
个人主页:日刷百题
系列专栏:〖C/C++小游戏〗〖Linux〗〖数据结构〗 〖C语言〗
🌎欢迎各位→点赞👍+收藏⭐️+留言📝

一、string类
这里我们对string类进行一个简单的总结:
- string是表示字符串的字符串类
- 该类的接口与常规容器的接口基本相同,再添加了一些专门用来操作string的常规操作。
- string在底层实际是:
//string是basic_string模板类的别名
typedef basic_string<char, char_traits, allocator> string;- 不能操作多字节或者变长字符的序列。
这里有一个需要注意的点:
在使用string类时,必须包含#include头文件以及using namespace std;
二、string类的常用接口
2.1 string对象常见构造(constructor)

| (constructor)函数名称 | 功能说明 |
| string()(重点) | 构造空的string类对象,即空字符串 |
| string(const char* s)(重点) | 用C-string来构造string类对象 |
| string(size_t n, char c) | string类对象中包含n个字符 |
| string(const string&s)(重点) | 拷贝构造函数 |
2.1.1 string()
- 构造空的string对象,即空字符串
//空构造函数
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{string s1;cout << s1 << endl;return 0;
}2.1.2 string(const char* s)
- 用C-string来构造string类对象
//常量字符串
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{string s1("hello world");cout << s1 << endl;return 0;
}

其实相当于将常量字符串拷贝到str中
2.1.3 string(size_t n, char c)
- 用n个相同的字符c去构造string类对象
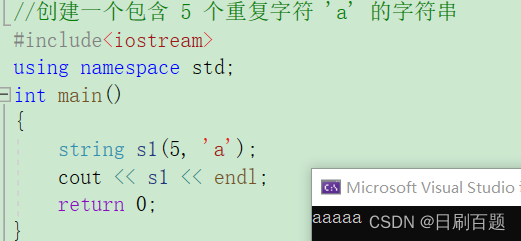
//创建一个包含 5 个重复字符 'a' 的字符串
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{string s1(5,'a');cout << s1 << endl;return 0;
}
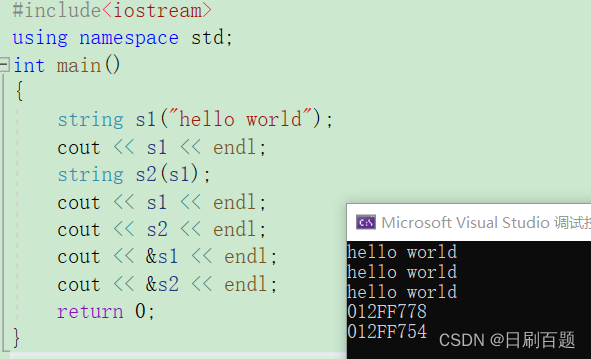
2.1.4 string(const string&s)
- 拷贝构造(深拷贝),只有调用默认拷贝构造才是浅拷贝
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{string s1("hello world");cout << s1 << endl;string s2(s1);cout << s1 << endl;cout << s2 << endl;cout << &s1 << endl;cout << &s2 << endl;return 0;
}
2.1.5 string (const string& str, size_t pos, size_t len = npos)
- 拷贝一个string类对象,读取从他的第pos个位置开始的往后的len个字符
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{string s1("hello world");cout << s1 << endl;string s2(s1, 6, 3);cout << s2 << endl;return 0;
}
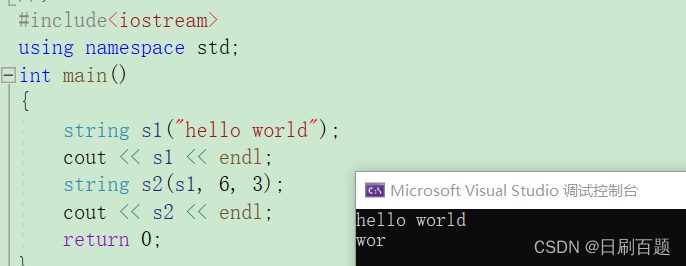
注:
如果拷贝的字符数量大于字符串的字符个数的话,就全部打印完;如果不给值,则是缺省值npos,值为-1,也是全部打完。
2.2 string类对象的容量操作(Capacity)
| 函数名称 | 功能说明 |
| size(重点) | 返回字符串有效字符长度 |
| length | 返回字符串有效字符长度 |
| capacity | 返回空间总大小 |
| empty (重点) | 检测字符串释放为空串,是返回true,否则返回false |
| clear (重点) | 清空有效字符 |
| reserve (重点) | 为字符串预留空间** |
| resize (重点) | 将有效字符的个数该成n个,多出的空间用字符c填充 |
2.2.1 size和length
- size和length其实是一样的, 都代表字符串的长度,但是早期STL还没出现的时候,strling类用的是length,但是后来STL出来后,里面大部分都是用的size,所以为了保持一致性又造了一个size出来,平时用哪个都可以的。
用法如下:
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{string s1("hello world");cout << s1.length() << endl;cout << s1.size() << endl;return 0;
}
注意:这里计算出来的是有效字符个数,也就是说不包括’\0’
2.2.2 capacity

