GlusterFS分布式存储系统
一,分布式文件系统理论基础
1.1 分布式文件系统出现
- 计算机通过文件系统管理,存储数据,而现在数据信息爆炸的时代中人们可以获取的数据成指数倍的增长,单纯通过增加硬盘个数来扩展计算机文件系统的存储容量的方式,已经不能满足目前的需求。
- 分布式文件系统可以有效解决数据的存储和管理难题,将固定于某个地点的某个文件系统,扩展到任意多个地点/多个文件系统,众多的节点组成一个文件系统网络。每个节点可以分布在不同的地点,通过网络进行节点间的通信和数据传输。人们在使用分布式文件系统时,无需关心数据是存储在哪个节点上,或者是从哪个节点从获取的,只需要像使用本地文件系统一样管理和存储文件系统中的数据。
1.2 典型代表NFS
NFS(Network File System)即网络文件系统,它允许网络中的计算机之间通过TCP/IP网络共享资源。在NFS的应用中,本地NFS的客户端应用可以透明地读写位于远端NFS服务器上的文件,就像访问本地文件一样。NFS的优点如下:
(1)节约使用的磁盘空间
客户端经常使用的数据可以集中存放在一台机器上,并使用NFS发布,那么网络内部所有计算机可以通过网络访问,不必单独存储。
(2)节约硬件资源
NFS还可以共享软驱,CDROM和ZIP等的存储设备,减少整个网络上的可移动设备的数量。
(3)用户主目录设定
对于特殊用户,如管理员等,为了管理的需要,可能会经常登陆到网络中所有的计算机,若每个客户端,均保存这个用户的主目录很繁琐,而且不能保证数据的一致性。实际上,经过NFS服务的设定,然后在客户端指定这个用户的主目录位置,并自动挂载,就可以在任何计算机上使用用户主目录的文件。
1.3 面临的问题
存储空间不足,需要更大容量的存储
直接用NFS挂载存储,有一定风险,存在单点故障
某些场景不能满足需求,大量的访问磁盘IO是瓶颈
1.4 GlusterFS概述
- GlusterFS是Scale-Out存储解决方案Gluster的核心,它是一个开源的分布式文件系统,具有强大的横向扩展能力,通过扩展能够支持数PB存储容量和处理数千客户端。GlusterFS借助TCP/IP或InfiniBand RDMA网络将物理分布的存储资源聚集在一起,使用单一全局命名空间来管理数据。
- GlusterFS支持运行在任何标准IP网络上标准应用程序的标准客户端,用户可以在全局统一的命令空间中使用NFS/CIFS等标准协议来访问应用程序。GlusterFS使得用户可摆脱原有的独立,高成本的封闭存储系统,能够利用普通廉价的存储设备来部署可集中管理,横向扩展,虚拟化的存储池,存储容量可扩展至TB/PB级。
2.1 GlusterFS 安装前的准备
- 电脑一台,内存>=4G,可用磁盘空间大于50G
- 安装VMWARE Workstation虚拟机软件
- 安装好四台CentOS-6-x86_64(6.2-6.8都可以)的虚拟机
- 基本系统:1核CPU+1024M内存+10G硬盘
- 网络选择:网络地址转换(NAT)
- 关闭iptables和SELinux
- 预装glusterfs软件包

#为了实验的准确性,请尽量和我用一个版本的Linux操作系统
#并用实验给的rpm包作为yum源
[root@localhost rpm]# cat /etc/redhat-release
CentOS release 6.5 (Final)
[root@localhost rpm]# uname -r
2.6.32-431.el6.x86_64
[root@localhost rpm]# pwd
/root/rpm
[root@localhost rpm]# ls
dbench-4.0-12.el6.x86_64.rpm libaio-0.3.107-10.el6.x86_64.rpm
glusterfs-3.7.20-1.el6.x86_64.rpm libevent-1.4.13-4.el6.x86_64.rpm
glusterfs-api-3.7.20-1.el6.x86_64.rpm libgssglue-0.1-11.el6.x86_64.rpm
glusterfs-api-devel-3.7.20-1.el6.x86_64.rpm libntirpc-1.3.1-1.el6.x86_64.rpm
glusterfs-cli-3.7.20-1.el6.x86_64.rpm libntirpc-devel-1.3.1-1.el6.x86_64.rpm
glusterfs-client-xlators-3.7.20-1.el6.x86_64.rpm libtirpc-0.2.1-13.el6_9.x86_64.rpm
glusterfs-coreutils-0.0.1-0.1.git0c86f7f.el6.x86_64.rpm nfs-utils-1.2.3-75.el6_9.x86_64.rpm
glusterfs-coreutils-0.2.0-1.el6_37.x86_64.rpm nfs-utils-lib-1.1.5-13.el6.x86_64.rpm
glusterfs-devel-3.7.20-1.el6.x86_64.rpm python-argparse-1.2.1-2.1.el6.noarch.rpm
glusterfs-extra-xlators-3.7.20-1.el6.x86_64.rpm python-gluster-3.7.20-1.el6.noarch.rpm
glusterfs-fuse-3.7.20-1.el6.x86_64.rpm pyxattr-0.5.0-1.el6.x86_64.rpm
glusterfs-ganesha-3.7.20-1.el6.x86_64.rpm repodata
glusterfs-geo-replication-3.7.20-1.el6.x86_64.rpm rpcbind-0.2.0-13.el6_9.1.x86_64.rpm
glusterfs-libs-3.7.20-1.el6.x86_64.rpm rsync-3.0.6-12.el6.x86_64.rpm
glusterfs-rdma-3.7.20-1.el6.x86_64.rpm userspace-rcu-0.7.16-2.el6.x86_64.rpm
glusterfs-resource-agents-3.7.20-1.el6.noarch.rpm userspace-rcu-0.7.7-1.el6.x86_64.rpm
glusterfs-server-3.7.20-1.el6.x86_64.rpm userspace-rcu-devel-0.7.16-2.el6.x86_64.rpm
keyutils-1.4-5.el6.x86_64.rpm userspace-rcu-devel-0.7.7-1.el6.x86_64.rpm
keyutils-libs-1.4-5.el6.x86_64.rpmcd /rpm
createrepo -v . #命令用于在当前目录中创建一个新的yum仓库。该命令将遍历当前目录中的RPM包,并生成repodata元数据,以供yum进行索引和使用。
2.2 GlusterFS 安装
