❣博主主页: 33的博客❣
▶️文章专栏分类:数据结构◀️
🚚我的代码仓库: 33的代码仓库🚚
🫵🫵🫵关注我带你学更多数据结构知识

目录
- 1.前言
- 2.概念
- 3.队列的使用
- 4.循环队列
- 5.双端队列
- 6.经典习题
- 6.1队列实现栈
- 6.2栈实现队列
- 7.总结
1.前言
同学们排队等过车吧,最先去排队的人就是第一个出队上车的人。这就是日常生活中的队列。在数据结构中,队列也是这样的,最先进队的人最先出队,那我们就通过这篇文章来了解队列的详细知识点吧。
2.概念
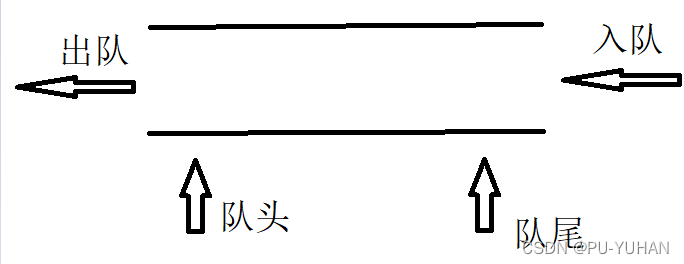
队列:只允许在一端进行插入数据操作,在另一端进行删除数据操作的特殊线性表,队列具有先进先出FIFO(First In First Out) 入队列:进行插入操作的一端称为队尾(Tail/Rear) 出队列:进行删除操作的一端称为队头(Head/Front)
3.队列的使用
在Java中,Queue是个接口,底层是通过链表实现的。

