目录
- SpringApplication new 分析
- 源码分析
- 步骤演示
- primarySources和Sources
- 应用类型webApplicationType
- setInitializers设置容器初始化器
- setListeners设置监听器
- 主类推断
- SpringApplication run 分析
- 主要步骤
- 步骤演示
- 事件发布
- 容器相关
- 执行 runner
- 准备Environment
- EnvironmentPostProcessor后处理器
- 环境参数与对象绑定
在我们 启动Spring Boot应用程序时,一般是下面这段代码:
SpringApplication.run(TestNewSpringApplication.class, args)
看下run方法,他是一个静态方法:
public static ConfigurableApplicationContext run(Class<?> primarySource, String... args) {return run(new Class[]{primarySource}, args);
}
再进去看下里面的run方法,还是一个静态方法:
public static ConfigurableApplicationContext run(Class<?>[] primarySources, String[] args) {return (new SpringApplication(primarySources)).run(args);
}
这个方法主要有两个步骤:
- 创建SpringApplication对象
- 调用SpringApplication对象的run方法
下面来分别分析下这两步。
SpringApplication new 分析
源码分析
下面来分析new SpringApplication()的代码,其源码如下:
public SpringApplication(ResourceLoader resourceLoader, Class<?>... primarySources) {this.resourceLoader = resourceLoader;Assert.notNull(primarySources, "PrimarySources must not be null");this.primarySources = new LinkedHashSet<>(Arrays.asList(primarySources));this.webApplicationType = WebApplicationType.deduceFromClasspath();this.bootstrapRegistryInitializers = new ArrayList<>(getSpringFactoriesInstances(BootstrapRegistryInitializer.class));setInitializers((Collection) getSpringFactoriesInstances(ApplicationContextInitializer.class));setListeners((Collection) getSpringFactoriesInstances(ApplicationListener.class));this.mainApplicationClass = deduceMainApplicationClass();
}
下面是主要步骤:
this.resourceLoader = resourceLoader:resourceLoader是资源加载器,用于加载资源,如配置文件、类文件等。这里是null,ResourceLoader的自动配置主要依赖于 Spring Boot 的自动配置机制。this.primarySources = new LinkedHashSet<>(Arrays.asList(primarySources)):源类this.primarySources通常是包含 Spring Boot 应用的@SpringBootApplication注解的类或者是定义了一些@Configuration的类。这些类用于定义 Spring 应用的上下文配置。primarySources指定的类会被 Spring Boot 扫描,以查找这些BeanDefinition,也可以说是BeanDefinition源。this.webApplicationType = WebApplicationType.deduceFromClasspath():WebApplicationType的deduceFromClasspath静态方法,根据类路径推断应用的Web类型(如是否为Servlet应用、Reactive Web应用或None)。this.bootstrapRegistryInitializers = new ArrayList<>(getSpringFactoriesInstances(BootstrapRegistryInitializer.class):getSpringFactoriesInstances方法,从Spring的META-INF/spring.factories文件中加载所有BootstrapRegistryInitializer的实现类。BootstrapRegistryInitializer是一个用于初始化BootstrapRegistry的回调接口,在使用BootstrapRegistry之前调用它。BootstrapRegistry可以用来注册一些对象,这些对象可以在从Spring Boot启动到Spring容器初始化完成的过程中使用。简单来说,在没有Spring容器之前,可以利用BootstrapRegistry来共享一些对象。setInitializers((Collection) getSpringFactoriesInstances(ApplicationContextInitializer.class)):从spring.factories文件中加载所有ApplicationContextInitializer的实现类,并将它们设置为ApplicationContext的初始化器。可以在创建ApplicationContext和refresh之间对ApplicationContext做一些扩展。setListeners((Collection) getSpringFactoriesInstances(ApplicationListener.class)):从spring.factories文件中加载所有ApplicationListener的实现类,并将它们设置为当前对象的事件监听器。this.mainApplicationClass = deduceMainApplicationClass():调用deduceMainApplicationClass方法推断主应用类,主应用类通常是包含main方法的类,用于启动Spring Boot应用。
注意,创建时,并没有去创建Spring容器,只有run时才会。
步骤演示
primarySources和Sources
这两个主要是定义了BeanDefinition源。primarySources是一开始new时,一般是启动类,主要的BeanDefinition源,也可以在Sources中自己添加。
首先看如下示例:
package com.cys.spring.chapter15;import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.context.ConfigurableApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;@Configuration
public class TestNewSpringApplication {public static void main(String[] args) {// 手动new一个SpringApplication,第一个参数就是初始的BeanDefinition源SpringApplication spring = new SpringApplication(TestNewSpringApplication.class);// 调用run方法,返回一个容器ConfigurableApplicationContext context = spring.run(args);// 打印容器里的BeanDefinitionfor (String name : context.getBeanDefinitionNames()) {System.out.println("name: " + name + " 来源:" + context.getBeanFactory().getBeanDefinition(name).getResourceDescription());}context.close();}static class Bean1 {}static class Bean2 {}static class Bean3 {}@Beanpublic Bean2 bean2() {return new Bean2();}运行报错如下:
Unable to start ServletWebServerApplicationContext due to missing ServletWebServerFactory bean.
