1. 移除链表元素
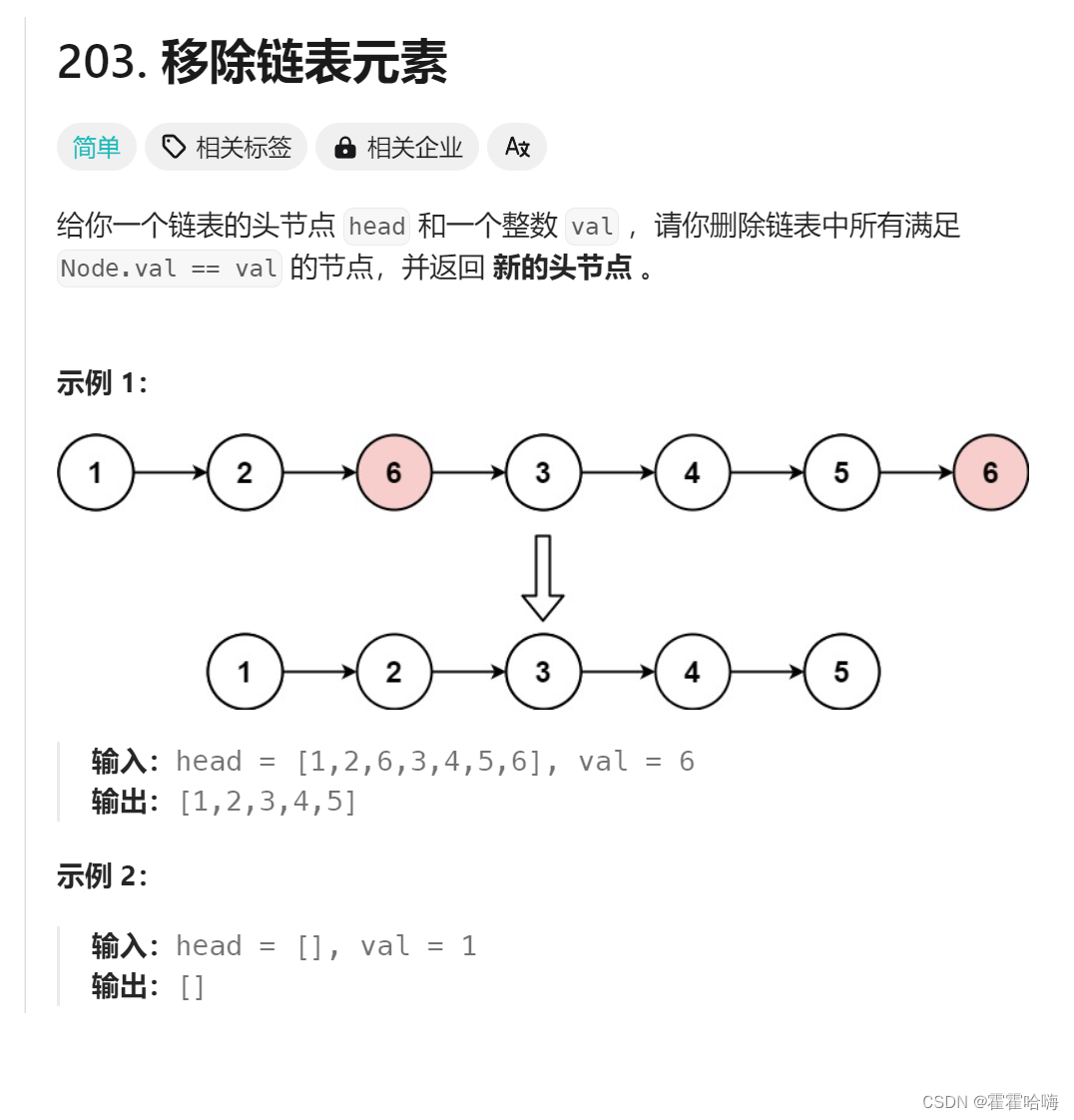
思路1:遍历原链表,将 val 所在的节点释放掉。(太麻烦)
思路2:创建新链表,再遍历原链表,找到不为 val 的节点尾插到新链表。

思路1代码实现如下:
注意:
1.当链表为空时,直接返回NULL即可。
2.当尾插上最后一个有效节点时,此时它的 next 可能还与最后一个节点相链接,一定要断开!
typedef struct ListNode ListNode;
struct ListNode* removeElements(struct ListNode* head, int val) {if (head == NULL)return NULL;//创建一个新链表ListNode* newHead, * newTail;newHead = newTail = NULL;ListNode* pcur = head;//遍历原链表,找不为val的节点尾插while (pcur){ListNode* next = pcur->next;if (pcur->val != val){//没有一个节点if (newHead == NULL){newHead = newTail = pcur;}else{//有一个节点以上newTail->next = pcur;newTail = newTail->next;}}pcur = next;}if (newTail)newTail->next = NULL;return newHead;}
2. 反转链表
