0. 引言
操作系统中与匿名页相对的是文件页,文件页的反向映射对比匿名页的反向映射更为简单。如果还不清楚匿名页反向映射逻辑的,请移步 匿名页反向映射
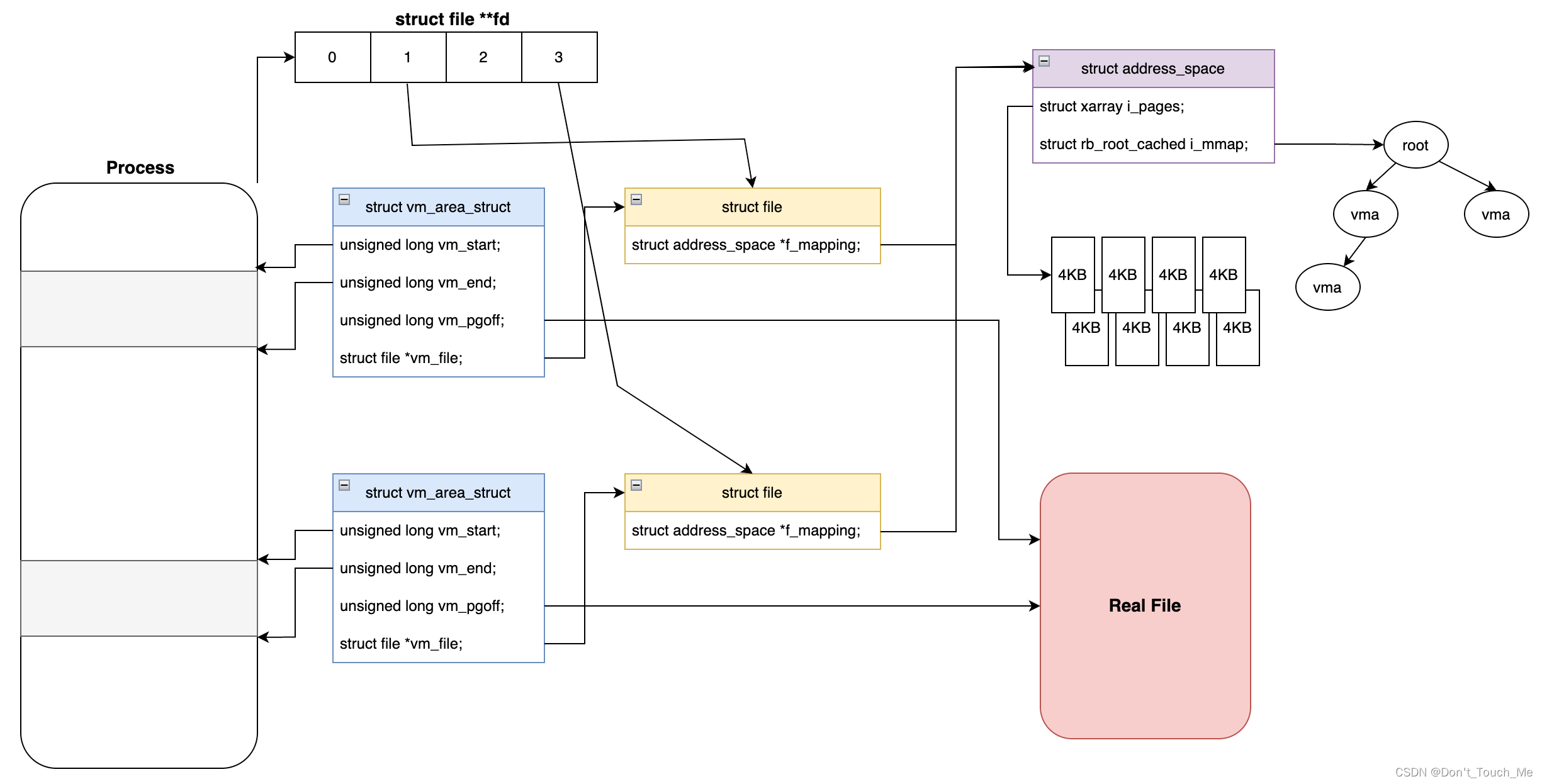
1. 文件页反向映射数据结构
struct file: 用户进程每open()一次文件,则会生成一个file对象,file->f_mapping指向该管理该文件页面对象
struct file {union {struct llist_node fu_llist;struct rcu_head fu_rcuhead;} f_u;struct path f_path;struct inode *f_inode; /* cached value */const struct file_operations *f_op;/** Protects f_ep_links, f_flags.* Must not be taken from IRQ context.*/spinlock_t f_lock;enum rw_hint f_write_hint;atomic_long_t f_count;unsigned int f_flags;fmode_t f_mode;struct mutex f_pos_lock;loff_t f_pos;struct fown_struct f_owner;const struct cred *f_cred;struct file_ra_state f_ra;u64 f_version;
#ifdef CONFIG_SECURITYvoid *f_security;
#endif/* needed for tty driver, and maybe others */void *private_data;#ifdef CONFIG_EPOLL/* Used by fs/eventpoll.c to link all the hooks to this file */struct list_head f_ep_links;struct list_head f_tfile_llink;
#endif /* #ifdef CONFIG_EPOLL */struct address_space *f_mapping; // 文件页缓冲区,文件页都放在该对象中进行管理errseq_t f_wb_err;errseq_t f_sb_err; /* for syncfs */
} __randomize_layout__attribute__((aligned(4))); /* lest something weird decides that 2 is OK */
struct address_space: 用来管理一个文件所有内容页面,一个真实的文件只对应一个address_space结构,其中address_space->i_pages是保存页面的结构,address_space->i_mmap是一个红黑树,红黑树上挂载着映射该文件的所有vma对象。
/*** struct address_space - Contents of a cacheable, mappable object.* @host: Owner, either the inode or the block_device.* @i_pages: Cached pages.* @gfp_mask: Memory allocation flags to use for allocating pages.* @i_mmap_writable: Number of VM_SHARED mappings.* @nr_thps: Number of THPs in the pagecache (non-shmem only).* @i_mmap: Tree of private and shared mappings.* @i_mmap_rwsem: Protects @i_mmap and @i_mmap_writable.* @nrpages: Number of page entries, protected by the i_pages lock.* @nrexceptional: Shadow or DAX entries, protected by the i_pages lock.* @writeback_index: Writeback starts here.* @a_ops: Methods.* @flags: Error bits and flags (AS_*).* @wb_err: The most recent error which has occurred.* @private_lock: For use by the owner of the address_space.* @private_list: For use by the owner of the address_space.* @private_data: For use by the owner of the address_space.*/
struct address_space {struct inode *host;struct xarray i_pages;gfp_t gfp_mask;atomic_t i_mmap_writable;
#ifdef CONFIG_READ_ONLY_THP_FOR_FS/* number of thp, only for non-shmem files */atomic_t nr_thps;
#endifstruct rb_root_cached i_mmap;struct rw_semaphore i_mmap_rwsem;unsigned long nrpages;unsigned long nrexceptional;pgoff_t writeback_index;const struct address_space_operations *a_ops;unsigned long flags;errseq_t wb_err;spinlock_t private_lock;struct list_head private_list;void *private_data;
} __attribute__((aligned(sizeof(long)))) __randomize_layout;
struct vm_area_struct: 用来描述用户进程的一段虚拟地址空间,其中vma->vm_start表示映射的起始虚拟地址,vma->vm_end表示映射的结束虚拟地址,vma->vm_file指向映射的文件对象,vma->vm_pgoff表示从文件哪里进行映射(以页面为单位)。