这是因为程序根据pom文件的依赖,推断他是一个基于Servlet实现的web服务器,因此需要使用ServletWebServerApplicationContext,从而需要ServletWebServerFactory。
我们给手动加上:
package com.cys.spring.chapter15;import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.web.embedded.tomcat.TomcatServletWebServerFactory;
import org.springframework.context.ConfigurableApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;@Configuration
public class TestNewSpringApplication {public static void main(String[] args) {// 手动new一个SpringApplication,第一个参数就是初始的BeanDefinition源SpringApplication spring = new SpringApplication(TestNewSpringApplication.class);// 调用run方法,返回一个容器ConfigurableApplicationContext context = spring.run(args);// 打印容器里的BeanDefinitionfor (String name : context.getBeanDefinitionNames()) {System.out.println("name: " + name + " 来源:" + context.getBeanFactory().getBeanDefinition(name).getResourceDescription());}context.close();}static class Bean1 {}static class Bean2 {}static class Bean3 {}@Beanpublic Bean2 bean2() {return new Bean2();}@Beanpublic TomcatServletWebServerFactory servletWebServerFactory() {return new TomcatServletWebServerFactory();}
}
再次运行结果如下:
name: org.springframework.context.annotation.internalConfigurationAnnotationProcessor 来源:null
name: org.springframework.context.annotation.internalAutowiredAnnotationProcessor 来源:null
name: org.springframework.context.annotation.internalCommonAnnotationProcessor 来源:null
name: org.springframework.context.event.internalEventListenerProcessor 来源:null
name: org.springframework.context.event.internalEventListenerFactory 来源:null
name: testNewSpringApplication 来源:null
name: org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.internalCachingMetadataReaderFactory 来源:null
name: bean2 来源:com.cys.spring.chapter15.TestNewSpringApplication
name: servletWebServerFactory 来源:com.cys.spring.chapter15.TestNewSpringApplication
上面结果可以看到,一些内置的无法查看到来源,像bean2和servletWebServerFactory都是我们自己定义的,可以分别看到他们的来源。
也可以自己添加source,如下:
package com.cys.spring.chapter15;import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.web.embedded.tomcat.TomcatServletWebServerFactory;
import org.springframework.context.ConfigurableApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;import java.util.HashSet;
import java.util.LinkedHashSet;
import java.util.Set;@Configuration
public class TestNewSpringApplication {public static void main(String[] args) {// 手动new一个SpringApplication,第一个参数就是初始的BeanDefinition源SpringApplication spring = new SpringApplication(TestNewSpringApplication.class);// 手动添加一个BeanDefinition源spring.setSources(new HashSet<String>() {{add("classpath:b01.xml");}});// 调用run方法,返回一个容器ConfigurableApplicationContext context = spring.run(args);// 打印容器里的BeanDefinitionfor (String name : context.getBeanDefinitionNames()) {System.out.println("name: " + name + " 来源:" + context.getBeanFactory().getBeanDefinition(name).getResourceDescription());}context.close();}static class Bean1 {}static class Bean2 {}static class Bean3 {}@Beanpublic Bean2 bean2() {return new Bean2();}@Beanpublic TomcatServletWebServerFactory servletWebServerFactory() {return new TomcatServletWebServerFactory();}
}
运行结果如下:

应用类型webApplicationType
先直接看源码
private static final String[] SERVLET_INDICATOR_CLASSES = { "javax.servlet.Servlet","org.springframework.web.context.ConfigurableWebApplicationContext" };private static final String WEBMVC_INDICATOR_CLASS = "org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet";private static final String WEBFLUX_INDICATOR_CLASS = "org.springframework.web.reactive.DispatcherHandler";private static final String JERSEY_INDICATOR_CLASS = "org.glassfish.jersey.servlet.ServletContainer";static WebApplicationType deduceFromClasspath() {// ClassUtils.isPresent用来判断类路径下是否含有某个类// 1. 如果包含WEBFLUX_INDICATOR_CLASS,并且不包含WEBMVC_INDICATOR_CLASS和JERSEY_INDICATOR_CLASS,则判断为REACTIVE类型if (ClassUtils.isPresent(WEBFLUX_INDICATOR_CLASS, null) && !ClassUtils.isPresent(WEBMVC_INDICATOR_CLASS, null)&& !ClassUtils.isPresent(JERSEY_INDICATOR_CLASS, null)) {return WebApplicationType.REACTIVE;}// 2. 如果SERVLET_INDICATOR_CLASSES里的都不含有,则判断为NONEfor (String className : SERVLET_INDICATOR_CLASSES) {if (!ClassUtils.isPresent(className, null)) {return WebApplicationType.NONE;}}// 3.最后判断为SERVLET类型return WebApplicationType.SERVLET;
}
主要有以下三步:
- 如果包含了REACTIVE相关的包,不包含servlet相关的包,就判断为REACTIVE类型
- 如果还不包含
javax.servlet.Servlet和org.springframework.web.context.ConfigurableWebApplicationContext,则判断为NONE - 否则,判断为SERVLET类型
代码演示:
package com.cys.spring.chapter15;import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.WebApplicationType;
import org.springframework.boot.web.embedded.tomcat.TomcatServletWebServerFactory;
import org.springframework.context.ConfigurableApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;import java.lang.reflect.InvocationTargetException;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
import java.util.HashSet;
import java.util.LinkedHashSet;
import java.util.Set;@Configuration