- 表示string当前的容量,一般来说是默认不算上’\0'
用法如下:
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{string s1("hello world");cout << s1.capacity() << endl;return 0;
}

注:vs用的是PJ版STL,字符串会先被存在_Bx数组中,是char[16]类型,超过之后才会去动态开辟空间,第一次开辟空间是32,然后从32开始进行1.5倍扩容。而g++是SGI版STL,直接就是从0开始,然后根据情况直接开始扩容,从0开始进行2倍扩容。
2.2.3 empty

- 字符串为空返回1,不为空返回0
用法如下:
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{string s1("hello world");cout << s1.empty() << endl;return 0;
}

2.2.4 clear
- 清空字符串
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{string s1("hello world");cout << s1 << endl;s1.clear();cout << s1 << endl;return 0;
}
2.2.5 reverse

- 作用是开空间,扩容
- 如果 n 大于当前字符串容量(capacity),则该函数会导致容器将其容量增加到 n 个字符(或更大)。
- 在所有其他情况下,它被视为一个非约束性的缩减字符串容量请求:容器实现可以自由优化,保持字符串的容量大于n。
- 此函数对字符串长度没有影响,也无法更改其内容。(当n小于对象当前的capacity时,什么也不做)
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{string s1("hello world");cout << s1.capacity() << endl;cout << s1.size() << endl;//1.5倍扩容s1.reserve(30);cout << s1.capacity() << endl;cout << s1.size() << endl;return 0;
}
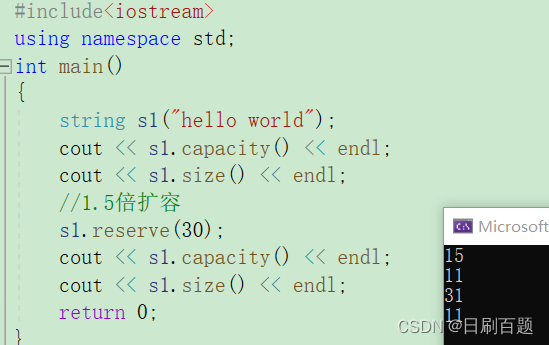
- 扩容不会改变size()。
- vs根据1.5倍的扩容规则,至少会扩容到超过你的要求。如果是g++的话,就是2被扩容。
2.2.6 resize

