驱动的含义
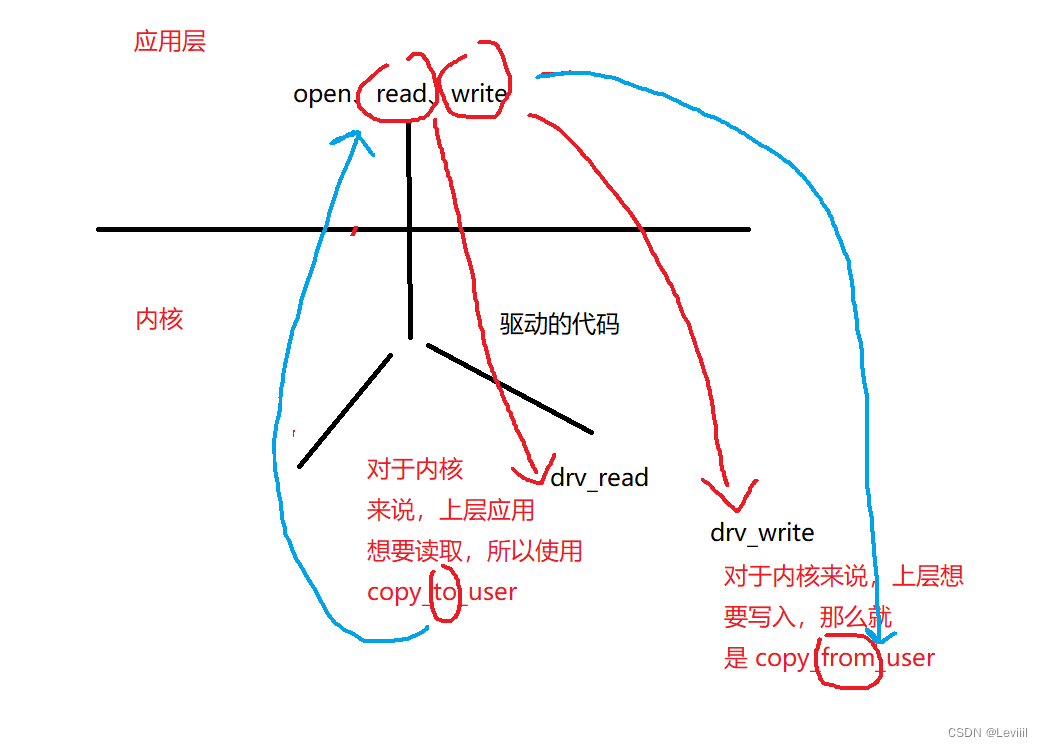
如何理解嵌入式的驱动呢,我个人认为,驱动就是嵌入式上层应用操控底层硬件的桥梁。因为上层应用是在用户态,是无法直接操控底层的硬件的。我们需要利用系统调用(open、read、write等),进入内核态,通过打开对应的设备节点,通过read、write等通过编写的驱动函数来操控设备节点。
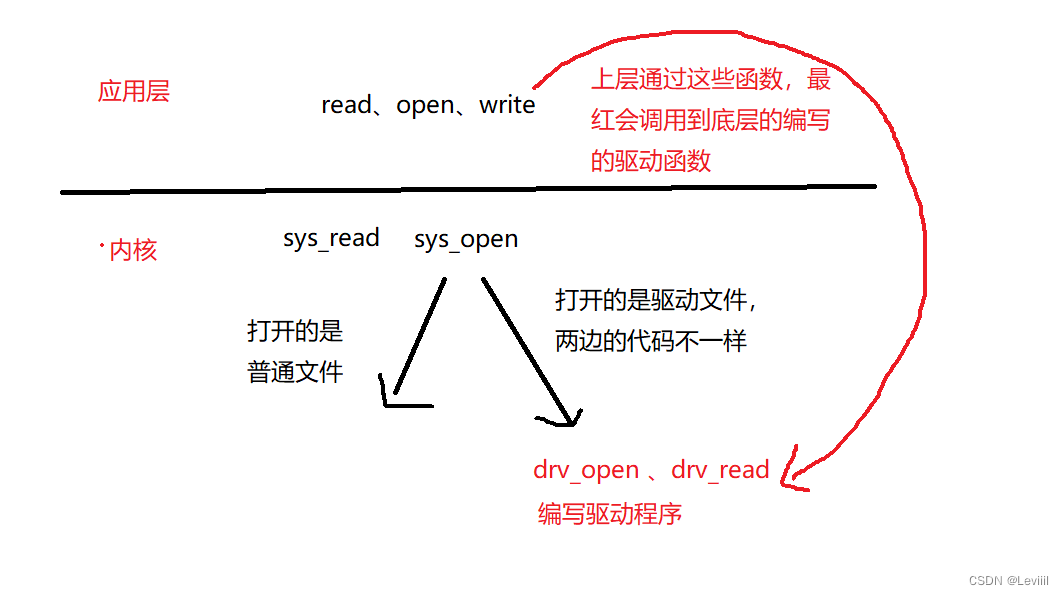
如何编写驱动
总的来说,驱动编写的大体步骤如下所示:
1、确定驱动的主设备号
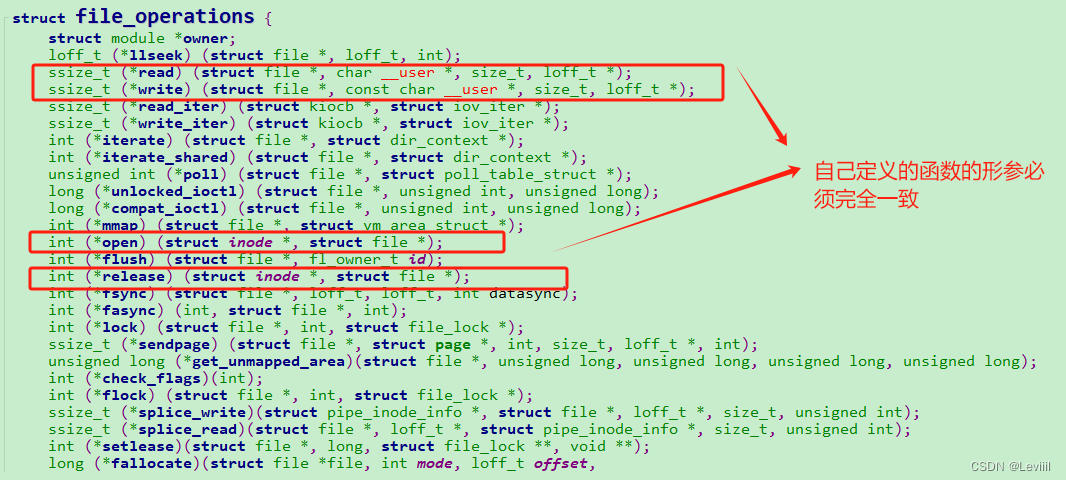
2、定义自己的file_operation结构体,这个结构体的成员包含了很多的函数指针
3、我们需要在驱动文件中实现对应的函数,传入结构体中
4、编写一个驱动入口函数(对应的,也需要一个驱动卸载函数)
5、在驱动入口函数中,把file_operation结构体注册到内核当中、创建节点(class)、创建设备(相应的在驱动卸载函数中定义结构体从内核中卸载、节点、设备的卸载方法)
6、使用如下两个宏分别修饰入口函数和出口函数
7、使用 MODULE_LICENSE("GPL"); 遵守GPL协议,否则无法使用
基于如上步骤,我们进行以下操作
首先,我们需要三个文件,一个作为底层驱动文件,一个是上层APP文件,一个是Makefile
驱动文件 hello_driver.c 上层应用文件 hello_drv.c Makefile 刚开始我们可能不知道到底要包含什么头文件,我们可以学习Linux内核中的文件来进行参考,我们可以打开 Linux-4.9.88\drivers\char\misc.c ,把里面的头文件拷贝过来使用。
首先我们需要定义一个全局变量作为驱动的设备号,然后定义一个file_operation结构体。需要注意,这两个变量都是全局变量,因为需要被多个函数使用。
file_operation结构体需要多个函数指针成员,在这里,我们定义四个函数,把函数指针赋值给结构体成员
其中需要注意的是,驱动和上层直接读写是需要通过两个函数来进行的,分别是 copy_to_user 和 copy_from_user,前者用于驱动中读的驱动函数,后者用于驱动中写的函数
同时,结构体成员函数的形参,返回值必须严格遵守一样的原则,否则会报错
#include <linux/module.h> #include <linux/fs.h> #include <linux/errno.h> #include <linux/miscdevice.h> #include <linux/kernel.h> #include <linux/major.h> #include <linux/mutex.h> #include <linux/proc_fs.h> #include <linux/seq_file.h> #include <linux/stat.h> #include <linux/init.h> #include <linux/device.h> #include <linux/tty.h> #include <linux/kmod.h> #include <linux/gfp.h>/* 确定主设备号 */ static int major = 0; /* 缓存数组 */ static char kernal_buf[1024];/* 数据超过1024,限制为1024 */ #define data_num(a,b) ( (a) < (b) ? (a) : (b) )/* 定义函数入口地址 */ static int hello_drv_open (struct inode *node, struct file *file) {printk("%s %s %d \n",__FILE__,__FUNCTION__,__LINE__);return 0; }static ssize_t hello_drv_read (struct file *file, char __user *buf, size_t size, loff_t *offset) {int return_size;printk("%s %s %d \n",__FILE__,__FUNCTION__,__LINE__);return_size = copy_to_user(buf, kernal_buf, data_num(1024,size));return return_size;} static ssize_t hello_drv_write (struct file *file, const char __user *buf, size_t size, loff_t *offset) {int return_size;printk("%s %s %d \n",__FILE__,__FUNCTION__,__LINE__);return_size = copy_from_user(kernal_buf, buf, data_num(1024,size));return return_size;} static int hello_drv_rease (struct inode *node, struct file *file) {printk("%s %s %d \n",__FILE__,__FUNCTION__,__LINE__);return 0; }/* 定义文件结构体读,写,打开,卸载 */ static struct file_operations hello_driver = {.owner = THIS_MODULE,.open = hello_drv_open,.read = hello_drv_read,.write = hello_drv_write,.release = hello_drv_rease, };当我们为file_operation结构体的成员指定了对应的函数指针后,我们需要指定一个入口函数以及一个出口函数,并且在入口函数中,把file_operation注册到内核、节点的创建和设备的创建,在出口函数中完成上述三个的卸载(节点需要另外创建一个全局变量,struct class类型)