2.2.1 修改主机名
略
2.2.2 添加hosts文件实现集群主机之间相互能够解析
[root@glusterfs01 ~]# cat /etc/hosts
127.0.0.1 localhost localhost.localdomain localhost4 localhost4.localdomain4
::1 localhost localhost.localdomain localhost6 localhost6.localdomain6
192.168.200.150 glusterfs01
192.168.200.151 glusterfs02
192.168.200.152 glusterfs03
192.168.200.153 glusterfs04
2.2.3 关闭selinux和防火墙
#关闭selinux
sed -i 's#SELINUX=enforcing#SELINUX=disabled#' /etc/sysconfig/selinux
#关闭iptables
service iptables stop
chkconfig iptables off
利用教程附带的rpm软件包组,充当本地定制化yum源
cd /etc/yum.repos.d
vim CentOS-M[c6-media]
name=CentOS-$releasever - Media
baseurl=file:///media/CentOS/file:///media/cdrom/file:///media/cdrecorder/
gpgcheck=1
enabled=0 #需要改成0否则会还是用默认光盘源
gpgkey=file:///etc/pki/rpm-gpg/RPM-GPG-KEY-CentOS-6[rpm]
name=rpm
baseurl=file:///root/rpm/
gpgcheck=0
enabled=1
[c6-media]
name=CentOS-$releasever - Media
baseurl=file:///media/CentOS/file:///media/cdrom/file:///media/cdrecorder/
gpgcheck=1
enabled=0
gpgkey=file:///etc/pki/rpm-gpg/RPM-GPG-KEY-CentOS-6[rpm]
name=rpm
baseurl=file:///root/rpm/
gpgcheck=0
enabled=1
[root@localhost yum.repos.d]# yum -y clean all
[root@localhost yum.repos.d]# yum -y install createrepo
[root@localhost ~]# yum -y install glusterfs-server glusterfs-cli glusterfs-geo-replication
2.3 配置glusterfs
2.3.1 查看glusterfs版本信息
[root@localhost ~]# which glusterfs
/usr/sbin/glusterfs
[root@localhost ~]# glusterfs -V
glusterfs 3.7.20 built on Jan 30 2017 15:39:27
Repository revision: git://git.gluster.com/glusterfs.git
Copyright (c) 2006-2013 Red Hat, Inc. <http://www.redhat.com/>
GlusterFS comes with ABSOLUTELY NO WARRANTY.
It is licensed to you under your choice of the GNU Lesser
General Public License, version 3 or any later version (LGPLv3
or later), or the GNU General Public License, version 2 (GPLv2),
in all cases as published by the Free Software Foundation.
2.3.2 启动停止服务
[root@glusterfs01 ~]# /etc/init.d/glusterd start #启动
Starting glusterd: [ OK ]
[root@glusterfs01 ~]# /etc/init.d/glusterd status
glusterd (pid 1356) is running...
[root@glusterfs01 ~]# chkconfig glusrerd on #添加开机启动
2.3.3 存储主机加入信任存储池
虚拟机添加信任存储池
**特别提示:**只需要让一个虚拟机进行添加操作即可。但自己并不需要添加信任自己
#确保所有的虚拟机的glusterd服务都处于开启状态,然后执行如下操作
[root@glusterfs01 ~]# gluster peer probe glusterfs02
peer probe: success.
[root@glusterfs01 ~]# gluster peer probe glusterfs03
peer probe: success.
[root@glusterfs01 ~]# gluster peer probe glusterfs04
peer probe: success.
2.3.4 查看虚拟机信任状态添加结果
[root@glusterfs01 ~]# gluster peer status
Number of Peers: 3
Hostname: glusterfs02
Uuid: 0b52290d-96b0-4b9c-988d-44062735a8a8
State: Peer in Cluster (Connected)
Hostname: glusterfs03
Uuid: c5dd23d5-c93c-427c-811b-3255da3c9691
State: Peer in Cluster (Connected)
Hostname: glusterfs04
Uuid: a43ac51b-641c-4fc4-be56-f6873423b462
State: Peer in Cluster (Connected)
可以查看每台虚拟机的信任状态,他们此时彼此都应该已经互有信任记录了
2.3.5 配置前的准备工作
#链接光盘源,安装xfs支持包(Centos7已经不再需要安装)
#所有都要装
yum -y install xfsprogs
在企业里我们还需要分区然后才能进行格式化。但是我们这里就省略了,我们直接格式化每台虚拟机的那块10G硬盘
[root@glusterfs01 ~]# mkfs.ext4 /dev/sdb
mke2fs 1.41.12 (17-May-2010)
/dev/sdb is entire device, not just one partition!
