目录
一.MyBatis是什么?
二.为什么学习MyBatis呢?
三.MyBatis的学习
3.1MyBatis的开发流程
3.2MyBatis项目
四.MyBatis的增删改操作
五.参数占位符 #{} 和 ${}
六.映射返回
七.映射失败
八.数据库连接池
九.动态SQL
9.1<if>标签
9.2<trim>标签
9.3<where>标签
9.4<set>标签
9.5<foreach>标签
9.6<include>标签
一.MyBatis是什么?
- MyBatis 是一款优秀的半自动的ORM持久层框架,它支持自定义 SQL、存储过程以及高级映射。
- MyBatis 免除了几乎所有的 JDBC 代码以及设置参数和获取结果集的工作。
- MyBatis 可以通过简单的 XML 或注解来配置和映射原始类型、接口和 Java POJO(Plain Old Java Objects,普通老式 Java 对象)为数据库中的记录。
ORM介绍:
ORM代表对象关系映射(Object-Relational Mapping),它是一种编程技术,用于在关系数据库和面向对象编程语言之间建立一种映射关系,从而将数据库中的数据以对象的形式进行操作和访问。
半自动的原因:
-
手动编写SQL语句:与全自动的ORM框架不同,MyBatis需要开发者手动编写SQL语句或者使用XML配置文件来定义SQL映射。这使得开发者可以更精确地控制SQL查询的逻辑,包括优化查询性能、处理复杂的查询需求等。
-
灵活的映射配置:MyBatis允许开发者通过XML配置文件或者注解来定义对象与数据库表之间的映射关系,包括字段映射、关联关系等。这种灵活性使得开发者可以根据具体需求进行定制化配置。
-
不强制使用领域模型:MyBatis不强制要求开发者使用特定的领域模型,开发者可以自由选择使用普通的Java对象或者自定义的POJO(Plain Old Java Object)作为持久化对象。这种灵活性使得开发者可以更加灵活地设计应用程序的数据模型。