/** This struct describes a virtual memory area. There is one of these* per VM-area/task. A VM area is any part of the process virtual memory* space that has a special rule for the page-fault handlers (ie a shared* library, the executable area etc).*/
struct vm_area_struct {/* The first cache line has the info for VMA tree walking. */unsigned long vm_start; /* Our start address within vm_mm. */ // 映射的起始虚拟地址unsigned long vm_end; /* The first byte after our end addresswithin vm_mm. */ // 映射的结束虚拟地址/* linked list of VM areas per task, sorted by address */struct vm_area_struct *vm_next, *vm_prev;struct rb_node vm_rb;/** Largest free memory gap in bytes to the left of this VMA.* Either between this VMA and vma->vm_prev, or between one of the* VMAs below us in the VMA rbtree and its ->vm_prev. This helps* get_unmapped_area find a free area of the right size.*/unsigned long rb_subtree_gap;/* Second cache line starts here. */struct mm_struct *vm_mm; /* The address space we belong to. *//** Access permissions of this VMA.* See vmf_insert_mixed_prot() for discussion.*/pgprot_t vm_page_prot;unsigned long vm_flags; /* Flags, see mm.h. *//** For areas with an address space and backing store,* linkage into the address_space->i_mmap interval tree.*/struct {struct rb_node rb;unsigned long rb_subtree_last;} shared;/** A file's MAP_PRIVATE vma can be in both i_mmap tree and anon_vma* list, after a COW of one of the file pages. A MAP_SHARED vma* can only be in the i_mmap tree. An anonymous MAP_PRIVATE, stack* or brk vma (with NULL file) can only be in an anon_vma list.*/struct list_head anon_vma_chain; /* Serialized by mmap_lock &* page_table_lock */struct anon_vma *anon_vma; /* Serialized by page_table_lock *//* Function pointers to deal with this struct. */const struct vm_operations_struct *vm_ops;/* Information about our backing store: */unsigned long vm_pgoff; /* Offset (within vm_file) in PAGE_SIZEunits */ // 该vma从文件哪里开始映射,以页面为单位struct file * vm_file; /* File we map to (can be NULL). */ // 映射的文件对象void * vm_private_data; /* was vm_pte (shared mem) */#ifdef CONFIG_SWAPatomic_long_t swap_readahead_info;
#endif
#ifndef CONFIG_MMUstruct vm_region *vm_region; /* NOMMU mapping region */
#endif
#ifdef CONFIG_NUMAstruct mempolicy *vm_policy; /* NUMA policy for the VMA */
#endifstruct vm_userfaultfd_ctx vm_userfaultfd_ctx;
} __randomize_layout;
2. 数据结构关系图
3. 建立文件反向映射流程
我们都是通过一个path去打开一个文件,然后再通过mmap()去将文件映射到进程的虚拟地址空间,后续通过访存这块虚拟地址空间来达到读写文件的目的。
int fd = open("/path/to/your/file", O_RDWR | O_CREAT, S_IRUSR | S_IWUSR);
void *ptr = mmap(NULL, size, PROT_READ | PROT_WRITE, MAP_SHARED, fd, 0);
// do something
munmap(ptr, size);
close(fd);
现在让我们从mmap()映射文件描述符这里看起。
arm64体系结构下,且内核是linux-5.10版本:
SYSCALL_DEFINE6(mmap, unsigned long, addr, unsigned long, len,unsigned long, prot, unsigned long, flags,unsigned long, fd, unsigned long, off)
{if (offset_in_page(off) != 0)return -EINVAL;return ksys_mmap_pgoff(addr, len, prot, flags, fd, off >> PAGE_SHIFT);
}unsigned long ksys_mmap_pgoff(unsigned long addr, unsigned long len,unsigned long prot, unsigned long flags,unsigned long fd, unsigned long pgoff)