- 改变size,减少的话就是变少(不会改变容量),如果增多的话就可能会扩容顺便帮助我们初始化,第一个版本的话初始化补\0,第二个版本的话就是初始化c字符
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{string s1("hello world");cout << s1.capacity() << endl;cout << s1.size() << endl;s1.resize(30);cout << s1.capacity() << endl;cout << s1.size() << endl;return 0;
}
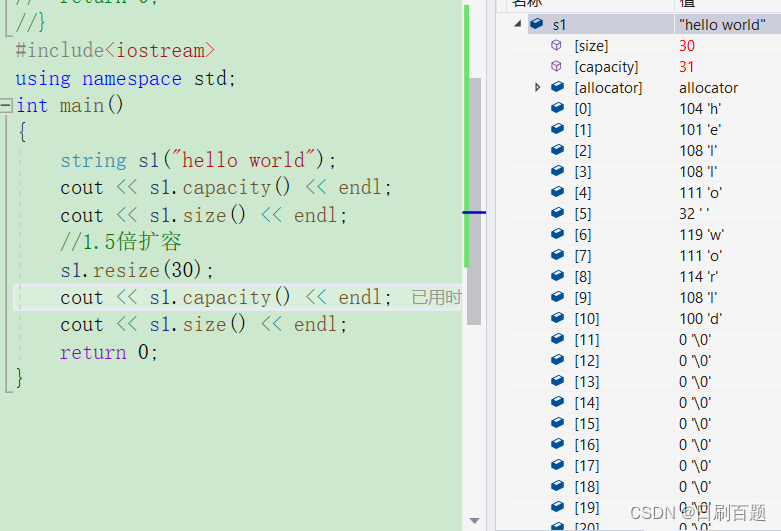
总结:
- **size()**与length()方法底层实现原理完全相同,引入size()的原因是为了与其他容器的接口保持一致,一般情况下基本都是用size(),它的长度不包括\0。
- clear()只是将string中有效字符清空,不改变底层空间大小。
- resize(size_t n) 与 resize(size_t n, char c)都是将字符串中有效字符个数改变到n个,不同的是当字符个数增多时:resize(n)用0来填充多出的元素空间,resize(size_t n, char c)用字符c来填充多出的元素空间。注意:resize在改变元素个数时,如果是将元素个数增多,可能会改变底层容量的大小,如果是将元素个数减少,底层空间总大小不变。
- reserve(size_t res_arg=0):为string预留空间,不改变有效元素个数,当reserve的参数小于string的底层空间总大小时,reserver不会改变容量大小。
2.3 string类对象的访问及遍历操作(Iterators)
| 函数名称 | 功能说明 |
| operator[] (重点) | 返回 pos 位置的字符, const string 类对象调用 |
| begin + end | begin 获取一个字符的迭代器 + end 获取最后一个字符下一个位置的迭 代器 |
| rbegin + rend | begin 获取一个字符的迭代器 + end 获取最后一个字符下一个位置的迭 代器 |
| 范围 for | C++11 支持更简洁的范围 for 的新遍历方式 |
2.3.1 operater[ ] 和 at()
- 返回该位置的字符
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{string const s1("hello world");for (int i = 0; i < s1.length(); i++){cout << s1[i];}cout << endl;return 0;
}
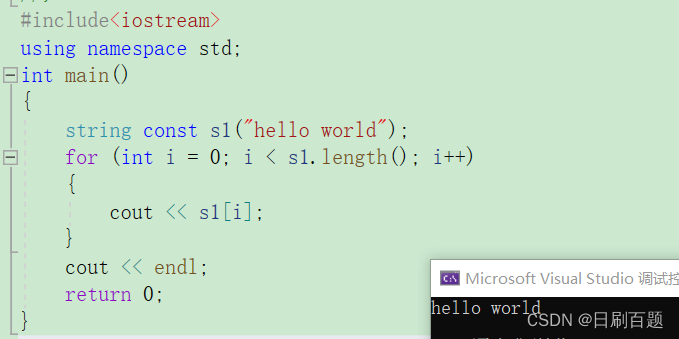
注:用[ ]越界是断言错误。
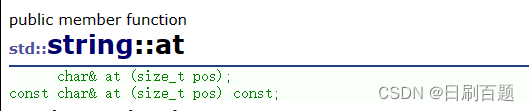
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{string const s1("hello world");for (int i = 0; i < s1.length(); i++){cout << s1.at(i);}cout << endl;return 0;
}
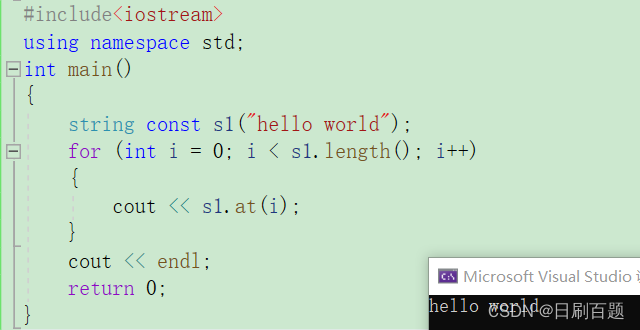
注:at()越界时候报的是非法。
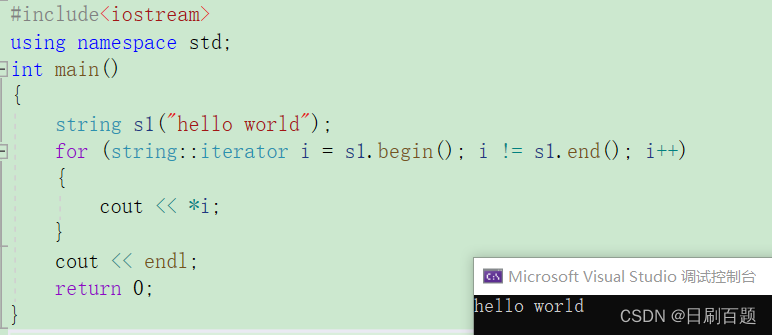
2.3.2 迭代器(iterator)遍历

