
文章目录
- 声明
- list的简单介绍
- list的简单使用
- list中sort效率测试
- list的简单模拟
- 封装迭代器
- insert模拟
- erase模拟
- 头插、尾插、头删、尾删模拟
- 自定义类型迭代器遍历
- const迭代器
- clear和析构函数
- 拷贝构造(传统写法)
- 拷贝构造(现代写法)
- 源码
声明
本文源代码已上传至我的gitee仓库,欢迎查看:list模拟实现源代码
list的简单介绍
在学习STL时,一定要先阅读C++文档
list使用文档
- list是可以在常数范围内在任意位置进行插入和删除的序列式容器,并且该容器可以前后双向迭代
- list的底层是双向链表结构,双向链表中每个元素存储在互不相关的独立节点中,在节点中通过指针指向其前一个元素和后一个元素。
- list与forward_list非常相似:最主要的不同在于forward_list是单链表,只能朝前迭代,已让其更简单高效。
- 与其他的序列式容器相比(array,vector,deque),list通常在任意位置进行插入、移除元素的执行效率更好。
- 与其他序列式容器相比,list和forward_list最大的缺陷是不支持任意位置的随机访问,比如:要访问list的第6个元素,必须从已知的位置(比如头部或者尾部)迭代到该位置,在这段位置上迭代需要线性的时间开销;list还需要一些额外的空间,以保存每个节点的相关联信息(对于存储类型较小元素的大list来说这可能是一个重要的因素)
list的简单使用
这里罗列列表的基本操作,非常简单,相信大家在学习完string、vector后学习list的功能非常简单
# define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
#include<iostream>
#include<list>using namespace std;int main()
{list<int> lt;lt.push_back(1);lt.push_back(2);lt.push_back(3);lt.push_back(4);lt.push_back(5);//迭代器list<int>::iterator it = lt.begin();while (it != lt.end()){cout << *it << " ";it++;}cout << endl;//范围forfor (auto e : lt){cout << e << " ";}cout << endl;//逆置lt.reverse();for (auto e : lt){cout << e << " ";}cout << endl;//排序lt.sort();for (auto e : lt){cout << e << " ";}cout << endl;//节点转移list<int> lt1;lt1.push_back(10);lt1.push_back(20);lt1.push_back(30);lt1.push_back(40);lt.splice(lt.begin(), lt1);for (auto e : lt){cout << e << " ";}cout << endl;for (auto e : lt1){cout << e << " ";}cout << endl;return 0;
}
运行结果:
1 2 3 4 5
1 2 3 4 5
5 4 3 2 1
1 2 3 4 5
10 20 30 40 1 2 3 4 5
list中sort效率测试
表示双向循环链表以及数据初始化:
void test_op()
{srand((unsigned int)time(NULL));const int N = 1000000;vector<int> v;v.reserve(N);list<int> lt1;list<int> lt2;for (int i = 0; i < N; ++i){int e = rand();lt1.push_back(e);lt2.push_back(e);}// 拷贝到vector排序,排完以后再拷贝回来int begin1 = clock();for (auto e : lt1){v.push_back(e);}sort(v.begin(), v.end());size_t i = 0;for (auto& e : lt1){e = v[i++];}int end1 = clock();//list调用自己的sortint begin2 = clock();lt2.sort();int end2 = clock();printf("vector sort:%d\n", end1 - begin1);printf("list sort:%d\n", end2 - begin2);
