一、基本介绍
1,什么是 AOP
(1)AOP 为 Aspect Oriented Programming 的缩写,意为:面向切面编程,通过预编译方式和运行期动态代理实现程序功能的统一维护的一种技术。
(2)利用 AOP 可以对业务逻辑的各个部分进行隔离,从而使得业务逻辑各部分之间的耦合度降低,提高程序的可重用性,同时提高了开发的效率。
一个 AOP 的使用场景:
假设一个已经上线的系统运行出现问题,有时运行得很慢。为了检测出是哪个环节出现了问题,就需要监控每一个方法的执行时间,再根据执行时间进行分析判断。
由于整个系统里的方法数量十分庞大,如果一个个方法去修改工作量将会十分巨大,而且这些监控方法在分析完毕后还需要移除掉,所以这种方式并不合适。
如果能够在系统运行过程中动态添加代码,就能很好地解决这个需求。这种在系统运行时动态添加代码的方式称为面向切面编程(AOP)
2,AOP 相关概念介绍
- Joinpoint(连接点):类里面可以被增强的方法即为连接点。例如,想要修改哪个方法的功能,那么该方法就是一个链接点。
- Target(目标对象):要增强的类成为 Target。
- Pointcut(切入点):对 Jointpoint 进行拦截的定义即为切入点。例如,拦截所有以 insert 开始的方法,这个定义即为切入点。
- Advice(通知):拦截到 Jointpoint 之后要做的事情就是通知。通知分为前置通知、后置通知、异常通知、最终通知和环绕通知。例如,前面说到的打印日志监控就是通知。
- Aspect(切面):即 Pointcut 和 Advice 的结合。
3,安装配置
Spring Boot 在 Spring 的基础上对 AOP 的配置提供了自动化配置解决方案,我们只需要修改 pom.xml 文件,添加 spring-boot-starter-aop 依赖即可。
<dependency><groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId><artifactId>spring-boot-starter-aop</artifactId></dependency>二、使用样例
1,创建 Service
首先创建一个 UserService(假设在 com.hmblogs.backend.service),内容如下:
package com.hmblogs.backend.service;import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;@Service
public class UserService {public String getUserById(Integer id) {System.out.println("getUserById(" + id + ")...");// 等待2秒try {Thread.sleep(2000);}catch(InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}return "hangge";}
}
2,创建切面
接着定义一个切面类,代码如下:
注解说明:
(1)@Aspect 注解:表明这是一个切面类。
(2)@Pointcut 注解:表明这是一个切入点。
- execution 中的第一个 * 表示方法返回任意值
- 第二个 * 表示 service 包下的任意类
- 第三个 * 表示类中的任意方法,括号中的两个点表示方法参数任意,即这里描述的切入点为 service 包下所有类中的所有方法。
(3)@Before 注解:表示这是一个前置通知,该方法在目标方法之前执行。
- 通过 JoinPoint 参数可以获取目标方法的方法名、修饰符等信息。
(4)@After 注解:表示这是一个后置通知,该方法在目标执行之后执行。
(5)@AfterReturning 注解:表示这是一个返回通知,在该方法中可以获取目标方法的返回值。
- returning 参数是指返回值的变量名,对应方法的参数。
- 注意:本样例在方法参数中定义 result 的类型为 Object,表示目标方法的返回值可以是任意类型。若 result 参数的类型为 Long,则该方法只能处理目标方法返回值为 Long 的情况。
(6)@AfterThrowing 注解:表示这是一个异常通知,即当目标方法发生异常,该方法会被调用。
- 样例中设置的异常类型为 Exception 表示所有的异常都会进入该方法中执行。
- 若异常类型为 ArithmeticException 则表示只有目标方法抛出的 ArithmeticException 异常才会进入该方法的处理。
(7) @Around 注解:表示这是一个环绕通知。环绕通知是所有通知里功能最为强大的通知,可以实现前置通知、后置通知、异常通知以及返回通知的功能。