{struct file *file = NULL;unsigned long retval;if (!(flags & MAP_ANONYMOUS)) { // 由于我们传递的flags是不包含MAP_ANONYMOUS,所以会走到这个分支里audit_mmap_fd(fd, flags);file = fget(fd); // 根据fd获取struct file对象,并增加引用计数if (!file) // 如果该fd没有对应的struct file对象,则返回-EBADF错误return -EBADF;if (is_file_hugepages(file)) {len = ALIGN(len, huge_page_size(hstate_file(file)));} else if (unlikely(flags & MAP_HUGETLB)) {retval = -EINVAL;goto out_fput;}} else if (flags & MAP_HUGETLB) {struct user_struct *user = NULL;struct hstate *hs;hs = hstate_sizelog((flags >> MAP_HUGE_SHIFT) & MAP_HUGE_MASK);if (!hs)return -EINVAL;len = ALIGN(len, huge_page_size(hs));/** VM_NORESERVE is used because the reservations will be* taken when vm_ops->mmap() is called* A dummy user value is used because we are not locking* memory so no accounting is necessary*/file = hugetlb_file_setup(HUGETLB_ANON_FILE, len,VM_NORESERVE,&user, HUGETLB_ANONHUGE_INODE,(flags >> MAP_HUGE_SHIFT) & MAP_HUGE_MASK);if (IS_ERR(file))return PTR_ERR(file);}flags &= ~(MAP_EXECUTABLE | MAP_DENYWRITE);// 进入到vm_mmap_pgoff处理retval = vm_mmap_pgoff(file, addr, len, prot, flags, pgoff);
out_fput:if (file)fput(file);return retval;
}unsigned long vm_mmap_pgoff(struct file *file, unsigned long addr,unsigned long len, unsigned long prot,unsigned long flag, unsigned long pgoff)
{unsigned long ret;struct mm_struct *mm = current->mm;unsigned long populate;LIST_HEAD(uf);ret = security_mmap_file(file, prot, flag);if (!ret) {if (mmap_write_lock_killable(mm))return -EINTR;// 进入do_mmap处理ret = do_mmap(file, addr, len, prot, flag, pgoff, &populate,&uf);mmap_write_unlock(mm);userfaultfd_unmap_complete(mm, &uf);if (populate)mm_populate(ret, populate);}return ret;
}
接下来我们进入到映射主要处理函数do_mmap()。
/** The caller must write-lock current->mm->mmap_lock.*/
unsigned long do_mmap(struct file *file, unsigned long addr,unsigned long len, unsigned long prot,unsigned long flags, unsigned long pgoff,unsigned long *populate, struct list_head *uf)
{struct mm_struct *mm = current->mm;vm_flags_t vm_flags;int pkey = 0;*populate = 0;if (!len) // 如果要映射的空间大小为0,则返回-EINVALreturn -EINVAL;/** Does the application expect PROT_READ to imply PROT_EXEC?** (the exception is when the underlying filesystem is noexec* mounted, in which case we dont add PROT_EXEC.)*/if ((prot & PROT_READ) && (current->personality & READ_IMPLIES_EXEC))if (!(file && path_noexec(&file->f_path)))prot |= PROT_EXEC;/* force arch specific MAP_FIXED handling in get_unmapped_area */if (flags & MAP_FIXED_NOREPLACE)flags |= MAP_FIXED;if (!(flags & MAP_FIXED))addr = round_hint_to_min(addr);/* Careful about overflows.. */len = PAGE_ALIGN(len); // 按页粒度对齐要映射的空间大小if (!len)return -ENOMEM;/* offset overflow? */if ((pgoff + (len >> PAGE_SHIFT)) < pgoff)return -EOVERFLOW;/* Too many mappings? */if (mm->map_count > sysctl_max_map_count)return -ENOMEM;/* Obtain the address to map to. we verify (or select) it and ensure* that it represents a valid section of the address space.