二.为什么学习MyBatis呢?
对于后端人员,获取数据库的信息,是需要从后端程序当中获取,而如何获取,最常用的方法就是JDBC方法!
往常使用JDBC的步骤:
- 创建数据库连接池 DataSource
- 通过 DataSource 获取数据库连接 Connection
- 编写要执⾏带 ? 占位符的 SQL 语句
- 通过 Connection 及 SQL 创建操作命令对象 Statement
- 替换占位符:指定要替换的数据库字段类型,占位符索引及要替换的值
- 使⽤ Statement 执⾏ SQL 语句
- 查询操作:返回结果集 ResultSet,更新操作:返回更新的数量
- 处理结果集
- 释放资源
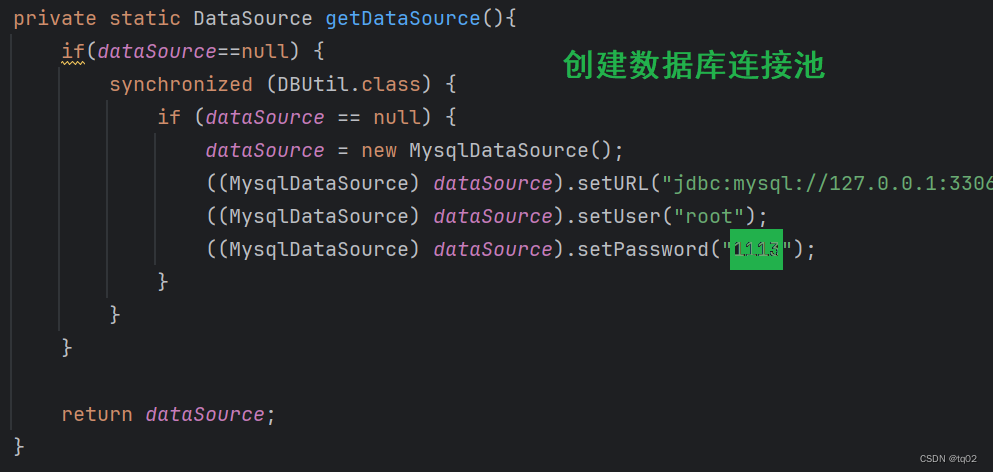
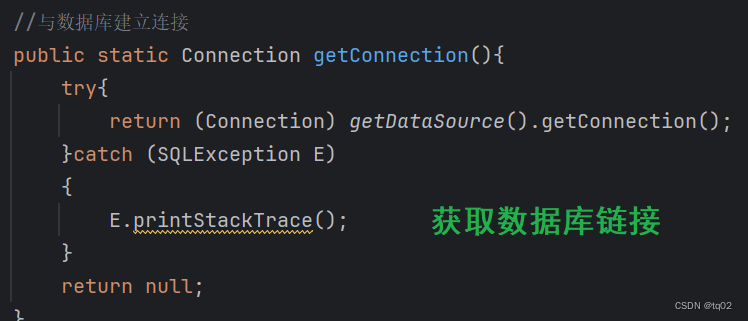
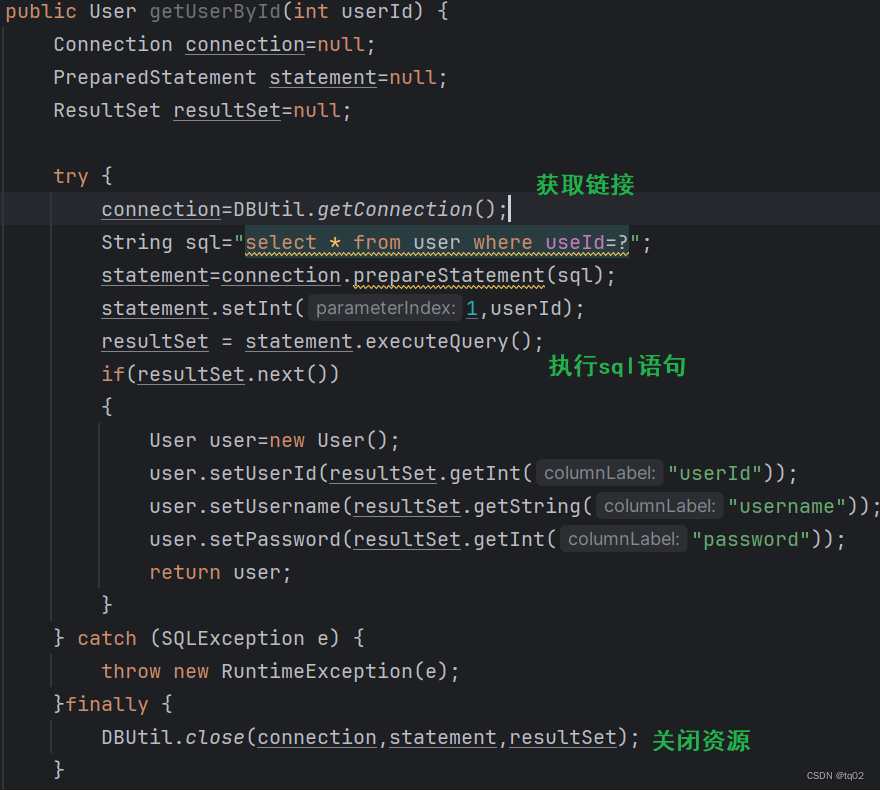
因此我们需要学习更为简便的MyBatis操作数据库
注:如果你硬要说可以使用ComboPooledDataSource也可以简化代码,我就不想用MyBatis,那你就杠吧!
三.MyBatis的学习
3.1MyBatis的开发流程
MyBatis 也是⼀个 ORM 框架, ORM(Object Relational Mapping),即对象关系映射。在⾯向对象编程语言中,将关系型数据库中的数据与对象建立起映射关系,进而自动的完成数据与对象的互相转换:
- 将输⼊数据(即传⼊对象)+SQL 映射成原生 SQL
- 将结果集映射为返回对象,即输出对象
所谓的映射(数据库<-->对象):
- 数据库表(table)--> 类(class)
- 记录(record,⾏数据)--> 对象(object)
- 字段(field) --> 对象的属性(attribute)