迭代器有两种,还有一个叫做反向迭代器,就是从尾部开始遍历,我们这里介绍正向迭代器
iterator是一个类型定义在string里面,所以它要指定类域,才能取到。
begin是开始的指针,end是指向‘\0’的指针,注意是左闭右开!!
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{string s1("hello world");for (string::iterator i = s1.begin(); i != s1.end(); i++){cout << *i;}cout<<endl;return 0;
}
反向迭代器就是从后开始往前移动:
这里要引出的是 reverse_iterator 其实这里的rbegin是字符串的最后一个位置(不是\0),并且这里的指针也是++,向前移动。
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{string s1("hello world");for (string::reverse_iterator i = s1.rbegin(); i != s1.rend(); i++){cout << *i;}cout<<endl;return 0;
}

注:迭代器像指针,但不是指针。
2.3.3 范围for
- 自动取容器中的数据,赋值给e,自动迭代,自动往后走,自动结束。
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{string s1("hello world");for (auto e:s1){cout << e;}cout<<endl;return 0;
}
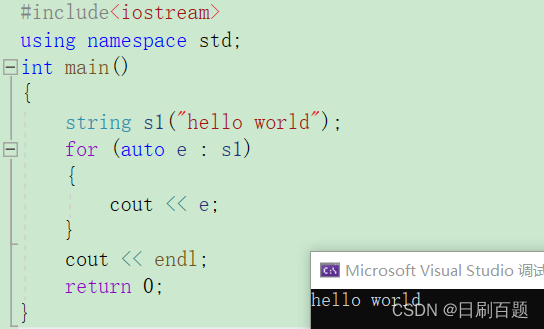
注:for循环的底层实现就是迭代器!
2.4 string类对象的修改操作(Modifiers)

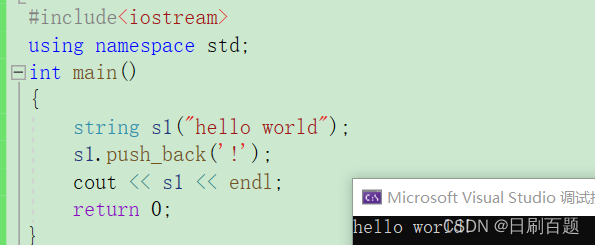
2.4.1 push_back
- 在字符串尾插字符C
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{string s1("hello world");s1.push_back('!');cout << s1 << endl;return 0;
}
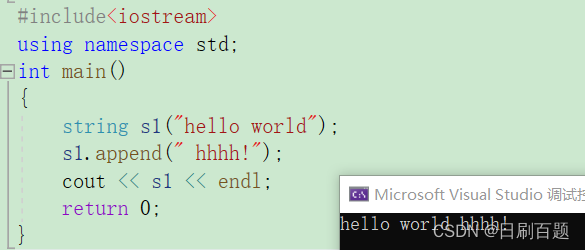
2.4.2 append
- append尾插,可以插入字符串
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{string s1("hello world");s1.append(" hhhh!");cout << s1 << endl;return 0;
}
2.2.3 operator+=
- operator+=可以实现在字符串后面追加字符或者字符串,并且函数的可读性更高,所以我们一般选择使用+=来实现对对象的追加
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{string s1("hello world");s1+=(" hhhh!");cout << s1 << endl;s1 += ('x');cout << s1 << endl;return 0;
}