- 目标方法进入环绕通知后,通过调用 ProceedingJointPoint 对象的 proceed 方法使目标方法继续执行,开发者可以再次修改目标方法的执行参数、返回值,并且可以在此目标方法的异常。
package com.hmblogs.backend.util;import org.aspectj.lang.JoinPoint;
import org.aspectj.lang.ProceedingJoinPoint;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.*;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;@Aspect
@Component
public class LogAspect {// 定义一个切入点@Pointcut("execution(* com.hmblogs.backend.service.*.*(..))")public void pc1(){}// 前置通知@Before(value = "pc1()")public void before(JoinPoint jp) {String name = jp.getSignature().getName();System.out.println(name + "方法开始执行...");}// 后置通知@After(value = "pc1()")public void after(JoinPoint jp) {String name = jp.getSignature().getName();System.out.println(name + "方法执行结束...");}// 返回通知@AfterReturning(value = "pc1()", returning = "result")public void afterReturning(JoinPoint jp, Object result) {String name = jp.getSignature().getName();System.out.println(name + "方法返回值为:" + result);}// 异常通知@AfterThrowing(value = "pc1()", throwing = "e")public void afterThrowing(JoinPoint jp, Exception e) {String name = jp.getSignature().getName();System.out.println(name + "方法抛异常了,异常是:" + e.getMessage());}// 环绕通知@Around("pc1()")public Object around(ProceedingJoinPoint pjp) throws Throwable {String name = pjp.getSignature().getName();// 统计方法执行时间long start = System.currentTimeMillis();Object result = pjp.proceed();long end = System.currentTimeMillis();System.out.println(name + "方法执行时间为:" + (end - start) + " ms");return result;}
}3,创建 Controller
配置完成后,接下来在 Controller 中创建接口调用 UserService 中的方法。
package com.hmblogs.backend.controller;import com.hmblogs.backend.service.UserService;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;@RestController
public class HelloController {@AutowiredUserService userService;@GetMapping("/test")public String test(Integer id) {return userService.getUserById(id);}
}
4,运行样例
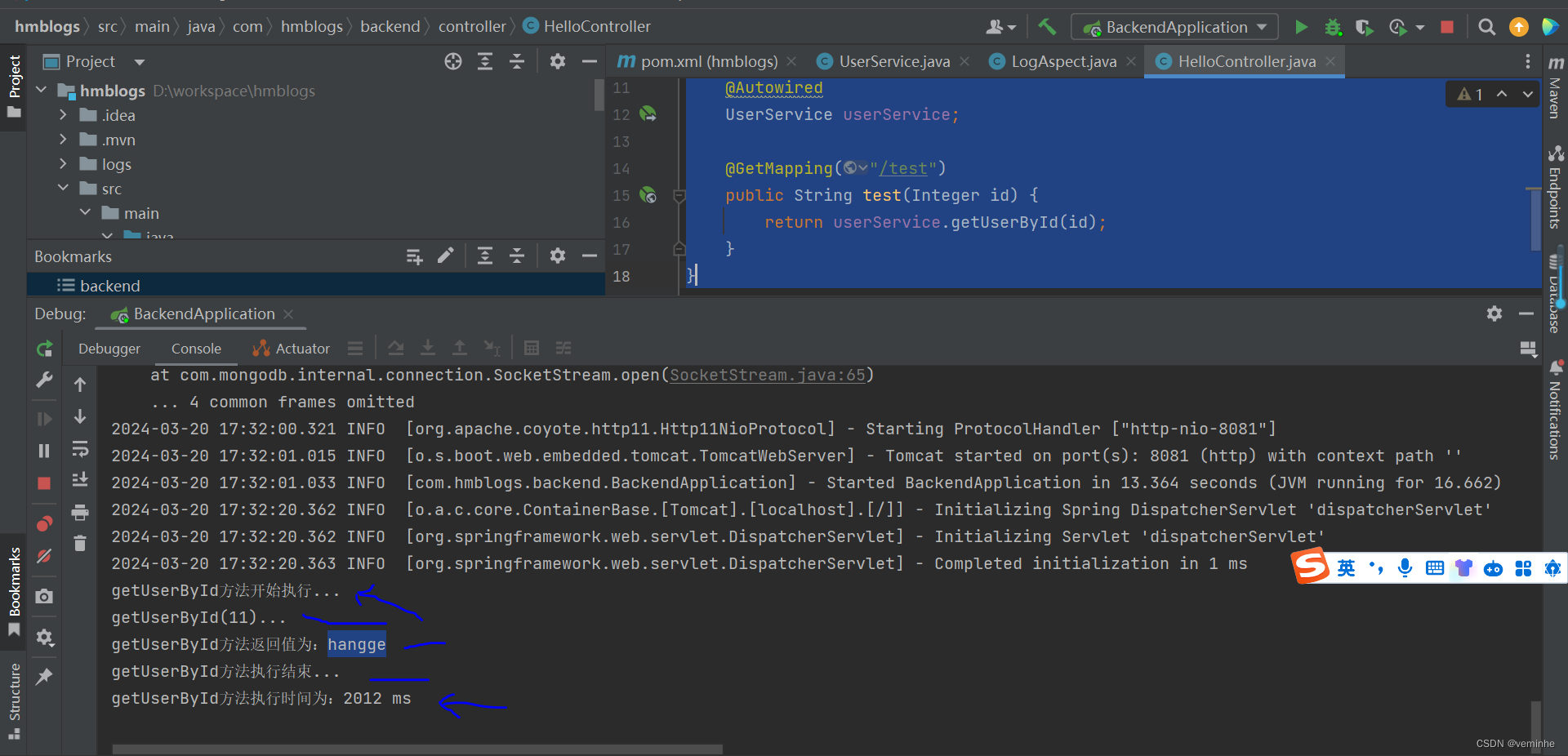
(1)使用浏览器访问如下地址:
- http://localhost:8081/test?id=11
(2)查看控制台信息,可以发现 LogAspect 中的代码动态地嵌入目标方法中执行了。
(五))


)








)




子数组最大累加和,子矩阵最大累加和)

