Reduction
Reduction算法从一组数值中产生单个数值。这个单个数值可以是所有元素中的总和、最大值、最小值等。
图1展示了一个求和Reduction的例子。
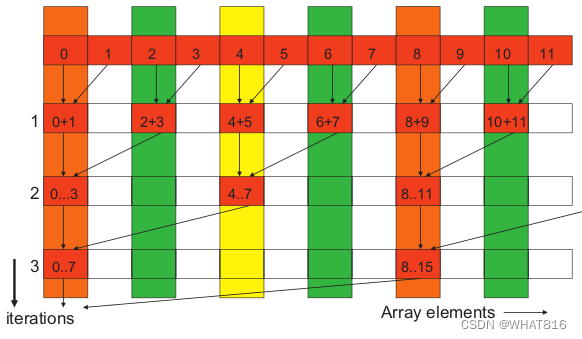
图1
线程层次结构
在Reduction算法中,线程的常见组织方式是为每个元素使用一个线程。下面将展示利用许多不同方式来组织线程。
Code
Host代码用随机值初始化输入向量,并调用kernel执行Reduction。
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
#include <ctime>
#include <cmath>
#include <cuda_runtime.h>
#include <thrust/host_vector.h>
#include <thrust/device_vector.h>//float array[6] = { 3, 1, 2, 3, 5, 4 };
//float* dev_array = 0;
//cudaMalloc(&dev_array, 4 * 6);
//cudaMemcpy(dev_array, array, 4 * 6, cudaMemcpyHostToDevice);
//thrust::device_ptr<float> dev_ptr(dev_array);
//thrust::reduce(dev_ptr, dev_ptr + 6);//由于dev_array指向device端,不能直接作为参数,需要对其封装
//
//thrust::host_vector<type> hvec;
//thrust::device_vector<type> dvec;
//dvec = hvec;
//thrust::reduce(dvec.begin(), dvec.end());//此时的参数是迭代器,不用也不能用device_ptr对其封装
//
上述的两种函数的调用方法也存在host端的版本,传入的指针或者迭代器都是host端数据
//thrust::reduce(array, array + 6);
//thrust::reduce(hvec.begin(), hvec.end());
//
从device_ptr中提取“原始”指针需要使用raw_pointer_cast函数
//float dev_array = thrust::raw_pointer_cast(dev_ptr);#include "helper_cuda.h"
#include "error.cuh"
#include "reductionKernels.cuh"const double EPSILON = 1.0;
const int TIMENUMS = 50;int main(void)