/* 节点的定义 全局变量 */ static struct class *hello_class;/* 入口函数 */ static int __init hello_init(void) {int err;printk("%s %s %d \n",__FILE__,__FUNCTION__,__LINE__);/* 注册结构体到内核后,返回主设备号 */major = register_chrdev(0, "hello", &hello_driver);//创建节点 /dev/hellohello_class = class_create(THIS_MODULE, "hello_class");err = PTR_ERR(hello_class);if (IS_ERR(hello_class)){printk("%s %s %d \n",__FILE__,__FUNCTION__,__LINE__);/* 创建失败的话摧毁内核中的hello结构体 */unregister_chrdev( major, "hello");return -1;}/* 创建了节点后,需要创建设备 */ device_create(hello_class, NULL, MKDEV(major, 0), NULL, "hello"); return 1; }/* 出口函数 */ static void __exit hello_exit(void) {printk("%s %s %d \n",__FILE__,__FUNCTION__,__LINE__);/* 把device卸载 */device_destroy(hello_class, MKDEV(major, 0));/* 把class卸载 */class_destroy(hello_class);/* 把file_operation从内核中卸载 */unregister_chrdev( major, "hello");}当写好了入口函数和出口函数后,还需通过两个宏声明,否则系统不知道这两个函数分别是入口函数和出口函数
/* 需要用某些宏表示上述两个函数分别是入口函数和出口函数 */ module_init(hello_init); module_exit(hello_exit);这就是一个驱动的具体框架了,整体完整代码如下
#include <linux/module.h>#include <linux/fs.h> #include <linux/errno.h> #include <linux/miscdevice.h> #include <linux/kernel.h> #include <linux/major.h> #include <linux/mutex.h> #include <linux/proc_fs.h> #include <linux/seq_file.h> #include <linux/stat.h> #include <linux/init.h> #include <linux/device.h> #include <linux/tty.h> #include <linux/kmod.h> #include <linux/gfp.h>/* 流程1.file_operation结构体,实现内部对应函数2.注册结构体到内核,同时使用宏声明入口和出口函数,指引进入3.