}
测试结果发现,list的sort排序效率很低,在实际应用中使用的很少
list的简单模拟
template<class T>struct ListNode{ListNode<T>* _next;ListNode<T>* _prev;T _data;ListNode(const T& x = T()):_next(nullptr), _prev(nullptr), _data(x){}};
模板类ListNode表示双向链表中的节点。该节点包括三个成员:_next(指向下一个节点的指针)、_prev(指向上一个节点的指针)和 _data(存储节点的数据)。
定义了一个构造函数,用于初始化节点的数据成员,如果不提供具体的数据,则使用默认值进行初始化。
实现简单的双向循环链表:
template<class T>class list{typedef ListNode<T> Node;public:list(){_head = new Node;_head->_next = _head;_head->_prev = _head;}void push_back(const T& x){Node* newnode = new Node(x);Node* tail = _head->_prev;tail->_next = newnode;newnode->_next = _head;_head->_prev = newnode;}private:Node* _head;};
定义了一个模板类 list,实现了简单的双向循环链表。在 list 中,使用了之前定义的 ListNode 作为节点,通过模板类的方式实现了对不同类型元素的支持。
构造函数中,创建了一个头节点,并将头节点的 _next 和 _prev 都指向自身,构成一个空的循环链表。
list(): 这是类的构造函数,用于初始化链表。在构造函数中,首先创建了一个头节点 _head,然后将头节点的 _next 和 _prev 都指向自身,从而形成一个空的循环链表。
void push_back(const T& x): 这是一个成员函数,用于在链表尾部插入新的元素。在函数中,首先创建了一个新的节点 newnode 并存储数据 x,然后找到当前尾节点 tail,将尾节点的 _next 指向新节点,新节点的 _next 指向头节点,头节点的 _prev 指向新节点,从而完成了新元素的插入。
封装迭代器
封装迭代器:
- 定义了一个名为
ListIterator的模板类
template<class T>
class ListIterator
{typedef ListNode<T> Node;typedef ListIterator<T> Self;Node* _node;typedef ListIterator<T> Self;:定义了一个别名Self,它代表了当前类的类型,这样就可以在类内部使用Self来引用当前类的对象。
Node* _node;:声明了一个指针成员变量_node,它用于指向链表中的节点。
- 成员函数的定义:
public:ListIterator(Node* node):_node(node){}构造函数ListIterator(Node* node):接受一个指向链表节点的指针作为参数,将其赋值给成员变量_node。
T& operator*(){return _node->_data;}解引用操作符operator*():返回当前迭代器指向的节点的数据成员的引用。
Self& operator++()
{_node = _node->_next;return *this;
}
前置递增操作符operator++():将迭代器指向下一个节点,并返回递增后的迭代器自身的引用。
Self operator++(int){Self tmp(*this);_node = _node->_next;return tmp;}后置递增操作符operator++(int):创建当前迭代器的副本tmp,然后将迭代器指向下一个节点,并返回tmp。
Self& operator--(){_node = _node->_prev;return *this;}Self operator--(int){Self tmp(*this);_node = _node->_prev;return tmp;}置和后置递减操作符的定义与递增操作符类似,只不过是将迭代器指向前一个节点。
bool operator!=(const Self& it){return _node != it._node;}
