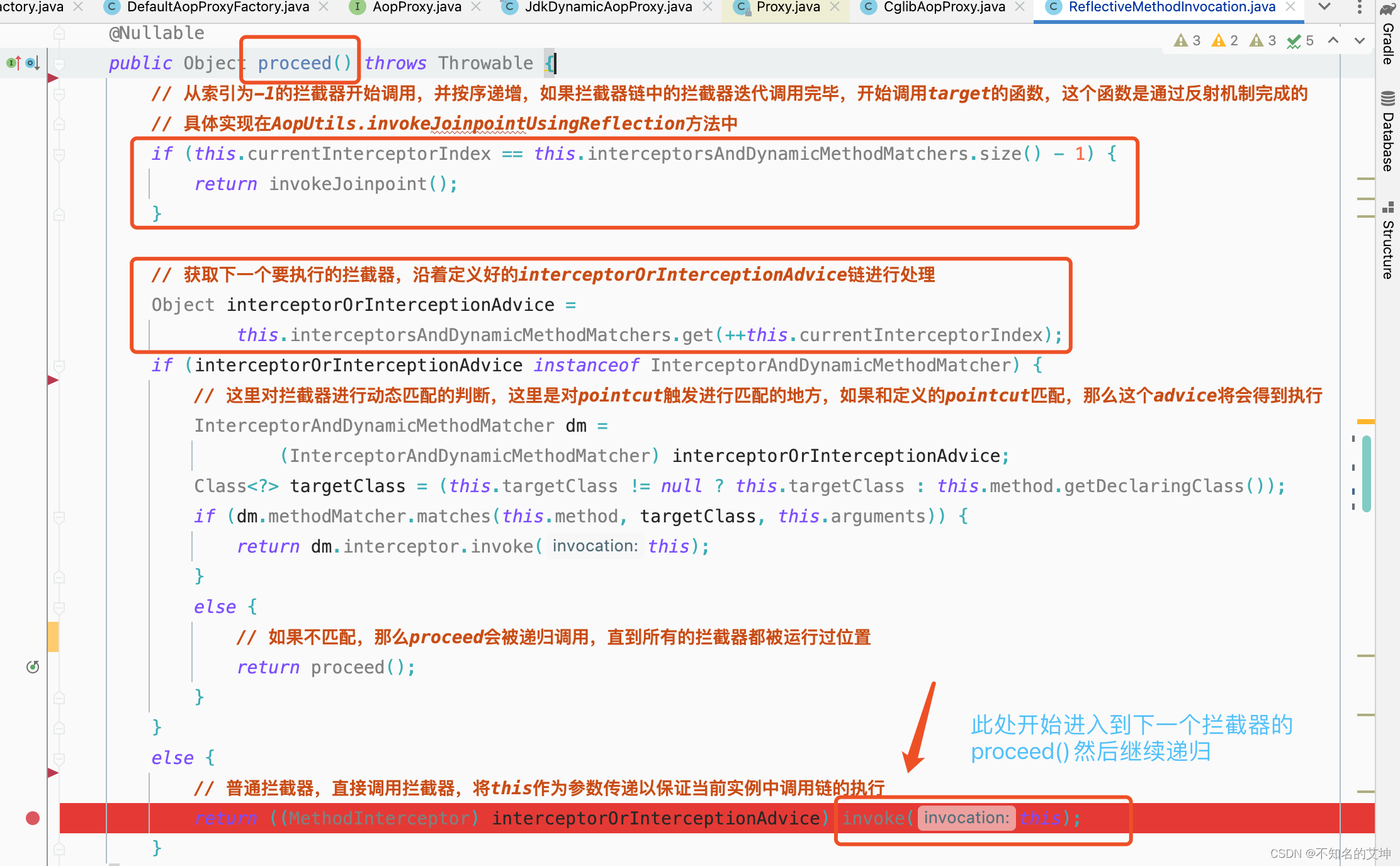
6、invocation.proceed()
invocation.proceed()方法中的调用用到了递归和责任链设计模式
public Object proceed() throws Throwable {//从-1开始,下标=拦截器的长度-1的条件满足表示执行到了最后一个拦截器的时候,此时执行目标方法if (this.currentInterceptorIndex == this.interceptorsAndDynamicMethodMatchers.size() - 1) {return invokeJoinpoint();}//获取第一个方法拦截器使用的是前++Object interceptorOrInterceptionAdvice =this.interceptorsAndDynamicMethodMatchers.get(++this.currentInterceptorIndex);if (interceptorOrInterceptionAdvice instanceof InterceptorAndDynamicMethodMatcher) {// Evaluate dynamic method matcher here: static part will already have// been evaluated and found to match.InterceptorAndDynamicMethodMatcher dm =(InterceptorAndDynamicMethodMatcher) interceptorOrInterceptionAdvice;if (dm.methodMatcher.matches(this.method, this.targetClass, this.arguments)) {return dm.interceptor.invoke(this);}else {// Dynamic matching failed.