*/addr = get_unmapped_area(file, addr, len, pgoff, flags); // 找到一块未映射的虚拟地址if (IS_ERR_VALUE(addr))return addr;if (flags & MAP_FIXED_NOREPLACE) {struct vm_area_struct *vma = find_vma(mm, addr);if (vma && vma->vm_start < addr + len)return -EEXIST;}if (prot == PROT_EXEC) {pkey = execute_only_pkey(mm);if (pkey < 0)pkey = 0;}/* Do simple checking here so the lower-level routines won't have* to. we assume access permissions have been handled by the open* of the memory object, so we don't do any here.*/vm_flags = calc_vm_prot_bits(prot, pkey) | calc_vm_flag_bits(flags) |mm->def_flags | VM_MAYREAD | VM_MAYWRITE | VM_MAYEXEC;if (flags & MAP_LOCKED)if (!can_do_mlock())return -EPERM;if (mlock_future_check(mm, vm_flags, len))return -EAGAIN;if (file) {struct inode *inode = file_inode(file);unsigned long flags_mask;if (!file_mmap_ok(file, inode, pgoff, len))return -EOVERFLOW;flags_mask = LEGACY_MAP_MASK | file->f_op->mmap_supported_flags;switch (flags & MAP_TYPE) {case MAP_SHARED:/** Force use of MAP_SHARED_VALIDATE with non-legacy* flags. E.g. MAP_SYNC is dangerous to use with* MAP_SHARED as you don't know which consistency model* you will get. We silently ignore unsupported flags* with MAP_SHARED to preserve backward compatibility.*/flags &= LEGACY_MAP_MASK;fallthrough;case MAP_SHARED_VALIDATE:if (flags & ~flags_mask)return -EOPNOTSUPP;if (prot & PROT_WRITE) {if (!(file->f_mode & FMODE_WRITE))return -EACCES;if (IS_SWAPFILE(file->f_mapping->host))return -ETXTBSY;}/** Make sure we don't allow writing to an append-only* file..*/if (IS_APPEND(inode) && (file->f_mode & FMODE_WRITE))return -EACCES;/** Make sure there are no mandatory locks on the file.*/if (locks_verify_locked(file))return -EAGAIN;vm_flags |= VM_SHARED | VM_MAYSHARE;if (!(file->f_mode & FMODE_WRITE))vm_flags &= ~(VM_MAYWRITE | VM_SHARED);fallthrough;case MAP_PRIVATE:if (!(file->f_mode & FMODE_READ))return -EACCES;if (path_noexec(&file->f_path)) {if (vm_flags & VM_EXEC)return -EPERM;vm_flags &= ~VM_MAYEXEC;}if (!file->f_op->mmap)return -ENODEV;if (vm_flags & (VM_GROWSDOWN|VM_GROWSUP))return -EINVAL;break;default:return -EINVAL;}} else {switch (flags & MAP_TYPE) {case MAP_SHARED:if (vm_flags & (VM_GROWSDOWN|VM_GROWSUP))return -EINVAL;/** Ignore pgoff.*/pgoff = 0;vm_flags |= VM_SHARED | VM_MAYSHARE;break;case MAP_PRIVATE:/** Set pgoff according to addr for anon_vma.*/pgoff = addr >> PAGE_SHIFT;break;default:return -EINVAL;}}/** Set 'VM_NORESERVE' if we should not account for the* memory use of this mapping.*/if (flags & MAP_NORESERVE) {/* We honor MAP_NORESERVE if allowed to overcommit */if (sysctl_overcommit_memory != OVERCOMMIT_NEVER)vm_flags |= VM_NORESERVE;/* hugetlb applies strict overcommit unless MAP_NORESERVE */if (file && is_file_hugepages(file))vm_flags |= VM_NORESERVE;}// 进入mmap_region进行下一步处理addr = mmap_region(file, addr, len, vm_flags, pgoff, uf);if (!IS_ERR_VALUE(addr) &&((vm_flags & VM_LOCKED) ||(flags & (MAP_POPULATE | MAP_NONBLOCK)) == MAP_POPULATE))*populate = len;return addr;
}unsigned long mmap_region(struct file *file, unsigned long addr,unsigned long len, vm_flags_t vm_flags, unsigned long pgoff,struct list_head *uf)