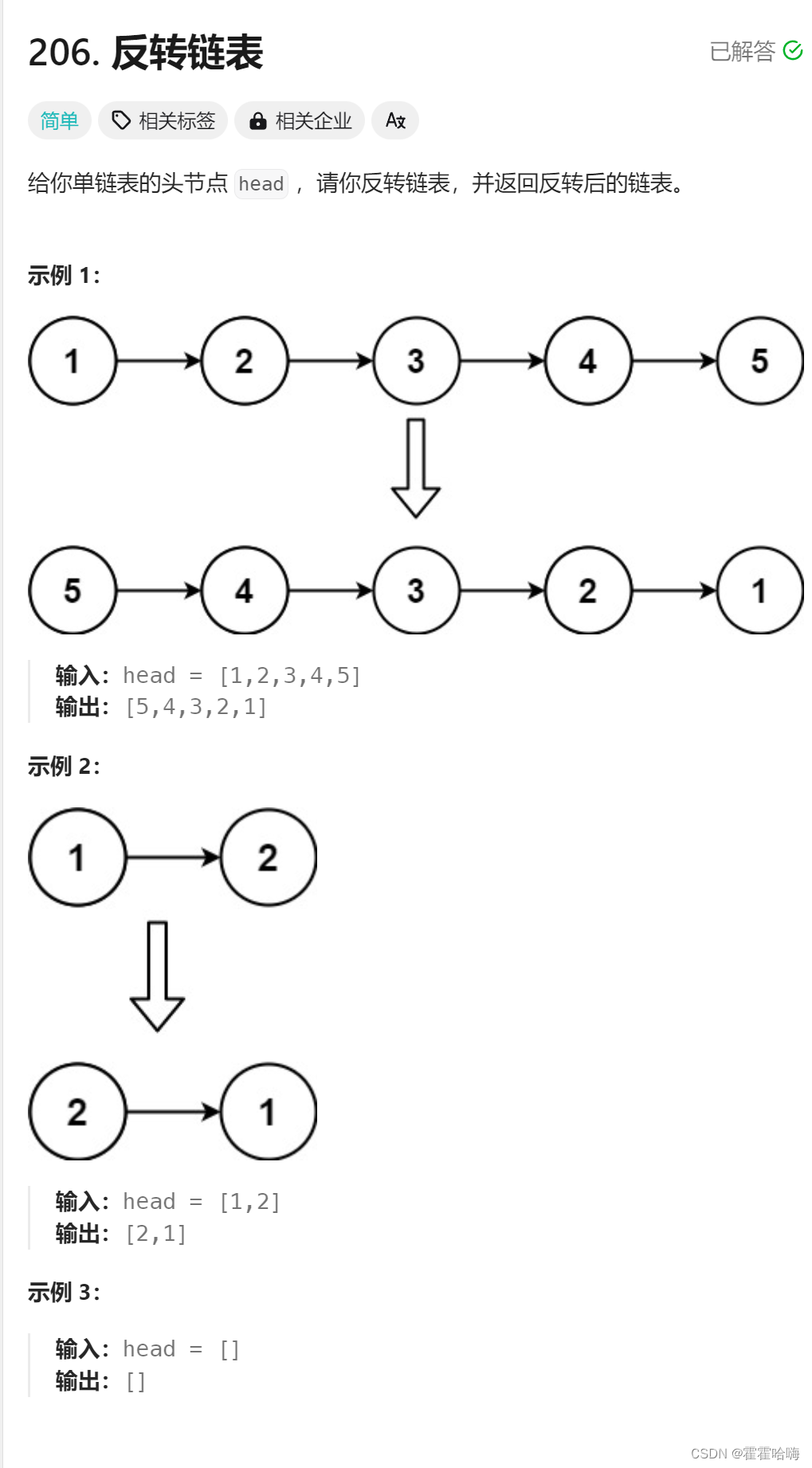
2.1反转指针法
思路:定义三个变量 n1,n2,n3,根据它们的指向关系进行迭代。
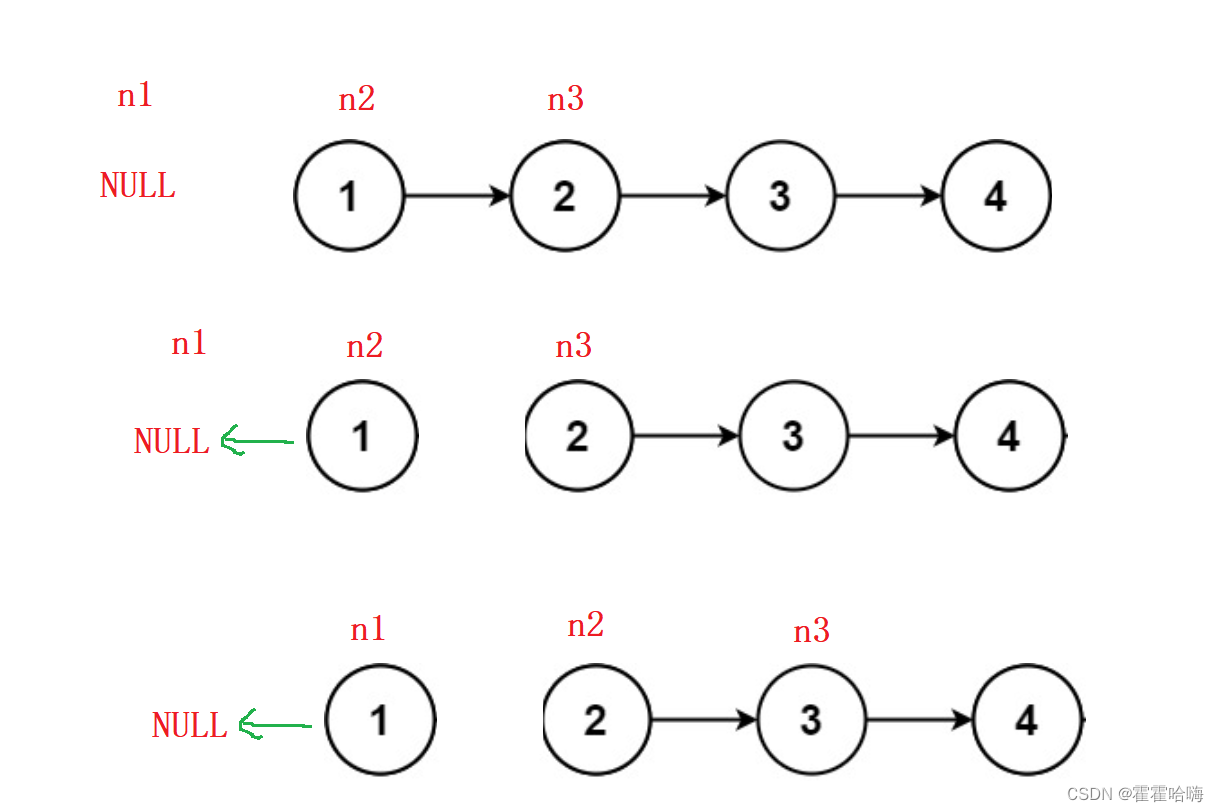
代码实现如下:
注意:
1.当链表为空时,直接返回NULL即可。
2.在迭代过程中别忘记判断 n3 ,防止对空指针解引用。
3.注意循环结束的条件,当 n2 为空时,n1 指向反转后的头,此时循环结束。
typedef struct ListNode ListNode;
struct ListNode* reverseList(struct ListNode* head) {if (head == NULL)return NULL;ListNode* n1, * n2, * n3;n1 = NULL, n2 = head, n3 = n2->next;while (n2){n2->next = n1;n1 = n2;n2 = n3;if (n3)n3 = n3->next;}return n1;
}
2.2 头插法
思路:创建一个新链表,遍历原链表,依次取下原链表的每一个节点头插到新链表中。
代码实现如下:
注意:
1.当链表为空时,直接返回NULL即可。
2.头插时可以不用判断没有节点和有节点的情况。
typedef struct ListNode ListNode;