注意
Queue是个接口,在实例化时必须实例化LinkedList的对象,因为LinkedList实现了Queue接口。
public static void main(String[] args) {Queue<Integer> q = new LinkedList<>();q.offer(1);q.offer(2);q.offer(3);q.offer(4);q.offer(5); // 从队尾入队列System.out.println(q.size());System.out.println(q.peek()); // 获取队头元素q.poll();System.out.println(q.poll()); // 从队头出队列,并将删除的元素返回if(q.isEmpty()){System.out.println("队列空");}else{System.out.println(q.size());}}
4.循环队列
实际中我们有时还会使用一种队列叫循环队列。如操作系统课程讲解生产者消费者模型时可以就会使用循环队列。环形队列通常使用数组实现。
设计循环队列:
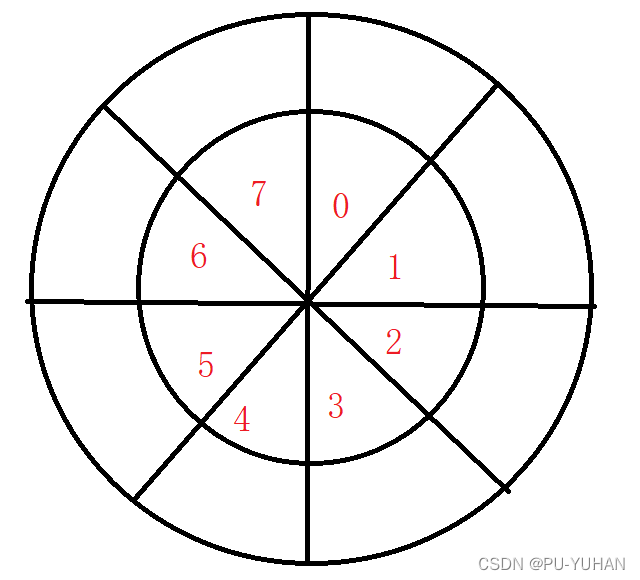
设计思路
1.首先要创建一个数组,我们再定义两个参数来确定环形数组的下个元素存放的下标end和第一个元素下标first。
2.当添加元素时,直接添加到end位置,end+1,但如果如上图,走到7的位置,那么end能直接+1吗?肯定是不行的,那么我们就可以把下一个下标定义为(end+1)%queue.length。
3.那么我们该如何判满和判空呢?我们通常认为如果end下标等于first下标就认为空,如果end是下一个元素的下标等于first元素下标,那么就认为队列满,这样判断我们就会浪费一个空间来,所以设置数组大小的时候为K+1
public class MyCircularQueue {int[] queue;int first=0;int end=0;MyCircularQueue(int k){queue=new int[k+1];}public int Front(){if(isEmpty()){return -1;}return queue[first];}public int Rear(){if (isEmpty()) {return -1;}if (end==0){return queue[queue.length-1];}else {return queue[end-1];}}public Boolean enQueue( int value){if(isFull()){return false;}queue[end]=value;end=(end+1)%queue.length;return true;}public Boolean deQueue(){if(isEmpty()){return false;}first=(first+1)%queue.length;return true;}public Boolean isEmpty(){if(first==end){return true;}else {return false;}}public Boolean isFull(){if((end+1)%queue.length==first){return true;} else {return false;}}
}
5.双端队列
***双端队列(deque)***是指允许两端都可以进行入队和出队操作的队列,deque 是 “double ended queue” 的简称。那就说明元素可以从队头出队和入队,也可以从队尾出队和入队。
Deque是一个接口,使用时必须创建LinkedList或者ArrayList的对象。
在实际工程中,使用Deque接口是比较多的,栈和队列均可以使用该接口。
Deque<Integer> stack = new ArrayDeque<>();//双端队列的线性实现
Deque<Integer> queue = new LinkedList<>();//双端队列的链式实现
6.经典习题
6.1队列实现栈
使用两个队列实现一个后入先出(LIFO)的栈:OJ链接
解题思路
插入元素的时候,哪一个队列不为空就插入哪一个队列
删除元素的时候,先把size-1个元素移到另外一个队列,再删除最会一个元素
易错点,不能定义stack.size()来表示从一个队列进入另一个队列的元素,因为size是一直在变的。
public class MyStack {public Queue<Integer> sq1;public Queue<Integer> sq2;public int size=0;public MyStack() {sq1=new LinkedList<>();sq2=new LinkedList<>();;}public void push(int x) {if(!sq1.isEmpty()){sq1.offer(x);}if(!sq2.isEmpty()){sq2.offer(x);}if(sq1.isEmpty()&&sq2.isEmpty()){sq1.offer(x);}size++;}public int pop() {if(!sq1.isEmpty()){for (int i=0;i<size-1;i++){int x= sq1.poll();sq2.offer(x);}size--;return sq1.poll();}else if(!sq2.isEmpty()){for (int i=0;i<size-1;i++){int x= sq2.poll();sq1.offer(x);}}size--;return sq2.poll();}public int top() {int x=-1;if(!sq1.isEmpty()){for (int i=0;i<size;i++){x= sq1.poll();sq2.offer(x);}}else if(!sq2.isEmpty()){for (int i=0;i<size;i++){x= sq2.poll();sq1.offer(x);}}return x;}public boolean empty() {return sq1.isEmpty()&&sq2.isEmpty();}}
6.2栈实现队列
请你仅使用两个栈实现先入先出队列:OJ链接
解题思路
定义两个栈s1,和s2,每次入队列存入s1中,每次出队列存入s2中。
当要出队列时,就把s1的元素依次出队,进入s2当中,s2再出队列
易错点,不能定义stack.size()来表示从s1进入s2的元素,因为s1的size是一直在变的。
class MyQueue {Stack<Integer> stack1;Stack<Integer> stack2;public MyQueue() {stack1=new Stack<>();stack2=new Stack<>();}public void push(int x) {stack1.push(x);}public int pop() {if(stack2.isEmpty()){while(!stack1.isEmpty()){stack2.push(stack1.pop());}} return stack2.pop();}public int peek() {if(stack2.isEmpty()){while(!stack1.isEmpty()){stack2.push(stack1.pop());}} return stack2.peek();}public boolean empty() {return stack2.isEmpty()&&stack1.isEmpty(); }
}
7.总结
本篇文章主要介绍了队列的使用,循环队列,双端队列,以及如何用队列实现栈,用栈实现队列。
下期预告:二叉树





:three.js简介)