Proceed anyway? (y,n) y
Filesystem label=
OS type: Linux
Block size=4096 (log=2)
Fragment size=4096 (log=2)
Stride=0 blocks, Stripe width=0 blocks
655360 inodes, 2621440 blocks
131072 blocks (5.00%) reserved for the super user
First data block=0
Maximum filesystem blocks=2684354560
80 block groups
32768 blocks per group, 32768 fragments per group
8192 inodes per group
Superblock backups stored on blocks:
32768, 98304, 163840, 229376, 294912, 819200, 884736, 1605632
Writing inode tables: done
Creating journal (32768 blocks): done
Writing superblocks and filesystem accounting information: done
This filesystem will be automatically checked every 28 mounts or
180 days, whichever comes first. Use tune2fs -c or -i to override.
在四台机器上执行mkdir -p /gluster/brick1 建立挂在块设备的目录挂载磁盘到文件系统(4台都做,步骤相同)**
[root@glusterfs01 ~]# mkdir -p /gluster/brick1
[root@glusterfs01 ~]# mount /dev/sdb /gluster/brick1
[root@glusterfs01 ~]# df -h
Filesystem Size Used Avail Use% Mounted on
/dev/mapper/VolGroup-lv_root 18G 1.1G 16G 7% /
tmpfs 491M 0 491M 0% /dev/shm
/dev/sda1 485M 33M 427M 8% /boot
/dev/sr0 4.2G 4.2G 0 100% /media/cdrom
/dev/sdb 9.9G 151M 9.2G 2% /gluster/brick1
继续重复以上步骤,将第二块磁盘sdc格式化,并挂载到每台虚拟机的/gluster/brick2上
4台虚拟机加入开机自动挂载
[root@glusterfs01 ~]# echo "mount /dev/sdb /gluster/brick1" >> /etc/rc.local
[root@glusterfs01 ~]# echo "mount /dev/sdc /gluster/brick2" >> /etc/rc.local
[root@glusterfs01 ~]# tail -2 /etc/rc.local
mount /dev/sdb /gluster/brick1
mount /dev/sdc /gluster/brick2
2.3.6 创建volume分布式卷
-
基本卷:
- 分布式卷(Distributed):
- 复制卷(Replicated):
- 条带式卷(Striped):
-
复合卷:
- 分布式复制卷(Distributed Replicated):
- 分布式条带卷(Distributed Striped):
- 复制条带卷(Replicated Striped):
- 分布式复制条带卷(Distributed Replicated Striped):
#创建分布式卷(在glusterfs01上操作)
[root@glusterfs01 ~]# gluster volume create gs1 glusterfs01:/gluster/brick1 glusterfs02:/gluster/brick1 force
volume create: gs1: success: please start the volume to access data
#启动创建的卷(在glusterfs01上操作)
[root@glusterfs01 ~]# gluster volume start gs1
volume start: gs1: success
#然后我们发现4台虚拟机都能看到如下信息(在任意虚拟机上操作)
[root@glusterfs04 ~]# gluster volume info
Volume Name: gs1 #卷名
Type: Distribute #分布式
Volume ID: 0f0adf7a-3b8f-4016-ac72-83f633e90fac #ID号
Status: Started #启动状态
Number of Bricks: 2 #一共两个块设备
Transport-type: tcp #tcp的连接方式
Bricks: #块信息
Brick1: glusterfs01:/gluster/brick1
Brick2: glusterfs02:/gluster/brick1
Options Reconfigured:
performance.readdir-ahead: on
2.3.7 volume的两种挂载方式
(1)以glusterfs方式挂载
#挂载卷到目录(在glusterfs01上操作)
[root@glusterfs01 ~]# mount -t glusterfs 127.0.0.1:/gs1 /mnt #将本地的分布式卷gs01挂载到/mnt目录下
[root@glusterfs01 ~]# df -h
Filesystem Size Used Avail Use% Mounted on
/dev/mapper/VolGroup-lv_root 18G 1.1G 16G 7% /
tmpfs 491M 0 491M 0% /dev/shm
/dev/sda1 485M 33M 427M 8% /boot
/dev/sr0 4.2G 4.2G 0 100% /media/cdrom
/dev/sdb 9.9G 151M 9.2G 2% /gluster/brick1
127.0.0.1:/gs1 20G 302M 19G 2% /mnt #挂载成功,我们看到磁盘空间已经整合
#在挂载好的/mnt目录里创建实验文件(在glusterfs01上操作)
[root@glusterfs01 ~]# touch /mnt/{1..5}
[root@glusterfs01 ~]# ls /mnt
1 2 3 4 5
#在其他虚拟机上挂载分布式卷gs1,查看同步挂载结果
[root@glusterfs02 rpm]# mount -t glusterfs 127.0.0.1:/gs1 /mnt
[root@glusterfs02 rpm]# ls /mnt
1 2 3 4 5
[root@glusterfs03 rpm]# mount -t glusterfs 127.0.0.1:/gs1 /mnt
[root@glusterfs03 rpm]# ls /mnt
1 2 3 4 5
[root@glusterfs04 ~]# mount -t glusterfs 127.0.0.1:/gs1 /mnt
[root@glusterfs04 ~]# ls /mnt
1 2 3 4 5
(2)以NFS方式进行挂载
在挂载之前我们先来看一下如何打开glusterfs的NFS挂载方式
#在glusterfs01上执行如下操作
[root@glusterfs01 ~]# gluster volume status #查看分布式卷的状态
Status of volume: gs1
Gluster process TCP Port RDMA Port Online Pid
------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Brick glusterfs01:/gluster/brick1 49152 0 Y 1911
Brick glusterfs02:/gluster/brick1 49152 0 Y 1695
NFS Server on localhost N/A N/A N N/A #本地分布式卷NFS挂载未开启
NFS Server on glusterfs04 2049 0 Y 2679
NFS Server on glusterfs02 2049 0 Y 2600 #出现具体的端口就表明开启了
NFS Server on glusterfs03 2049 0 Y 2608
Task Status of Volume gs1
------------------------------------------------------------------------------
There are no active volume tasks
以上结果是是什么原因呢?