{struct mm_struct *mm = current->mm;struct vm_area_struct *vma, *prev, *merge;int error;struct rb_node **rb_link, *rb_parent;unsigned long charged = 0;/* Check against address space limit. */if (!may_expand_vm(mm, vm_flags, len >> PAGE_SHIFT)) {unsigned long nr_pages;/** MAP_FIXED may remove pages of mappings that intersects with* requested mapping. Account for the pages it would unmap.*/nr_pages = count_vma_pages_range(mm, addr, addr + len);if (!may_expand_vm(mm, vm_flags,(len >> PAGE_SHIFT) - nr_pages))return -ENOMEM;}/* Clear old maps, set up prev, rb_link, rb_parent, and uf */if (munmap_vma_range(mm, addr, len, &prev, &rb_link, &rb_parent, uf))return -ENOMEM;/** Private writable mapping: check memory availability*/if (accountable_mapping(file, vm_flags)) {charged = len >> PAGE_SHIFT;if (security_vm_enough_memory_mm(mm, charged))return -ENOMEM;vm_flags |= VM_ACCOUNT;}/** Can we just expand an old mapping?*/vma = vma_merge(mm, prev, addr, addr + len, vm_flags,NULL, file, pgoff, NULL, NULL_VM_UFFD_CTX);if (vma)goto out;/** Determine the object being mapped and call the appropriate* specific mapper. the address has already been validated, but* not unmapped, but the maps are removed from the list.*/vma = vm_area_alloc(mm); // 分配一个新的vma管理结构对象if (!vma) {error = -ENOMEM;goto unacct_error;}vma->vm_start = addr; // 填充vma信息,vma的起始虚拟地址是addrvma->vm_end = addr + len; // vma的结束虚拟地址是addr + lenvma->vm_flags = vm_flags;vma->vm_page_prot = vm_get_page_prot(vm_flags);vma->vm_pgoff = pgoff; // vma的vm_pgoff保存的是相对于文件起始地址的偏移量,是以页为单位if (file) {if (vm_flags & VM_DENYWRITE) {error = deny_write_access(file);if (error)goto free_vma;}if (vm_flags & VM_SHARED) {error = mapping_map_writable(file->f_mapping);if (error)goto allow_write_and_free_vma;}/* ->mmap() can change vma->vm_file, but must guarantee that* vma_link() below can deny write-access if VM_DENYWRITE is set* and map writably if VM_SHARED is set. This usually means the* new file must not have been exposed to user-space, yet.*/vma->vm_file = get_file(file); // 再次增加struct file对象引用计数error = call_mmap(file, vma); // call_mmap()是为了填充vma->vm_ops,page fault时使用if (error)goto unmap_and_free_vma;/* Can addr have changed??** Answer: Yes, several device drivers can do it in their* f_op->mmap method. -DaveM* Bug: If addr is changed, prev, rb_link, rb_parent should* be updated for vma_link()*/WARN_ON_ONCE(addr != vma->vm_start);addr = vma->vm_start;/* If vm_flags changed after call_mmap(), we should try merge vma again* as we may succeed this time.*/if (unlikely(vm_flags != vma->vm_flags && prev)) {merge = vma_merge(mm, prev, vma->vm_start, vma->vm_end, vma->vm_flags,NULL, vma->vm_file, vma->vm_pgoff, NULL, NULL_VM_UFFD_CTX);if (merge) {/* ->mmap() can change vma->vm_file and fput the original file. So* fput the vma->vm_file here or we would add an extra fput for file* and cause general protection fault ultimately.