};不等于操作符operator!=:比较两个迭代器的_node成员,如果它们不相等,则返回true;否则返回false。
源代码:
template<class T>struct ListConstIterator{typedef ListNode<T> Node;typedef ListConstIterator<T> Self;Node* _node;ListConstIterator(Node* node):_node(node){}// *itconst T& operator*(){return _node->_data;}// it->const T* operator->(){return &_node->_data;}// ++itSelf& operator++(){_node = _node->_next;return *this;}Self operator++(int){Self tmp(*this);_node = _node->_next;return tmp;}Self& operator--(){_node = _node->_prev;return *this;}Self operator--(int){Self tmp(*this);_node = _node->_prev;return tmp;}bool operator!=(const Self& it){return _node != it._node;}bool operator==(const Self& it){return _node == it._node;}};
关于链表开始和结束的定义:
typedef ListConstIterator<T> iterator;iterator begin(){return iterator(_head->_next);}iterator end(){return iterator(_head);}
begin()函数返回一个迭代器,它指向链表中的第一个元素(也就是头节点的下一个节点)。
end()函数返回一个迭代器,它指向链表中最后一个元素的下一个位置(也就是头节点本身)。
insert模拟
模拟实现insert:
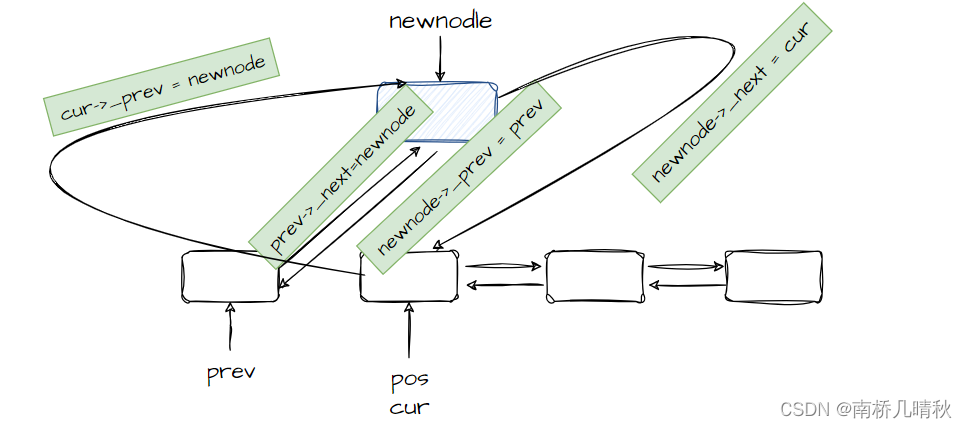
void insert(iterator pos, const T& val){Node* cur = pos._node;Node* newnode = new Node(val); Node* prev = cur->_prev;//prev newnode curprev->_next = newnode;newnode->_prev = prev;newnode->_next = cur;cur->_prev = newnode;}
erase模拟
模拟实现erase:
iterator earse(iterator pos){Node* cur = pos._node;Node* prev = cur->_prev;Node* next = cur->_next;prev->_next = next;next->_prev = prev;delete cur;return iterator(next);}
注意:最后,返回一个指向下一个节点的迭代器,以便在调用方继续操作链表。
头插、尾插、头删、尾删模拟
在刚刚插入和删除的基础上,模拟实现头插、尾插、头删、尾删:
void push_back(const T& x){insert(end(), x);}void push_front(const T& x){insert(begin(), x);}void pop_back(){erase(--end());}void pop_front(){erase(begin());}
自定义类型迭代器遍历
自定义一个结构体A,然后进行插入删除操作:
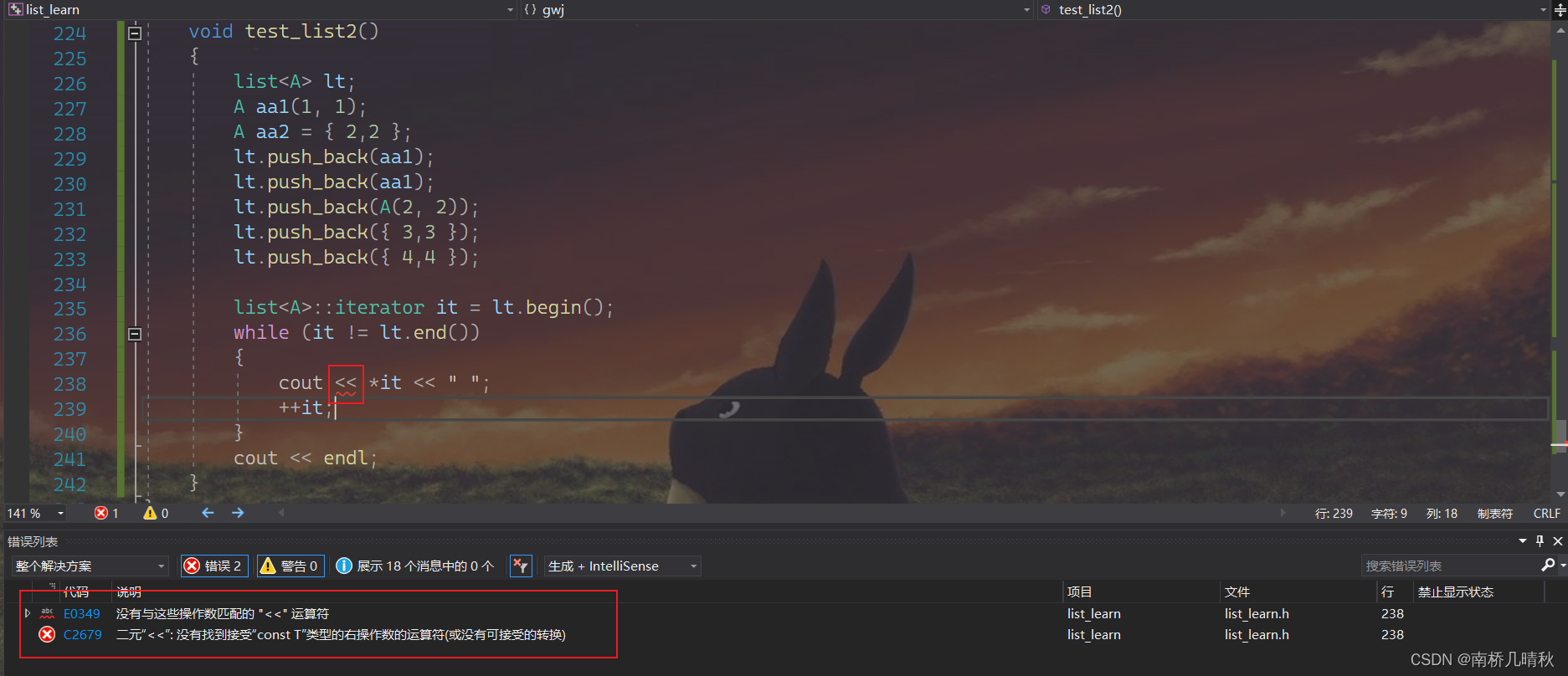
struct A{int _a1;int _a2;A(int a1=0,int a2=0):_a1(a1),_a2(a2){}};void test_list2(){list<A> lt;A aa1(1, 1);A aa2 = { 2,2 };lt.push_back(aa1);lt.push_back(aa1);lt.push_back(A(2, 2));lt.push_back({ 3,3 });lt.push_back({ 4,4 });list<A>::iterator it = lt.begin();while (it != lt.end()){cout << *it << " ";++it;}cout << endl;}
运行一下,报错了!!!
