
目录
- 1.背景
- 2.算法原理
- 2.1算法思想
- 2.2算法过程
- 3.结果展示
- 4.参考文献
1.背景
2023年,VSDM Sahu等人受到霸王龙狩猎行为启发,提出了霸王龙优化算法(Tyrannosaurus Optimization Algorithm, TROA)。

2.算法原理
2.1算法思想
TROA模拟了霸王龙狩猎行为,主要分为:初始化、捕猎和选择。捕猎阶段模拟了霸王龙的狩猎行为,通过搜索空间寻找最优解。在选择阶段,根据预定的标准选择最佳解。
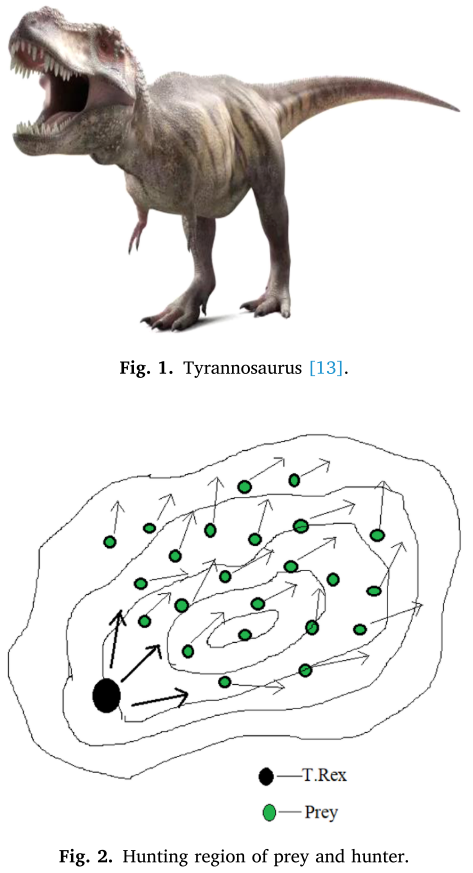
2.2算法过程
狩猎和追逐
霸王龙看到离它最近的猎物时,它会试图捕猎。有时是为了保护自己不被捕猎,有时是为了逃跑:
x n e w = { x n e w i f r a n d ( ) < E r Random e l s e } (1) x_{new}=\begin{Bmatrix}x_{new}&if&rand()<Er\\\text{Random}&else\end{Bmatrix}\tag{1} xnew={xnewRandomifelserand()<Er}(1)
其中,r为到达分散猎物的估计,即当霸王龙开始捕猎时,通过更新位置来捕猎猎物:
x n e w = x + r a n d ( ) ∗ s r ∗ ( t p o s ∗ t r − t a r g e t ∗ p r ) (2) x_{new}=x+rand()*sr*(tpos*tr-target*pr)\tag{2} xnew=x+rand()∗sr∗(tpos∗tr−target∗pr)(2)
sr为狩猎成功率,介于[0.1,1]之间。如果成功率为0,则表示猎物已经逃脱,狩猎失败,猎物位置必须相应地更新。
选择阶段
选择过程取决于猎物的位置,即目标猎物现在的位置和以前的位置:
X i k + 1 = { u p d a t e t h e t a r g e t p o s i t i o n i f f ( X ) < f ( X n e w ) t a r g e t i s z e r o o t h e r w i s e (3) \left.X_i^{k+1}=\left\{\begin{matrix}update\text{ }the\text{ }target\text{ }position&if&f(X)<f(X_{new})\\target\text{ }is\text{ }zero&otherwise\end{matrix}\right.\right.\tag{3} Xik+1={update the target positiontarget is zeroifotherwisef(X)<f(Xnew)(3)
伪代码