// Skip this interceptor and invoke the next in the chain.return proceed();}}else {return ((MethodInterceptor) interceptorOrInterceptionAdvice).invoke(this);}}
7、((MethodInterceptor) interceptorOrInterceptionAdvice).invoke(this)
重点处
① ExposeInvocationInterceptor.invoke()
public Object invoke(MethodInvocation mi) throws Throwable {MethodInvocation oldInvocation = invocation.get();invocation.set(mi);try {return mi.proceed();}finally {invocation.set(oldInvocation);}}
② AspectJAfterThrowingAdvice.invoke()
public Object invoke(MethodInvocation mi) throws Throwable {try {//执行下一个通知/拦截器return mi.proceed();}catch (Throwable ex) {//抛出异常if (shouldInvokeOnThrowing(ex)) {//执行异常通知invokeAdviceMethod(getJoinPointMatch(), null, ex);}throw ex;}}
③ AfterReturningAdviceInterceptor.invoke()
public Object invoke(MethodInvocation mi) throws Throwable {//执行下一个通知/拦截器Object retVal = mi.proceed();//返回通知方法this.advice.afterReturning(retVal, mi.getMethod(), mi.getArguments(), mi.getThis());return retVal;}
④ AspectJAfterAdvice.invoke()
public Object invoke(MethodInvocation mi) throws Throwable {try {//执行下一个通知/拦截器return mi.proceed();}finally {//后置通知的方法总是会被执行 原因就在这finallyinvokeAdviceMethod(getJoinPointMatch(), null, null);}}
⑤ AspectJAroundAdvice.invoke
public Object invoke(MethodInvocation mi) throws Throwable {if (!(mi instanceof ProxyMethodInvocation)) {throw new IllegalStateException("MethodInvocation is not a Spring ProxyMethodInvocation: " + mi);}ProxyMethodInvocation pmi = (ProxyMethodInvocation) mi;ProceedingJoinPoint pjp = lazyGetProceedingJoinPoint(pmi);JoinPointMatch jpm = getJoinPointMatch(pmi);return invokeAdviceMethod(pjp, jpm, null, null);}
⑥ MethodBeforeAdviceInterceptor.invoke