解决方法有两种:
- 第一种:
在循环内部,通过cout << (*it)._a1 << ":" << (*it)._a2 << endl;语句打印当前迭代器it指向的A类型对象的_a1和_a2成员变量的值,中间用冒号分隔,并在末尾换行。这里使用了解引用操作符(*)来获取迭代器指向的对象,然后通过点操作符(.)访问对象的成员变量_a1和_a2
(*it)._a1:(*it)是迭代器it指向的元素,即链表中的一个A类型对象,.是成员访问运算符,_a1是这个A类型对象的成员变量_a1的值。所以(*it)._a1表示获取当前迭代器指向的对象的_a1成员变量的值。
void test_list2(){list<A> lt;A aa1(1, 1);A aa2 = { 2,2 };lt.push_back(aa1);lt.push_back(aa1);lt.push_back(A(2, 2));lt.push_back({ 3,3 });lt.push_back({ 4,4 });list<A>::iterator it = lt.begin();while (it != lt.end()){cout << (*it)._a1 << ":" << (*it)._a2 << endl;++it;}cout << endl;}
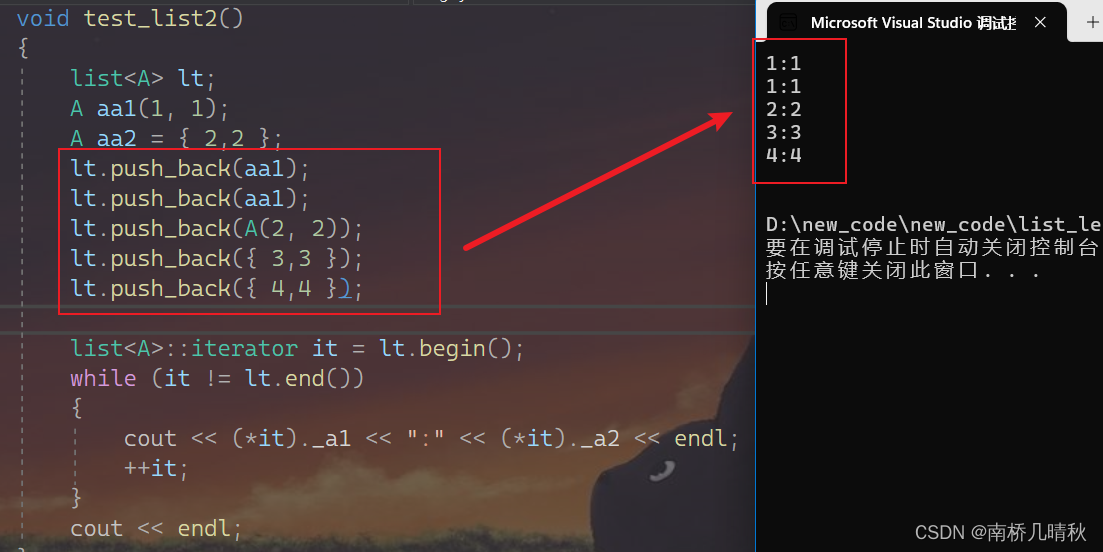
- 第二种:
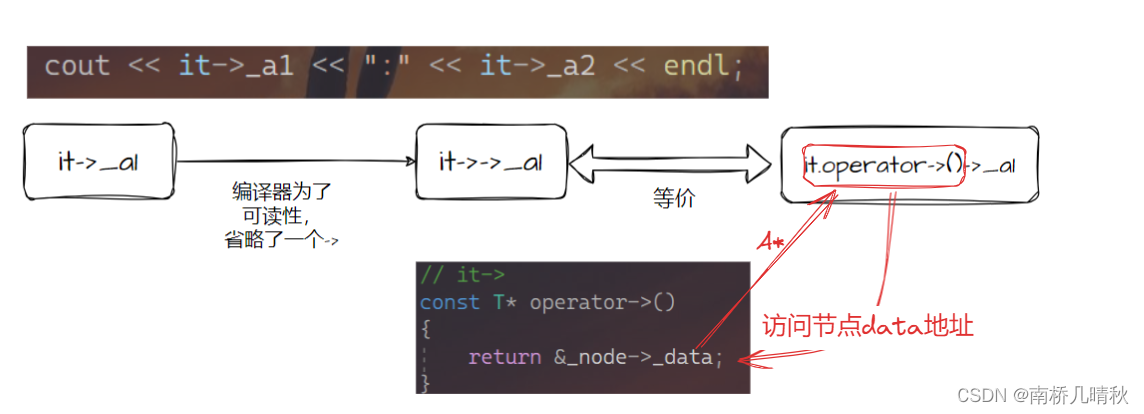
定义了一个operator->()重载函数,箭头运算符用于访问对象的成员,而对于指向对象的指针,使用箭头运算符来访问成员会更方便
const T*: 这是函数的返回类型,表示返回一个指向类型为T的常量数据的指针。也就是说,该函数返回的是一个指向T类型常量数据的指针。
operator->(): 这是重载的箭头运算符函数名。当我们通过指向某个对象的指针使用箭头运算符时,就会调用此函数来执行操作。
{ return &_node->_data; }: 函数体内部,返回了一个指向_node->_data的指针。在这里,_node是一个指向节点的指针,_data是节点中存储的数据。通过返回&_node->_data,实际上是返回了指向节点数据的指针。
// it->
const T* operator->()
{return &_node->_data;
}
遍历:
void test_list2(){list<A> lt;A aa1(1, 1);A aa2 = { 2,2 };lt.push_back(aa1);lt.push_back(aa1);lt.push_back(A(2, 2));lt.push_back({ 3,3 });lt.push_back({ 4,4 });list<A>::iterator it = lt.begin();while (it != lt.end()){cout << it->_a1 << ":" << it->_a2 << endl;++it;}cout << endl;}
it->_a1和it->_a2就是使用迭代器it来访问链表中当前元素的成员变量_a1和_a2的值。这里的it->_a1和it->_a2相当于(*it)._a1和(*it)._a2
const迭代器
cont迭代器是迭代器指向的内容不能修改
注意:
const_iterator是迭代器指向的内容不能修改,迭代器指向的元素不可修改,模拟实现的是const T* p2const iterator是迭代器本身不能修改,这个const修饰的是iterator,iterator是自定义类型,前面加了const那就是不能修改这个自定义类型,模拟实现的是T* const p1
const_iterator begin() const{return iterator(_head->_next);}const_iterator end() const{return iterator(_head);}
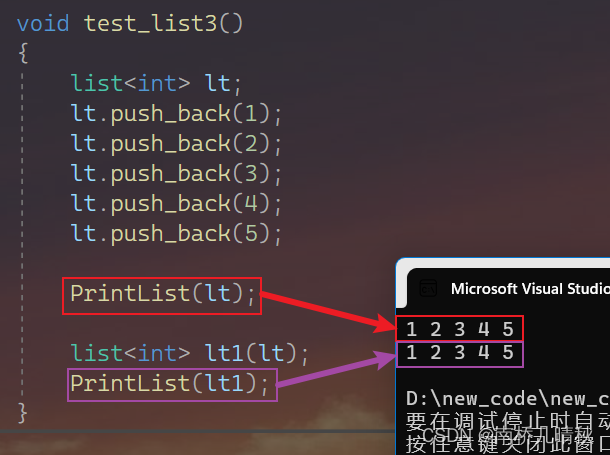
void PrintList(const list<int>& clt){list<int>::const_iterator it = clt.begin();while (it != clt.end()){cout << *it << " ";++it;}cout << endl;}void test_list3(){list<int> lt;lt.push_back(1);lt.push_back(2);lt.push_back(3);lt.push_back(4);lt.push_back(5);PrintList(lt);}