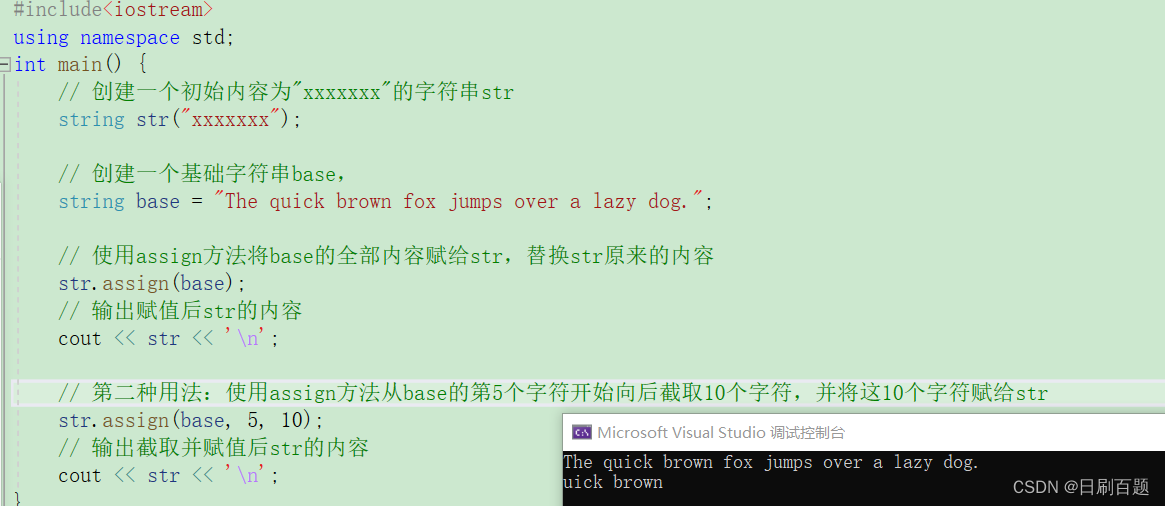
2.2.4 assign(了解即可)
- assign赋值,字符覆盖
void test_string9() {// 创建一个初始内容为"xxxxxxx"的字符串strstring str("xxxxxxx");// 创建一个基础字符串base,string base = "The quick brown fox jumps over a lazy dog.";// 使用assign方法将base的全部内容赋给str,替换str原来的内容str.assign(base);// 输出赋值后str的内容cout << str << '\n';// 第二种用法:使用assign方法从base的第5个字符开始截取10个字符,并将这10个字符赋给strstr.assign(base, 5, 10);// 输出截取并赋值后str的内容cout << str << '\n';
}
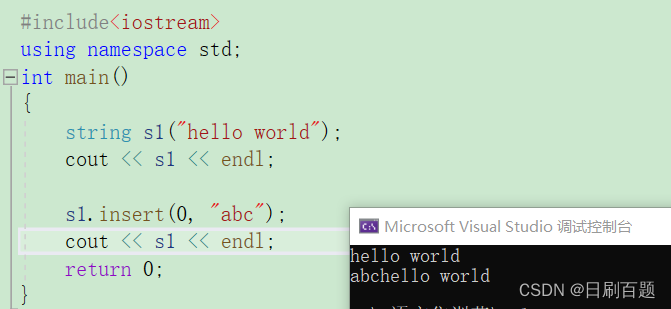
2.2.5 insert
- insert都是在当前位置的前面插入
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{string s1("hello world");cout << s1 << endl;s1.insert(0, "abc");cout << s1 << endl;return 0;
}
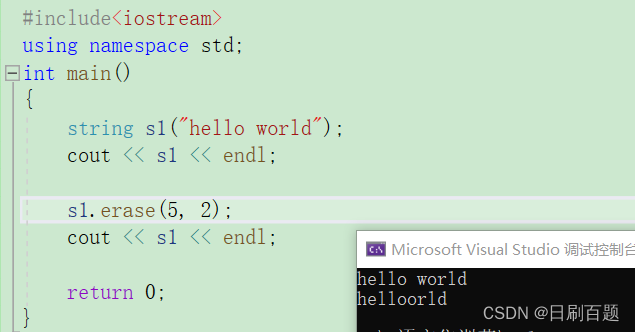
2.2.6 erase