如果NFS Server的挂载端口显示N/A表示未开启挂载功能,这是由于要先进行nfs挂载是需要装两个nfs的软件包的rpcbind和nfs-utils
当然就算系统装了这两个软件包,那么我们也需要开启rpcbind服务,然后在重启glusterfs服务才能够进行nfs挂载的操作。
现在我们就来开启glusterfs01的nfs挂载功能,如下:
#在glusterfs01上执行如下操作
[root@glusterfs01 ~]# rpm -qa nfs-utils #查看是否安装nfs-utils
nfs-utils-1.2.3-75.el6_9.x86_64
[root@glusterfs01 ~]# rpm -qa rpcbind #查看是否安装rpcbind
rpcbind-0.2.0-13.el6_9.1.x86_64
[root@glusterfs01 ~]# /etc/init.d/rpcbind status #查看rpcbind服务状态
rpcbind is stopped
[root@glusterfs01 ~]# /etc/init.d/rpcbind start #开启rpcbind服务
Starting rpcbind: [ OK ]
[root@glusterfs01 ~]# /etc/init.d/glusterd stop #停止glusterd服务
Stopping glusterd: [ OK ]
[root@glusterfs01 ~]# /etc/init.d/glusterd start #开启glusterd服务
Starting glusterd: [ OK ]
root@glusterfs01 ~]# gluster volume status #这里需要等几秒再查看,就会发现nfs挂载方式开启了
Status of volume: gs1
Gluster process TCP Port RDMA Port Online Pid
------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Brick glusterfs01:/gluster/brick1 49152 0 Y 1911
Brick glusterfs02:/gluster/brick1 49152 0 Y 1695
NFS Server on localhost 2049 0 Y 2984 #已经开启
NFS Server on glusterfs04 2049 0 Y 2679
NFS Server on glusterfs03 2049 0 Y 2608
NFS Server on glusterfs02 2049 0 Y 2600
Task Status of Volume gs1
------------------------------------------------------------------------------
There are no active volume tasks
接下来,我们尝试在准备好的第五台虚拟机WebServer上进行nfs方式的挂载
#在Webserver上进行如下操作
[root@WebServer ~]# rpm -qa nfs-utils #查看nfs-utils是否安装
nfs-utils-1.2.3-39.el6.x86_64
[root@WebServer ~]# mount -t nfs 192.168.200.150:/gs1 /mnt #以nfs方式远程挂载分布式卷
mount.nfs: rpc.statd is not running but is required for remote locking.
mount.nfs: Either use '-o nolock' to keep locks local, or start statd.
mount.nfs: an incorrect mount option was specified #根据提示我们加上-o nolock参数
[root@WebServer ~]# mount -o nolock -t nfs 192.168.200.150:/gs1 /mnt
[root@WebServer ~]# ls /mnt #挂载成功
1 2 3 4 5 6 666 sss yunjisuan
[root@WebServer ~]# touch /mnt/benet #创建文件测试
[root@WebServer ~]# ls /mnt
1 2 3 4 5 6 666 benet sss yunjisuan
#在glusterfs任意虚拟机上进行如下操作
[root@glusterfs04 ~]# mount -t glusterfs 127.0.0.1:/gs1 /mnt
[root@glusterfs04 ~]# ls /mnt
1 2 3 4 5 6 666 benet sss yunjisuan #数据已经同步
2.3.8 创建分布式复制卷
#在任意一台gluster虚拟机上进行如下操作
[root@glusterfs01 ~]# gluster volume create gs2 replica 2 glusterfs03:/gluster/brick1 glusterfs04:/gluster/brick1 force
volume create: gs2: success: please start the volume to access data
[root@glusterfs01 ~]# gluster volume info gs2
Volume Name: gs2
Type: Replicate #复制卷
Volume ID: c76fe8fd-71a7-4395-9dd2-ef1dc85163b8
Status: Created
Number of Bricks: 1 x 2 = 2
Transport-type: tcp
Bricks:
Brick1: glusterfs03:/gluster/brick1
Brick2: glusterfs04:/gluster/brick1
Options Reconfigured:
performance.readdir-ahead: on
[root@glusterfs01 ~]# gluster volume start gs2 #启动卷
volume start: gs2: success
2.3.9 创建分布式条带卷
[root@glusterfs01 ~]# gluster volume create gs3 stripe 2 glusterfs01:/gluster/brick2 glusterfs02:/gluster/brick2 force
volume create: gs3: success: please start the volume to access data
[root@glusterfs01 ~]# gluster volume info gs3
Volume Name: gs3
Type: Stripe #条带卷
Volume ID: 6d2e27c7-f5a1-4473-9df8-a7261851a2ed
Status: Created
Number of Bricks: 1 x 2 = 2
Transport-type: tcp
Bricks:
Brick1: glusterfs01:/gluster/brick2
Brick2: glusterfs02:/gluster/brick2