public class TestNewSpringApplication {public static void main(String[] args) throws NoSuchMethodException, InvocationTargetException, IllegalAccessException {System.out.println("1. 演示获取 Bean Definition 源");// 手动new一个SpringApplication,第一个参数就是初始的BeanDefinition源SpringApplication spring = new SpringApplication(TestNewSpringApplication.class);// 手动添加一个BeanDefinition源spring.setSources(new HashSet<String>() {{add("classpath:b01.xml");}});System.out.println("2. 演示推断应用类型");Method deduceFromClasspath = WebApplicationType.class.getDeclaredMethod("deduceFromClasspath");deduceFromClasspath.setAccessible(true);System.out.println("\t应用类型为:"+deduceFromClasspath.invoke(null));// 调用run方法,返回一个容器ConfigurableApplicationContext context = spring.run(args);// 打印容器里的BeanDefinitionfor (String name : context.getBeanDefinitionNames()) {System.out.println("name: " + name + " 来源:" + context.getBeanFactory().getBeanDefinition(name).getResourceDescription());}context.close();}static class Bean1 {}static class Bean2 {}static class Bean3 {}@Beanpublic Bean2 bean2() {return new Bean2();}@Beanpublic TomcatServletWebServerFactory servletWebServerFactory() {return new TomcatServletWebServerFactory();}
}
打印如下:
1. 演示获取 Bean Definition 源
2. 演示推断应用类型应用类型为:SERVLET
setInitializers设置容器初始化器
此步骤用来设置ApplicationContext的初始化器。ApplicationContext的初始化器主要用来在创建ApplicationContext后,refresh之前对ApplicationContext做一些扩展。
下面手动添加一个看下:
package com.cys.spring.chapter15;import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.WebApplicationType;
import org.springframework.boot.web.embedded.tomcat.TomcatServletWebServerFactory;
import org.springframework.context.ConfigurableApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.context.support.GenericApplicationContext;import java.lang.reflect.InvocationTargetException;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
import java.util.HashSet;
import java.util.LinkedHashSet;
import java.util.Set;@Configuration
public class TestNewSpringApplication {public static void main(String[] args) throws NoSuchMethodException, InvocationTargetException, IllegalAccessException {System.out.println("1. 演示获取 Bean Definition 源");// 手动new一个SpringApplication,第一个参数就是初始的BeanDefinition源SpringApplication spring = new SpringApplication(TestNewSpringApplication.class);// 手动添加一个BeanDefinition源spring.setSources(new HashSet<String>() {{add("classpath:b01.xml");}});System.out.println("2. 演示推断应用类型");Method deduceFromClasspath = WebApplicationType.class.getDeclaredMethod("deduceFromClasspath");deduceFromClasspath.setAccessible(true);System.out.println("\t应用类型为:"+deduceFromClasspath.invoke(null));System.out.println("3. 演示 ApplicationContext 初始化器");spring.addInitializers(applicationContext -> {if (applicationContext instanceof GenericApplicationContext) {GenericApplicationContext gac = (GenericApplicationContext) applicationContext;// 手动注册一个Bean3gac.registerBean("bean3", Bean3.class);}});// 调用run方法,返回一个容器ConfigurableApplicationContext context = spring.run(args);// 打印容器里的BeanDefinitionfor (String name : context.getBeanDefinitionNames()) {System.out.println("name: " + name + " 来源:" + context.getBeanFactory().getBeanDefinition(name).getResourceDescription());}context.close();}static class Bean1 {}static class Bean2 {}static class Bean3 {}@Beanpublic Bean2 bean2() {return new Bean2();}@Beanpublic TomcatServletWebServerFactory servletWebServerFactory() {return new TomcatServletWebServerFactory();}
}
运行:

发现Bean3被注册进容器。
setListeners设置监听器
ApplicationListener,即事件监听器。用于监听容器中发布的事件。它是事件驱动模型开发的一部分,允许开发者在特定事件发生时执行相应的操作。
ApplicationListener监听ApplicationEvent及其子事件。通过实现ApplicationListener接口,你可以创建自定义的监听器来监听并响应特定的应用事件。例如,当使用ConfigurableApplicationContext接口中的refresh()、start()、stop()或close()方法时,会发布相应的事件(如ContextRefreshedEvent、ContextStartedEvent、ContextStoppedEvent和ContextClosedEvent),你可以创建监听器来监听这些事件,并在事件发生时执行必要的操作,如初始化资源、启动服务、清理资源或关闭应用等。
示例:
package com.cys.spring.chapter15;import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.WebApplicationType;
import org.springframework.boot.web.embedded.tomcat.TomcatServletWebServerFactory;
import org.springframework.context.ConfigurableApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.context.support.GenericApplicationContext;import java.lang.reflect.InvocationTargetException;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
import java.util.HashSet;
import java.util.LinkedHashSet;
import java.util.Set;@Configuration
public class TestNewSpringApplication {public static void main(String[] args) throws NoSuchMethodException, InvocationTargetException, IllegalAccessException {System.out.println("1. 演示获取 Bean Definition 源");// 手动new一个SpringApplication,第一个参数就是初始的BeanDefinition源SpringApplication spring = new SpringApplication(TestNewSpringApplication.class);// 手动添加一个BeanDefinition源spring.setSources(new HashSet<String>() {{add("classpath:b01.xml");}});System.out.println("2. 演示推断应用类型");Method deduceFromClasspath = WebApplicationType.class.getDeclaredMethod("deduceFromClasspath");deduceFromClasspath.setAccessible(true);System.out.println("\t应用类型为:"+deduceFromClasspath.invoke(null));System.out.println("3. 演示 ApplicationContext 初始化器");spring.addInitializers(applicationContext -> {if (applicationContext instanceof GenericApplicationContext) {GenericApplicationContext gac = (GenericApplicationContext) applicationContext;// 手动注册一个Bean3gac.registerBean("bean3", Bean3.class);}});System.out.println("4. 演示监听器与事件");// 添加一个监听器监听所有事件spring.addListeners(event -> System.out.println("\t事件为:" + event.getClass()));// 调用run方法,返回一个容器ConfigurableApplicationContext context = spring.run(args);// 打印容器里的BeanDefinitionfor (String name : context.getBeanDefinitionNames()) {System.out.println("name: " + name + " 来源:" + context.getBeanFactory().getBeanDefinition(name).getResourceDescription());}context.close();}static class Bean1 {}static class Bean2 {}static class Bean3 {}@Beanpublic Bean2 bean2() {return new Bean2();}@Beanpublic TomcatServletWebServerFactory servletWebServerFactory() {return new TomcatServletWebServerFactory();}