- erase删除:表示第pos个位置开始后len个字符删除,len的默认值是npos
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{string s1("hello world");cout << s1 << endl;s1.erase(5, 2);cout << s1 << endl;return 0;
}
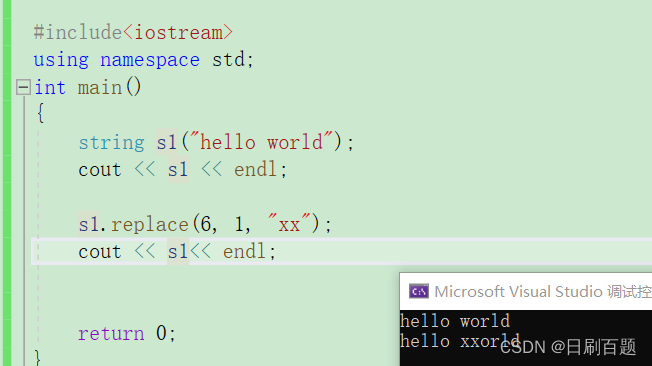
2.2.7 replace
- replace替换:将pos位置开始的len个字符替换成字符串
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{string s1("hello world");cout << s1 << endl;s1.replace(6, 1, "xx");cout << s1<< endl;return 0;
}
2.2.8 swap
- 交换2个string类对象的指针指向
void test_string9()
{string s2("hello world hello abcd");string s3;s3.reserve(s2.size());for (auto ch : s2){if (ch != ' '){s3 += ch;}else{s3 += "20%";}}cout << s3 << endl;s2.swap(s3);cout << s2 << endl;
}

总结:
- 在string尾部追加字符时,s.push_back / s.append() / += 三种的实现方式差不多,一般情况下string类的+=操作用的比较多,+=操作不仅可以连接单个字符,还可以连接字符串。
- 对string操作时,如果能够大概预估到放多少字符,可以先通过reserve把空间预留好。
2.5 string类对象的操作(operations)
| c_str(重点) | 返回c格式的字符串 |
| find | 从字符串pos位置开始往后找字符c,返回该字符在字符串中的位置 |
| rfind | 从字符串pos位置开始往前找字符c,返回该字符在字符串中的位置 |
| substr | 在str中从pos位置开始,截取n个字符,然后将其返回 |
2.5.1 c_str
- 以C语言的方式打印字符串
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{string s1("hello world");cout << s1.c_str() << endl;return 0;
}

注:不能通果c_str 返回的指针去修改字符串,因为它指向的是常量区域。
2.5.2 find
- find从字符串pos位置开始往后找字符c,返回该字符在字符串中的位置,如果没有找到会返回npos
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
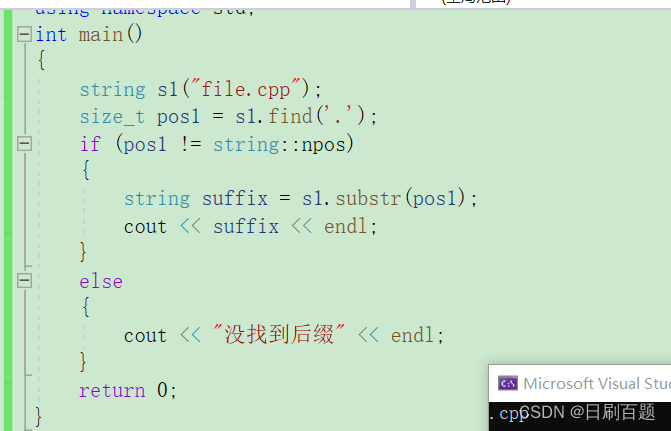
{string s1("file.cpp");size_t pos1 = s1.find('.');if (pos1 != string::npos){string suffix = s1.substr(pos1);cout << suffix << endl;}else{cout << "没找到后缀" << endl;}return 0;
}
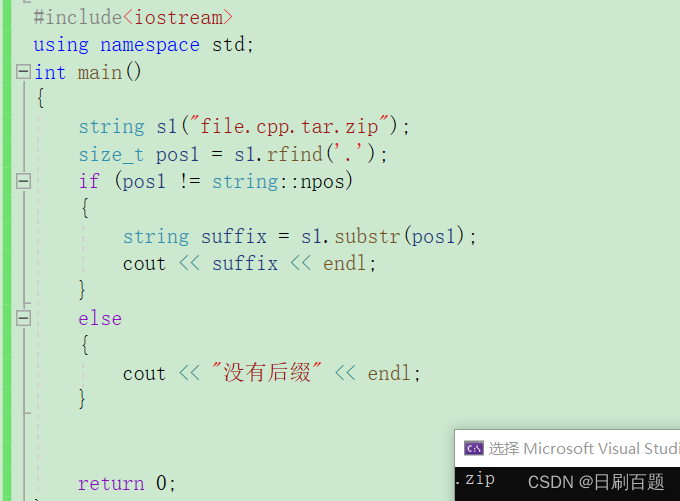
2.5.3 refind
- rfind从字符串pos位置开始向前找字符c,返回该字符在字符串中的位置,如果没有找到会返回npos
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{string s1("file.cpp.tar.zip");size_t pos1 = s1.rfind('.');if (pos1 != string::npos){string suffix = s1.substr(pos1);cout << suffix << endl;}else{cout << "没有后缀" << endl;}return 0;
}
2.5.4 substr
- 在str中从pos位置开始,截取n个字符,然后将其返回
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{string s1("hello world");cout << s1.substr(3, 4) << endl;cout << s1.substr(3, 12) << endl;
}