Options Reconfigured:
performance.readdir-ahead: on
[root@glusterfs01 ~]# gluster volume start gs3 #启动卷
volume start: gs3: success
三,进行卷的数据写入测试
在WebServer服务器挂载创建的三种类型卷gs1,gs2,gs3,进行数据写入测试
3.1 分布式卷gs1的数据写入测试
#在WebServer上进行数据写入操作
[root@WebServer ~]# mount -o nolock -t nfs 192.168.200.150:/gs1 /mnt
[root@WebServer ~]# df -h
Filesystem Size Used Avail Use% Mounted on
/dev/mapper/VolGroup-lv_root 18G 1014M 16G 7% /
tmpfs 491M 0 491M 0% /dev/shm
/dev/sda1 485M 33M 427M 8% /boot
/dev/sr0 4.2G 4.2G 0 100% /media/cdrom
192.168.200.150:/gs1 20G 301M 19G 2% /mnt
[root@WebServer ~]# touch /mnt/{1..10}
[root@WebServer ~]# ls /mnt/
1 10 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9
#在glusterfs01和glusterfs02上进行查看(看看数据到底写入了哪个盘)
[root@glusterfs01 ~]# ls /gluster/brick1
1 5 7 8 9
[root@glusterfs02 ~]# ls /gluster/brick1
10 2 3 4 6
结论:分布式卷的数据存储方式是将数据平均写入到每个整合的磁盘中,类似于raid0,写入速度快,但这样磁盘一旦损坏没有纠错能力。
3.2 分布式复制卷gs2的数据写入测试
#在WebServer上进行数据写入操作
[root@WebServer ~]# mount -o nolock -t nfs 192.168.200.150:/gs2 /mnt
[root@WebServer ~]# df -h
Filesystem Size Used Avail Use% Mounted on
/dev/mapper/VolGroup-lv_root 18G 1014M 16G 7% /
tmpfs 491M 0 491M 0% /dev/shm
/dev/sda1 485M 33M 427M 8% /boot
/dev/sr0 4.2G 4.2G 0 100% /media/cdrom
192.168.200.150:/gs2 9.9G 151M 9.2G 2% /mnt #可用容量减半
[root@WebServer ~]# ls /mnt
lost+found
[root@WebServer ~]# touch /mnt/{1..10}
[root@WebServer ~]# ls /mnt
1 10 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 lost+found
#在glusterfs03和glusterfs04上进行查看(看看数据到底写入了哪个盘)
[root@glusterfs03 ~]# ls /gluster/brick1
1 10 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 lost+found
[root@glusterfs04 ~]# ls /gluster/brick1
1 10 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 lost+found
结论:分布式复制卷的数据存储方式为,每个整合的磁盘中都写入同样的数据内容,类似于raid1,数据非常安全,读取性能高,占磁盘容量。
3.3 分布式条带卷gs3的数据写入测试
#在WebServer上进行数据写入操作
[root@WebServer ~]# umount /mnt
[root@WebServer ~]# mount -o nolock -t nfs 192.168.200.150:/gs3 /mnt
[root@WebServer ~]# df -h
Filesystem Size Used Avail Use% Mounted on
/dev/mapper/VolGroup-lv_root 18G 1014M 16G 7% /
tmpfs 491M 0 491M 0% /dev/shm
/dev/sda1 485M 33M 427M 8% /boot
/dev/sr0 4.2G 4.2G 0 100% /media/cdrom
192.168.200.150:/gs3 20G 301M 19G 2% /mnt
[root@WebServer ~]# dd if=/dev/zero of=/root/test bs=1024 count=262144 #创建大小为256M的文件
262144+0 records in
262144+0 records out
268435456 bytes (268 MB) copied, 1.81006 s, 148 MB/s
[root@WebServer ~]# du -sh test
256M test
[root@WebServer ~]# cp test /mnt/ #复制到/mnt目录下
[root@WebServer ~]# ls /mnt
test
[root@WebServer ~]# du -sh /mnt/test #查看大小为256M
256M /mnt/test
#在glusterfs01和glusterfs02上进行查看(看看数据到底是怎么存的)
[root@glusterfs01 ~]# du -sh /gluster/brick2/test
129M /gluster/brick2/test
[root@glusterfs02 ~]# du -sh /gluster/brick2/test
129M /gluster/brick2/test
结论:我们发现分布式条带卷,是将数据的容量平均分配到了每个整合的磁盘节点上。大幅提高大文件的并发读访问。
四,存储卷中brick块设备的扩容
4.1 分布式复制卷的扩容
[root@glusterfs01 ~]# gluster volume add-brick gs2 replica 2 glusterfs03:/gluster/brick2 glusterfs04:/gluster/brick2 force #添加两个块设备
volume add-brick: success
[root@glusterfs01 ~]# gluster volume info gs2
Volume Name: gs2
Type: Distributed-Replicate
Volume ID: c76fe8fd-71a7-4395-9dd2-ef1dc85163b8
Status: Started
Number of Bricks: 2 x 2 = 4 #已经扩容
Transport-type: tcp
Bricks:
Brick1: glusterfs03:/gluster/brick1