{int n, t_x;n = 4096;t_x = 1024;thrust::host_vector<double> h_A(n);for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {h_A[i] = rand() / (double)RAND_MAX;}double h_res = thrust::reduce(h_A.begin(), h_A.end(), 0.0f, thrust::plus<double>());int temp = n;thrust::device_vector<double> d_A;//device vector 和 host vector 可以直接用等号进行传递,对应于cudaMemcpy的功能thrust::device_vector<double> d_B = h_A;dim3 threads(t_x);dim3 gridDim;cudaEvent_t start, stop;float elapsed_time;float sumTime = 0;for (int i = 0; i < TIMENUMS; i++) {temp = n;d_B = h_A;do {gridDim = dim3((temp + threads.x - 1) / threads.x);d_A = d_B;d_B.resize(gridDim.x);checkCudaErrors(cudaEventCreate(&start));checkCudaErrors(cudaEventCreate(&stop));checkCudaErrors(cudaEventRecord(start));reduction1<double> << <gridDim, threads, threads.x * sizeof(double) >> > (thrust::raw_pointer_cast(d_A.data()),temp,thrust::raw_pointer_cast(d_B.data()));checkCudaErrors(cudaEventRecord(stop));checkCudaErrors(cudaEventSynchronize(stop));checkCudaErrors(cudaEventElapsedTime(&elapsed_time, start, stop));sumTime += elapsed_time;temp = gridDim.x;//std::cout << "\t" << h_res << " != " << d_B[0] << "\t" << d_B[1] << std::endl;} while (temp > 1);}printf("Time = %g ms.\n", sumTime / TIMENUMS);if (abs(h_res - d_B[0]) > 0.01)std::cout << "Error (Reduction 1):" << h_res << " != " << d_B[0] << std::endl;elsestd::cout << "Reduction 1: Success!" << std::endl;sumTime = 0;for (int i = 0; i < TIMENUMS; i++) {temp = n;d_B = h_A;do {gridDim = dim3((temp + threads.x - 1) / threads.x);d_A = d_B;d_B.resize(gridDim.x);checkCudaErrors(cudaEventRecord(start));reduction2<double> << <gridDim, threads, threads.x * sizeof(double) >> > (thrust::raw_pointer_cast(d_A.data()),temp,thrust::raw_pointer_cast(d_B.data()));checkCudaErrors(cudaEventRecord(stop));checkCudaErrors(cudaEventSynchronize(stop));checkCudaErrors(cudaEventElapsedTime(&elapsed_time, start, stop));sumTime += elapsed_time;temp = gridDim.x;} while (temp > 1);}printf("Time = %g ms.\n", sumTime / TIMENUMS);if (abs(h_res - d_B[0] > 0.01))std::cout << "Error (Reduction 2): " << h_res << " != " << d_B[0] << std::endl;elsestd::cout << "Reduction 2: Success!" << std::endl;sumTime = 0;for (int i = 0; i < TIMENUMS; i++) {temp = n;d_B = h_A;do {gridDim = dim3((temp + threads.x - 1) / threads.x);d_A = d_B;d_B.resize(gridDim.x);checkCudaErrors(cudaEventRecord(start));reduction3<double> << <gridDim, threads, threads.x * sizeof(double) >> > (thrust::raw_pointer_cast(d_A.data()),temp,thrust::raw_pointer_cast(d_B.data()));checkCudaErrors(cudaEventRecord(stop));checkCudaErrors(cudaEventSynchronize(stop));checkCudaErrors(cudaEventElapsedTime(&elapsed_time, start, stop));sumTime += elapsed_time;temp = gridDim.x;} while (temp > 1);}printf("Time = %g ms.\n", sumTime / TIMENUMS);if (abs(h_res - d_B[0] > 0.01))std::cout << "Error (Reduction 3): " << h_res << " != " << d_B[0] << std::endl;elsestd::cout << "Reduction 3: Success!" << std::endl;sumTime = 0;for (int i = 0; i < TIMENUMS; i++) {temp = n;d_B = h_A;//checkCudaErrors(cudaEventRecord(start));do {gridDim = dim3((temp + threads.x - 1) / threads.x);d_A = d_B;d_B.resize(gridDim.x);checkCudaErrors(cudaEventRecord(start));reduction4<double> << <gridDim, threads, threads.x * sizeof(double) >> > (thrust::raw_pointer_cast(d_A.data()),temp,thrust::raw_pointer_cast(d_B.data()));checkCudaErrors(cudaEventRecord(stop));checkCudaErrors(cudaEventSynchronize(stop));checkCudaErrors(cudaEventElapsedTime(&elapsed_time, start, stop));sumTime += elapsed_time;temp = gridDim.x;} while (temp > 1);}printf("Time = %g ms.\n", sumTime / TIMENUMS);if (abs(h_res - d_B[0] > 0.01))std::cout << "Error (Reduction 4): " << h_res << " != " << d_B[0] << std::endl;elsestd::cout << "Reduction 4: Success!" << std::endl;sumTime = 0;for (int i = 0; i < TIMENUMS; i++) {temp = n;d_B = h_A;do {gridDim = dim3((temp + threads.x - 1) / threads.x);d_A = d_B;d_B.resize(gridDim.x);checkCudaErrors(cudaEventRecord(start));reduction5<double> << <gridDim, threads, threads.x * sizeof(double) >> > (thrust::raw_pointer_cast(d_A.data()),temp,thrust::raw_pointer_cast(d_B.data()));checkCudaErrors(cudaEventRecord(stop));checkCudaErrors(cudaEventSynchronize(stop));checkCudaErrors(cudaEventElapsedTime(&elapsed_time, start, stop));sumTime += elapsed_time;temp = gridDim.x;} while (temp > 1);}printf("Time = %g ms.\n", sumTime / TIMENUMS);if (abs(h_res - d_B[0] > 0.01))std::cout << "Error (Reduction 5): " << h_res << " != " << d_B[0] << std::endl;elsestd::cout << "Reduction 5: Success!" << std::endl;return 0;