struct ListNode* reverseList(struct ListNode* head) {if (head == NULL)return NULL;ListNode* newHead, * newTail;newHead = newTail = NULL;ListNode* pcur = head;//一个一个拿下来头插while (pcur){ListNode* next = pcur->next;pcur->next = newHead;newHead = pcur;pcur = next;}return newHead;
}
3. 合并两个有序链表
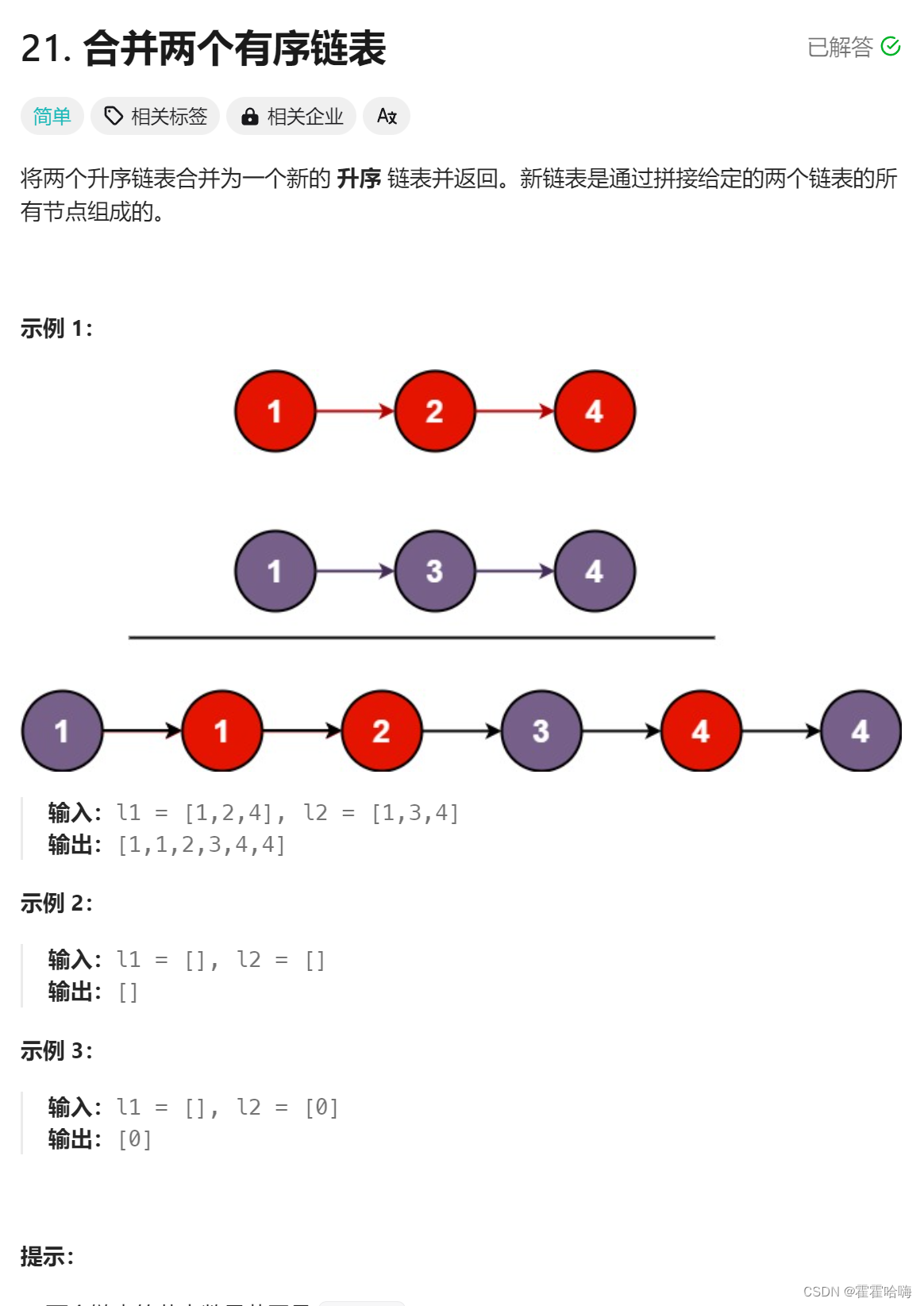
思路:创建一个带哨兵位的新链表,遍历两个原链表,比较两个节点的值,哪个小就先尾插到新链表中。
代码实现如下:
注意:
1.当其中一个链表为空时,返回另一个链表即可。
2.创建哨兵位节点,方便尾插。
3.注意循环结束条件,当其中有一个链表走完时,跳出循环。
4.剩下的没走完的那个链表直接链接到后面。不需要用循环链接,因为它们本来就是连在一起的。
5.别忘记释放释放哨兵位节点,释放前要保存下一个节点。
typedef struct ListNode ListNode;
struct ListNode* mergeTwoLists(struct ListNode* list1, struct ListNode* list2) {ListNode* n1, * n2;n1 = list1;n2 = list2;if (n1 == NULL)return n2;if (n2 == NULL)return n1;//创建哨兵位节点ListNode* phead = (ListNode*)malloc(sizeof(ListNode));ListNode* newHead, * newTail;newHead = newTail = phead;while (n1 && n2){//比较两个链表中数据的大小,谁小就先尾插到新链表if (n1->val < n2->val){newTail->next = n1;n1 = n1->next;newTail = newTail->next;}else{newTail->next = n2;n2 = n2->next;newTail = newTail->next;}}if (n1)newTail->next = n1;if (n2)newTail->next = n2;ListNode* ret = newHead->next;free(newHead);return ret;}
4. 分隔链表
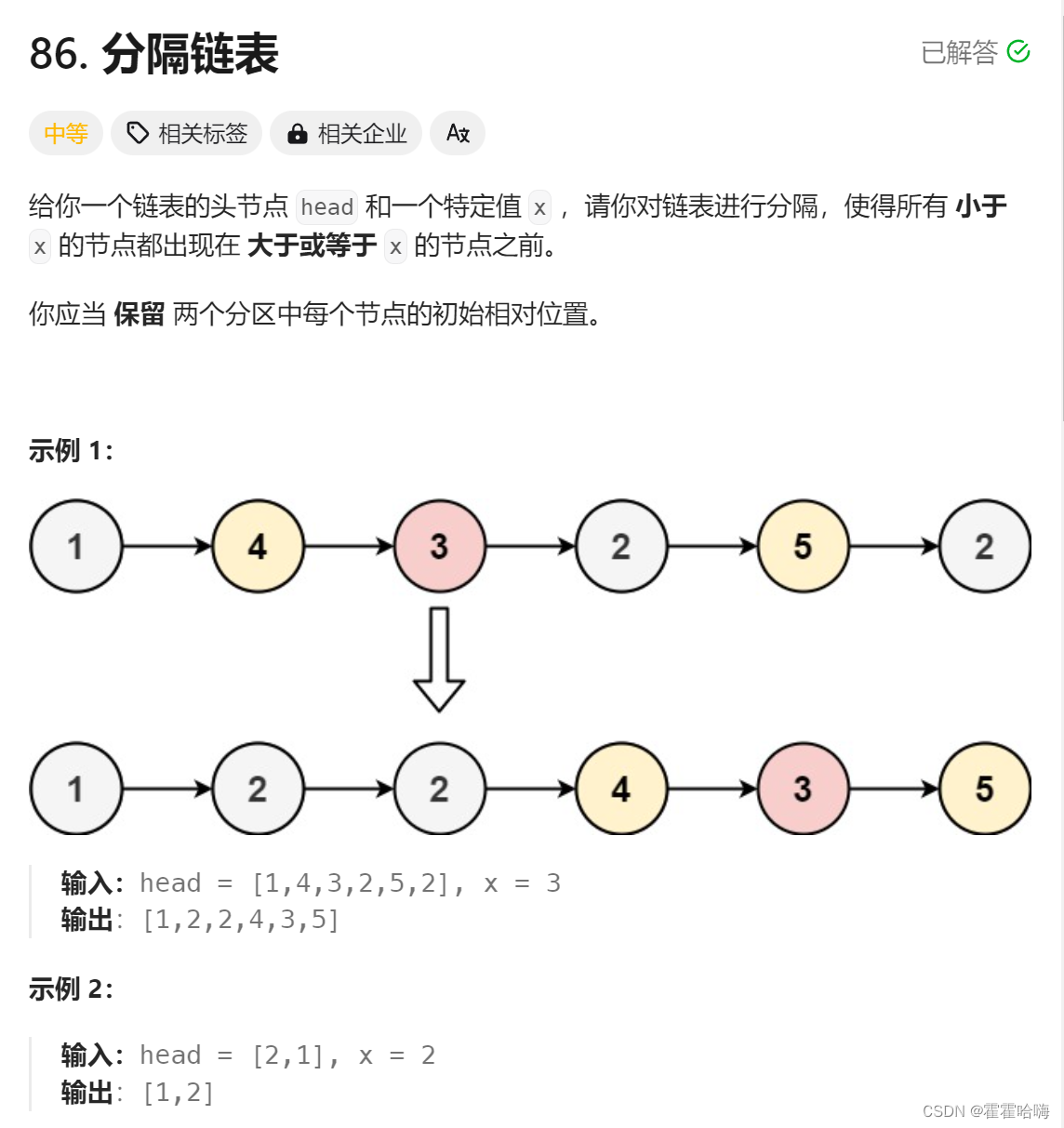
思路:创建两个带哨兵位的新链表 less 和 greater 。遍历原链表,把小于x 的节点尾插到 less 链表中,把大于等于x 的节点尾插到greater 链表中。最后把 less 链表中的尾结点的 next 链接到 greater链表中的头结点上。
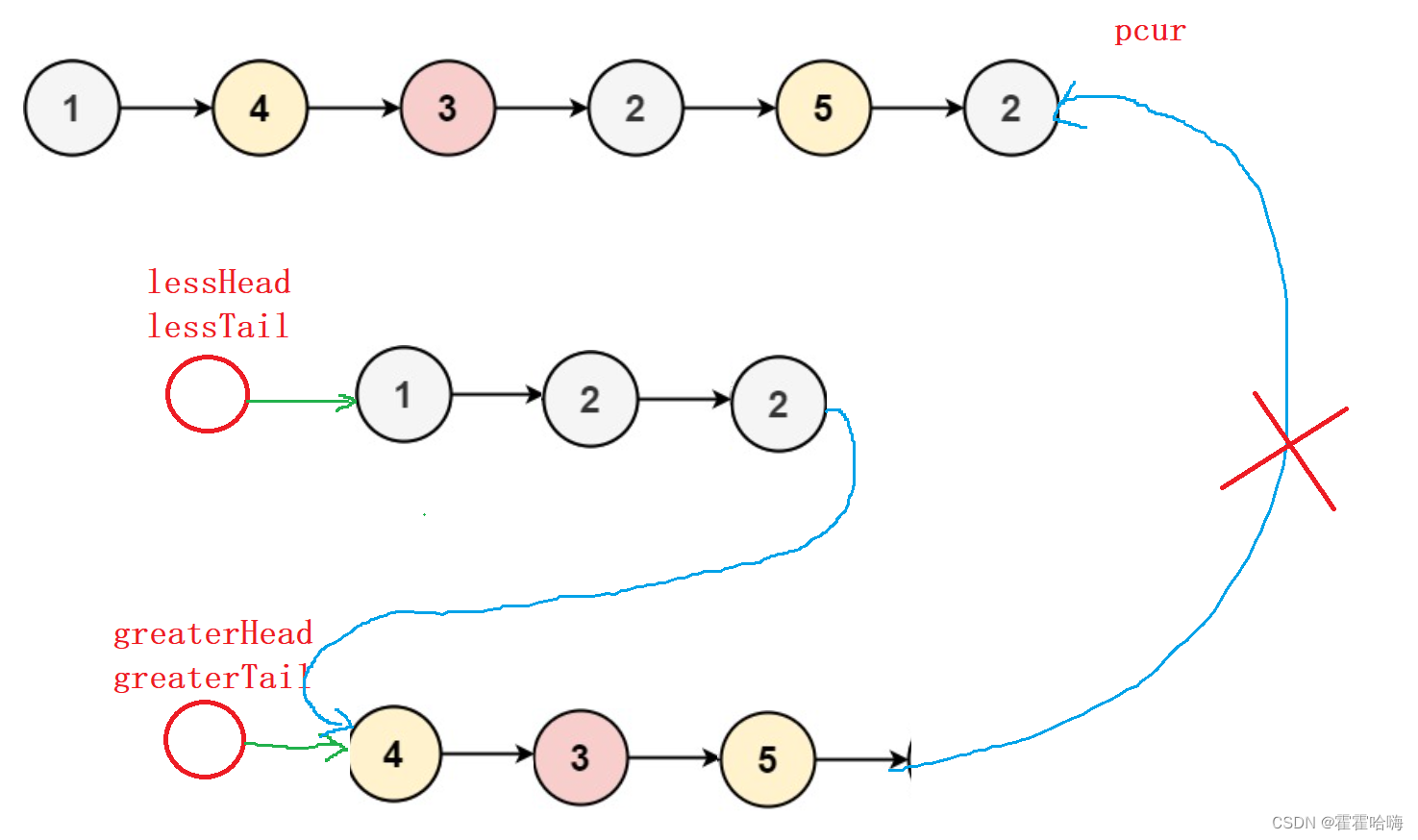
代码实现如下:
注意:
1.当链表尾空时,直接返回NULL即可。
2.有可能存在greater 链表中的最后一个结点与原链表中的最后一个结点仍然相链接的情况,一定要断开!