创建节点,让上层应用函数可以打开 /dev/...,节点class创建完毕后,创建deviceclass提供了一种更高层次的设备抽象,而device则代表了具体的硬件设备*//* 确定主设备号 */ static int major = 0; /* 缓存数组 */ static char kernal_buf[1024]; /* 节点的定义 */ static struct class *hello_class;/* 读多少的宏定义 */ #define data_num(a,b) ( (a) < (b) ? (a) : (b) )/* 定义函数入口地址 */ static int hello_drv_open (struct inode *node, struct file *file) {printk("%s %s %d \n",__FILE__,__FUNCTION__,__LINE__);return 0; }static ssize_t hello_drv_read (struct file *file, char __user *buf, size_t size, loff_t *offset) {int return_size;printk("%s %s %d \n",__FILE__,__FUNCTION__,__LINE__);return_size = copy_to_user(buf, kernal_buf, data_num(1024,size));return return_size;} static ssize_t hello_drv_write (struct file *file, const char __user *buf, size_t size, loff_t *offset) {int return_size;printk("%s %s %d \n",__FILE__,__FUNCTION__,__LINE__);return_size = copy_from_user(kernal_buf, buf, data_num(1024,size));return return_size;} static int hello_drv_rease (struct inode *node, struct file *file) {printk("%s %s %d \n",__FILE__,__FUNCTION__,__LINE__);return 0; }/* 定义文件结构体读,写,打开,卸载 */ static struct file_operations hello_driver = {.owner = THIS_MODULE,.open = hello_drv_open,.read = hello_drv_read,.write = hello_drv_write,.release = hello_drv_rease, };/* 把结构体注册到内核为了能够把该结构体注册到内核需要init函数 */ static int __init hello_init(void) {int err;printk("%s %s %d \n",__FILE__,__FUNCTION__,__LINE__);/* 注册结构体到内核后,返回主设备号 */major = register_chrdev(0, "hello", &hello_driver);//创建节点 /dev/hellohello_class = class_create(THIS_MODULE, "hello_class");err = PTR_ERR(hello_class);if (IS_ERR(hello_class)){printk("%s %s %d \n",__FILE__,__FUNCTION__,__LINE__);/* 创建失败的话摧毁内核中的hello结构体 */unregister_chrdev( major, "hello");return -1;}/* 创建了节点后,需要创建设备 */ device_create(hello_class, NULL, MKDEV(major, 0), NULL, "hello"); return 1; }/* 有注册函数就有卸载函数 */ static void __exit hello_exit(void) {printk("%s %s %d \n",__FILE__,__FUNCTION__,__LINE__);/* 把device卸载 */device_destroy(hello_class, MKDEV(major, 0));/* 把class卸载 */class_destroy(hello_class);/* 把file_operation从内核中卸载 */unregister_chrdev( major, "hello");}/* 需要用某些宏表示上述两个函数分别是入口函数和出口函数 */ module_init(hello_init); module_exit(hello_exit);/* 遵循GPL协议 */ MODULE_LICENSE("GPL");
如上,驱动程序hello_driver.c就完成了 ,在这里我们通过上层应用来打开驱动节点,然后往里面写入数据,然后在从里面读取数据。应用的代码如下
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>/** ./hello_drv_test -w abc* ./hello_drv_test -r*/
int main(int argc, char **argv)
{int fd;char buf[1024];int len;/* 1. 判断参数 */if (argc < 2) {printf("Usage: %s -w <string>\n", argv[0]);printf(" %s -r\n", argv[0]);return -1;}/* 2. 打开文件 */fd = open("/dev/hello", O_RDWR);if (fd == -1){printf("can not open file /dev/hello\n");return -1;}/* 3. 写文件或读文件 */if ((0 == strcmp(argv[1], "-w")) && (argc == 3)){len = strlen(argv[2]) + 1;len = len < 1024 ? len : 1024;write(fd, argv[2], len);}else{len = read(fd, buf, 1024); buf[1023] = '\0';printf("APP read : %s\n", buf);}close(fd);return 0;