}Note:
helper_cuda.h 与error.cuh头文件为错误查验工具。后续会发布到Github。
去除checkCudaErrors等错误查验函数不影响程序运行。
Reduction 1: Interleaved Addressing - Diverge Warps
template<typename T> __global__
void reduction1(T* X, uint32_t n, T* Y){extern __shared__ uint8_t shared_mem[];T* partial_sum = reinterpret_cast<T*>(shared_mem);uint32_t tx = threadIdx.x;uint32_t i = blockIdx.x * blockDim.x + threadIdx.x;// Load the elements of the array into the shared memorypartial_sum[tx] = i < n ? X[i] : 0;__syncthreads();// Accumulate the elements using reductionfor(uint32_t stride = 1; stride < blockDim.x; stride <<= 1){if(tx % (2 * stride) == 0)partial_sum[tx] += tx + stride < n ? partial_sum[tx + stride] : 0;__syncthreads();}if(tx == 0) Y[blockIdx.x] = partial_sum[0];
}首先,kernel将数组的元素加载到共享内存中。然后,在每次迭代中,它将上次迭代的相邻元素相加。第一次迭代会添加相邻的元素。第二次迭代会添加相隔2个元素的元素,依此类推。当步幅大于块中线程数时,循环结束。
最后,kernel将结果写入输出数组。如图2所示:
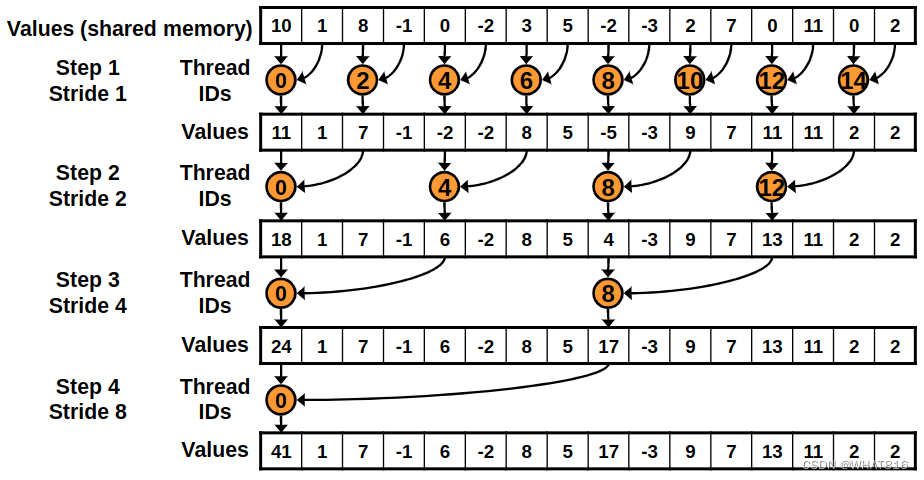
图2
使用这个kernel,添加元素的线程不是连续的,而且在每次迭代中,线程之间的差距会更大。这将导致warp需要重新运行大量的代码。
Reduction 2: Interleaved Addressing - Bank Conflicts
template<typename T> __global__
void reduction2(T* X, uint32_t n, T* Y){extern __shared__ uint8_t shared_mem[];T* partial_sum = reinterpret_cast<T*>(shared_mem);uint32_t tx = threadIdx.x;uint32_t i = blockIdx.x * blockDim.x + threadIdx.x;// Load the elements of the array into the shared memorypartial_sum[tx] = i < n ? X[i] : 0;__syncthreads();// Accumulate