typedef struct ListNode ListNode;
struct ListNode* partition(struct ListNode* head, int x) {if (head == NULL)return NULL;ListNode* lessHead, * lessTail, * greaterHead, * greaterTail;ListNode* pcur = head;//创建哨兵位节点,方便尾插lessHead = lessTail = (ListNode*)malloc(sizeof(ListNode));greaterHead = greaterTail = (ListNode*)malloc(sizeof(ListNode));lessTail->next = NULL;greaterTail->next = NULL;while (pcur){if (pcur->val < x){lessTail->next = pcur;lessTail = lessTail->next;}else{greaterTail->next = pcur;greaterTail = greaterTail->next;}pcur = pcur->next;}lessTail->next = greaterHead->next;greaterTail->next = NULL;return lessHead->next;}
5. 环形链表
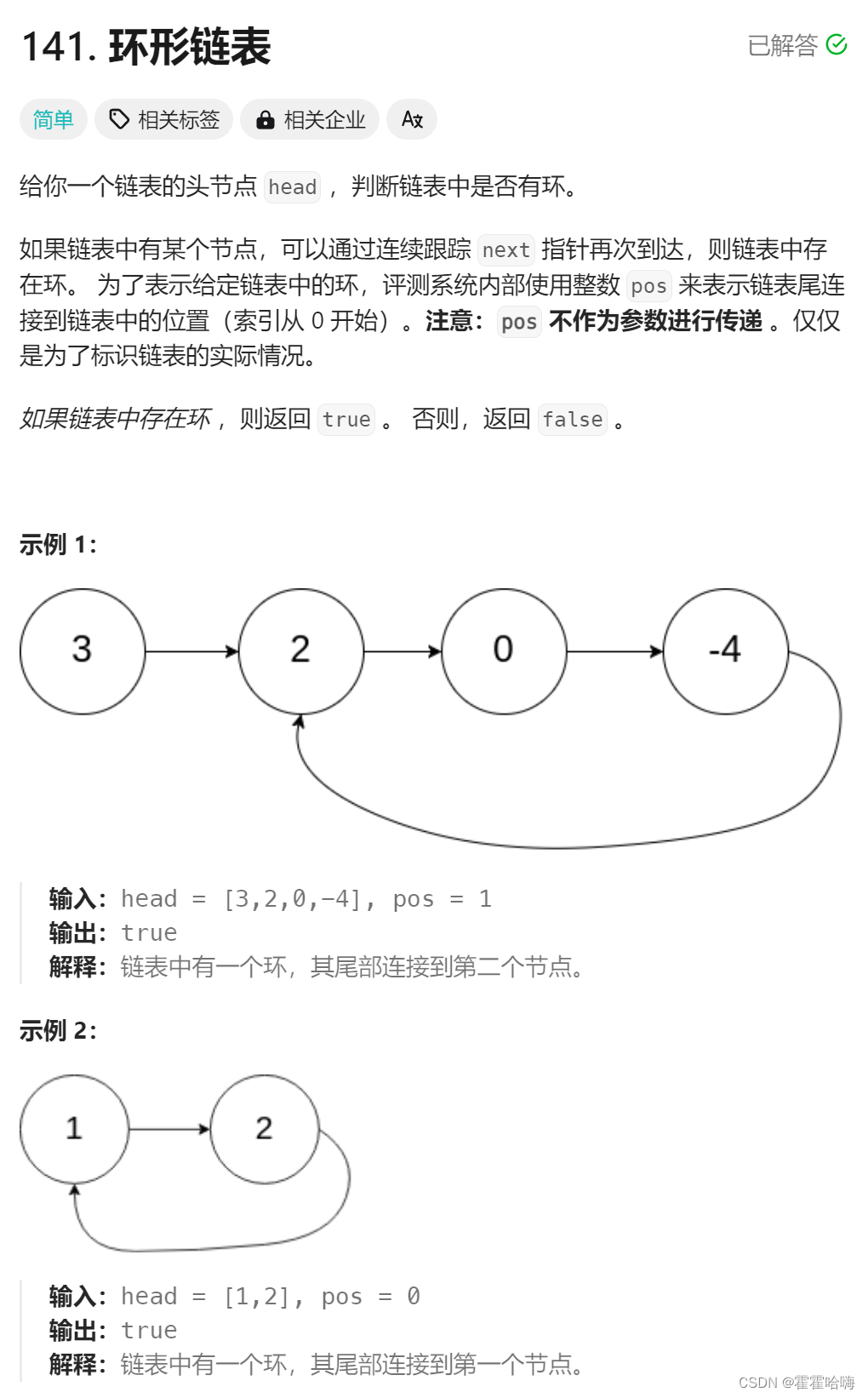
这是一个非常经典的例题,它要用上一种非常经典的算法:快慢指针法。
定义一个 slow 变量,fast 变量,从链表的头结点开始,slow 每次走一步,fast 每次走两步,当 slow 进入环中时,fast 开始追逐。若成环,则必会在环内的某处相遇,否则 fast 或是 fast->next 最后会走到NULL。
代码实现如下:
注意:
1.当链表节点个数为偶数个时,若不成环,最终 fast == NULL。
当链表节点个数为奇数个时,若不成环,最终 fast->next == NULL.
2.循环条件 fast && fast->next 的位置不能交换。因为当为偶数个节点,fast走到NULL时,如果是 fast->next && fast ,那就是先执行 fast->next ,对空指针解引用,错误!!
typedef struct ListNode ListNode;
bool hasCycle(struct ListNode* head) {ListNode* slow, * fast;slow = fast = head;while (fast && fast->next){slow = slow->next;fast = fast->next->next;if (fast == slow)return true;}return false;
}