}
结果打印出很多时间,如下:
1. 演示获取 Bean Definition 源
2. 演示推断应用类型应用类型为:SERVLET
3. 演示 ApplicationContext 初始化器
4. 演示监听器与事件事件为:class org.springframework.boot.context.event.ApplicationStartingEvent事件为:class org.springframework.boot.context.event.ApplicationEnvironmentPreparedEvent. ____ _ __ _ _/\\ / ___'_ __ _ _(_)_ __ __ _ \ \ \ \
( ( )\___ | '_ | '_| | '_ \/ _` | \ \ \ \\\/ ___)| |_)| | | | | || (_| | ) ) ) )' |____| .__|_| |_|_| |_\__, | / / / /=========|_|==============|___/=/_/_/_/:: Spring Boot :: (v2.6.13)事件为:class org.springframework.boot.context.event.ApplicationContextInitializedEvent
2024-03-10 12:25:54.085 INFO 50655 --- [ main] c.c.s.c.TestNewSpringApplication : Starting TestNewSpringApplication using Java 11.0.2 on testdeMBP with PID 50655 (/Users/fltech/Desktop/cys/学习笔记/sping高级-heima/sping-advanced/target/classes started by test in /Users/fltech/Desktop/cys/学习笔记/sping高级-heima/sping-advanced)
2024-03-10 12:25:54.092 INFO 50655 --- [ main] c.c.s.c.TestNewSpringApplication : No active profile set, falling back to 1 default profile: "default"事件为:class org.springframework.boot.context.event.ApplicationPreparedEvent
2024-03-10 12:25:54.960 INFO 50655 --- [ main] o.s.b.w.embedded.tomcat.TomcatWebServer : Tomcat initialized with port(s): 8080 (http)
2024-03-10 12:25:54.973 INFO 50655 --- [ main] o.apache.catalina.core.StandardService : Starting service [Tomcat]
2024-03-10 12:25:54.973 INFO 50655 --- [ main] org.apache.catalina.core.StandardEngine : Starting Servlet engine: [Apache Tomcat/9.0.68]
2024-03-10 12:25:55.226 INFO 50655 --- [ main] o.a.c.c.C.[Tomcat].[localhost].[/] : Initializing Spring embedded WebApplicationContext
2024-03-10 12:25:55.227 INFO 50655 --- [ main] w.s.c.ServletWebServerApplicationContext : Root WebApplicationContext: initialization completed in 811 ms
2024-03-10 12:25:55.313 INFO 50655 --- [ main] o.s.b.w.embedded.tomcat.TomcatWebServer : Tomcat started on port(s): 8080 (http) with context path ''事件为:class org.springframework.boot.web.servlet.context.ServletWebServerInitializedEvent事件为:class org.springframework.context.event.ContextRefreshedEvent
2024-03-10 12:25:55.331 INFO 50655 --- [ main] c.c.s.c.TestNewSpringApplication : Started TestNewSpringApplication in 2.021 seconds (JVM running for 2.673)事件为:class org.springframework.boot.context.event.ApplicationStartedEvent事件为:class org.springframework.boot.availability.AvailabilityChangeEvent事件为:class org.springframework.boot.context.event.ApplicationReadyEvent事件为:class org.springframework.boot.availability.AvailabilityChangeEvent
name: org.springframework.context.annotation.internalConfigurationAnnotationProcessor 来源:null
name: org.springframework.context.annotation.internalAutowiredAnnotationProcessor 来源:null
name: org.springframework.context.annotation.internalCommonAnnotationProcessor 来源:null
name: org.springframework.context.event.internalEventListenerProcessor 来源:null
name: org.springframework.context.event.internalEventListenerFactory 来源:null
name: bean3 来源:null
name: testNewSpringApplication 来源:null
name: bean1 来源:class path resource [b01.xml]
name: org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.internalCachingMetadataReaderFactory 来源:null
name: bean2 来源:com.cys.spring.chapter15.TestNewSpringApplication
name: servletWebServerFactory 来源:com.cys.spring.chapter15.TestNewSpringApplication事件为:class org.springframework.boot.availability.AvailabilityChangeEvent事件为:class org.springframework.context.event.ContextClosedEvent
主类推断
主类推断即用来推断含有main方法的启动Spring Boot应用的主类。
可使用反射查看
Method deduceMainApplicationClass = SpringApplication.class.getDeclaredMethod("deduceMainApplicationClass");
deduceMainApplicationClass.setAccessible(true);
System.out.println("\t主类是:"+deduceMainApplicationClass.invoke(spring))
SpringApplication run 分析
主要步骤
下面先看下主要步骤概览:
-
得到 SpringApplicationRunListeners,名字取得不好,实际是事件发布器
- 发布 application starting 事件1️⃣
-
封装启动 args
-
准备 Environment 添加命令行参数(*)
-
ConfigurationPropertySources 处理(*)
- 发布 application environment 已准备事件2️⃣
-
通过 EnvironmentPostProcessorApplicationListener 进行 env 后处理(*)
- application.properties,由 StandardConfigDataLocationResolver 解析
- spring.application.json
-
绑定 spring.main 到 SpringApplication 对象(*)
-
打印 banner(*)
-
创建容器
-
准备容器
- 发布 application context 已初始化事件3️⃣
-
加载 bean 定义
- 发布 application prepared 事件4️⃣
-
refresh 容器
- 发布 application started 事件5️⃣
-
执行 runner
-
发布 application ready 事件6️⃣
-
这其中有异常,发布 application failed 事件7️⃣
-
带 * 的有独立的示例
下面逐一演示下步骤
步骤演示
事件发布
对应第1步
演示时,先获取到时间发布器,在Springboot中,自动配置过程中,在自动配置文件org/springframework/boot/spring-boot/2.6.13/spring-boot-2.6.13.jar!/META-INF/spring.factories中会定义实现类有哪些。
示例:
package com.cys.spring.chapter15;import org.springframework.boot.DefaultBootstrapContext;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplicationRunListener;
import org.springframework.context.support.GenericApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.core.env.StandardEnvironment;
import org.springframework.core.io.support.SpringFactoriesLoader;import java.lang.reflect.Constructor;
import java.lang.reflect.InvocationTargetException;