the elements using reductionfor(uint32_t stride = 1; stride < blockDim.x; stride <<= 1){int index = 2 * stride * tx;if (index < blockDim.x)partial_sum[index] += index + stride < n ? partial_sum[index + stride] : 0;__syncthreads();}if(tx == 0) Y[blockIdx.x] = partial_sum[0];
}这个kernel和以前那个很相似。唯一的区别是添加元素的线程是连续的。这样可以让线程更有效地运行代码。如图3
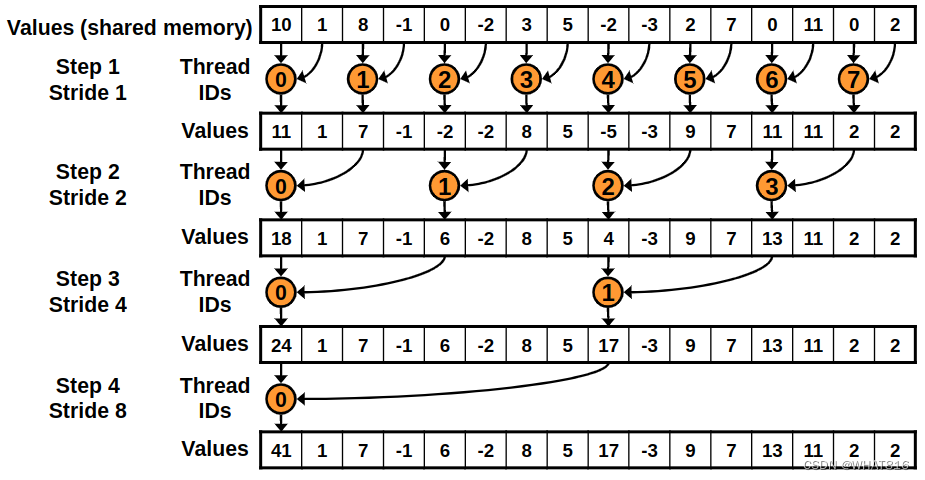
图3
这个kernel的问题在于它引发了Bank Conflicts(板块冲突)。当两个线程访问共享内存的同一个存储区时就会发生Bank Conflicts。计算能力在2.0及以上的设备有32个32位宽的存储区。如果两个线程访问相同的存储区,第二次访问将延迟直到第一次访问完成。
Reduction 3: Sequential Addressing
template<typename T> __global__
void reduction3(T* X, uint32_t n, T* Y){extern __shared__ uint8_t shared_mem[];T* partial_sum = reinterpret_cast<T*>(shared_mem);uint32_t tx = threadIdx.x;uint32_t i = blockIdx.x * blockDim.x + threadIdx.x;// Load the elements of the array into the shared memorypartial_sum[tx] = i < n ? X[i] : 0;__syncthreads();// Accumulate the elements using reductionfor(uint32_t stride = blockDim.x / 2; stride > 0; stride >>= 1){if(tx < stride)partial_sum[tx] += partial_sum[tx + stride];__syncthreads();}if(tx == 0) Y[blockIdx.x] = partial_sum[0];
}为了避免Bank Conflicts,这个kernel使用顺序寻址。在每次迭代中,线程和元素都是连续的。如图4所示:
这个kernel的问题是,一半的线程在第一次循环迭代中是空闲的。
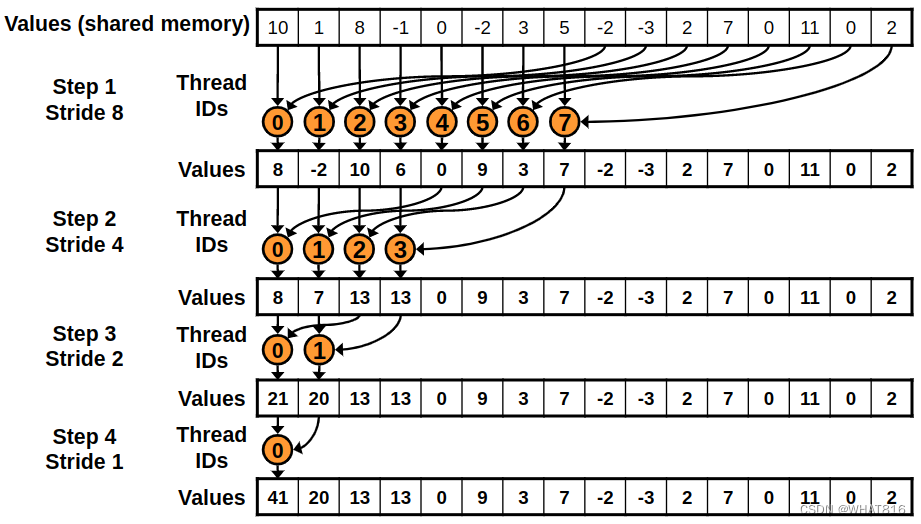
图4
Reduction 4: First Add During Load
template<typename T> __global__