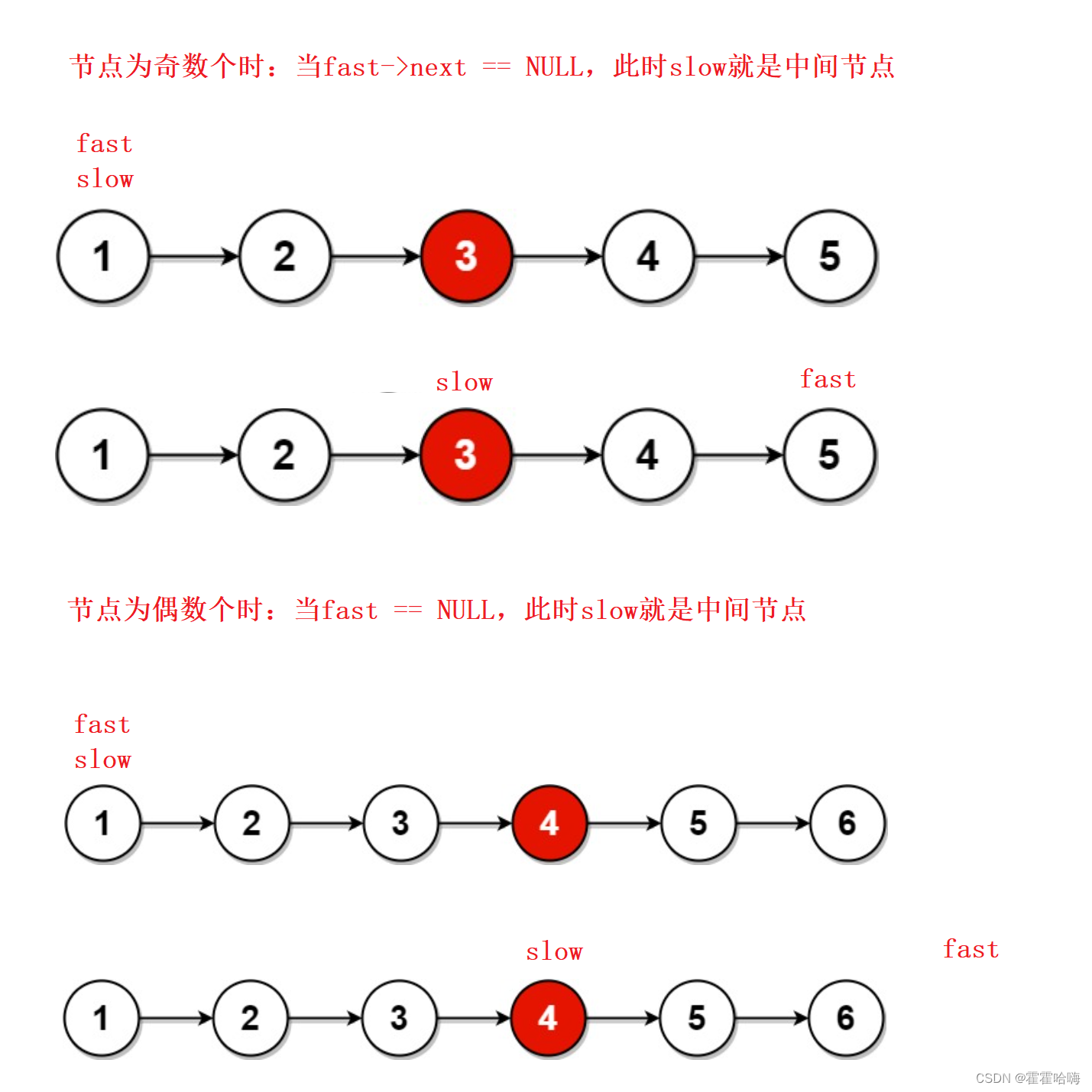
6. 链表的中间节点
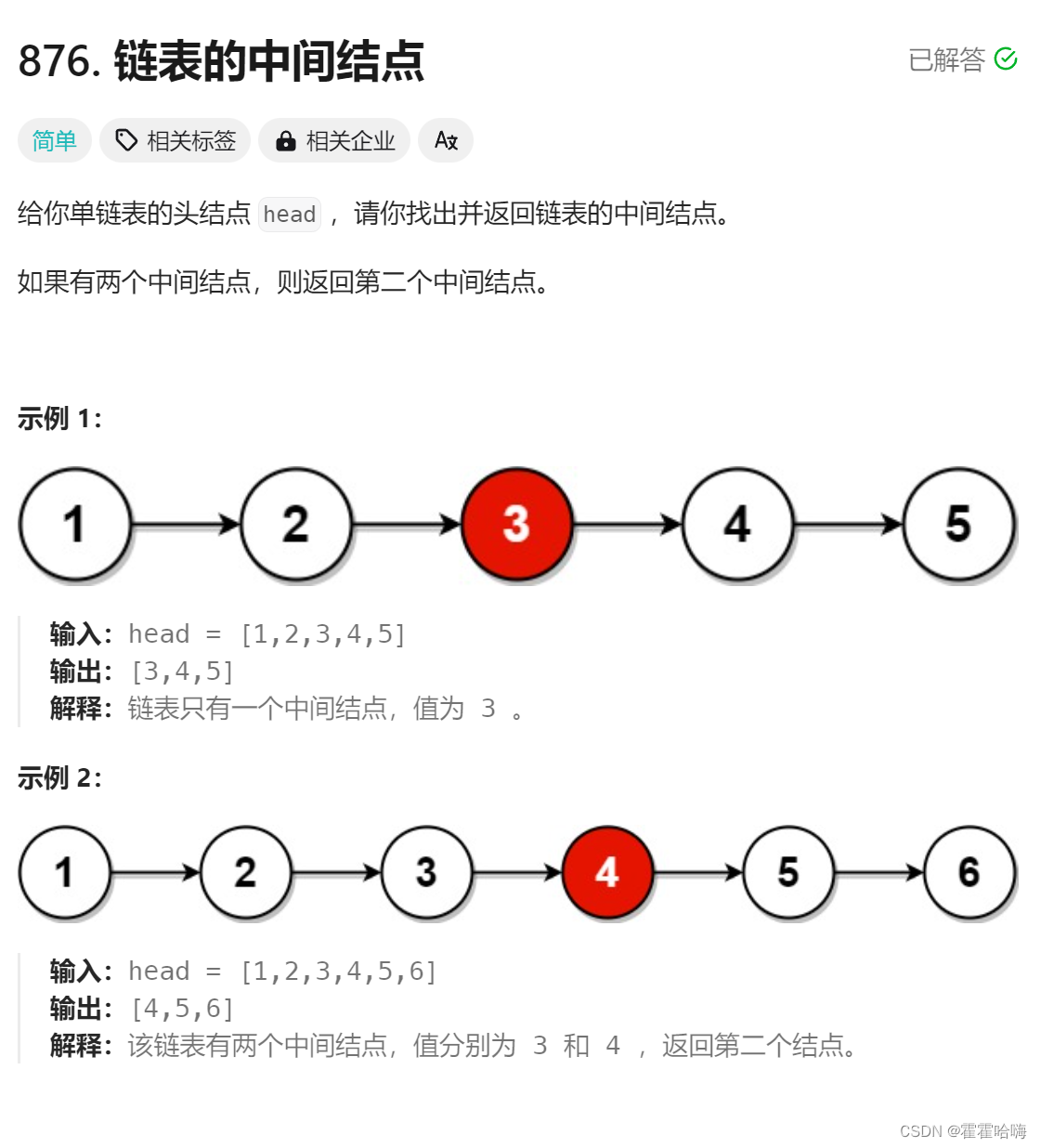
也要用快慢指针法。也要分两种情况:
代码实现如下:
注意:
循环条件 fast && fast->next 的位置不能交换。因为当为偶数个节点,fast走到NULL时,如果是 fast->next && fast ,那就是先执行 fast->next ,对空指针解引用,错误!!
typedef struct ListNode ListNode;struct ListNode* middleNode(struct ListNode* head) {ListNode* slow = head;ListNode* fast = head;while (fast && fast->next){slow = slow->next;fast = fast->next->next;}return slow;}
7. 链表中倒数第K个节点
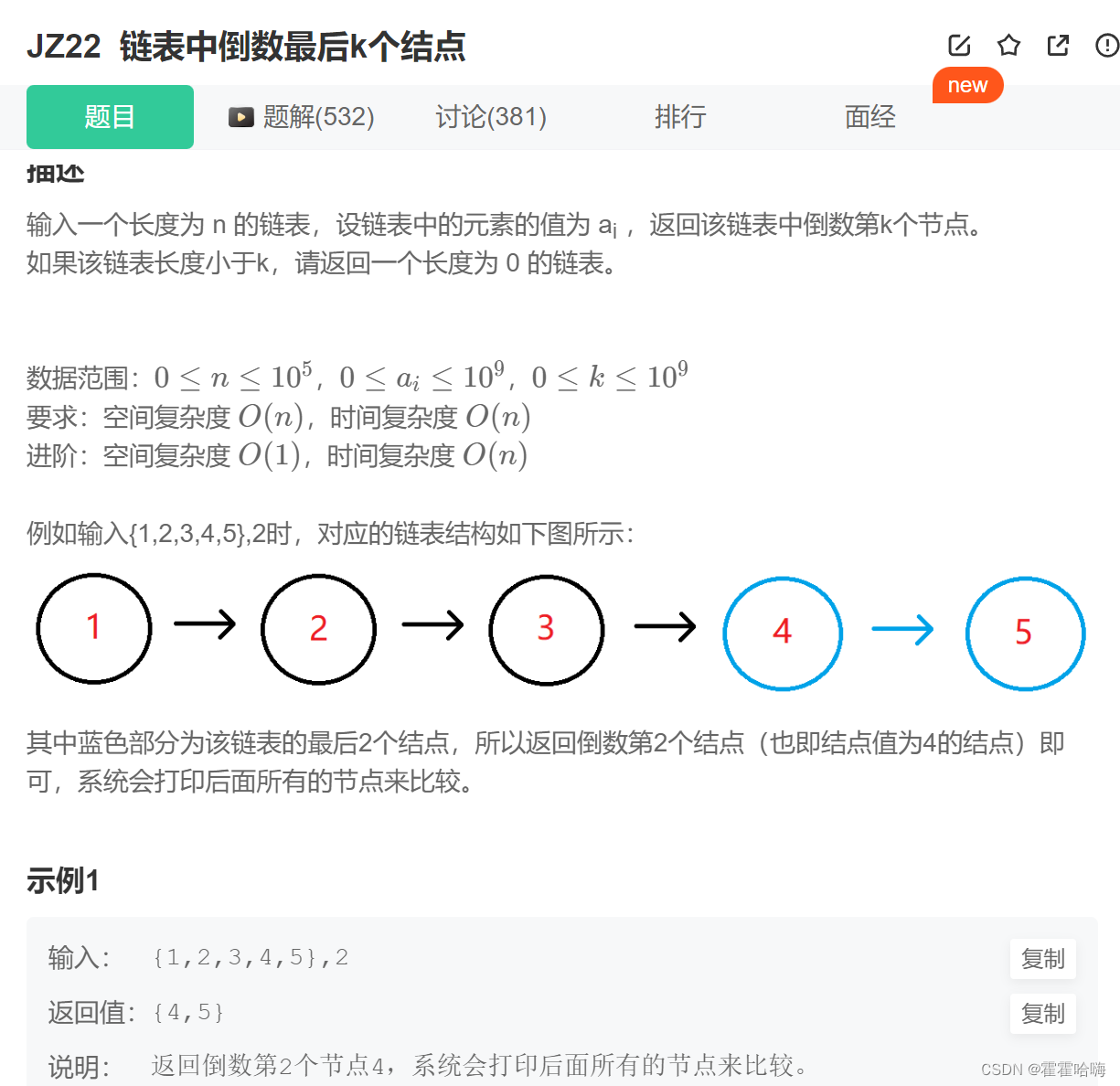
思路:
(1) fast 先走 k 步;
(2) slow 和 fast 再一起走,当 fast == NULL 时,slow 就是倒数第 k 个节点。
代码实现如下:
注意:
当 k 大于链表长度时,fast 会走到 NULL ,不能对空指针解引用,直接返回 NULL。
typedef struct ListNode ListNode;
struct ListNode* FindKthToTail(struct ListNode* pHead, int k ) {ListNode* fast ,*slow;fast = slow = pHead;//fast先走K步while(k--){//K大于链表长度时,直接返回NULLif(fast == NULL){return NULL;}fast = fast->next;}//再两者一起走while(fast){fast = fast->next;slow = slow->next;}return slow;}
8. 相交链表

首先要明确什么是相交链表:
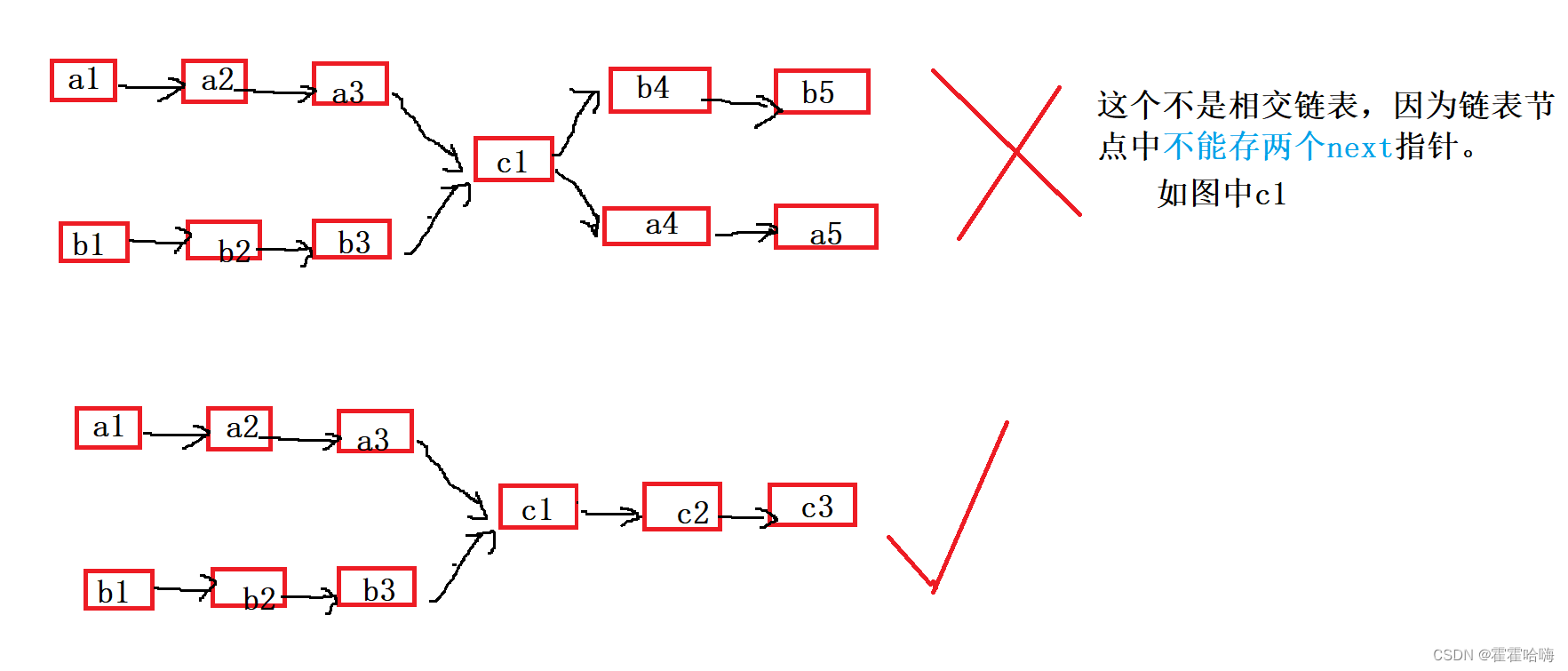
思路1:暴力求解,时间复杂度O(N*N)
依次取A链表中的每个节点跟B链表中的所有节点比较。如果有相同地址的节点,则相交,第一次相同地址的节点就是交点,否则就不相交。
思路2:时间复杂度O(N)
(1) 先找到两个链表的尾,同时计算出两个链表的长度;
(2) 求出长度差;
(3) 判断哪个是长链表;
(4) 让长链表先走长度差步;
(5) 最后长短链表一起走,直到找到交点。
思路2代码实现如下:
注意:
要注意步骤(3)中判断长短链表的巧妙方法。可以避免写重复代码。
typedef struct ListNode ListNode;