调用者向Controller层请求数据,因此会逐层调用到Mapper层,Mapper层通过接口和配置文件.xml来进行调用数据库的数据。因此很明显,我们需要配置的环境有两个地方,一个是xml配置文件,一个是接口的定义。
当然,我们需要在application.yml当中配置好数据库连接配置 ,后期在创建项目当中会有详细讲解。
3.2MyBatis项目
第一步.我们创建一个SpringBoot项目。并且勾选好需要的依赖!

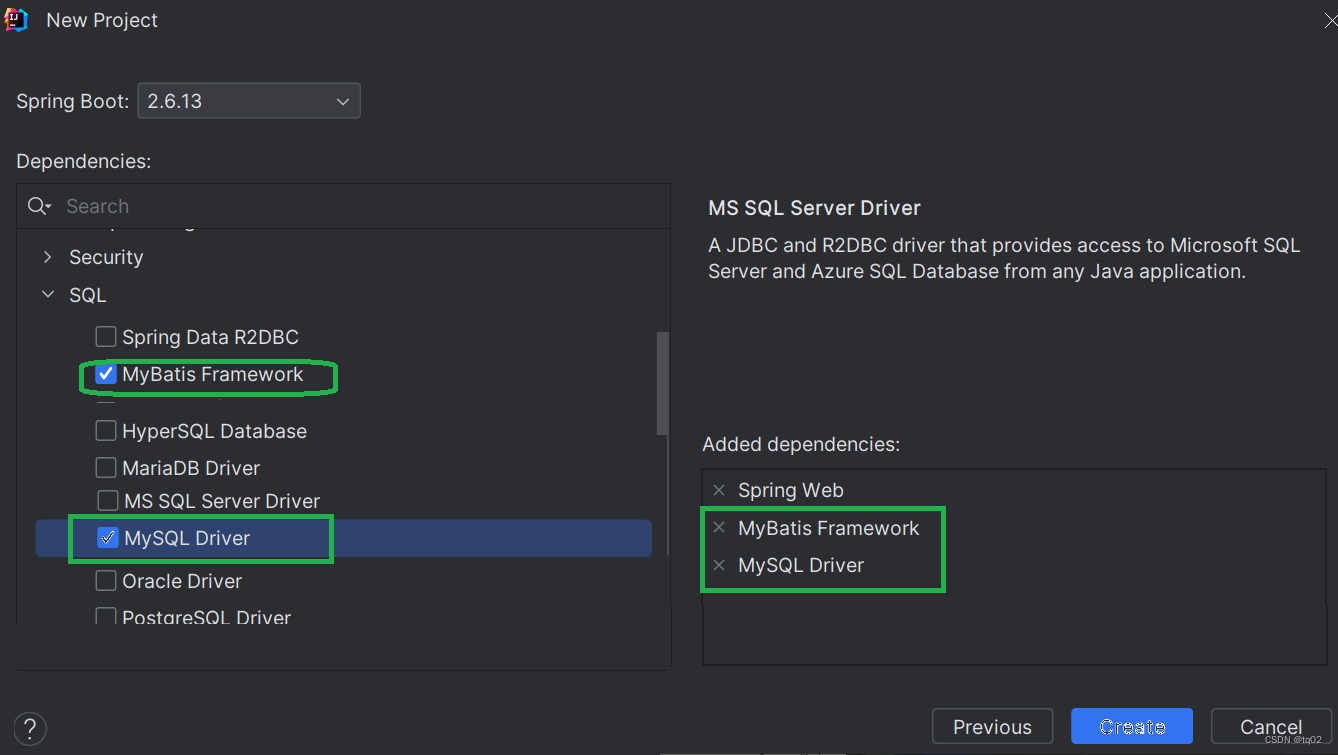
问:或许有人问,我都添加了MyBatis依赖,我为什么还要添加MySql驱动呢?
答:MyBatis只是一个持久层框架,它本身并不包含数据库驱动,而是依赖于特定的数据库驱动来连接和操作数据库。MySQL数据库驱动是一个单独的库,它负责与MySQL数据库建立连接、执行SQL语句等数据库操作。因此,你需要将MySQL数据库驱动添加到项目的依赖中,以便MyBatis能够使用它来与MySQL数据库进行交互。
第二步:创建数据库 名MyBatis,在其中搞一个表
create database MyBatis DEFAULT CHARACTER SET utf8mb4;
-- 使⽤数据数据
use mycnblog;
-- 创建表[⽤户表]
drop table if exists userinfo;
create table userinfo(id int primary key auto_increment,username varchar(100) not null,password varchar(32) not null,photo varchar(500) default '',createtime datetime default now(),updatetime datetime default now(),`state` int default 1
) default charset 'utf8mb4';自己插入一系列数据:

第三步:配置好数据库连接的yml文件和MyBatis的xml路径
spring:datasource:url: jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/库名?characterEncoding=utf8&useSSL=falseusername: rootpassword: 密码driver-class-name: com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver# 配置 mybatis xml 的⽂件路径,在 resources/mapper 创建所有表的 xml ⽂件
mybatis:mapper-locations: classpath:mapper/**Mapper.xml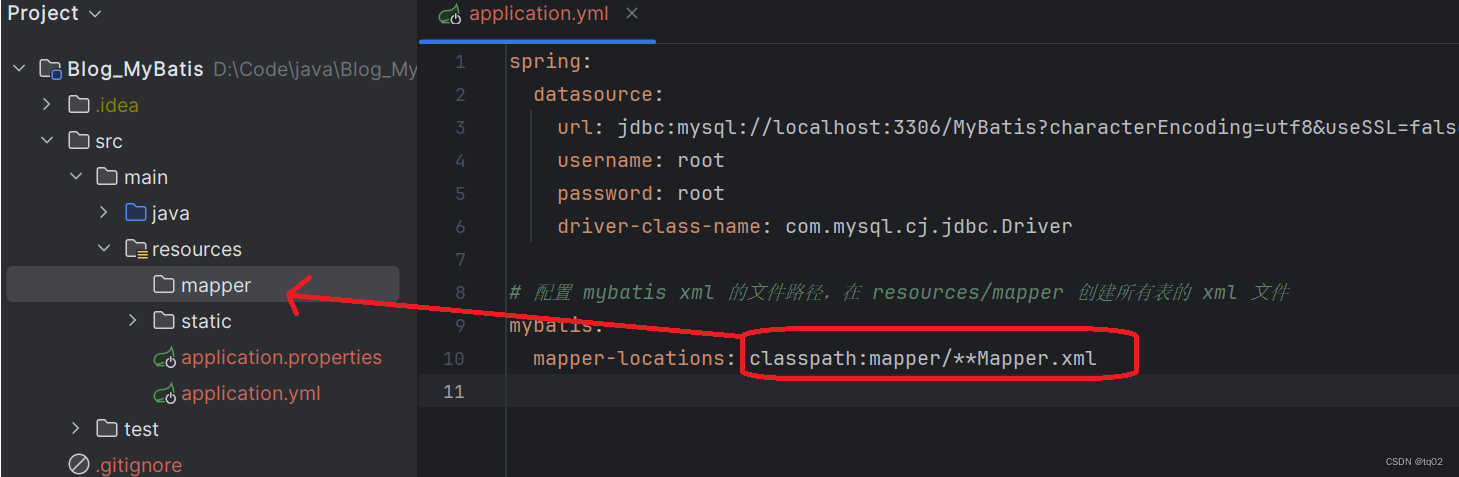
解析:设置MyBatis的xml路径,是为了告诉MyBatis去指定的位置寻找mapper文件,以便读取其中的SQL语句和映射配置
第四步:添加实体类
添加的实体类当中的属性需要和我们创建的表字段名一致,这是一致性!
import lombok.Data;
import java.util.Date;
@Data
public class User {private Integer id;private String username;private String password;private String photo;private Date createTime;private Date updateTime;
}第五步:添加mapper接口
数据持久层的接口定义:
import org.apache.ibatis.annotations.Mapper;
import java.util.List;
@Mapper
public interface UserMapper {public List<User> getAll();
}第六步:添加UserMapper.xml
如果想要实现数据持久层的,我们需要添加一个Mapper的xml格式!
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<!DOCTYPE mapper PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Mapper 3.0//EN" "http://mybati
s.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd">
<mapper namespace="com.example.demo.mapper.UserMapper"><select id="getAll" resultType="com.example.demo.model.User">select * from userinfo</select>
</mapper>详细说明:
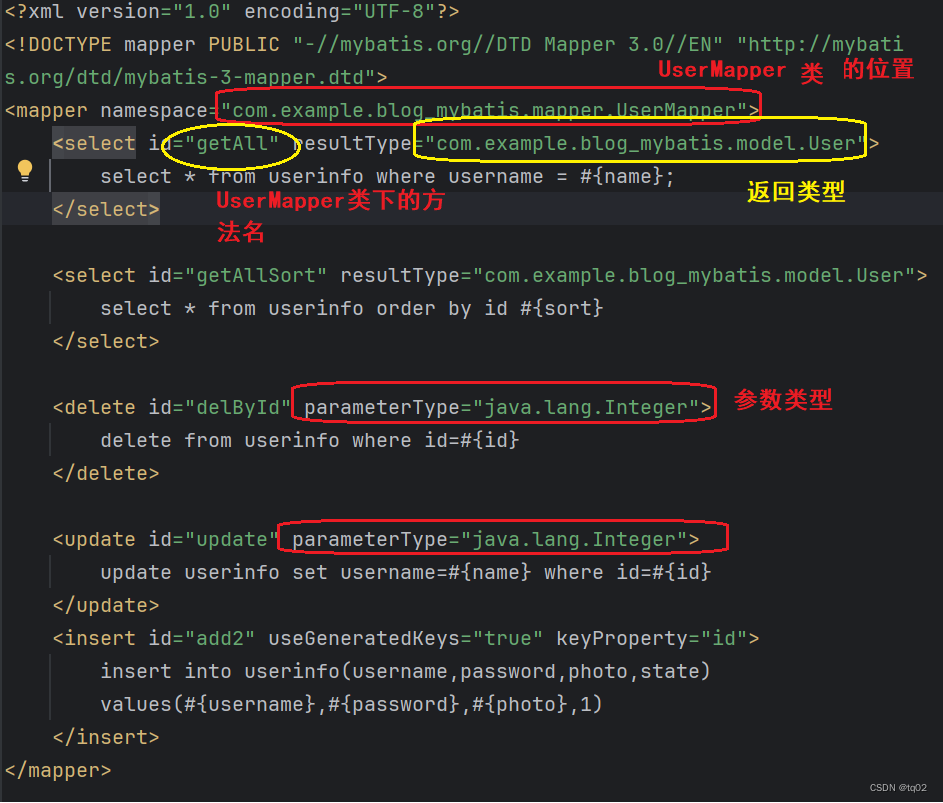
- <mapper>标签:需要指定 namespace 属性,表示命名空间,值为 mapper 接⼝的全限定 名,包括全包名.类名。
- <select>查询标签:是⽤来执⾏数据库的查询操作的:
- id:是和 Interface(接⼝)中定义的⽅法名称⼀样的,表示对接⼝的具体实现⽅法resultType:是返回的数据类型,也就是开头我们定义的实体类。
第五、六步化作一步的方法:
我们直接在Mapper接口上使用sql语句,执行调用。代码如下:
@Mapper
public interface UserMapper {@Select("select * from userinfo")public List<User> getAll();
}不需要配置文件,直接调用,然后就会执行该方法
第七步:添加Service
这一步是为了Controller层调用而使用
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import javax.annotation.Resource;
import java.util.List;
@Service
public class UserService {@Resourceprivate UserMapper userMapper;public List<User> getAll() {return userMapper.getAll();}
}第八步:Controller层不调用,直接进行测试代码
@SpringBootTest
class BlogMyBatisApplicationTests {@Autowiredprivate UserService userService;@Testvoid contextLoads() {List<User> t1= userService.getAll();for(User user: t1){System.out.println(user.toString());}}
}结果:

四.MyBatis的增删改操作
MyBatis要实现增加、删除和修改的操作,对应使⽤ MyBatis 的标签如下:
- <insert>标签:插⼊语句
- <update>标签:修改语句
- <delete>标签:删除语句
没有主键的插入代码:
<insert id="add2" useGeneratedKeys="true" keyProperty="id">insert into userinfo(username,password,photo,state)values(#{username},#{password},#{photo},1)
</insert>- useGeneratedKeys:这会令 MyBatis 使⽤ JDBC 的 getGeneratedKeys ⽅法来取出由数据 库内部生成的主键(比如:像 MySQL 和 SQL Server 这样的关系型数据库管理系统的自动递增字段),默认值:false。
- keyColumn:设置⽣成键值在表中的列名,在某些数据库(像 PostgreSQL)中,当主键列不是表中的第⼀列的时候,是必须设置的。如果生成列不止⼀个,可以⽤逗号分隔多个属性 名称。
- keyProperty:指定能够唯⼀识别对象的属性,MyBatis 会使⽤ getGeneratedKeys 的返回值或 insert 语句的 selectKey ⼦元素设置它的值,默认值:未设置(unset)。如果生成列不止⼀个,可以⽤逗号分隔多个属性名称。
修改操作:
<update id="update">update userinfo set username=#{name} where id=#{id}
</update>删除操作:
<delete id="delById" parameterType="java.lang.Integer">delete from userinfo where id=#{id}
</delete>parameterType:表示的是删除的行数。
五.参数占位符 #{} 和 ${}
在增删查找里,我们可以发现我们使用了#{} 或者 ${},那么两者之间的区别?
或许你看不懂,但是我直接举例几种常见的情况:
情况一:使用${}的情况下,字符串会变成单引号:
UserMapper接口:
@Mapper
public interface UserMapper {User get(String name);
}Service服务层:
@Service
public class UserService {@Resourceprivate UserMapper userMapper;public User get(String name) {return userMapper.get(name);}
}配置文件:

测试方法:
@Autowiredprivate UserService userService;@Testvoid contextLoads() {String name = "tq02";User t1= userService.get(name);System.out.println(t1.toString());}测试结果:
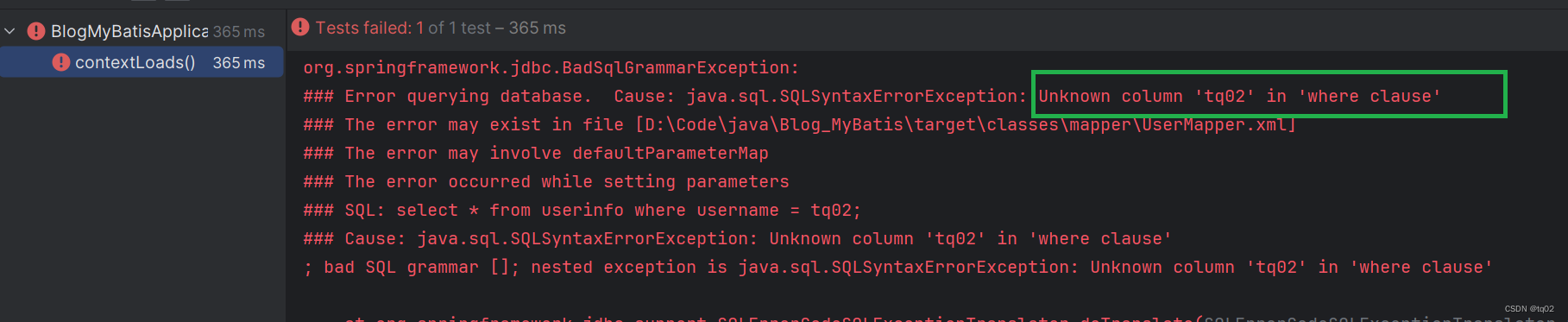 解析:获取tq02字符串时,实际获取的是 'tq02' ,而不是tq02.想要避免这种情况,从配置文件入手,在${name}上,添加一个单引号:
解析:获取tq02字符串时,实际获取的是 'tq02' ,而不是tq02.想要避免这种情况,从配置文件入手,在${name}上,添加一个单引号:
<select id="get" resultType="com.example.blog_mybatis.model.User">select * from userinfo where username = '${name}';</select>情况二:使用${}的情况下,却不传递任何值
配置文件:
<select id="getAllBySort" parameterType="java.lang.String" resultType="com.
example.demo.model.User">select * from userinfo order by id ${sort}
</select>Mapper接口:
@Mapper
public interface UserMapper {void getAllBySor();
}编译结果:
当 ${sort} 没有传递数据时,MyBatis 会将 ${sort} 原封不动地插入到 SQL 查询语句中,导致最终执行的 SQL 查询语句:select * from userinfo order by id
情况三:使用${}的情况下,却乱传递值
配置文件 UserMapper.xml:
<select id="getUsersByCondition" resultType="User">SELECT * FROM user WHERE name = '${name}'
</select>接口还是第一种的方式,但是我传递的值如果是 tq03' or '1' = '1 呢?
你会发现返回值不再是一个User类,而是表的全部结果,因为 or '1' = '1 ' 总是为真
而这种情况就是SQL 注入攻击
情况四:使用#{}的情况下,传递值为String类型
和情况一,一样,只不过把#变成$。
你会发现,会正常运行,返回数据。
情况五:使用${}的情况下,不传递值

会报错,sql语句会显示?
情况五:使用#{}的情况下,胡乱传递
与情况三的操作一致,只不过唯一的区别是,$变为了# ,就会变成:
SELECT * FROM userinfo WHERE username = 'tq02\' OR \'1\'=\'1'
这种情况下\’会变成空字符:也就是后半部分为:username = ' tq02' OR 1'=1' '
在传统的 SQL 查询中,通常使用单引号 ' 来表示字符串的开始和结束因此,如果在字符串中需要包含单引号本身,需要使用转义字符
\来转义,表示单引号不是字符串的结束,而是字符串的一部分。
表中数据存在时:

只不过在数据库查询时,我们不能直接使用单引号,我们需要转义字符 \’
情况六:使用#{}的情况下,模糊查询 like
like查询不能直接使用 #{}
<select id="findUserByName2" resultType="com.example.demo.model.User">select * from userinfo where username like '%#{username}%';</select>相当于:
sql语句:select * from userinfo where username like '%'username'%';
这种情况也不能使用${}的,我们需要使用内置函数concat() 来处理,
<select id="findUserByName3" resultType="com.example.demo.model.User">select * from userinfo where username like concat('%',#{usernam
e},'%');
</select>六.映射返回
1.增、删、改返回的是影响的行数,但是在mapper.xml 中是可以不设置返回的类型。但如果是数据,例如是String类型的数据,不返回就报错!
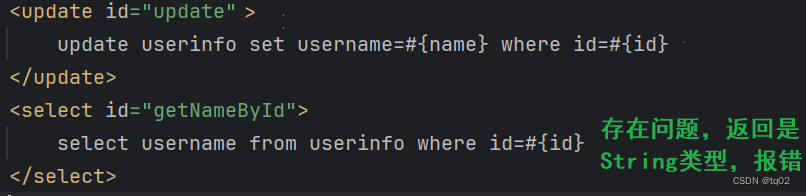
正确情况下,使用resultType:
<select id="getNameById" resultType="java.lang.String">select username from userinfo where id=#{id}
</select>2.parameterType和resultType:
parameterType可以来明确指定传递的参数类型,但是简单情况下,可以不设置,MyBatis 会尝试根据传递的参数来推断参数类型,然后将参数传递给 SQL 语句。
特殊情况下:
<update id="update" parameterType="java.lang.Integer">update userinfo set username=#{name} where id=#{id}</update>这种情况下,指定传递的参数类型为int,但是我的username却是String类型啊
解析:尽管 parameterType 被设置为 java.lang.Integer,但你仍然可以在 SQL 语句中引用其他类型的参数,只要参数名正确匹配即可。因此,设置 parameterType 的目的是为了提高代码的可读性和可维护性,以及防止类型不匹配或错误的结果发生。
ResultType用于指定查询结果的类型的属性。在 MyBatis 中, ResultType 用于映射 SQL 查询的结果到 Java 对象或基本数据类型,和parameterType不一样,当需要返回值不为影响的行数时,必须写上去。
3.返回字典映射:resultMap
- 字段名称和程序中的属性名不同的情况,可使⽤ resultMap 配置映射;
- ⼀对⼀和⼀对多关系可以使⽤ resultMap 映射并查询数据。
我们的表中字段和数据库字段名不同:

而类中实际的属性:

对比发现:表中的password变成了pas,那我们进行查询时,这个属性是永远装到不表中的password数据,
此时此刻,我们为了让这个类和我们的数据表匹配,可以使用:resultMap
<resultMap id="BaseMap" type="com.example.demo.model.User"><id column="id" property="id"></id><result column="username" property="username"></result><result column="password" property="pwd"></result>
</resultMap>
此时此刻,我们查询就有了结果的。
一对一的表映射的情况
换句话,一对一的映射就是指,一个类和一张表对应,只不过,我们使用一些标签使其属性和字段名映射成功。
<resultMap id="BaseMap" type="com.example.demo.model.ArticleInfo"><id property="id" column="id"></id><result property="title" column="title"></result><result property="content" column="content"></result<result property="createtime" column="createtime"></result><result property="updatetime" column="updatetime"></result><result property="uid" column="uid"></result><result property="rcount" column="rcount"></result><result property="state" column="state"></result><association property="user"resultMap="com.example.demo.mapper.UserMapper.BaseMap"columnPrefix="u_"></association>
</resultMap><select id="getAll" resultMap="BaseMap">select a.*,u.* from articleinfo aleft join userinfo u on u.id=a.uid</select>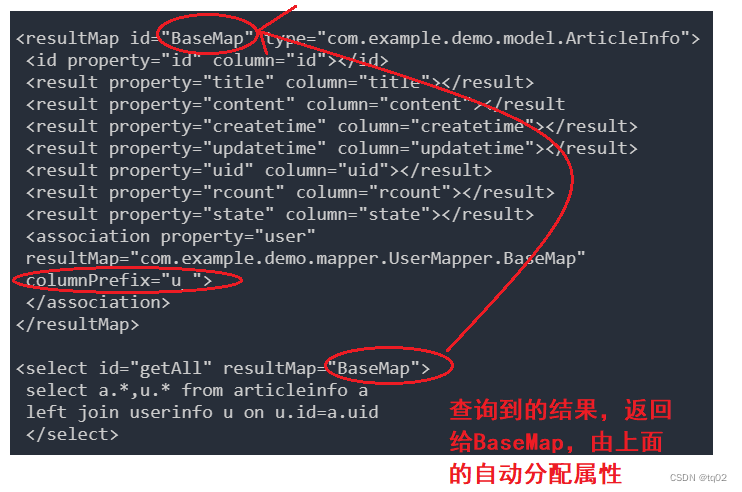
如上图,我们使用了<association>标签,表示⼀对⼀的结果映射:
- property 属性:指定 Article 中对应的属性,即⽤户。
- resultMap 属性:指定关联的结果集映射,将基于该映射配置来组织⽤户数据。
- columnPrefix 属性:指定了关联查询中,关联表(
userinfo表)的列名前缀,效果类似 as
注:columnPrefix 属性不能省略,原因:省略当联表中如果有相同的字段,那么就会导致查询出来的列名会有重复。重复情况下:
id列有2行,可见性差。
一对多的情况下:
一对多指的是一个类中有一个列表,而数据库却不能存在改字段:
例如:两个实体类 User 和 Article
public class User {private Long id;private String username;private List<Article> articles; // 用户拥有的文章列表,使用集合类型表示// 省略其他属性和方法
}public class Article {private Long id;private String title;private Long userId; // 文章所属用户的ID,用于关联查询// 省略其他属性和方法
}
假设你有两表,结构如下:
-
uer_info表包含用户信息:
- id
- username
-
article_info表包含文章信息:- id
- title
- user_id (对应用户表中的 id)