使用模板封装一个迭代器:
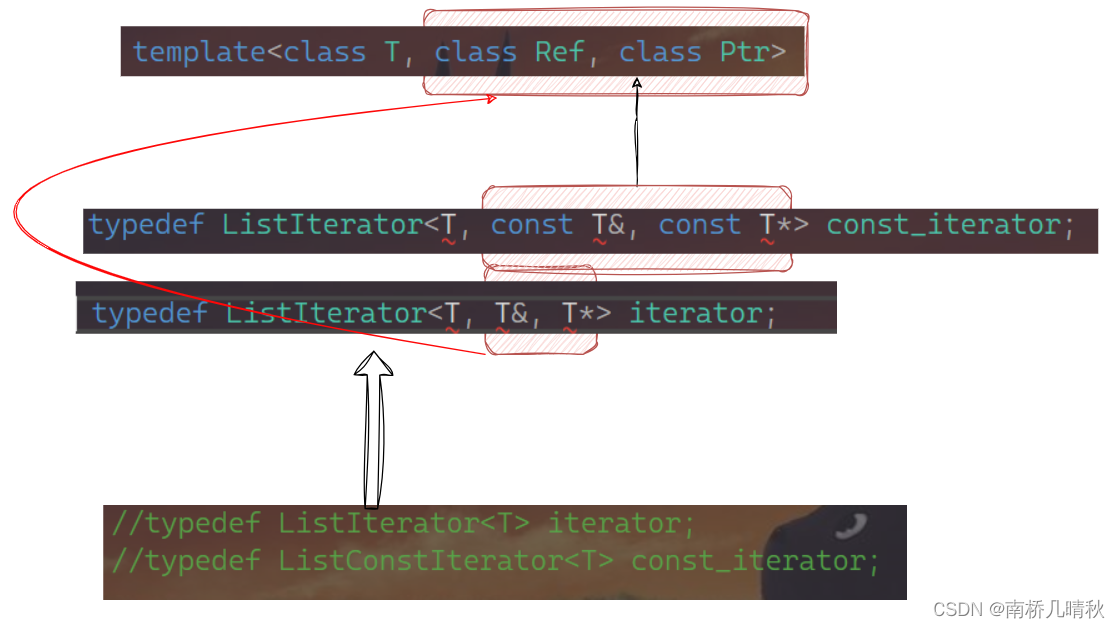
template<class T, class Ref, class Ptr>struct ListIterator{typedef ListNode<T> Node;typedef ListIterator<T, Ref, Ptr> Self;Node* _node;ListIterator(Node* node):_node(node){}// *it//T& operator*()Ref operator*(){return _node->_data;}// it->//T* operator->()Ptr operator->(){return &_node->_data;}// ++itSelf& operator++(){_node = _node->_next;return *this;}Self operator++(int){Self tmp(*this);_node = _node->_next;return tmp;}Self& operator--(){_node = _node->_prev;return *this;}Self operator--(int){Self tmp(*this);_node = _node->_prev;return tmp;}bool operator!=(const Self& it){return _node != it._node;}bool operator==(const Self& it){return _node == it._node;}};
template<class T, class Ref, class Ptr>:模板声明,用来定义模板类 ListIterator,它有三个模板参数 T、Ref 和 Ptr。
在这个模板类中,class T、class Ref 和 class Ptr 是模板参数,它们的作用如下:
T:表示节点中存储的数据类型。通过模板参数 T,可以让 ListIterator 类型适用于不同类型的链表,例如整数、字符串、自定义对象等。Ref:表示引用类型。在 C++ 中,引用类型通常用来表示对某个对象的引用,通过模板参数Ref,可以指定迭代器返回的数据的引用类型,例如T&(对T类型的对象的引用)。Ptr:表示指针类型。通过模板参数Ptr,可以指定迭代器返回数据的指针类型,例如T*(指向T类型的指针)。
clear和析构函数
void clear(){iterator it = begin();while (it != end()){it = erase(it);}}~list(){clear();delete _head;_head = nullptr;}
-
clear() 方法:
首先创建一个迭代器 it 并初始化为链表的头部(即第一个节点)。
然后通过循环遍历链表中的每个节点,调用 erase() 方法来删除当前节点,并将返回的下一个节点的迭代器赋值给 it。
循环直到 it == end(),即遍历完整个链表。 -
析构函数 ~list():
在析构函数中首先调用 clear() 方法,清空链表中的所有节点。
然后释放链表的头节点 _head 所占用的内存,避免内存泄漏。
最后将 _head 指针设置为 nullptr,确保不再指向已释放的内存。
通过在析构函数中调用 clear() 方法,可以确保在销毁链表对象时,先清空链表中的所有节点,然后再释放头节点的内存。这样做有助于避免内存泄漏,并正确地释放链表所占用的资源。
拷贝构造(传统写法)
void empty_init(){_head = new Node;_head->_next = _head;_head->_prev = _head;_size = 0;}list(){empty_init();}// lt2(lt1)list(const list<T>& lt){empty_init();for (auto& e : lt){push_back(e);}}
-
empty_init() :
初始化空的链表。它创建了一个新的节点作为头结点,并将头结点的指针指向自己,形成一个循环链表。同时,将链表的大小 _size 初始化为 0。 -