}同时,我们还需要编写Makefile,Makefile和具体的解析如下所示
1、KERN_DIR = /home/book/100ask_imx6ull-sdk/Linux-4.9.88
定义了KERN_DIR变量,指向了内核的目录
2、all:
标记了Makefile的第一个目标,执行make的时候执行
3、make -C $(KERN_DIR) M=`pwd` modules
-C $(KERN_DIR):这是make的一个选项,用于改变到另一个目录并读取那里的Makefile。这告诉make工具首先进入这个目录,并在那里查找Makefile。
M=`pwd` modules:M的意思是指定模块源代码的的位置,当指定了module作为目标后,就是告诉系统想要构建内核模块。内核构建系统会查找当前目录(由M变量指定)中的模块源代码,并生成相应的模块文件(通常是.ko文件)。
4、$(CROSS_COMPILE)gcc -o hello_drv_test hello_drv_test.c
CROSS_COMPILE是环境变量,这列的意思是使用交叉编译器编译hello_drv_test.c 生成hello_drv_test.o。如果不存在交叉编译器会使用gcc
5、obj-m += hello_driver.o
这行告诉内核构建系统hello_driver.o是一个要构建的对象文件(即内核模块)
KERN_DIR = /home/book/100ask_imx6ull-sdk/Linux-4.9.88all:make -C $(KERN_DIR) M=`pwd` modules $(CROSS_COMPILE)gcc -o hello_drv_test hello_drv_test.c clean:make -C $(KERN_DIR) M=`pwd` modules cleanrm -rf modules.orderrm -f hello_drv_testobj-m += hello_driver.o
驱动的安装、卸载和现象
当我们在服务器上面编译完成后,会生成如下几个文件
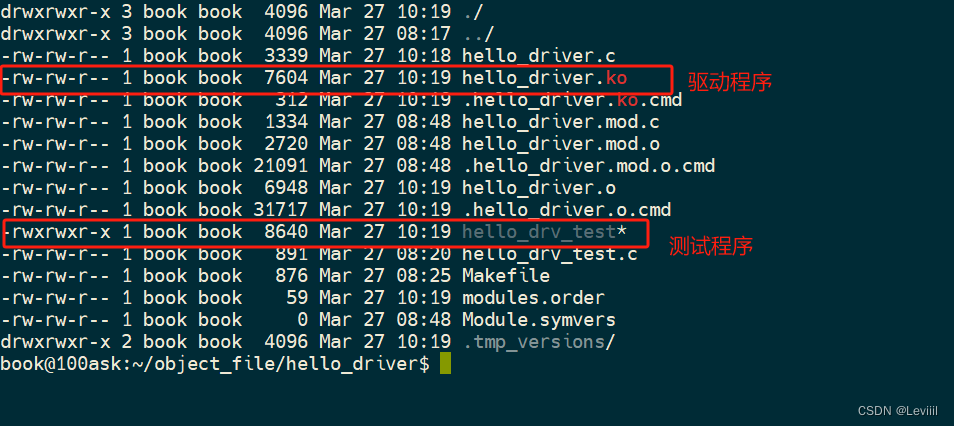
我们通过挂载,把这两个文件挂载到开发板上
当前挂载的目录下存在 hello_driver.ko hello_drv_test这两个文件。
首先,我们需要安装驱动,使用 insmod + 驱动名 ,来安装驱动
(lsmod也可以查看安装的驱动程序)
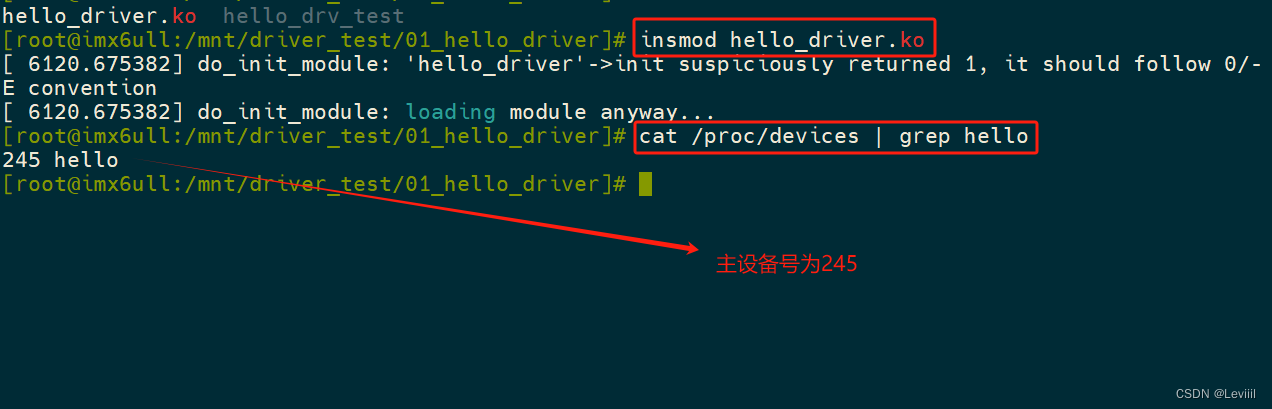
如上图,驱动程序成功的安装了
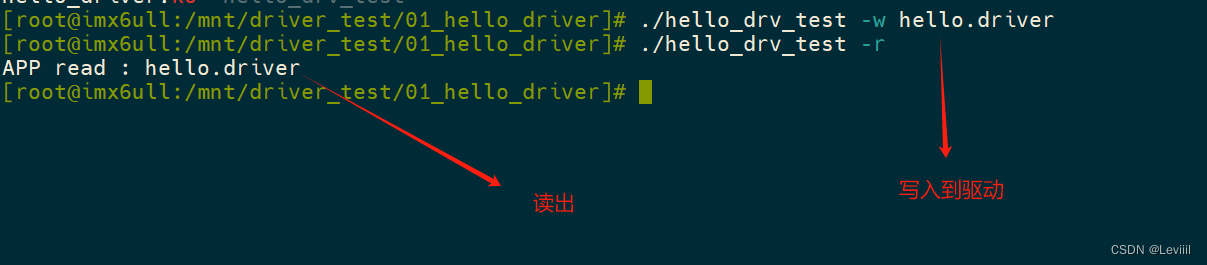
在这里我们使用应用文件写入驱动程序,再从中读出
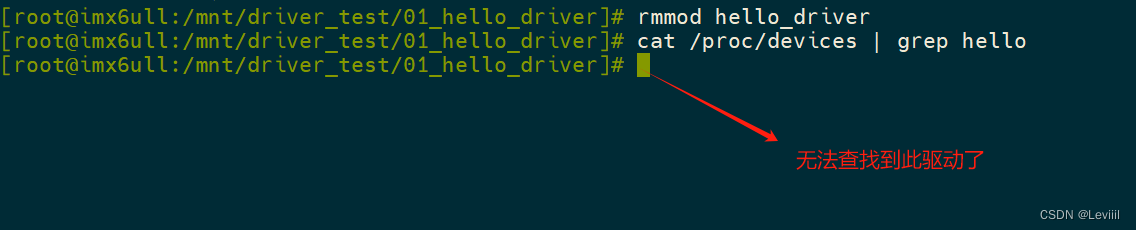
当我们不使用驱动的时候,使用 rmmod+驱动名 卸载


)



SpringBoot整合RocketMQ发送单向消息)

)