Brick2: glusterfs04:/gluster/brick1
Brick3: glusterfs03:/gluster/brick2
Brick4: glusterfs04:/gluster/brick2
Options Reconfigured:
performance.readdir-ahead: on
特别提示:
对分布式复制卷和分布式条带卷进行扩容时,要特别注意,如果创建卷之初的时候选择的是replica 2 或者stripe 2。那么扩容时,就必须一次性扩容两个或两个的倍数的块设备。
例如你给一个分布式复制卷的replica为2,你在增加bricks的时候数量必须为2,4,6,8等。
4.2 查看扩容后的容量并进行写入测试
#在WebServer上挂载gs2并查看挂载目录的容量
[root@WebServer ~]# umount /mnt
[root@WebServer ~]# mount -o nolock -t nfs 192.168.200.150:/gs2 /mnt
[root@WebServer ~]# df -h
Filesystem Size Used Avail Use% Mounted on
/dev/mapper/VolGroup-lv_root 18G 1.3G 16G 8% /
tmpfs 491M 0 491M 0% /dev/shm
/dev/sda1 485M 33M 427M 8% /boot
/dev/sr0 4.2G 4.2G 0 100% /media/cdrom
192.168.200.150:/gs2 20G 301M 19G 2% /mnt #已经扩容
我们再次写入数据
#在WebServer上进行数据写入操作
[root@WebServer ~]# touch /mnt/{11..20}
[root@WebServer ~]# ls /mnt
1 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 2 20 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 lost+found
#在glusterfs03和glusterfs04上查看数据存到哪里去了
[root@glusterfs03 ~]# gluster volume info gs2
Volume Name: gs2
Type: Distributed-Replicate
Volume ID: c76fe8fd-71a7-4395-9dd2-ef1dc85163b8
Status: Started
Number of Bricks: 2 x 2 = 4
Transport-type: tcp
Bricks:
Brick1: glusterfs03:/gluster/brick1 #组成gs2的块设备就在03和04上
Brick2: glusterfs04:/gluster/brick1
Brick3: glusterfs03:/gluster/brick2
Brick4: glusterfs04:/gluster/brick2
Options Reconfigured:
performance.readdir-ahead: on
[root@glusterfs03 ~]# ls /gluster/brick1
1 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 2 20 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 lost+found
[root@glusterfs03 ~]# ls /gluster/brick2
lost+found #什么都没有
[root@glusterfs04 ~]# ls /gluster/brick1
1 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 2 20 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 lost+found
[root@glusterfs04 ~]# ls /gluster/brick2
lost+found #还是什么都没有
通过对扩容的gs2进行写入测试,我们发现数据并没有被写入到新加入的块设备中,这是为甚什么?
这是因为,为了数据的安全,新扩容块设备的卷,默认必须先做一次磁盘平衡(块设备同步),如此才能正常开始使用。
4.3 进行磁盘存储的平衡
注意:平衡布局是很有必要的,因为布局结构是静态的,当新的bricks加入现有卷,新创建的文件会分布到旧的bricks中,所以需要平衡布局结构,使新加入的bricks生效。布局平衡只是使新布局生效,并不会在新的布局移动老的数据,如果你想在新布局生效后,重新平衡卷中的数据,还需要对卷中的数据进行平衡。
#对gs2进行磁盘存储平衡
[root@glusterfs01 ~]# gluster volume rebalance gs2 start
volume rebalance: gs2: success: Rebalance on gs2 has been started successfully. Use rebalance status command to check status of the rebalance process.
ID: 0024338c-84df-4edb-b68c-107415a27506
#检查gs2块设备磁盘平衡结果
[root@glusterfs03 ~]# ls /gluster/brick1
10 12 14 15 16 17 2 3 4 6 lost+found
[root@glusterfs03 ~]# ls /gluster/brick2
1 11 13 18 19 20 5 7 8 9 lost+found
[root@glusterfs04 ~]# ls /gluster/brick1
10 12 14 15 16 17 2 3 4 6 lost+found
[root@glusterfs04 ~]# ls /gluster/brick2
1 11 13 18 19 20 5 7 8 9 lost+found
执行磁盘存储平衡以后,我们发现数据被复制成了4份在4个块设备中。
五,存储卷的缩减与删除
(1)对存储卷中的brick进行缩减
注意:你可能想在线缩小卷的大小,例如:当硬件损坏或者网络故障的时候,你可能想在卷中移除相关的bricks。注意,当你移除bricks的时候,你在gluster的挂载点将不能继续访问是数据,只有配置文件中的信息移除后你才能继续访问bricks的数据。当移除分布式复制卷或者分布式条带卷的时候,移除的bricks数目必须是replica或者stripe的倍数。例如:一个分布式条带卷的stripe是2,当你移除bricks的时候必须是2,4,6,8等。
#先停止卷gs2
[root@glusterfs01 ~]# gluster volume stop gs2
Stopping volume will make its data inaccessible. Do you want to continue? (y/n) y
volume stop: gs2: success
#然后移除卷,因为是复制卷且replica为2,因此每次移除必须是2的倍数