七.映射失败
当数据库的表名和属性不一致时,有三种解决方法:
- 起别名
- 结果映射 ,第6部分写了详细内容,这里再举其他方式
- 开启驼峰命名

起别名:
@Select("select id, username, 'password', age, gender, phone, delete_flag as del"create_time as createTime, update_time as updateTime from userinfo")public List<UserInfo> queryAllUser();结果映射:
@Select("select delete_flag, creat_time,update_time from userinfo)@Results({@Result(column = "delete_flag",property = "deleteFlag"),@Result(column = "create_time",property = "createTime"),@Result(column = "update_time",property = "updateTime")
})
List<UserInfo> queryAllUser();
colum:表示数据库的字段,porperty表示类的属性,
如果我查询很多语句,那我岂不是要重写很多段@Results注解?
便利方法: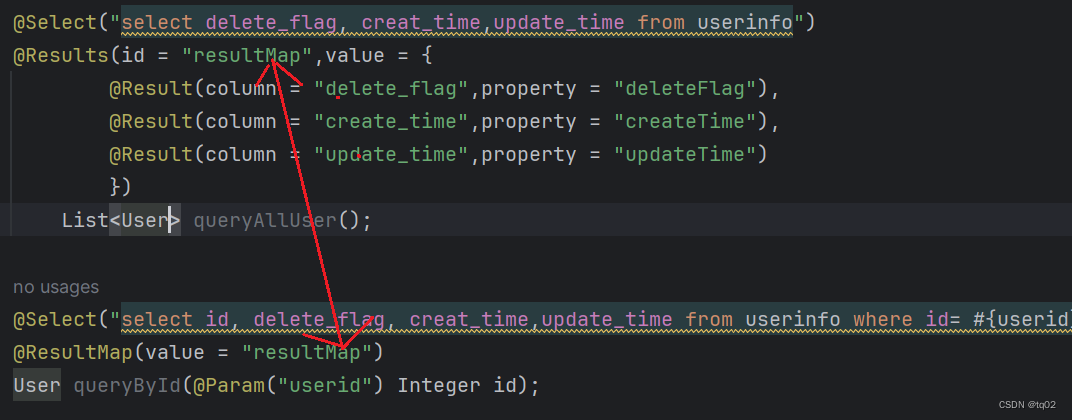
开启驼峰命名
数据库字段和类属性的不一致,原因:数据库列使⽤蛇形命名法进⾏命名(下划线分割各个单词), ⽽ Java 属性⼀般遵循驼峰命名法约定.
解决方法:为了在这两种命名⽅式之间启⽤⾃动映射,需要将 mapUnderscoreToCamelCase 设置为 true。
mybatis:configuration:map-underscore-to-camel-case: true #配置驼峰⾃动转换八.数据库连接池
连接池介绍: 数据库连接池负责分配、管理和释放数据库连接,它允许应⽤程序重复使⽤⼀个现有的数据库连接。⽽不是再重新建⽴⼀个(开销太大了)