*/fput(vma->vm_file);vm_area_free(vma);vma = merge;/* Update vm_flags to pick up the change. */vm_flags = vma->vm_flags;goto unmap_writable;}}vm_flags = vma->vm_flags;} else if (vm_flags & VM_SHARED) {error = shmem_zero_setup(vma);if (error)goto free_vma;} else {vma_set_anonymous(vma);}/* Allow architectures to sanity-check the vm_flags */if (!arch_validate_flags(vma->vm_flags)) {error = -EINVAL;if (file)goto unmap_and_free_vma;elsegoto free_vma;}// 建立页面映射vma_link(mm, vma, prev, rb_link, rb_parent);/* Once vma denies write, undo our temporary denial count */if (file) {
unmap_writable:if (vm_flags & VM_SHARED)mapping_unmap_writable(file->f_mapping);if (vm_flags & VM_DENYWRITE)allow_write_access(file);}file = vma->vm_file;
out:perf_event_mmap(vma);vm_stat_account(mm, vm_flags, len >> PAGE_SHIFT);if (vm_flags & VM_LOCKED) {if ((vm_flags & VM_SPECIAL) || vma_is_dax(vma) ||is_vm_hugetlb_page(vma) ||vma == get_gate_vma(current->mm))vma->vm_flags &= VM_LOCKED_CLEAR_MASK;elsemm->locked_vm += (len >> PAGE_SHIFT);}if (file)uprobe_mmap(vma);/** New (or expanded) vma always get soft dirty status.* Otherwise user-space soft-dirty page tracker won't* be able to distinguish situation when vma area unmapped,* then new mapped in-place (which must be aimed as* a completely new data area).*/vma->vm_flags |= VM_SOFTDIRTY;vma_set_page_prot(vma);return addr;unmap_and_free_vma:vma->vm_file = NULL;fput(file);/* Undo any partial mapping done by a device driver. */unmap_region(mm, vma, prev, vma->vm_start, vma->vm_end);charged = 0;if (vm_flags & VM_SHARED)mapping_unmap_writable(file->f_mapping);
allow_write_and_free_vma:if (vm_flags & VM_DENYWRITE)allow_write_access(file);
free_vma:vm_area_free(vma);
unacct_error:if (charged)vm_unacct_memory(charged);return error;
}
这里终于到了给文件页建立反向映射,主要处理函数是vma_link()。
static void vma_link(struct mm_struct *mm, struct vm_area_struct *vma,struct vm_area_struct *prev, struct rb_node **rb_link,struct rb_node *rb_parent)
{struct address_space *mapping = NULL;if (vma->vm_file) {mapping = vma->vm_file->f_mapping;i_mmap_lock_write(mapping);}// 将vma加到mm->mm_rb红黑树中,另外也加到mm->mmap vma链表中__vma_link(mm, vma, prev, rb_link, rb_parent);// 建立文件页反向映射__vma_link_file(vma);if (mapping)i_mmap_unlock_write(mapping);mm->map_count++;validate_mm(mm);
}static void __vma_link_file(struct vm_area_struct *vma)
{struct file *file;file = vma->vm_file;if (file) {// 获取文件的address_spacestruct address_space *mapping = file->f_mapping;if (vma->vm_flags & VM_DENYWRITE)put_write_access(file_inode(file));if (vma->vm_flags & VM_SHARED)mapping_allow_writable(mapping);flush_dcache_mmap_lock(mapping);// 将vma加入到address_space->i_mmap红黑树中vma_interval_tree_insert(vma, &mapping->i_mmap);flush_dcache_mmap_unlock(mapping);}
}
4. 回收文件页时使用反向映射
这里以kswapd进行文件页回收为例,与直接回收的路径下半部分是重合的(从shrink_node()函数开始)
kswapd()
-> balance_pgdat()
--> kswapd_shrink_node()
---> shrink_node()
----> shrink_node_memcgs()
-----> shrink_lruvec()
------> shrink_list()
-------> shrink_inactive_list()
--------> shrink_page_list()
---------> try_to_unmap()
在回收文件页的时候,需要使用到反向映射,所以我们来看一下**try_to_unmap()**对于文件页都做了哪些操作,