默认构造函数 list():
在这个构造函数中,它调用了 empty_init() 方法来初始化一个空的链表。 -
拷贝构造函数 list(const list& lt):
这个构造函数通过调用 empty_init() 方法来初始化一个空的链表(即新建一个头结点)。然后通过遍历传入的链表 lt,将其中的元素逐个添加到新建的链表中,使用 push_back(e) 方法将元素添加到新链表的末尾。
拷贝构造(现代写法)
void swap(list<T>& lt)
{std::swap(_head, lt._head);std::swap(_size, lt._size);
}// lt1 = lt3
list<T>& operator=(list<T> lt)
{swap(lt);return *this;
}
-
swap:
交换两个链表对象的内容。它通过调用std::swap函数交换当前链表对象的头结点_head和大小_size与传入的链表对象lt的对应成员的值。这样可以在不需要额外内存分配的情况下快速交换两个链表的内容。 -
赋值运算符重载函数
operator=:
这个赋值运算符重载函数接受一个传值参数lt,在函数内部会对传入的链表 lt 调用swap方法,将传入链表的内容与当前链表对象进行交换。
通过传值参数的方式,会触发拷贝构造函数,从而创建传入链表lt的一个副本。然后,调用swap(lt)来交换当前链表对象和副本链表对象的内容,最终实现将传入链表lt中的内容赋值给当前链表对象。
最后,返回*this,即当前链表对象的引用,以支持链式赋值操作。
源码
#pragma once
#include<assert.h>
namespace gwj
{template<class T>struct ListNode{ListNode<T>* _next;ListNode<T>* _prev;T _data;ListNode(const T& x = T()):_next(nullptr), _prev(nullptr), _data(x){}};//typedef ListIterator<T, T&, T*> iterator;//typedef ListIterator<T, const T&, const T*> const_iterator;template<class T, class Ref, class Ptr>struct ListIterator{typedef ListNode<T> Node;typedef ListIterator<T, Ref, Ptr> Self;Node* _node;ListIterator(Node* node):_node(node){}// *it//T& operator*()Ref operator*(){return _node->_data;}// it->//T* operator->()Ptr operator->(){return &_node->_data;}// ++itSelf& operator++(){_node = _node->_next;return *this;}Self operator++(int){Self tmp(*this);_node = _node->_next;return tmp;}Self& operator--(){_node = _node->_prev;return *this;}Self operator--(int){Self tmp(*this);_node = _node->_prev;return tmp;}bool operator!=(const Self& it){return _node != it._node;}bool operator==(const Self& it){return _node == it._node;}};//template<class T>//struct ListConstIterator//{// typedef ListNode<T> Node;// typedef ListConstIterator<T> Self;// Node* _node;// ListConstIterator(Node* node)// :_node(node)// {}// // *it// const T& operator*()// {// return _node->_data;// }// // it->// const T* operator->()// {// return &_node->_data;// }// // ++it// Self& operator++()// {// _node = _node->_next;// return *this;// }// Self operator++(int)// {// Self tmp(*this);// _node = _node->_next;// return tmp;// }// Self& operator--()// {// _node = _node->_prev;// return *this;// }// Self operator--(int)// {// Self tmp(*this);// _node = _node->_prev;// return tmp;// }// bool operator!=(const Self& it)// {// return _node != it._node;// }// bool operator==(const Self& it)// {// return _node == it._node;// }//};template<class T>class list{typedef ListNode<T> Node;public://typedef ListIterator<T> iterator;//typedef ListConstIterator<T> const_iterator;typedef ListIterator<T, T&, T*> iterator;typedef ListIterator<T, const T&, const T*> const_iterator;//iterator begin()//{// //return iterator(_head->_next);// iterator it(_head->_next);// return it;//}iterator begin(){return _head->_next;}iterator end(){return _head;}// const迭代器,需要是迭代器不能修改,还是迭代器指向的内容?// 迭代器指向的内容不能修改!const iterator不是我们需要const迭代器// T* const p1// const T* p2const_iterator begin() const{return _head->_next;}const_iterator end() const{return _head;}void empty_init(){_head = new Node;_head->_next = _head;_head->_prev = _head;_size = 0;}list(){empty_init();}// lt2(lt1)list(const list<T>& lt){empty_init();for (auto& e : lt){push_back(e);}}void swap(list<T>& lt){std::swap(_head, lt._head);std::swap(_size, lt._size);}// lt1 = lt3list<T>& operator=(list<T> lt){swap(lt);return *this;}// 需要析构,一般就需要自己写深拷贝// 不需要析构,一般就不需要自己写深拷贝,默认浅拷贝就可以void clear(){iterator it = begin();while (it != end()){it = erase(it);}}~list(){clear();delete _head;_head = nullptr;}//void push_back(const T& x)//{// Node* newnode = new Node(x);// Node* tail = _head->_prev;// tail->_next = newnode;// newnode->_next = _head;// _head->_prev = newnode;//}void push_back(const T& x){insert(end(), x);}void push_front(const