public Object invoke(MethodInvocation mi) throws Throwable {//执行前置通知的方法this.advice.before(mi.getMethod(), mi.getArguments(), mi.getThis());//执行下一个通知/拦截器,但是该拦截器是最后一个了,所以会调用目标方法return mi.proceed();}
四、Spring AOP前置环节分析
@EnableAspectJAutoProxy作用
@EnableAspectJAutoProxy注解开启aop支持,@EnableAspectJAutoProxy到底做了什么?
1、入口处通过import导入一个类
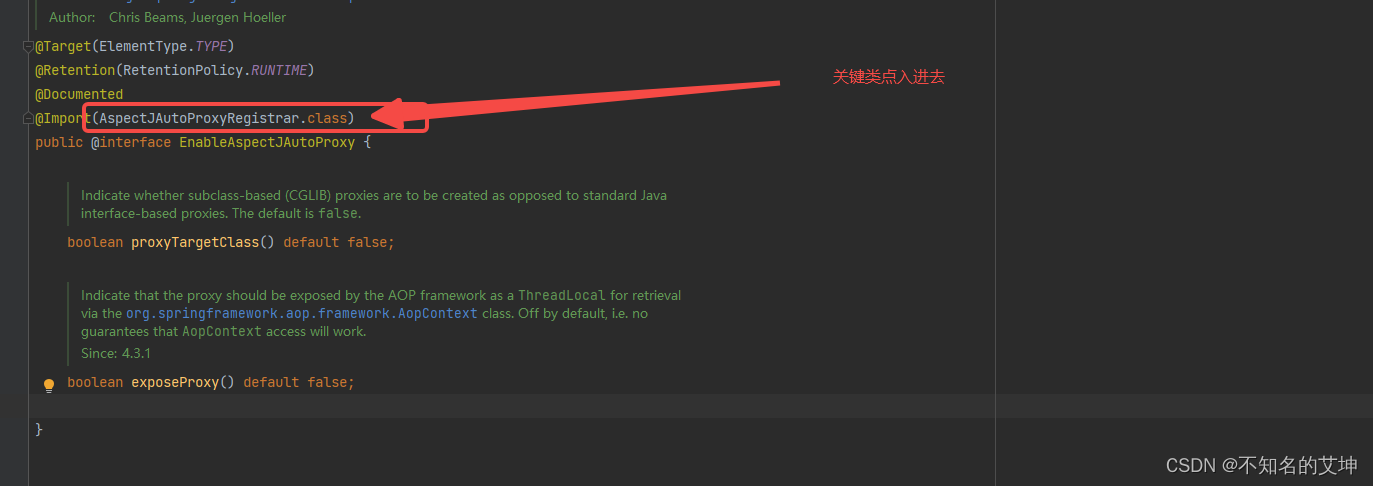
2、注册AnnotationAwareAspectJAutoProxyCreator的BeanDefinition
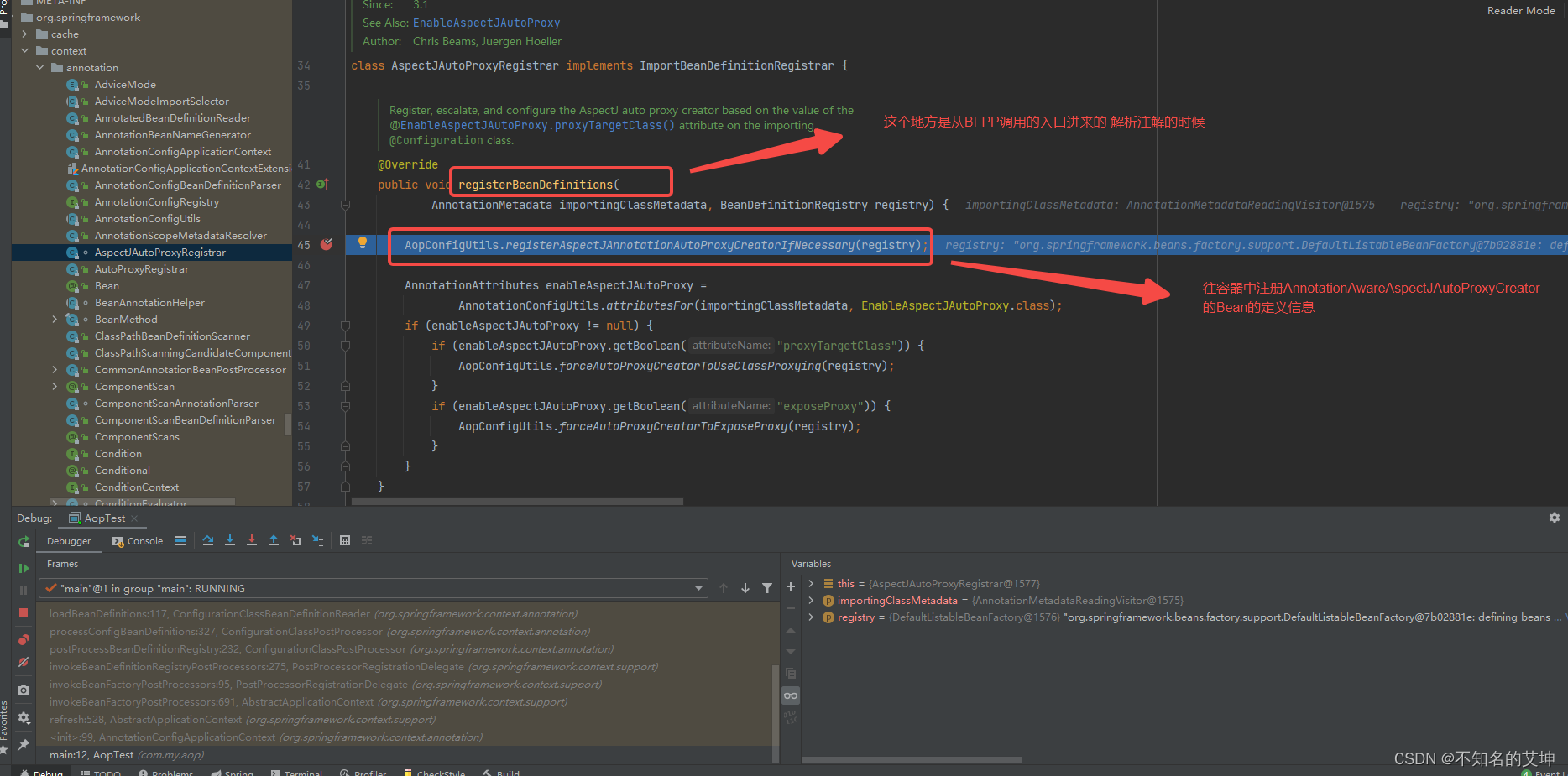
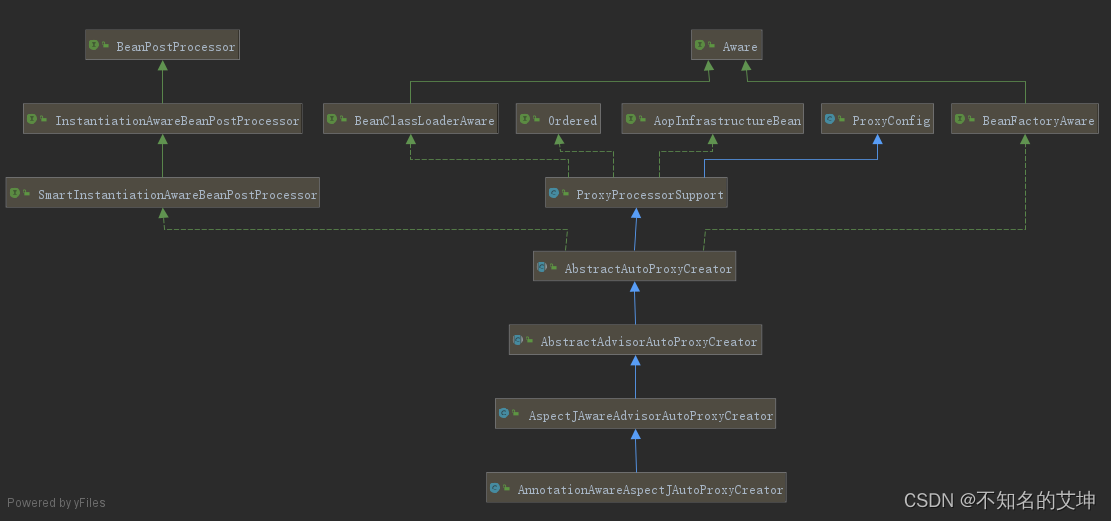
3、AnnotationAwareAspectJAutoProxyCreator继承图
AnnotationAwareAspectJAutoProxyCreator继承了AbstractAutoProxyCreator实现了InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor接口:
同时实现了postProcessBeforeInstantiation()和postProcessAfterInstantiation();
resolveBeforeInstantiation方法进去就会调到AbstractAutoProxyCreator的postProcessBeforeInstantiation方法,
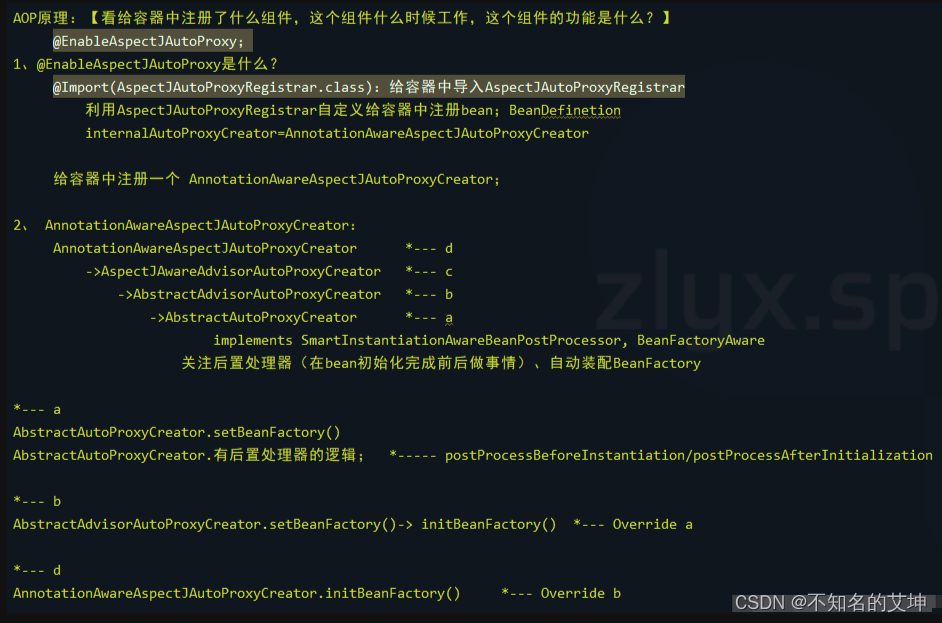
五、SpringAOP流程总结








--- qsort函数(快速排序)的使用和(用冒泡排序)模拟实现)









)
)