/*** try_to_unmap - try to remove all page table mappings to a page* @page: the page to get unmapped* @flags: action and flags** Tries to remove all the page table entries which are mapping this* page, used in the pageout path. Caller must hold the page lock.** If unmap is successful, return true. Otherwise, false.*/
bool try_to_unmap(struct page *page, enum ttu_flags flags)
{struct rmap_walk_control rwc = {.rmap_one = try_to_unmap_one,.arg = (void *)flags,.done = page_mapcount_is_zero,.anon_lock = page_lock_anon_vma_read,};/** During exec, a temporary VMA is setup and later moved.* The VMA is moved under the anon_vma lock but not the* page tables leading to a race where migration cannot* find the migration ptes. Rather than increasing the* locking requirements of exec(), migration skips* temporary VMAs until after exec() completes.*/if ((flags & (TTU_MIGRATION|TTU_SPLIT_FREEZE))&& !PageKsm(page) && PageAnon(page))rwc.invalid_vma = invalid_migration_vma;if (flags & TTU_RMAP_LOCKED)rmap_walk_locked(page, &rwc);else// 文件页走这里rmap_walk(page, &rwc);return !page_mapcount(page) ? true : false;
}void rmap_walk(struct page *page, struct rmap_walk_control *rwc)
{if (unlikely(PageKsm(page)))rmap_walk_ksm(page, rwc);else if (PageAnon(page))rmap_walk_anon(page, rwc, false);else// 文件页走这里rmap_walk_file(page, rwc, false);
}/** rmap_walk_file - do something to file page using the object-based rmap method* @page: the page to be handled* @rwc: control variable according to each walk type** Find all the mappings of a page using the mapping pointer and the vma chains* contained in the address_space struct it points to.** When called from try_to_munlock(), the mmap_lock of the mm containing the vma* where the page was found will be held for write. So, we won't recheck* vm_flags for that VMA. That should be OK, because that vma shouldn't be* LOCKED.*/
static void rmap_walk_file(struct page *page, struct rmap_walk_control *rwc,bool locked)
{struct address_space *mapping = page_mapping(page); // 获取到该page对应的映射pgoff_t pgoff_start, pgoff_end;struct vm_area_struct *vma;/** The page lock not only makes sure that page->mapping cannot* suddenly be NULLified by truncation, it makes sure that the* structure at mapping cannot be freed and reused yet,* so we can safely take mapping->i_mmap_rwsem.*/VM_BUG_ON_PAGE(!PageLocked(page), page);if (!mapping)return;pgoff_start = page_to_pgoff(page); // 这点忘记介绍了,可以通过page找到该page是映射到文件的哪个位置,便于找到该page在哪个vma中有映射pgoff_end = pgoff_start + thp_nr_pages(page) - 1;if (!locked)i_mmap_lock_read(mapping);vma_interval_tree_foreach(vma, &mapping->i_mmap, // 从address_space->i_mmap红黑树中查找映射了该page到vmapgoff_start, pgoff_end) {unsigned long address = vma_address(page, vma);cond_resched();if (rwc->invalid_vma && rwc->invalid_vma(vma, rwc->arg))continue;if (!rwc->rmap_one(page, vma, address, rwc->arg))goto done;if (rwc->done && rwc->done(page))goto done;}done:if (!locked)i_mmap_unlock_read(mapping);
}
至此文件页的反向映射处理和使用流程介绍完毕,感谢各位读者浏览!








)



)