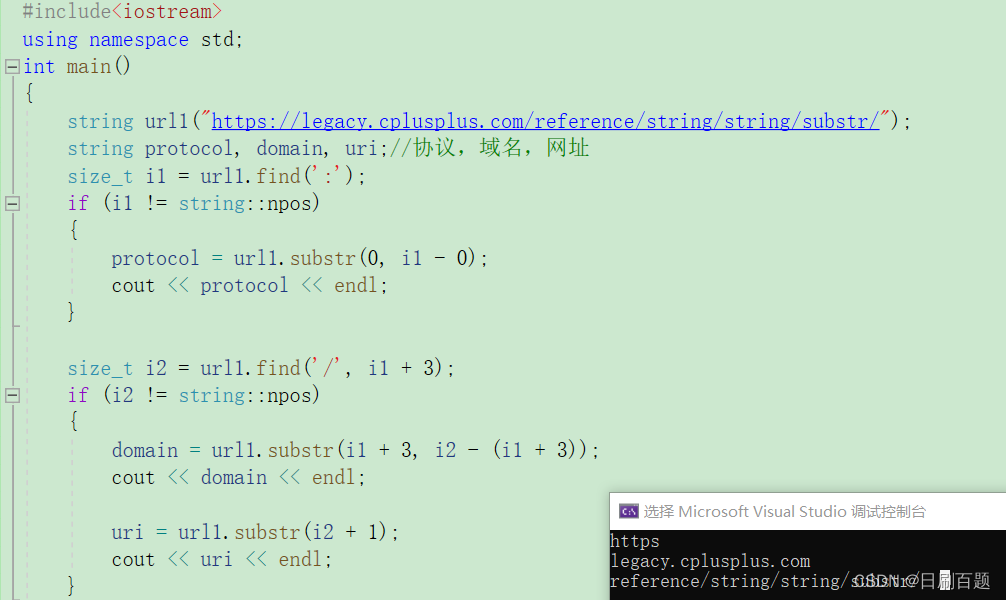
如何利用上面接口,区分开网站的协议,域名,网址呢?
void test_string10()
{string url1("https://legacy.cplusplus.com/reference/string/string/substr/");string protocol, domain, uri;//协议,域名,网址size_t i1 = url1.find(':');if (i1 != string::npos){protocol = url1.substr(0, i1 - 0);cout << protocol << endl;}size_t i2 = url1.find('/',i1+3);if (i2 != string::npos){domain = url1.substr(i1+3, i2-(i1+3));cout << domain << endl;uri = url1.substr(i2+1);cout << uri << endl;}
}
2.6 string类非成员函数
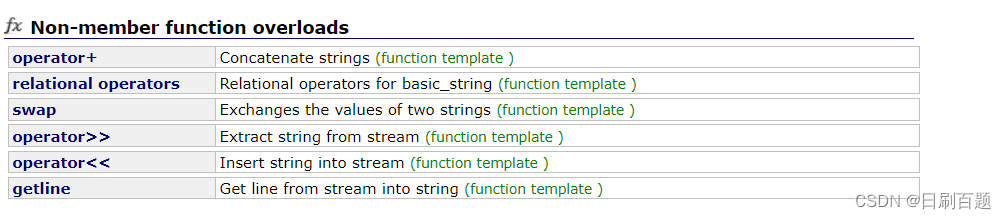
其实这里用的不多,不做过多的讲解
但是这个getline函数是可以用到一些题目中来读取字符串的,他遇到换行符就会停止读取,遇到空格不会.
2.6.1 getline

获得一个字符串(hello word!)里面最后一个单词的长度
#include<iostream>
#include<string>
using namespace std;
int main()
{string line;// 不要使用cin>>line,因为会它遇到空格就结束了// while(cin>>line)while (getline(cin, line)){size_t pos = line.rfind(' ');cout << line.size() - (pos+1) << endl;}return 0;
}


)



)
-- 何为参数(parameters))



)



)