[root@glusterfs01 ~]# gluster volume remove-brick gs2 replica 2 glusterfs03:/gluster/brick2 glusterfs04:/gluster/brick2 force
Removing brick(s) can result in data loss. Do you want to Continue? (y/n) y
volume remove-brick commit force: success
#我们发现gs2的卷已经被移除
[root@glusterfs01 ~]# gluster volume info gs2
Volume Name: gs2
Type: Replicate
Volume ID: c76fe8fd-71a7-4395-9dd2-ef1dc85163b8
Status: Stopped
Number of Bricks: 1 x 2 = 2
Transport-type: tcp
Bricks:
Brick1: glusterfs03:/gluster/brick1
Brick2: glusterfs04:/gluster/brick1
Options Reconfigured:
performance.readdir-ahead: on
#重新启动卷gs2
[root@glusterfs01 ~]# gluster volume start gs2
volume start: gs2: success
(2)对存储卷进行删除
#停止卷gs1
[root@glusterfs01 ~]# gluster volume stop gs1
Stopping volume will make its data inaccessible. Do you want to continue? (y/n) y
volume stop: gs1: success
#删除卷gs1
[root@glusterfs01 ~]# gluster volume delete gs1
Deleting volume will erase all information about the volume. Do you want to continue? (y/n) y
volume delete: gs1: success
#查看卷信息,发现gs1已经没了
[root@glusterfs01 ~]# gluster volume info
Volume Name: gs2
Type: Replicate
Volume ID: c76fe8fd-71a7-4395-9dd2-ef1dc85163b8
Status: Started
Number of Bricks: 1 x 2 = 2
Transport-type: tcp
Bricks:
Brick1: glusterfs03:/gluster/brick1
Brick2: glusterfs04:/gluster/brick1
Options Reconfigured:
performance.readdir-ahead: on
Volume Name: gs3
Type: Stripe
Volume ID: 6d2e27c7-f5a1-4473-9df8-a7261851a2ed
Status: Started
Number of Bricks: 1 x 2 = 2
Transport-type: tcp
Bricks:
Brick1: glusterfs01:/gluster/brick2
Brick2: glusterfs02:/gluster/brick2
Options Reconfigured:
performance.readdir-ahead: on
特别提示:
无论是缩减卷还是删除卷,并不会是清除卷中的数据。数据仍旧会保存在对应磁盘上。
六,构建企业级分布式存储
6.1 硬件要求
一般选择2U的机型,磁盘STAT盘4T,如果I/O要求比较高,可以采购SSD固态硬盘。为了充分保证系统的稳定性和性能,要求所有glusterfs服务器硬件配置尽量一致,尤其是硬盘数量和大小。机器的RAID卡需要带电池,缓存越大,性能越好。一般情况下,建议做RAID10,如果出于空间要求考虑,需要做RAID5,建议最好能有1-2块硬盘的热备盘。
6.2 系统要求和分区划分
系统要求使用CentOS6.x,安装完成后升级到最新版本,安装的时候,不要使用LVM,建议/boot分区200M,根分区100G,swap分区和内存一样大小,剩余空间给gluster使用,划分单独的硬盘空间。系统安装软件没有特殊要求,建议除了开发工具和基本的管理软件,其他软件一律不装。
6.3 网络环境
网络要求全部千兆环境,gluster服务器至少有2块网卡,1块网卡绑定供gluster使用,剩余一块分配管理网络ip,用于系统管理。如果有条件购买万兆交换机,服务器配置万兆网卡,存储性能会更好。网络方面如果安全性要求高,可以多网卡绑定。
6.4 服务器摆放分布
服务器主备机器要放在不同的机柜,连接不同的交换机,即使一个机柜出现问题,还有一份数据正常访问。

6.5 构建高性能,高可用存储
一般在企业中,采用的是分布式复制卷,因为有数据备份,数据相对安全,分布式条带卷目前对glusterfs来说没有完全成熟,存在一定的是数据安全风险。
6.5.1 开启防火墙端口
一般在企业应用中Linux防火墙是打开的,开通服务器之间访问的端口
iptables -I INPUT -p tcp --dport 24007:24011 -j ACCEPT
iptables -I INPUT -p tcp --dport 49152:49162 -j ACCEPT
[root@glusterfs01 ~]# cat /etc/glusterfs/glusterd.vol
volume management
type mgmt/glusterd
option working-directory /var/lib/glusterd
option transport-type socket,rdma
option transport.socket.keepalive-time 10
option transport.socket.keepalive-interval 2
option transport.socket.read-fail-log off
option ping-timeout 0
option event-threads 1
# option base-port 49152 #默认端口可以在这里改,因为这个端口可能会和企业里的kvm端口冲突
6.5.2 Glusterfs文件系统优化
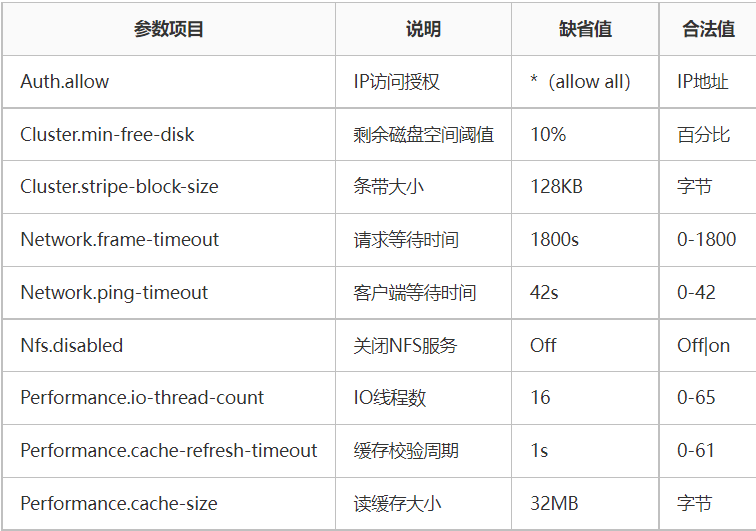
Performance.quick-read:优化读取小文件的性能Performance.read-ahead:用预读的方式提高读取的性能,有利于应用频繁持续性的访问文件,当应用完成当前数据块读取的时候,下一个数据块就已经准备好了。**Performance.write-behind:写入数据时,先写入缓存内,再写入硬盘内,以提高写入的性能。Performance.io-cache:缓存已经被读过的。
调整方法:
Glusster volume set <卷> <参数>
[root@glusterfs01 ~]# gluster volume info gs2
Volume Name: gs2
Type: Replicate
Volume ID: c76fe8fd-71a7-4395-9dd2-ef1dc85163b8