import java.util.List;public class TestSpringApplicationRun {public static void main(String[] args) throws ClassNotFoundException, NoSuchMethodException, InvocationTargetException, InstantiationException, IllegalAccessException {SpringApplication app = new SpringApplication();/*** 1. 演示事件发布*/// 添加时间监听器app.addListeners(e -> System.out.println(e.getClass()));// 获取事件发送器实现类名,实现类名在配置文件org/springframework/boot/spring-boot/2.6.13/spring-boot-2.6.13.jar!/META-INF/spring.factories中// 配置如下:org.springframework.boot.SpringApplicationRunListener=org.springframework.boot.context.event.EventPublishingRunListener// 下面可以通过SpringFactoriesLoader.loadFactoryNames获取实现类的类名有哪些,这里就一个List<String> names = SpringFactoriesLoader.loadFactoryNames(SpringApplicationRunListener.class, TestSpringApplicationRun.class.getClassLoader());for (String name : names) {System.out.println(name);// 获取类型Class<?> clazz = Class.forName(name);// 获取构造方法Constructor<?> constructor = clazz.getConstructor(SpringApplication.class, String[].class);// 创建发布器SpringApplicationRunListener publisher = (SpringApplicationRunListener) constructor.newInstance(app, args);// 开始发布各种事件// 有些事件发布需要一个容器DefaultBootstrapContext bootstrapContext = new DefaultBootstrapContext();publisher.starting(bootstrapContext); // spring boot 开始启动publisher.environmentPrepared(bootstrapContext, new StandardEnvironment()); // 环境信息准备完毕GenericApplicationContext context = new GenericApplicationContext();publisher.contextPrepared(context); // 在 spring 容器创建,并调用初始化器之后,发送此事件publisher.contextLoaded(context); // 所有 bean definition 加载完毕context.refresh();publisher.started(context); // spring 容器初始化完成(refresh 方法调用完毕)publisher.running(context); // spring boot 启动完毕publisher.failed(context, new Exception("出错了")); // spring boot 启动出错}}
}
容器相关
对应8,9,10,11步
这里容器相关的步骤主要是:创建容器、容器增强、加载 BeanDefinition、refresh 容器。
代码如下:
package com.cys.spring.chapter15;import org.springframework.beans.factory.support.DefaultListableBeanFactory;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.xml.XmlBeanDefinitionReader;
import org.springframework.boot.*;
import org.springframework.boot.web.embedded.tomcat.TomcatServletWebServerFactory;
import org.springframework.boot.web.reactive.context.AnnotationConfigReactiveWebServerApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.boot.web.servlet.context.AnnotationConfigServletWebServerApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.boot.web.servlet.server.ServletWebServerFactory;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContextInitializer;
import org.springframework.context.ConfigurableApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.*;
import org.springframework.context.support.GenericApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.core.io.ClassPathResource;import java.util.Arrays;public class TestSpringApplicationRun2 {public static void main(String[] args) {SpringApplication app = new SpringApplication();// 添加初始化器,模拟初始化增强,会在地8步后,容器创建好菜可以被调用app.addInitializers(new ApplicationContextInitializer<ConfigurableApplicationContext>() {@Overridepublic void initialize(ConfigurableApplicationContext applicationContext) {System.out.println("执行初始化器增强...");}});System.out.println(">>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>> 8. 创建容器");GenericApplicationContext context = createApplicationContext(WebApplicationType.SERVLET);System.out.println(">>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>> 9. 准备容器");// 这里就模拟给容器做些增强for (ApplicationContextInitializer initializer : app.getInitializers()) {initializer.initialize(context);}System.out.println(">>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>> 10. 加载 bean 定义");// 先获取容器的BeanFactoryDefaultListableBeanFactory beanFactory = context.getDefaultListableBeanFactory();// 1. 创建根据注解获取BeanDefinition的读取器AnnotatedBeanDefinitionReader reader1 = new AnnotatedBeanDefinitionReader(beanFactory);// 解析Config中的注解,获取BeanDefinition,并在到容器中reader1.register(Config.class);// 2. 创建根据xml获取BeanDefinition的读取器XmlBeanDefinitionReader reader2 = new XmlBeanDefinitionReader(beanFactory);reader2.loadBeanDefinitions(new ClassPathResource("b03.xml"));// 23. 扫描获取BeanDefinition的读取器ClassPathBeanDefinitionScanner scanner = new ClassPathBeanDefinitionScanner(beanFactory);scanner.scan("com.cys.spring.chapter15.beans");System.out.println(">>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>> 11. refresh 容器");context.refresh();for (String name : context.getBeanDefinitionNames()) {System.out.println("name:" + name + " 来源:" + beanFactory.getBeanDefinition(name).getResourceDescription());}}/*** 辅助函数:根据类型参数获取不同的容器类型** @param type* @return*/private static GenericApplicationContext createApplicationContext(WebApplicationType type) {GenericApplicationContext context = null;switch (type) {case SERVLET : context = new AnnotationConfigServletWebServerApplicationContext();break;case REACTIVE : context = new AnnotationConfigReactiveWebServerApplicationContext();break;case NONE : context = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext();break;}return context;}static class Bean4 {}static class Bean5 {}static class Bean6 {}@Configurationstatic class Config {@Beanpublic Bean5 bean5() {return new Bean5();}@Beanpublic ServletWebServerFactory servletWebServerFactory() {return new TomcatServletWebServerFactory();}}
}
运行结果,打印如下:
>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>> 8. 创建容器
>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>> 9. 准备容器
执行初始化器增强...
