


#include "opencv2/core.hpp" // 包含OpenCV核心功能头文件
#include "opencv2/core/utility.hpp" // 包含OpenCV实用程序头文件
#include "opencv2/imgproc.hpp" // 包含OpenCV图像处理头文件
#include "opencv2/imgcodecs.hpp" // 包含OpenCV图像编解码头文件
#include "opencv2/highgui.hpp" // 包含OpenCV高层GUI(图形用户界面)头文件#include <stdio.h> // 包含标准输入输出头文件using namespace cv; // 使用OpenCV命名空间
using namespace std; // 使用标准库命名空间// 帮助信息函数定义
static void help(const char ** argv)
{printf("\nThis program demonstrated the use of the discrete Fourier transform (dft)\n""The dft of an image is taken and its power spectrum is displayed.\n""Usage:\n %s [image_name -- default lena.jpg]\n",argv[0]);
}// 命令行参数的键定义
const char* keys =
{"{help h||}{@image|lena.jpg|input image file}"
};// 主函数入口
int main(int argc, const char ** argv)
{help(argv); // 显示帮助信息CommandLineParser parser(argc, argv, keys); // 创建命令行参数解析器if (parser.has("help")) // 如果有"help"参数{help(argv); // 显示帮助信息return 0; // 正常退出程序}string filename = parser.get<string>(0); // 从命令行获取文件名Mat img = imread(samples::findFile(filename), IMREAD_GRAYSCALE); // 读取图片文件,转换为灰度图if( img.empty() ) // 如果图片为空{help(argv); // 显示帮助信息printf("Cannot read image file: %s\n", filename.c_str()); // 输出错误信息return -1; // 异常退出程序}int M = getOptimalDFTSize( img.rows ); // 获取最优的DFT(离散傅里叶变换)尺寸int N = getOptimalDFTSize( img.cols ); // 获取最优的DFT尺寸Mat padded; // 声明一个新的矩阵用于扩展图像边界// 使用边界拷贝方式将图像扩展到最优DFT尺寸copyMakeBorder(img, padded, 0, M - img.rows, 0, N - img.cols, BORDER_CONSTANT, Scalar::all(0));// 将扩展后的图像分成两个通道,Real和ImaginaryMat planes[] = {Mat_<float>(padded), Mat::zeros(padded.size(), CV_32F)};Mat complexImg; // 声明一个复数图像矩阵merge(planes, 2, complexImg); // 合并通道dft(complexImg, complexImg); // 对复数图像进行DFT变换// 计算幅度谱的对数表示,用于显示split(complexImg, planes); // 分离通道magnitude(planes[0], planes[1], planes[0]); // 计算幅度Mat mag = planes[0]; // 获取幅度矩阵mag += Scalar::all(1); // 为了避免对数为负无穷做的偏移log(mag, mag); // 计算对数// 如果幅度谱的行或列数是奇数,则裁剪mag = mag(Rect(0, 0, mag.cols & -2, mag.rows & -2));// 重新排列傅里叶图像的象限,使原点位于图像中心int cx = mag.cols/2;int cy = mag.rows/2;Mat tmp; // 临时矩阵// 定义象限矩阵Mat q0(mag, Rect(0, 0, cx, cy));Mat q1(mag, Rect(cx, 0, cx, cy));Mat q2(mag, Rect(0, cy, cx, cy));Mat q3(mag, Rect(cx, cy, cx, cy));// 交换象限(左上与右下互换)q0.copyTo(tmp);q3.copyTo(q0);tmp.copyTo(q3);// 交换象限(右上与左下互换)q1.copyTo(tmp);q2.copyTo(q1);tmp.copyTo(q2);// 对数幅度谱进行归一化到0到1normalize(mag, mag, 0, 1, NORM_MINMAX);// 显示图像幅度谱imshow("spectrum magnitude", mag);waitKey(); // 等待用户按键return 0; // 正常退出程序
}这段代码是用于演示如何使用离散傅里叶变换(DFT)并显示图像的功率谱。首先,程序定义了简单的帮助信息,解析命令行参数,并尝试加载指定的图像文件。如果加载成功,程序将计算最优的DFT尺寸,对图像进行边缘填补,以满足DFT的最优尺寸要求。之后,程序创建一个复数图像,将其通道合并,并对其执行DFT变换。接下来对变换结果的幅度进行对数转换,以便于显示,并且将幅度矩阵中心移到图像的中心。最后,程序通过imshow显示转换后的图像幅度谱,并通过waitKey等待用户的按键操作。
如何利用图像的功率谱对图像进行增强或减弱?

有哪些常见的滤波器可以用于图像增强?

mag = mag(Rect(0, 0, mag.cols & -2, mag.rows & -2));
copyMakeBorder(img, padded, 0, M - img.rows, 0, N - img.cols, BORDER_CONSTANT, Scalar::all(0));
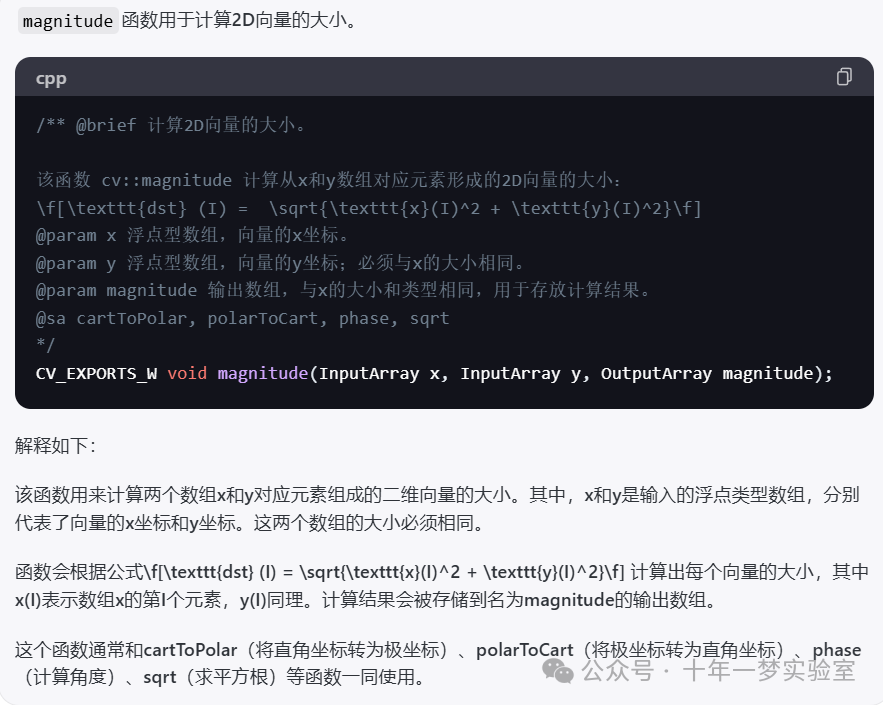
magnitude(planes[0], planes[1], planes[0]);

)








(代码模板))
)
)

)