Status: Started
Number of Bricks: 1 x 2 = 2
Transport-type: tcp
Bricks:
Brick1: glusterfs03:/gluster/brick1
Brick2: glusterfs04:/gluster/brick1
Options Reconfigured:
performance.readdir-ahead: on
[root@glusterfs01 ~]# gluster volume set gs2 performance.read-ahead on #设置预缓存优化
volume set: success
[root@glusterfs01 ~]# gluster volume info gs2
Volume Name: gs2
Type: Replicate
Volume ID: c76fe8fd-71a7-4395-9dd2-ef1dc85163b8
Status: Started
Number of Bricks: 1 x 2 = 2
Transport-type: tcp
Bricks:
Brick1: glusterfs03:/gluster/brick1
Brick2: glusterfs04:/gluster/brick1
Options Reconfigured:
performance.read-ahead: on #已经添加上了
performance.readdir-ahead: on
[root@glusterfs01 ~]# gluster volume set gs2 performance.cache-size 256MB #设置读缓存大小
volume set: success
[root@glusterfs01 ~]# gluster volume info gs2
Volume Name: gs2
Type: Replicate
Volume ID: c76fe8fd-71a7-4395-9dd2-ef1dc85163b8
Status: Started
Number of Bricks: 1 x 2 = 2
Transport-type: tcp
Bricks:
Brick1: glusterfs03:/gluster/brick1
Brick2: glusterfs04:/gluster/brick1
Options Reconfigured:
performance.cache-size: 256MB #已经添加上了
performance.read-ahead: on
performance.readdir-ahead: on
6.5.3 监控及日常维护
使用Zabbix自带模板即可。Cpu,内存,主机存活,磁盘空间,主机运行时间,系统load。日常情况要查看服务器的监控值,遇到报警要及时处理。
#以下命令在复制卷的场景下才会有
#gluster volume status gs2 查看节点NFS是否在线
(开没开端口)
#gluster volume heal gs2 full 启动完全修复
#gluster volume heal gs2 info 查看需要修复的文件
#gluster volume heal gs2 info healed 查看修复成功的文件
#gluster volume heal gs2 info heal-failed 查看修复失败文件
#gluster volume heal gs2 info split-brain 查看脑裂的文件
#gluster volume quota gs2 enable --激活quota功能
#gluster volume quota gs2 disable --关闭quota功能
#gluster volume quota gs2 limit-usage /data 10GB --/gs2/data 目录限制
#gluster volume quota gs2 list --quota 信息列表
#gluster volume quota gs2 list /data --限制目录的quota信息
#gluster volume set gs2 features.quota-timeout 5 --设置信息的超时事实上时间
#gluster volume quota gs2 remove /data -删除某个目录的quota设置
备注:
1)quota 功能,主要是对挂载点下的某个目录进行空间限额。如:/mnt/glusterfs/data目录,而不是对组成卷组的空间进行限制
七 生产环境遇到常见故障处理
7.1 硬盘故障
因为底层做了raid配置,有硬件故障,直接更换硬盘,会自动同步数据。(raid5)
7.2 一台主机故障
一台节点故障的情况包括以下类型:
1,物理故障
2,同时有多块硬盘故障,造成是数据丢失
3,系统损坏不可修复
解决方法:
找一台完全一样的机器,至少要保证硬盘数量和大小一致,安装系统,配置和故障机同样的ip,安装gluster软件,保证配置一样,在其他健康的节点上执行命令gluster peer status,查看故障服务器的uuid
#例如:
[root@glusterfs03 ~]# gluster peer status
Number of Peers: 3
Hostname: glusterfs02
Uuid: 0b52290d-96b0-4b9c-988d-44062735a8a8
State: Peer in Cluster (Connected)
Hostname: glusterfs04
Uuid: a43ac51b-641c-4fc4-be56-f6873423b462
State: Peer in Cluster (Connected)
Hostname: glusterfs01
Uuid: 198f2c7c-1104-4671-8989-b430b77540e9
State: Peer in Cluster (Connected)
[root@glusterfs03 ~]#
修改新加机器的/var/lib/glusterd/glusterd.info和故障机器的一样
[root@glusterfs04 ~]# cat /var/lib/glusterd/glusterd.info
UUID=a43ac51b-641c-4fc4-be56-f6873423b462
operating-version=30712
在新机器挂载目录上执行磁盘故障的操作(任意节点)
[root@glusterfs04 ~]# gluster volume heal gs2 full
Launching heal operation to perform full self heal on volume gs2 has been successful
Use heal info commands to check status
就会自动开始同步,但是同步的时候会影响整个系统的性能
可以查看状态
[root@glusterfs04 ~]# gluster volume heal gs2 info
Brick glusterfs03:/gluster/brick1
Status: Connected
Number of entries: 0
Brick glusterfs04:/gluster/brick1
Status: Connected
Number of entries: 0


)








)
)
)
如何配置)