struct ListNode *getIntersectionNode(struct ListNode *headA, struct ListNode *headB) {ListNode* TailA,*TailB;TailA = headA;TailB = headB;//找尾同时计算长度int lenA = 0;int lenB = 0;while(TailA->next){TailA = TailA->next;lenA++;}while(TailB->next){TailB = TailB->next;lenB++;}//不相交if(TailA != TailB){return NULL;}//求出长度差int gap = abs(lenA - lenB);//判断哪个是长链表ListNode* longList = headA;//先默认A是长链表ListNode* shortList = headB;if(lenA < lenB){shortList = headA;longList = headB;}//让长链表走长度差步while(gap--){longList = longList->next;}//最后长短链表一起走,找交点while(longList != shortList){longList = longList->next;shortList = shortList->next;}return longList;}
9. 环形链表的约瑟夫问题
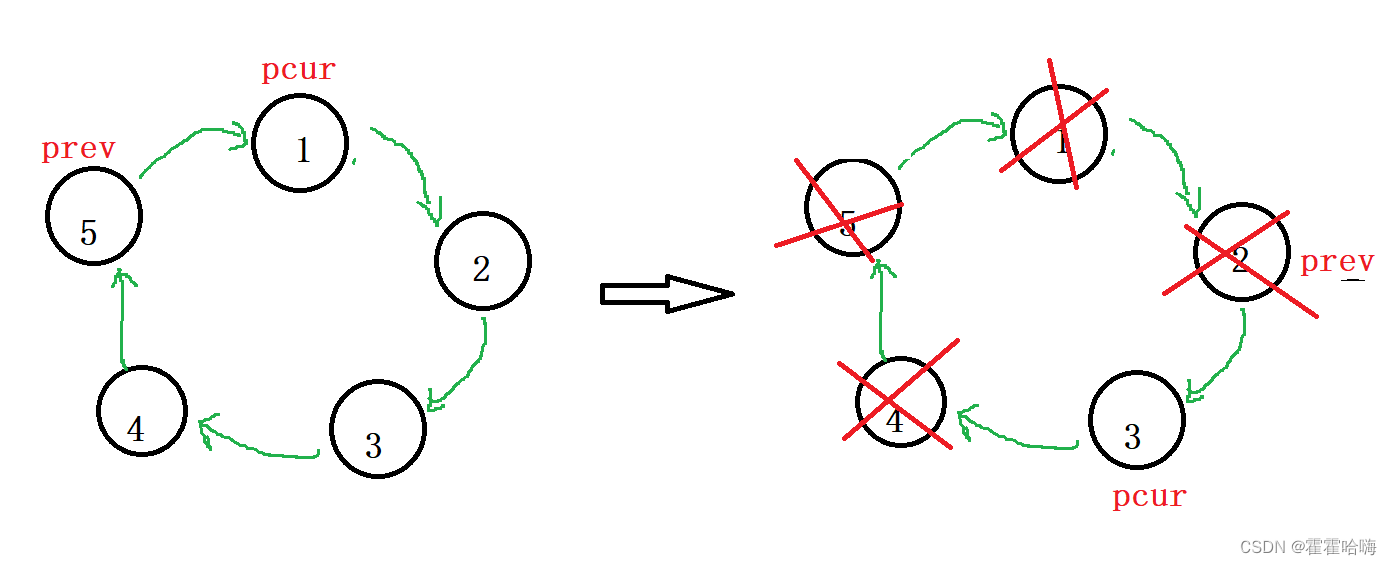
思路:
首先要创建一个循环链表,定义一个计数器 count 用于数数,再遍历循环链表,当结点的 val == count 时,就"杀死",即销毁该节点。
代码实现如下:
注意:
要学习创建循环链表的方法!
typedef struct ListNode ListNode;//创建节点ListNode* BuyNode(int x){ListNode* newnode = (ListNode*)malloc(sizeof(ListNode));if(newnode == NULL){exit(-1);}newnode->val = x;newnode->next = NULL;return newnode;}//1.创建循环链表ListNode* Createnodecircle(int n){ListNode* phead = BuyNode(1);ListNode* ptail = phead;for(int i=2;i<=n;i++){ptail->next = BuyNode(i);ptail = ptail->next;}//尾连头,成环ptail->next = phead;return ptail;}int ysf(int n, int m ) {ListNode* prev = Createnodecircle(n);ListNode* pcur = prev->next;//开始数数int count = 1;while(pcur->next!=prev->next){if(count == m){prev->next = pcur->next;free(pcur);pcur = prev->next;count = 1;}else{prev = pcur;pcur = pcur->next;count++;}}return pcur->val;}10. 链表的回文结构