>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>> 10. 加载 bean 定义
>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>> 11. refresh 容器
name:org.springframework.context.annotation.internalConfigurationAnnotationProcessor 来源:null
name:org.springframework.context.annotation.internalAutowiredAnnotationProcessor 来源:null
name:org.springframework.context.annotation.internalCommonAnnotationProcessor 来源:null
name:org.springframework.context.event.internalEventListenerProcessor 来源:null
name:org.springframework.context.event.internalEventListenerFactory 来源:null
name:testSpringApplicationRun2.Config 来源:null
name:bean4 来源:class path resource [b03.xml]
name:bean7 来源:file [.../classes/com/cys/spring/chapter15/beans/Bean7.class]
name:org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.internalCachingMetadataReaderFactory 来源:null
name:bean5 来源:com.cys.spring.chapter15.TestSpringApplicationRun2$Config
name:servletWebServerFactory 来源:com.cys.spring.chapter15.TestSpringApplicationRun2$Config
执行 runner
对应地2,12步
在Spring Boot中,CommandLineRunner和ApplicationRunner是两个常用的接口,它们允许你在Spring Boot应用启动后立即执行一些自定义的代码。这些接口特别有用,当你需要在应用启动之后立即进行一些初始化工作,比如数据加载、缓存预热、检查配置等。
下面来看下如何主动调用,示例:
package com.cys.spring.chapter15;import org.springframework.beans.factory.support.DefaultListableBeanFactory;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.xml.XmlBeanDefinitionReader;
import org.springframework.boot.*;
import org.springframework.boot.web.embedded.tomcat.TomcatServletWebServerFactory;
import org.springframework.boot.web.reactive.context.AnnotationConfigReactiveWebServerApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.boot.web.servlet.context.AnnotationConfigServletWebServerApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.boot.web.servlet.server.ServletWebServerFactory;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContextInitializer;
import org.springframework.context.ConfigurableApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.*;
import org.springframework.context.support.GenericApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.core.io.ClassPathResource;import java.util.Arrays;public class TestSpringApplicationRun2 {public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {SpringApplication app = new SpringApplication();// 添加初始化器,模拟初始化增强,会在地8步后,容器创建好菜可以被调用app.addInitializers(new ApplicationContextInitializer<ConfigurableApplicationContext>() {@Overridepublic void initialize(ConfigurableApplicationContext applicationContext) {System.out.println("执行初始化器增强...");}});System.out.println(">>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>> 2. 封装启动 args");// 执行runner使用DefaultApplicationArguments arguments = new DefaultApplicationArguments(args);System.out.println(">>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>> 8. 创建容器");GenericApplicationContext context = createApplicationContext(WebApplicationType.SERVLET);System.out.println(">>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>> 9. 准备容器");// 这里就模拟给容器做些增强for (ApplicationContextInitializer initializer : app.getInitializers()) {initializer.initialize(context);}System.out.println(">>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>> 10. 加载 bean 定义");// 先获取容器的BeanFactoryDefaultListableBeanFactory beanFactory = context.getDefaultListableBeanFactory();// 1. 创建根据注解获取BeanDefinition的读取器AnnotatedBeanDefinitionReader reader1 = new AnnotatedBeanDefinitionReader(beanFactory);// 解析Config中的注解,获取BeanDefinition,并在到容器中reader1.register(Config.class);// 2. 创建根据xml获取BeanDefinition的读取器XmlBeanDefinitionReader reader2 = new XmlBeanDefinitionReader(beanFactory);reader2.loadBeanDefinitions(new ClassPathResource("b03.xml"));// 23. 