3.结果展示
使用测试框架,测试HGS性能 一键run.m
- 【智能算法】省时方便,智能算法统计指标——一键运行~
CEC2005-F7
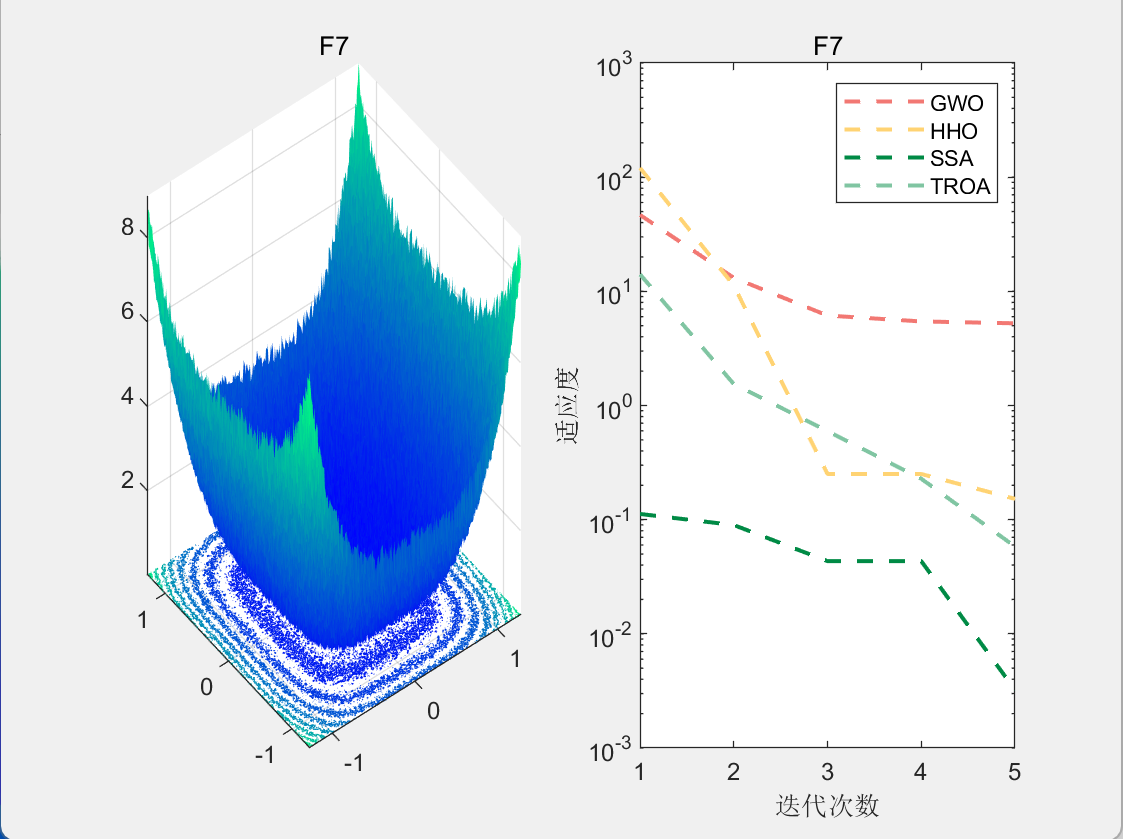
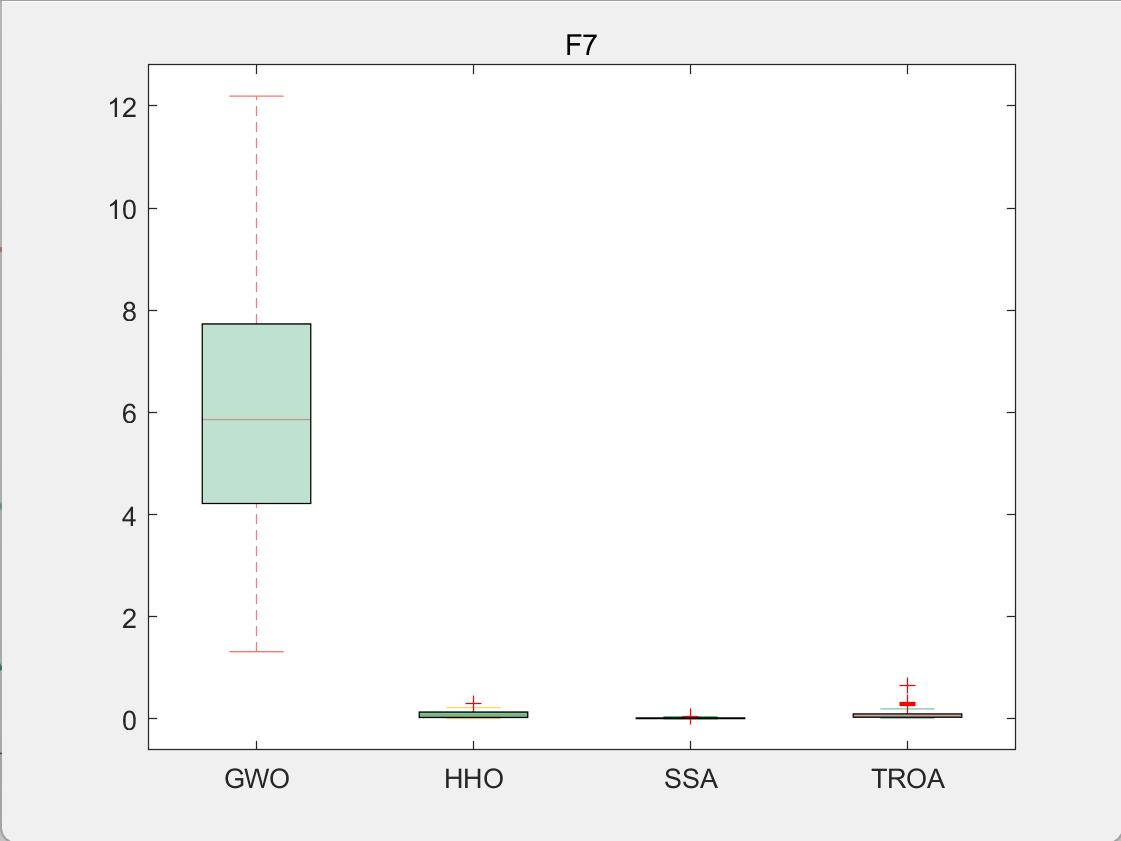

4.参考文献
[1] Sahu V S D M, Samal P, Panigrahi C K. Tyrannosaurus optimization algorithm: A new nature-inspired meta-heuristic algorithm for solving optimal control problems[J]. e-Prime-Advances in Electrical Engineering, Electronics and Energy, 2023, 5: 100243.

)







)






)