这个题在牛客网中不能用C语言实现,我们可以选C++,因为C++是兼容C的,在C++中可以使用C的语法。
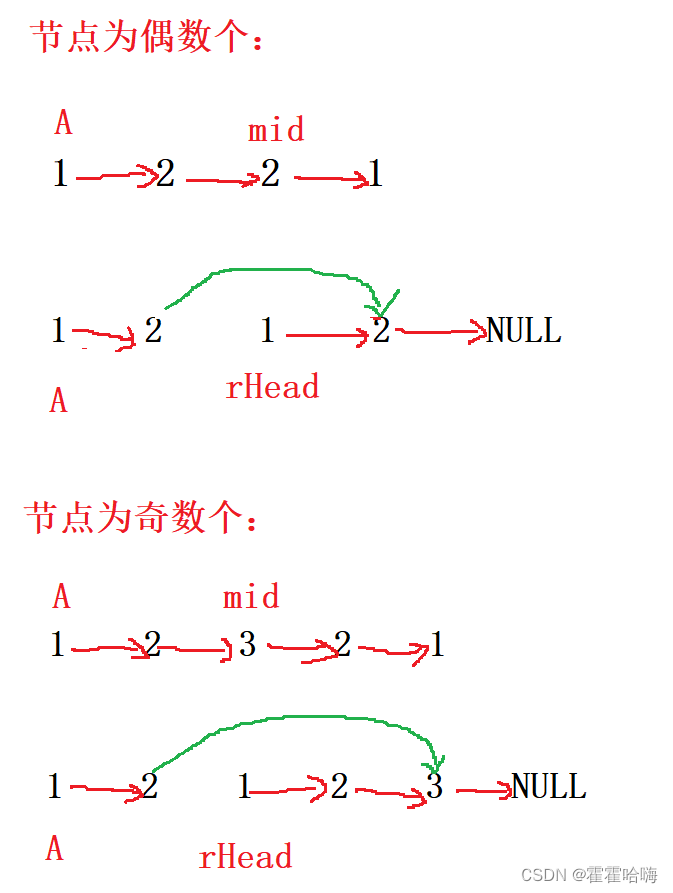
思路:
(1) 找到链表的中间节点;
(2) 把中间节点后面的链表进行逆置;
(3) 最后把逆置后的链表的值与中间节点之前的链表的值进行比较,若所有节点相等,则是回文链表,否则不是。有一个链表结束则比较结束。
代码实现如下:
注意:
逆置完之后,中间节点与前一个结点的链接可以不用断开,因为就算链接在一起也不影响判断。若强行断开,徒增麻烦。
//找中间结点
struct ListNode* middleNode(struct ListNode* head) {struct ListNode* slow = head;struct ListNode* fast = head;while (fast && fast->next){slow = slow->next;fast = fast->next->next;}return slow;}//对中间结点之后的链表进行逆置
struct ListNode* reverseList(struct ListNode* head) {if (head == NULL)return NULL;struct ListNode* n1, * n2, * n3;n1 = NULL, n2 = head, n3 = n2->next;while (n2){n2->next = n1;n1 = n2;n2 = n3;if (n3)n3 = n3->next;}return n1;
}class PalindromeList {public:bool chkPalindrome(ListNode* A) {struct ListNode* mid = middleNode(A);struct ListNode* rHead = reverseList(mid);struct ListNode* curA = A;struct ListNode* curR = rHead;//把逆置后的链表与中间结点之前的链表进行比较while(curA && curR){if(curA->val != curR->val){return false;}else{curA = curA->next;curR = curR->next;}}return true;}};




-缓存机制)







)



:深入理解 Kubernetes 中的污点(Taints)与容忍度(Tolerations))

)