扫描获取BeanDefinition的读取器ClassPathBeanDefinitionScanner scanner = new ClassPathBeanDefinitionScanner(beanFactory);scanner.scan("com.cys.spring.chapter15.beans");System.out.println(">>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>> 11. refresh 容器");context.refresh();for (String name : context.getBeanDefinitionNames()) {System.out.println("name:" + name + " 来源:" + beanFactory.getBeanDefinition(name).getResourceDescription());}System.out.println(">>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>> 12. 执行 runner");for (CommandLineRunner runner : context.getBeansOfType(CommandLineRunner.class).values()) {runner.run(args);}for (ApplicationRunner runner : context.getBeansOfType(ApplicationRunner.class).values()) {runner.run(arguments);}}/*** 辅助函数:根据类型参数获取不同的容器类型** @param type* @return*/private static GenericApplicationContext createApplicationContext(WebApplicationType type) {GenericApplicationContext context = null;switch (type) {case SERVLET : context = new AnnotationConfigServletWebServerApplicationContext();break;case REACTIVE : context = new AnnotationConfigReactiveWebServerApplicationContext();break;case NONE : context = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext();break;}return context;}static class Bean4 {}static class Bean5 {}static class Bean6 {}@Configurationstatic class Config {@Beanpublic Bean5 bean5() {return new Bean5();}@Beanpublic ServletWebServerFactory servletWebServerFactory() {return new TomcatServletWebServerFactory();}@Beanpublic CommandLineRunner commandLineRunner() {return new CommandLineRunner() {@Overridepublic void run(String... args) throws Exception {System.out.println("commandLineRunner()..." + Arrays.toString(args));}};}@Beanpublic ApplicationRunner applicationRunner() {return new ApplicationRunner() {@Overridepublic void run(ApplicationArguments args) throws Exception {// 可以拿到Application里的各种参数System.out.println("applicationRunner()..." + Arrays.toString(args.getSourceArgs()));System.out.println(args.getOptionNames());System.out.println(args.getOptionValues("server.port"));System.out.println(args.getNonOptionArgs());}};}}
}
运行打印结果如下:
>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>> 12. 执行 runner
commandLineRunner()...[]
applicationRunner()...[]
[]
null
[]
准备Environment
对应第3步
这里以Springboot中的ApplicationEnvironment为例。
ApplicationEnvironment是一个用于访问应用环境信息的接口。它通常用于读取应用的环境属性,例如配置文件中的属性、命令行参数、系统属性等。ApplicationEnvironment继承自Spring框架的Environment接口,并添加了Spring Boot特有的功能。
其类图如下:
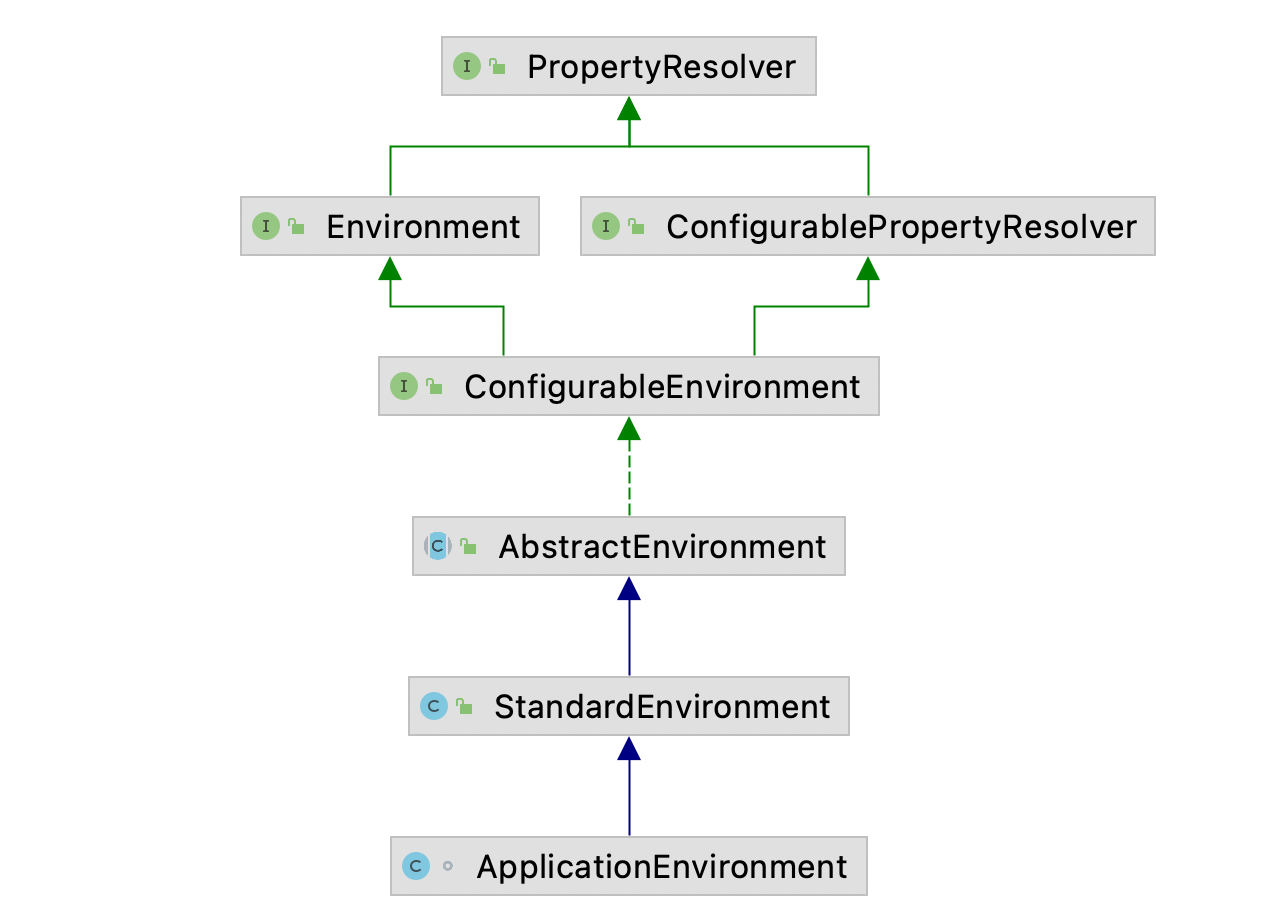
ApplicationEnvironment的主要用途包括:
- 读取属性:通过
getProperty方法读取属性值。这些属性可能来自application.properties或application.yml配置文件、命令行参数、环境变量或系统属性等。 - 属性源管理:
ApplicationEnvironment管理着多个属性源(Property Sources),每个属性源都包含一组键值对。Spring Boot按照特定的顺序(例如,命令行参数优先级最高,然后是配置文件等)来解析属性值。 - 自定义属性源:你可以向
ApplicationEnvironment添加自定义的属性源,以便在应用启动时加载特定的配置。 - 激活的配置文件:Spring Boot支持配置文件的激活,例如
application-dev.properties用于开发环境,application-prod.properties用于生产环境。ApplicationEnvironment提供了方法来获取当前激活的配置文件。 - 环境检查:通过
Environment接口的方法,你可以检查应用是否处于特定环境(如测试环境或生产环境),这对于条件性地配置应用行为非常有用。
在Spring Boot应用中,你通常不需要直接实例化ApplicationEnvironment,因为Spring Boot会自动配置并注入它。你可以在你的组件中通过依赖注入来获取并使用它。
由于这个类在org.springframework.boot中,并不对外开放,需要在内部测试:
package org.springframework.boot;import org.springframework.core.env.PropertySource;
import org.springframework.core.env.SimpleCommandLinePropertySource;
import org.springframework.core.io.ClassPathResource;
import org.springframework.core.io.support.ResourcePropertySource;import java.io.IOException;public class Step3 {public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {ApplicationEnvironment env = new ApplicationEnvironment(); // 系统环境变量, properties, yaml// 加一个配置源到最后一位env.getPropertySources().addLast(new ResourcePropertySource(new ClassPathResource("step3.properties")));// 加油一个配置源到第一位env.getPropertySources().addFirst(new SimpleCommandLinePropertySource(args));for (PropertySource<?> ps : env.getPropertySources()) {System.out.println(ps);}System.out.println(env.getProperty("JAVA_HOME"));System.out.println(env.getProperty("server.port"));}