T& x){insert(begin(), x);}void pop_back(){erase(--end());}void pop_front(){erase(begin());}void insert(iterator pos, const T& val){Node* cur = pos._node;Node* newnode = new Node(val); Node* prev = cur->_prev;//prev newnode curprev->_next = newnode;newnode->_prev = prev;newnode->_next = cur;cur->_prev = newnode;_size++;}iterator erase(iterator pos){Node* cur = pos._node;Node* prev = cur->_prev;Node* next = cur->_next;prev->_next = next;next->_prev = prev;delete cur;_size--;return iterator(next);}bool empty(){return _size == 0;}private:Node* _head;size_t _size;};void test_list1(){list<int> lt;lt.push_back(1);lt.push_back(2);lt.push_back(3);lt.push_back(4);lt.push_back(5);list<int>::iterator it = lt.begin();while (it != lt.end()){cout << *it << " ";++it;}cout << endl;lt.push_front(10);lt.push_front(20);lt.push_front(30);for (auto e : lt){cout << e << " ";}cout << endl;lt.pop_back();lt.pop_front();for (auto e : lt){cout << e << " ";}cout << endl;}struct A{int _a1;int _a2;A(int a1=0,int a2=0):_a1(a1),_a2(a2){}};void test_list2(){list<A> lt;A aa1(1, 1);A aa2 = { 2,2 };lt.push_back(aa1);lt.push_back(aa1);lt.push_back(A(2, 2));lt.push_back({ 3,3 });lt.push_back({ 4,4 });list<A>::iterator it = lt.begin();while (it != lt.end()){//cout << (*it)._a1 << ":" << (*it)._a2 << endl;cout << it->_a1 << ":" << it->_a2 << endl;++it;}cout << endl;}void PrintList(const list<int>& clt){list<int>::const_iterator it = clt.begin();while (it != clt.end()){cout << *it << " ";++it;}cout << endl;}void test_list3(){list<int> lt;lt.push_back(1);lt.push_back(2);lt.push_back(3);lt.push_back(4);lt.push_back(5);PrintList(lt);list<int> lt1(lt);PrintList(lt1);}
}



![[word] word文字间隙怎么调整? #媒体#职场发展](http://pic.xiahunao.cn/[word] word文字间隙怎么调整? #媒体#职场发展)







)



)
![[知识点]c++运算符重载](http://pic.xiahunao.cn/[知识点]c++运算符重载)


![[数据集][目标检测]叶子计数检测数据集VOC+YOLO格式240张1类别](http://pic.xiahunao.cn/[数据集][目标检测]叶子计数检测数据集VOC+YOLO格式240张1类别)