void reduction4(T* X, uint32_t n, T* Y){extern __shared__ uint8_t shared_mem[];T* partial_sum = reinterpret_cast<T*>(shared_mem);uint32_t tx = threadIdx.x;uint32_t i = blockIdx.x * (blockDim.x * 2) + threadIdx.x;// Load the elements of the array into the shared memorypartial_sum[tx] = i < n ? X[i] : 0;partial_sum[tx] += i + blockDim.x < n ? X[i + blockDim.x] : 0;__syncthreads();// Accumulate the elements using reductionfor(uint32_t stride = blockDim.x / 2; stride > 0; stride >>= 1){if(tx < stride)partial_sum[tx] += partial_sum[tx + stride];__syncthreads();}if(tx == 0) Y[blockIdx.x] = partial_sum[0];
}这个kernel和Reduction 3的kernel类似。唯一的区别是在迭代开始之前,每个线程加载并添加数组的两个元素。
Reduction 5: Unroll Last Warp
template<typename T> __device__
void warpReduce(volatile T* partial_sum, uint32_t tx){partial_sum[tx] += partial_sum[tx + 32];partial_sum[tx] += partial_sum[tx + 16];partial_sum[tx] += partial_sum[tx + 8];partial_sum[tx] += partial_sum[tx + 4];partial_sum[tx] += partial_sum[tx + 2];partial_sum[tx] += partial_sum[tx + 1];
}template<typename T, int block_size> __global__
void reduction5(T* X, uint32_t n, T* Y){extern __shared__ uint8_t shared_mem[];T* partial_sum = reinterpret_cast<T*>(shared_mem);uint32_t tx = threadIdx.x;uint32_t i = blockIdx.x * (blockDim.x * 2) + threadIdx.x;// Load the elements of the array into the shared memorypartial_sum[tx] = i < n ? X[i] : 0;partial_sum[tx] += i + blockDim.x < n ? X[i + blockDim.x] : 0;__syncthreads(); // Accumulate the elements using reductionfor(uint32_t stride = blockDim.x / 2; stride > 32; stride >>= 1){if(tx < stride)partial_sum[tx] += partial_sum[tx + stride];__syncthreads();}if(tx < 32) warpReduce(partial_sum, tx);if(tx == 0) Y[blockIdx.x] = partial_sum[0];