}
EnvironmentPostProcessor后处理器
对应第5步。
EnvironmentPostProcessor主要功能是在Spring Boot环境加载后,动态加载其他配置文件中的一些信息到环境变量里面。通过这个接口,我们可以添加或修改环境配置,实现多个微服务共同配置的修改与维护。
当项目需要在不同环境(如开发、测试、生产等)中运行时,每套环境可能有专属的配置文件。EnvironmentPostProcessor允许我们在项目启动时读取环境变量或启动命令参数,从而获取特定环境下的配置信息(如服务地址、命名空间名称、分组名称等)。然后,根据这些配置参数或环境变量,我们可以读取不同的配置文件,实现不同环境使用不同的配置文件,而无需修改代码或本地配置文件。
使用EnvironmentPostProcessor时,我们需要实现该接口,并覆盖其postProcessEnvironment方法。在这个方法中,我们可以加载对应的配置文件到环境变量中。同时,还需要在spring.factories文件中进行相应配置,以便Spring Boot在启动时能够识别并加载我们的EnvironmentPostProcessor实现类。
在Springboot中通过ApplicationListener监听器EnvironmentPostProcessorApplicationListener,来监听并执行下面那些后处理器,如下图:

示例:
public class Step5 {public static void main(String[] args) {SpringApplication app = new SpringApplication();app.addListeners(new EnvironmentPostProcessorApplicationListener());/*List<String> names = SpringFactoriesLoader.loadFactoryNames(EnvironmentPostProcessor.class, Step5.class.getClassLoader());for (String name : names) {System.out.println(name);}*/EventPublishingRunListener publisher = new EventPublishingRunListener(app, args);ApplicationEnvironment env = new ApplicationEnvironment();System.out.println(">>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>> 增强前");for (PropertySource<?> ps : env.getPropertySources()) {System.out.println(ps);}publisher.environmentPrepared(new DefaultBootstrapContext(), env);System.out.println(">>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>> 增强后");for (PropertySource<?> ps : env.getPropertySources()) {System.out.println(ps);}}
}
环境参数与对象绑定
底层通过Binder来绑定:
示例:
package org.springframework.boot;import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.context.properties.ConfigurationProperties;
import org.springframework.boot.context.properties.bind.BindResult;
import org.springframework.boot.context.properties.bind.Bindable;
import org.springframework.boot.context.properties.bind.Binder;
import org.springframework.core.env.StandardEnvironment;
import org.springframework.core.io.ClassPathResource;
import org.springframework.core.io.support.ResourcePropertySource;import java.io.IOException;public class Step6 {// 绑定 spring.main 前缀的 key value 至 SpringApplication, 请通过 debug 查看public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {SpringApplication application = new SpringApplication();ApplicationEnvironment env = new ApplicationEnvironment();// 把step4.properties配置源加到环境env.getPropertySources().addLast(new ResourcePropertySource("step4", new ClassPathResource("step4.properties")));// 把step6.properties配置源加到环境env.getPropertySources().addLast(new ResourcePropertySource("step6", new ClassPathResource("step6.properties")));// User user = Binder.get(env).bind("user", User.class).get();
// System.out.println(user);// User user = new User();
// Binder.get(env).bind("user", Bindable.ofInstance(user));
// System.out.println(user);System.out.println(application);Binder.get(env).bind("spring.main", Bindable.ofInstance(application));System.out.println(application);}static class User {private String firstName;private String middleName;private String lastName;public String getFirstName() {return firstName;}public void setFirstName(String firstName) {this.firstName = firstName;}public String getMiddleName() {return middleName;}public void setMiddleName(String middleName) {this.middleName = middleName;}public String getLastName() {return lastName;}public void setLastName(String lastName) {this.lastName = lastName;}@Overridepublic String toString() {return "User{" +"firstName='" + firstName + '\'' +", middleName='" + middleName + '\'' +", lastName='" + lastName + '\'' +'}';}}
}













)