在常见的连接池当中,我们常用的几种:
- C3P0
- DBCP
- Druid
- Hikari
在MyBatis当中,以及内置好了连接池,可以直接使用,而默认的是Hikari,证据如下:
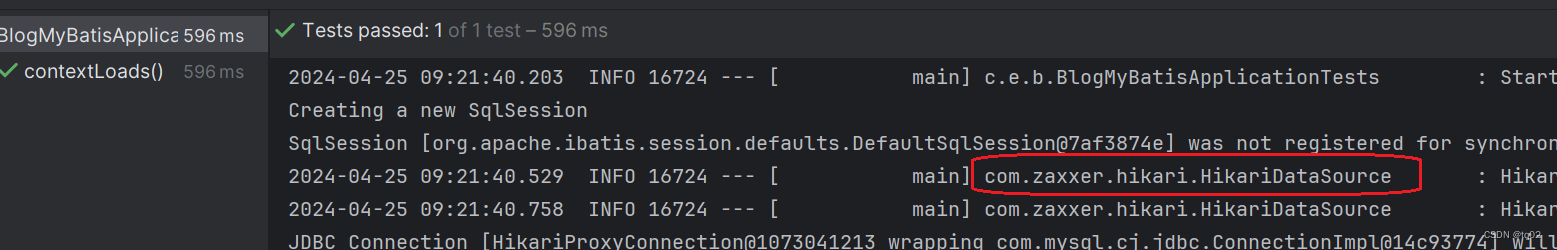
如果我们想使用其他连接池,可以通过加载对应的jar包。
九.动态SQL
动态 SQL 在 MyBatis 中的存在是为了处理那些需要在运行时根据条件动态生成的 SQL 语句。这种特性允许我们在一个映射文件中编写复杂的 SQL 查询,并根据不同的条件生成不同的 SQL 语句,而不需要写多个相似的 SQL 查询。
9.1<if>标签
例如,查询操作,当你查询某个人时,可以通过姓名、性别、年龄等查询,但查询时,我们难道应该写多个sql语句吗?进行分别查询吗?
nonono!
我们可以直接使用动态语句:
<select id="getUsers" parameterType="map" resultType="User">SELECT * FROM user_infowhere<if test="username != null">AND username = #{username}</if><if test="sex != null">AND sex = #{sex}</if><if test="age != null">AND age = #{age}</if>
</select>
<if> 标签根据传入的参数来动态生成 WHERE 子句,如果 username 和 sex和age 参数哪些存在,则会同时根据存在的条件查询用户信息。
9.2<trim>标签
和<if>标签搭配使用,当你查询或者插入某个人的信息时,如果没有可查询的信息或者插入,则不会使用trim标签:
<select id="getUsers" parameterType="map" resultType="User">SELECT * FROM user_info<trim prefix="WHERE" prefixOverrides="AND | OR" suffixOverrides="AND | OR"><if test="username != null">AND username = #{username}</if><if test="email != null">AND email = #{email}</if></trim>
</select>- prefix:表⽰整个语句块,以prefix的值作为前缀,如果数据存在,则添加在sql首部
- suffix:表⽰整个语句块,以suffix的值作为后缀,如果数据存在,则加入sql语句尾部
- prefixOverrides:表⽰整个语句块要去除掉的前缀,如果首部是约定的存在,则删除
- suffixOverrides:表⽰整个语句块要去除掉的后缀,如果尾部部是约定的存在,则删除
当username和email不存在时,sql语句就相当于:
SELECT * FROM user_info
当username不存在,email存在时,sql语句相当于:
SELECT * FROM user_info where email = #{email};
当username和email存在时,sql语句就相当于:
SELECT * FROM user_info where username = #{username} and email = #{email};
9.3<where>标签
和<trim>标签有异曲同工之妙,不过它只能限定where。
<select id="queryByCondition" resultType="com.example.demo.model.UserInfo">select id, username, age, gender, phone, delete_flag, create_time, update_tifrom userinfo<where><if test="age != null">and age = #{age}</if><if test="gender != null">and gender = #{gender}</if><if test="deleteFlag != null">and delete_flag = #{deleteFlag}</if></where>
</select>9.4<set>标签
<set>就是sql语句当中的修改update当中的set
<update id="updateUserByCondition">update userinfo<set><if test="username != null">username = #{username},</if><if test="age != null">age = #{age},</if><if test="deleteFlag != null">delete_flag = #{deleteFlag},</if></set>where id = #{id}
</update>9.5<foreach>标签
- collection:绑定⽅法参数中的集合,如 List,Set,Map或数组对象
- item:遍历时的每⼀个对象
- open:语句块开头的字符串
- close:语句块结束的字符串
- separator:每次遍历之间间隔的字符串
接口方法:
void deleteByIds(List<Integer> ids);<delete id="deleteByIds">delete from userinfowhere id in<foreach collection="ids" item="id" separator="," open="(" close=")">#{id}</foreach>
</delete>通过这种方式,可以动态生成一个类似于 DELETE FROM userinfo WHERE id IN (id1, id2, id3) 的 SQL 语句。
9.6<include>标签
在sql语句当中,不同的语句,但是会有大量冗余的代码,例如:我们查询所有用户信息、查询指定用户信息、查询条件用户信息,但是他们查询的字段名都是一样的,那么我们能不能简便一点呢?
<select id="queryAllUser" resultMap="BaseMap">
select id, username, age, gender, phone, delete_flag, create_time, update_time
from userinfo
</select>
<select id="queryById" resultType="com.example.demo.model.UserInfo">
select id, username, age, gender, phone, delete_flag, create_time, update_time
from userinfo where id= #{id}</select>
<select id="queryByCondition" resultType="com.example.demo.model.UserInfo">
select id, username, age, gender, phone, delete_flag, create_time, update_time from userinfo where id = #{id} and age >18;
解决方法:
抽取重复代码片段,通过<sql>标签封装到SQL片段,再使用<include>标签引用。
- <sql> :定义可重⽤的SQL⽚段
- <include> :通过属性refid,指定包含的SQL⽚段
<sql id="allColumn">id, username, age, gender, phone, delete_flag, create_time, update_time
</sql><select id="queryAllUser" resultMap="BaseMap">select<include refid="allColumn"></include>from userinfo</select>结尾小注:要动起你们的小手,敲哦!






)




)
)


,404,错误处理页面)
)
Linux环境安装ZLMediaKit实现视频推流)