}kernel再次与Reduction 4相似。唯一的区别是最后一个warp是展开的。这将使warp能够在无控制分歧的情况下运行代码。
性能分析
运行时间:
向量维度:4096
线程块维度:1024
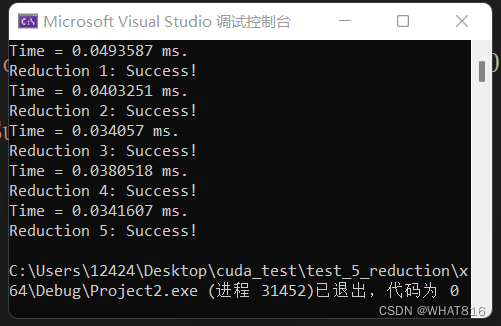
由运行时间分析,前三种算法耗时逐次递减。Reduction 4、5,较Reduction 3,虽然再加载共享内存时多计算了一次,但是引入了更多的全局内存访问,所以Reduction 4表现与Reduction 3相比略差,但是同时Reduction 4、5会减少设备与host的传输次数,当传输数据量大时Reduction 4、5整体上可能有更好的表现。Reduction 5相比Reduction 4,减少了线程束的重复执行,所以耗时略有减少。
Note:单次运行可能因为设备启动原因,各种算法运行时间差异较大,可采用循环20次以上取平均值。
笔者采用设备:RTX3060 6GB
PMPP项目提供的分析
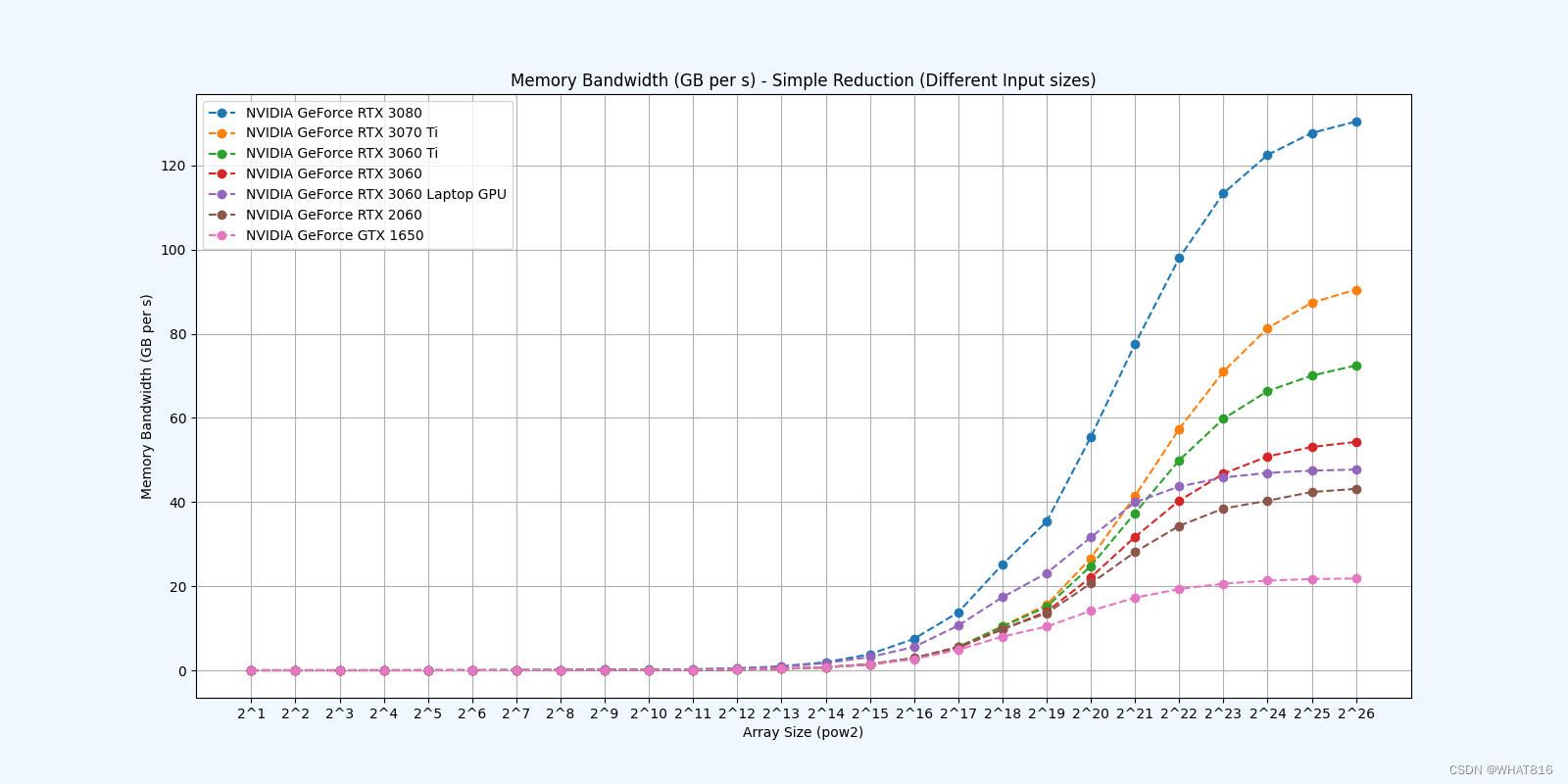
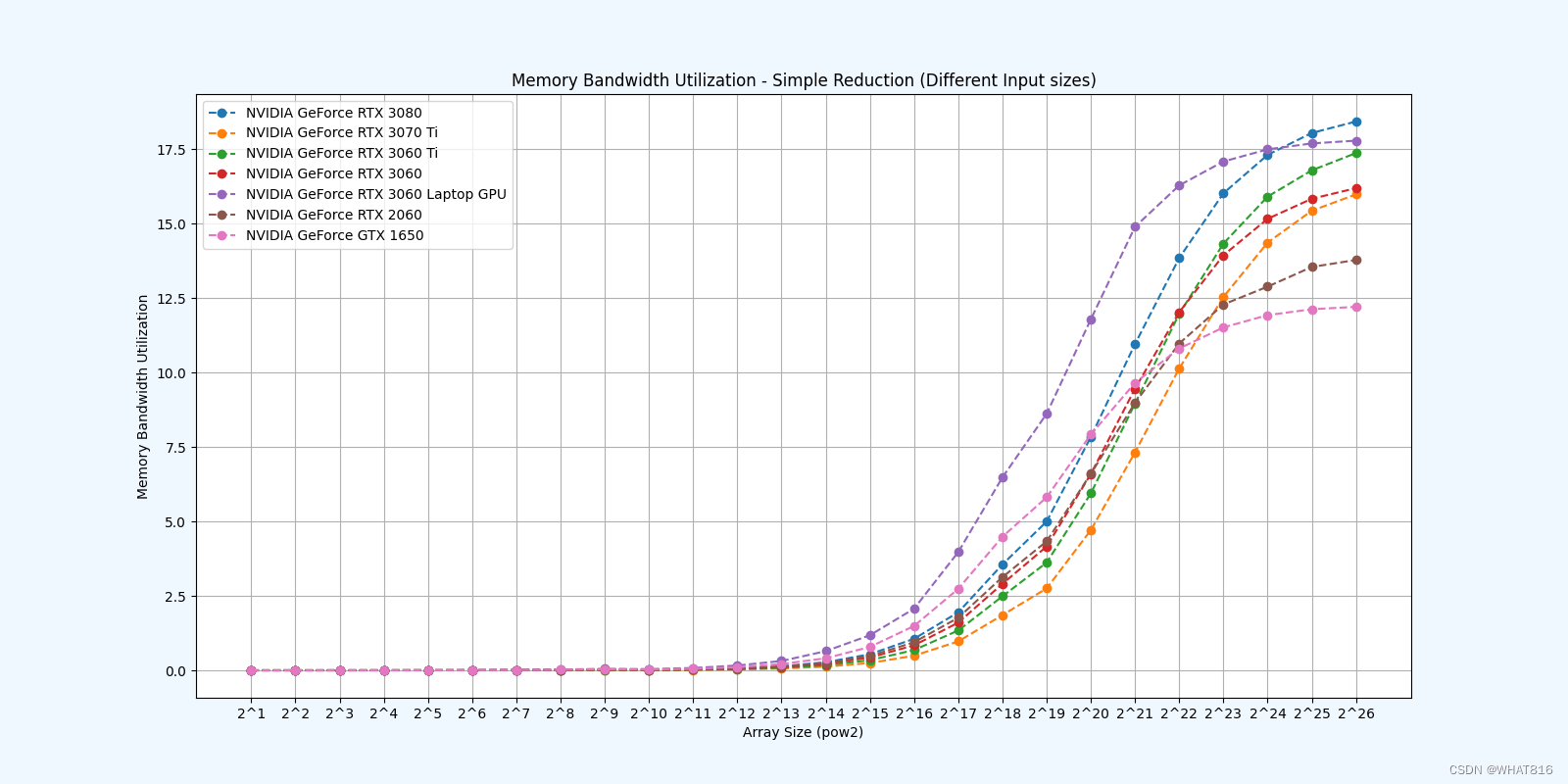
kernel的性能是使用NvBench项目在多个gpu中测量的。研究的性能测量方法有:
内存带宽:每秒传输的数据量。
内存带宽利用率:占用内存带宽的百分比。
Reduction 1: Interleaved Addressing - Diverge Warps
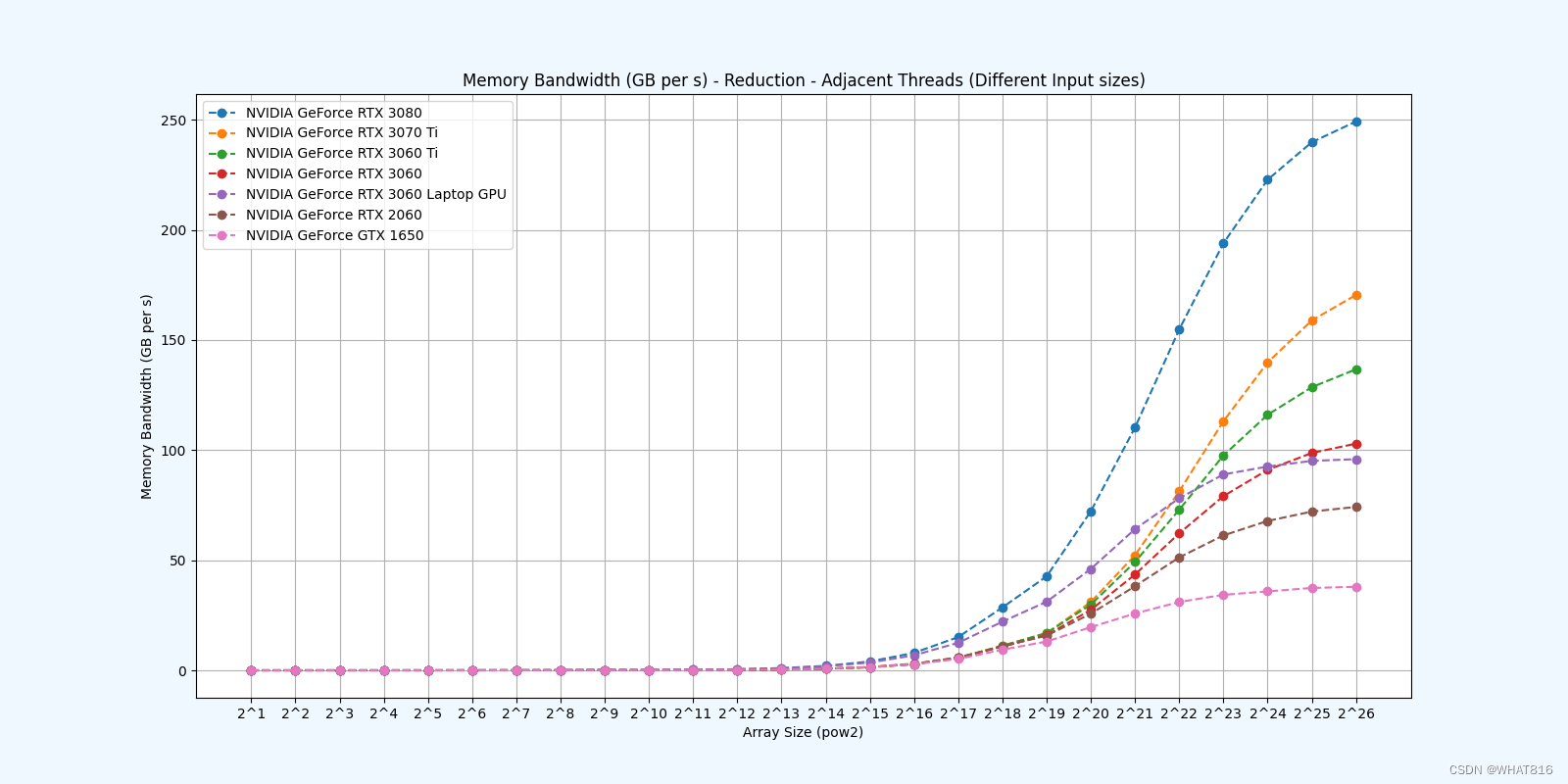
Reduction 2: Interleaved Addressing - Bank Conflicts

Reduction 3: Sequential Addressing
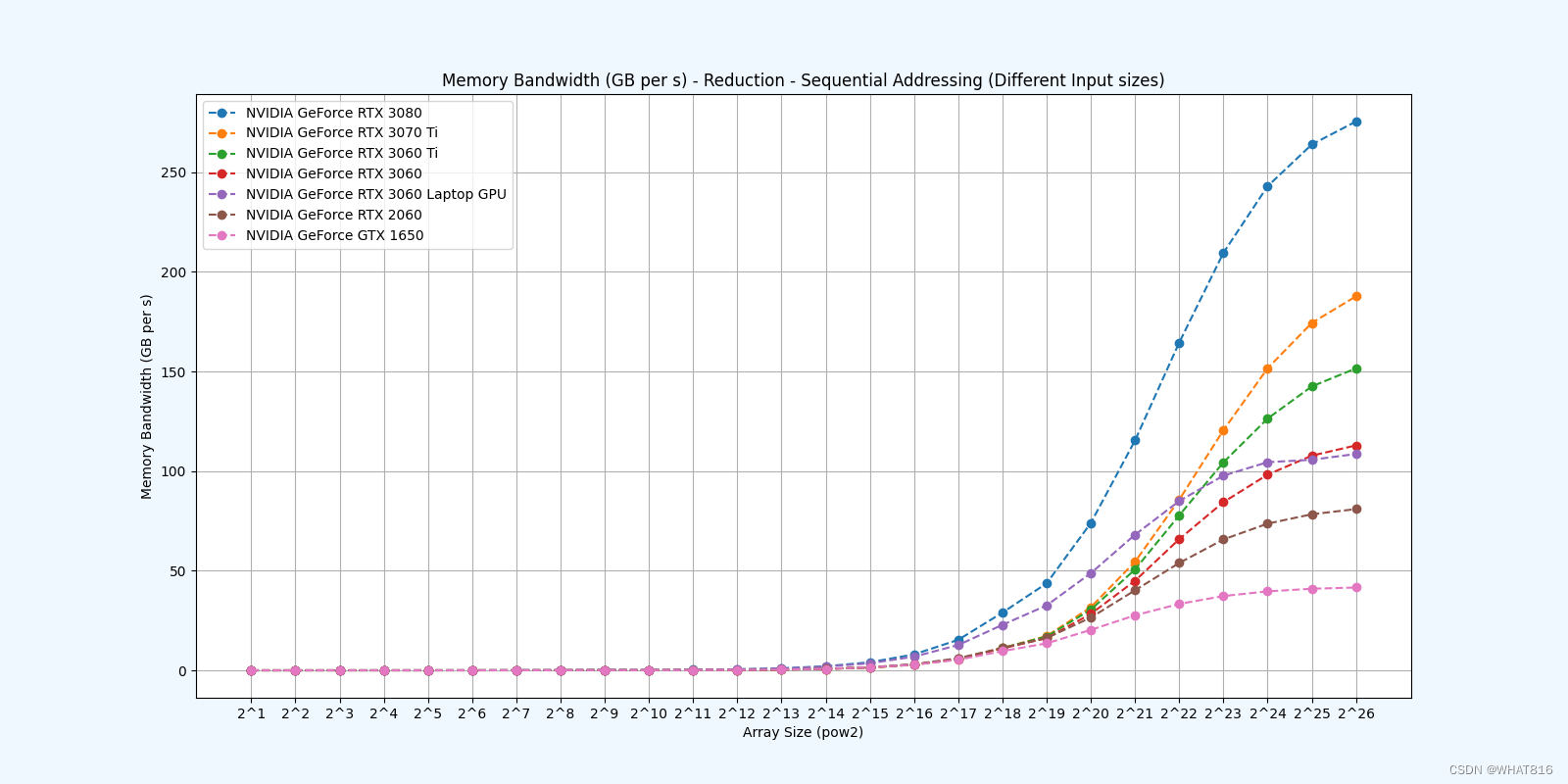
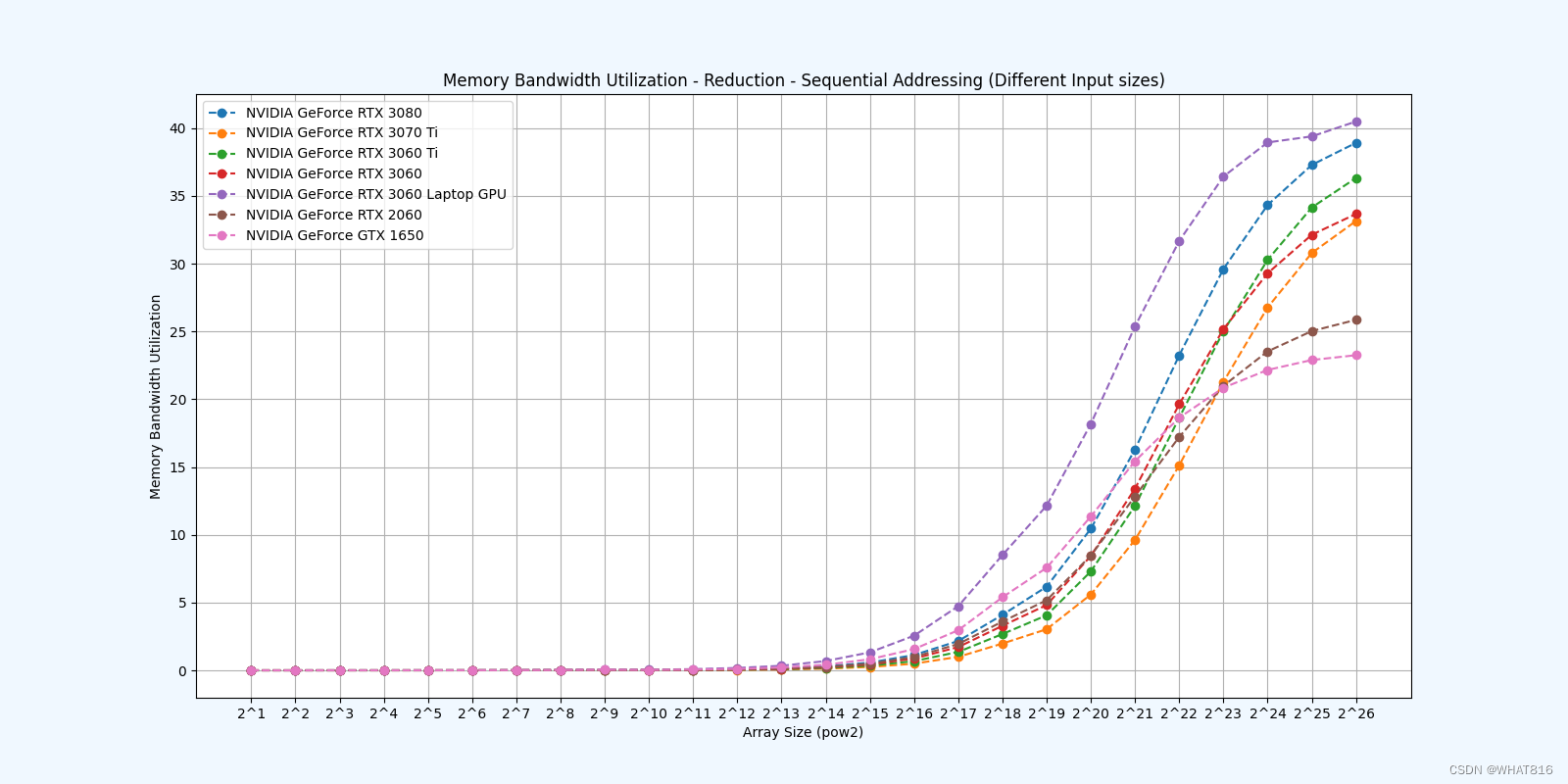
Reduction 4: First Add During Load
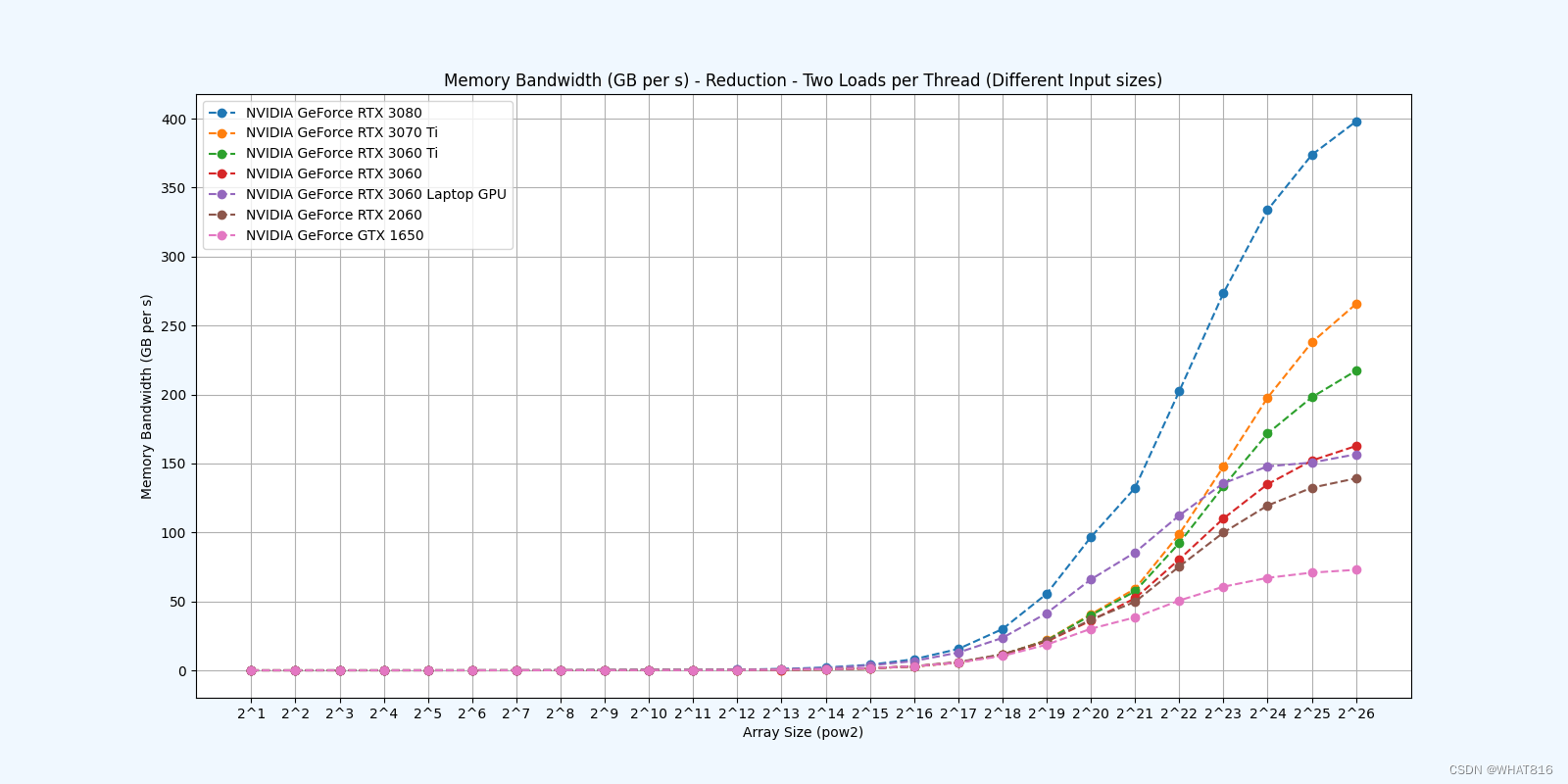
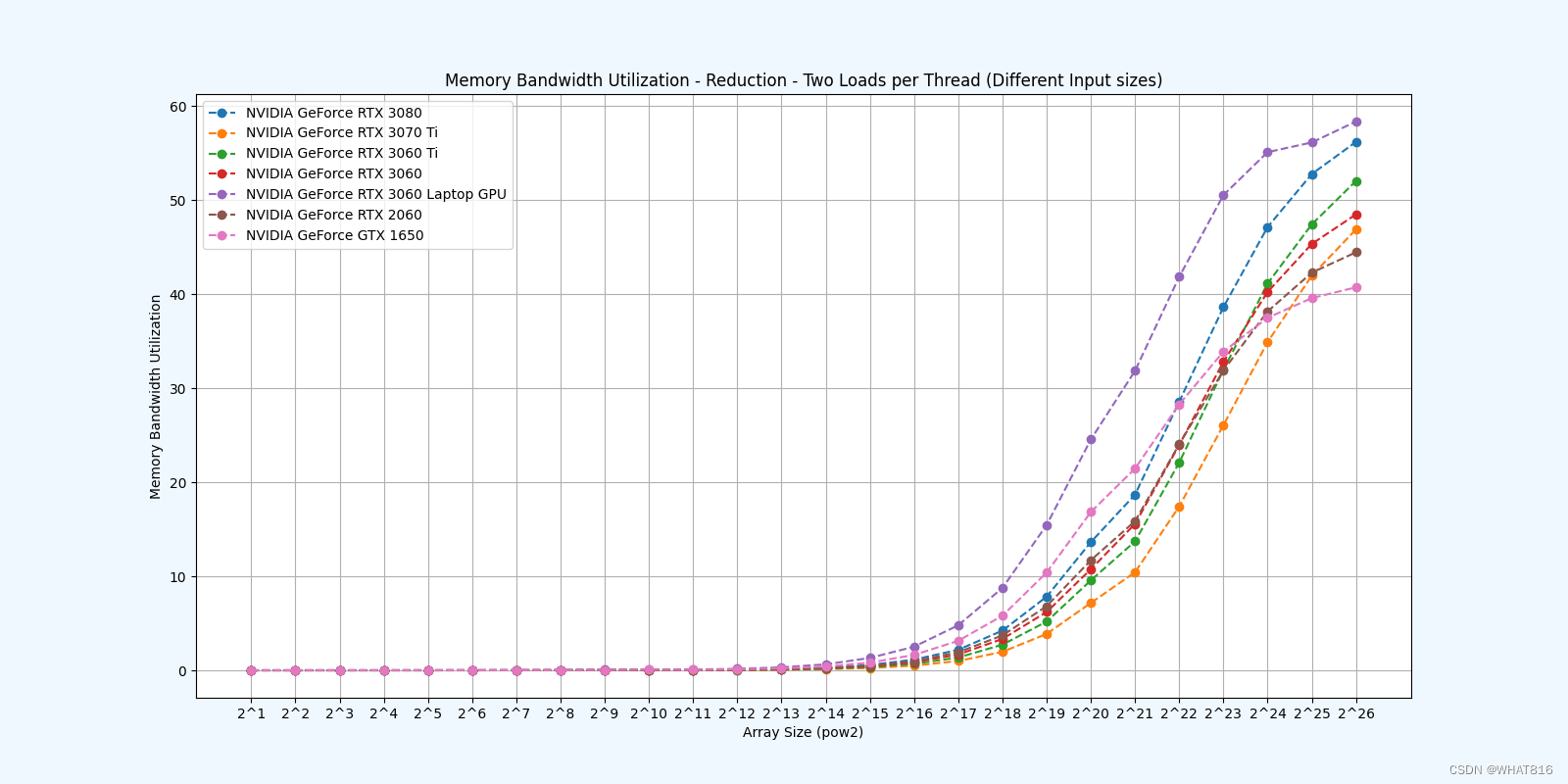
Reduction 5: Unroll Last Warp
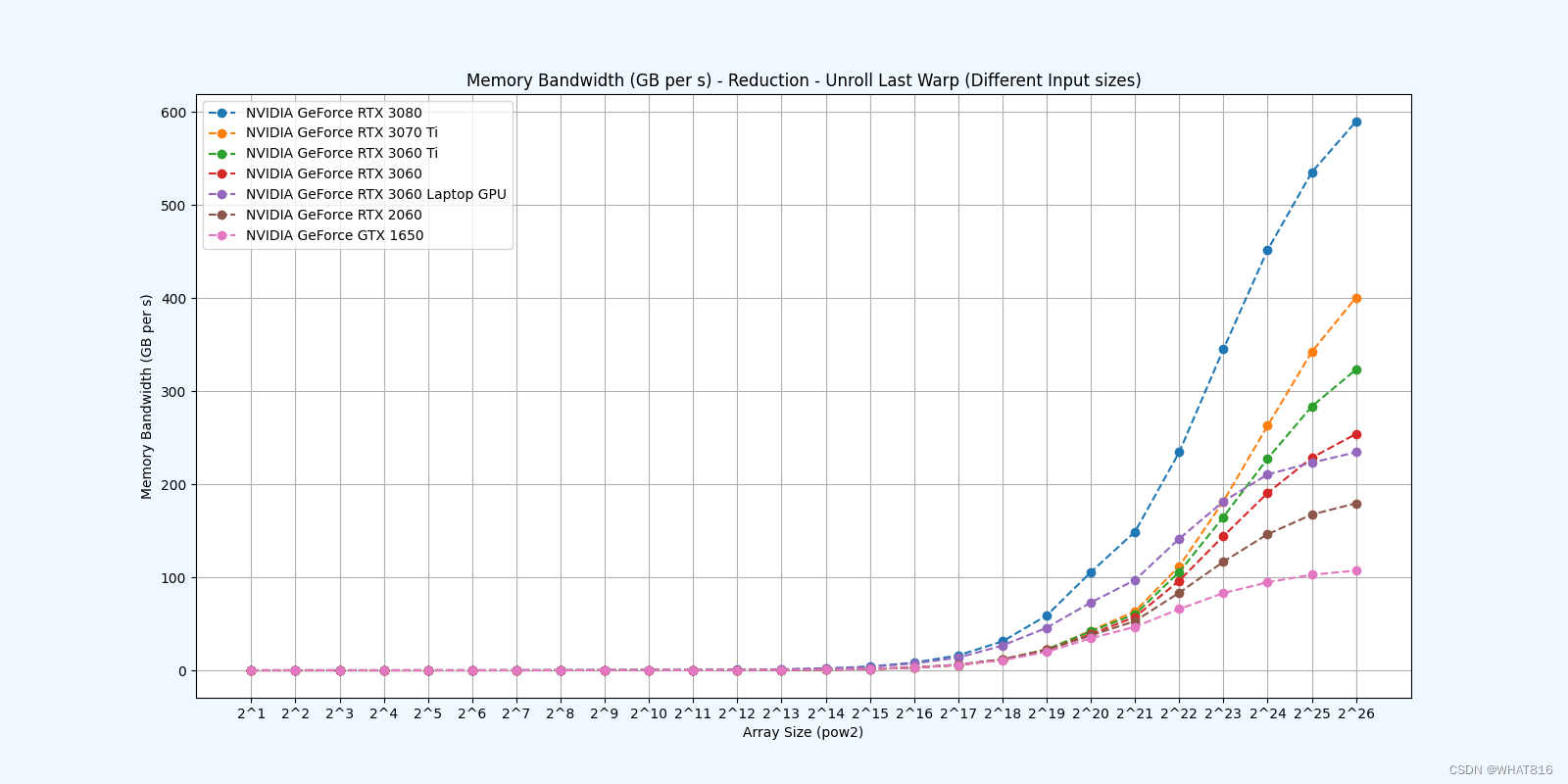
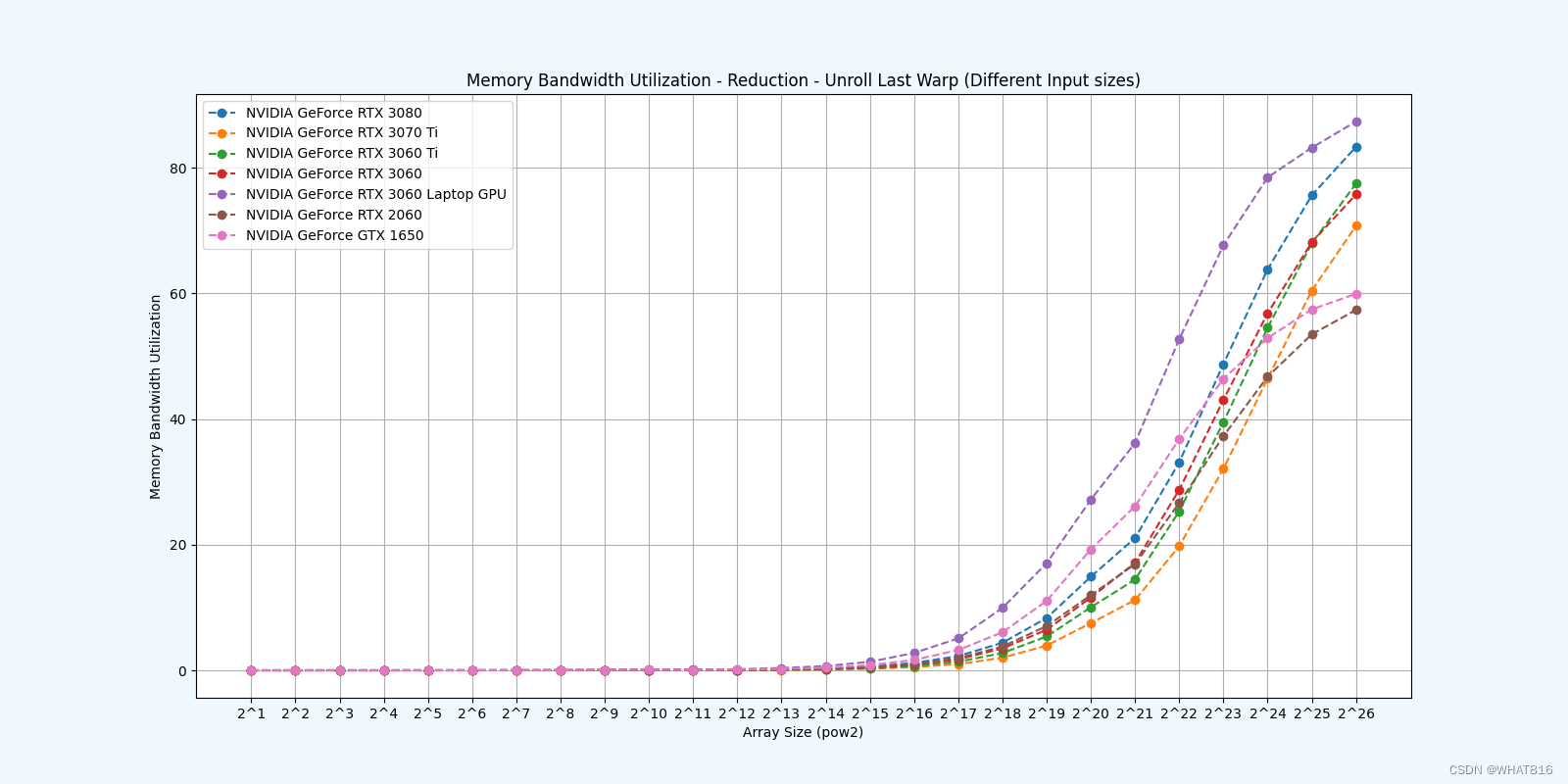
参考文献:
1、大规模并行处理器编程实战(第2版)
2、PPMP





)












![[笔记] 卷积 - 02 滤波器在时域的等效形式](http://pic.xiahunao.cn/[笔记] 卷积 - 02 滤波器在时域的等效形式)
