题目
实现一个二叉搜索树迭代器类BSTIterator ,表示一个按中序遍历二叉搜索树(BST)的迭代器:
BSTIterator(TreeNode root) 初始化 BSTIterator 类的一个对象。BST 的根节点 root 会作为构造函数的一部分给出。指针应初始化为一个不存在于 BST 中的数字,且该数字小于 BST 中的任何元素。
boolean hasNext() 如果向指针右侧遍历存在数字,则返回 true ;否则返回 false 。
int next()将指针向右移动,然后返回指针处的数字。
注意,指针初始化为一个不存在于 BST 中的数字,所以对 next() 的首次调用将返回 BST 中的最小元素。
你可以假设 next() 调用总是有效的,也就是说,当调用 next() 时,BST 的中序遍历中至少存在一个下一个数字。
示例:
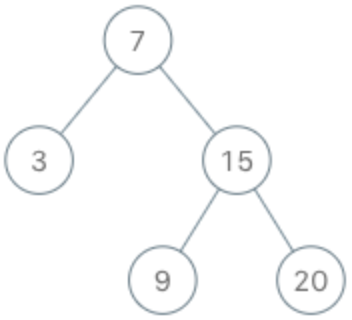
输入
[“BSTIterator”, “next”, “next”, “hasNext”, “next”, “hasNext”, “next”, “hasNext”, “next”, “hasNext”]
[[[7, 3, 15, null, null, 9, 20]], [], [], [], [], [], [], [], [], []]
输出
[null, 3, 7, true, 9, true, 15, true, 20, false]
解释
BSTIterator bSTIterator = new BSTIterator([7, 3, 15, null, null, 9, 20]);
bSTIterator.next(); // 返回 3
bSTIterator.next(); // 返回 7
bSTIterator.hasNext(); // 返回 True
bSTIterator.next(); // 返回 9
bSTIterator.hasNext(); // 返回 True
bSTIterator.next(); // 返回 15
bSTIterator.hasNext(); // 返回 True
bSTIterator.next(); // 返回 20
bSTIterator.hasNext(); // 返回 False
解
class BSTIterator {LinkedList<TreeNode> stack;TreeNode cur;public BSTIterator(TreeNode root) {stack = new LinkedList<>();cur = root;}public int next() {while (cur != null) {stack.push(cur);cur = cur.left;}cur = stack.pop();int result = cur.val;cur = cur.right;return result;}public boolean hasNext() {return (!stack.isEmpty() || cur != null);}
}
)
)
(4)(数组)(万字详解版))
![[C++] 类型转换操作符(static_cast、dynamic_cast、const_cast、reinterpret_cast)](http://pic.xiahunao.cn/[C++] 类型转换操作符(static_cast、dynamic_cast、const_cast、reinterpret_cast))





)



)




(二))
