线程模型
- 一、背景
- 1.socket网络通信
- 2.IO模型与线程模型
- 3.线程模型分类
- 3.1 阻塞模型
- 3.2 Reactor模型
- 3.3 Proactor模式
- 二、阻塞模型
- 1.代码示例
- 三、Reactor模型
- 1.单Reactor单线程
- 1.1 处理过程
- 1.2 优缺点
- 1.3 代码示例
- 2.单Reactor多线程
- 2.1 处理机制
- 2.2 优缺点
- 3.主从Reactor
- 3.1 处理机制
- 3.2 优缺点
- 参考链接
一、背景
服务器需要等待客户端请求,在进行业务处理之后,将结果返回到客户端。其中服务器应用通过内核与网卡进行数据交互,具体原理和交互方式已在上一篇网络通信与IO多路复用中进行了详细介绍。
1.socket网络通信
客户端与服务器进行通信需要经过建立连接、请求、返回、关闭连接等步骤,而服务器需要监听客户端发起的创建连接、读取数据、业务处理、返回数据、关闭连接等步骤。

2.IO模型与线程模型
- IO模型
就是应用与内核读取socket数据的交互方式,已经在上一篇网络通信与IO多路复用中进行了详细介绍。 - 线程模型
服务器利用线程对从监听、创建连接、业务处理、关闭连接整个过程的处理方式。
3.线程模型分类
服务器处理一个网络请求需要经过以下步骤:
- read:从socket读取数据
- decode:解码,将网络上的流式byte转化成请求
- compute:计算,主要是进行业务处理
- encode:编码,将请求转化成流式byte数据
线程模型主要分为以下三类:
3.1 阻塞模型
服务端为每个客户端建立线程进行以上处理,一个线程为一个客户端服务。
3.2 Reactor模型
基于IO模型中的IO多路复用,服务端一个线程为多个客户端服务。
3.3 Proactor模式
基于IO模型中的异步IO,服务端一个线程为多个客户端服务。
二、阻塞模型
阻塞模型是针对每个客户端都会开启一个线程进行读事件处理以及业务处理。
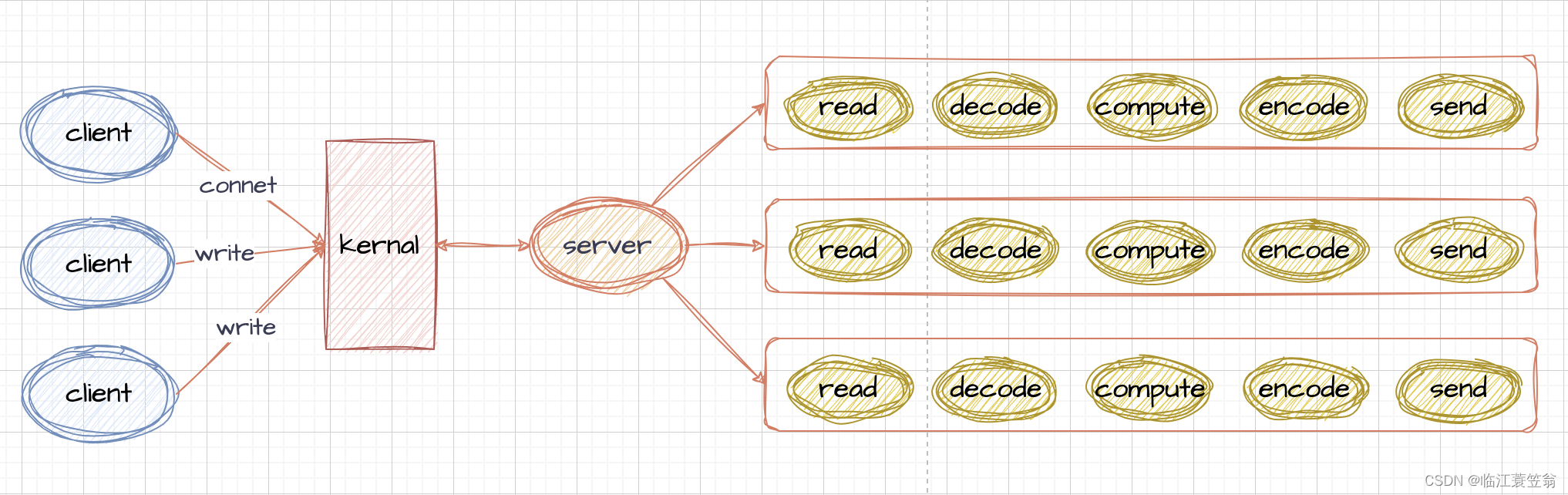
1.代码示例
Reactor代码:
public static void main(String[] args) {try {ServerSocket serverSocket = new ServerSocket(9696);Socket socket = serverSocket.accept();new Thread(() -> {try {byte[] byteRead = new byte[1024];socket.getInputStream().read(byteRead);String req = new String(byteRead, StandardCharsets.UTF_8);//encode// do somethingbyte[] byteWrite = "Hello".getBytes(StandardCharsets.UTF_8);//decodesocket.getOutputStream().write(byteWrite);} catch (IOException e) {e.printStackTrace();}}).start();} catch (IOException e) {e.printStackTrace();}}
三、Reactor模型
Reactor模型主要是利用IO多路复用,利用少量线程为处理所有客户端的连接请求和读写请求。主要包含一下几部份:
- Reactor:利用IO多路复用,监控连接请求就绪和读写请求就绪
- Acceptor:接受客户端连接请求并创建连接,然后注册到Reactor的多路复用Selector中
- Handle:对客户端的写请求进行读写编码和业务处理
1.单Reactor单线程
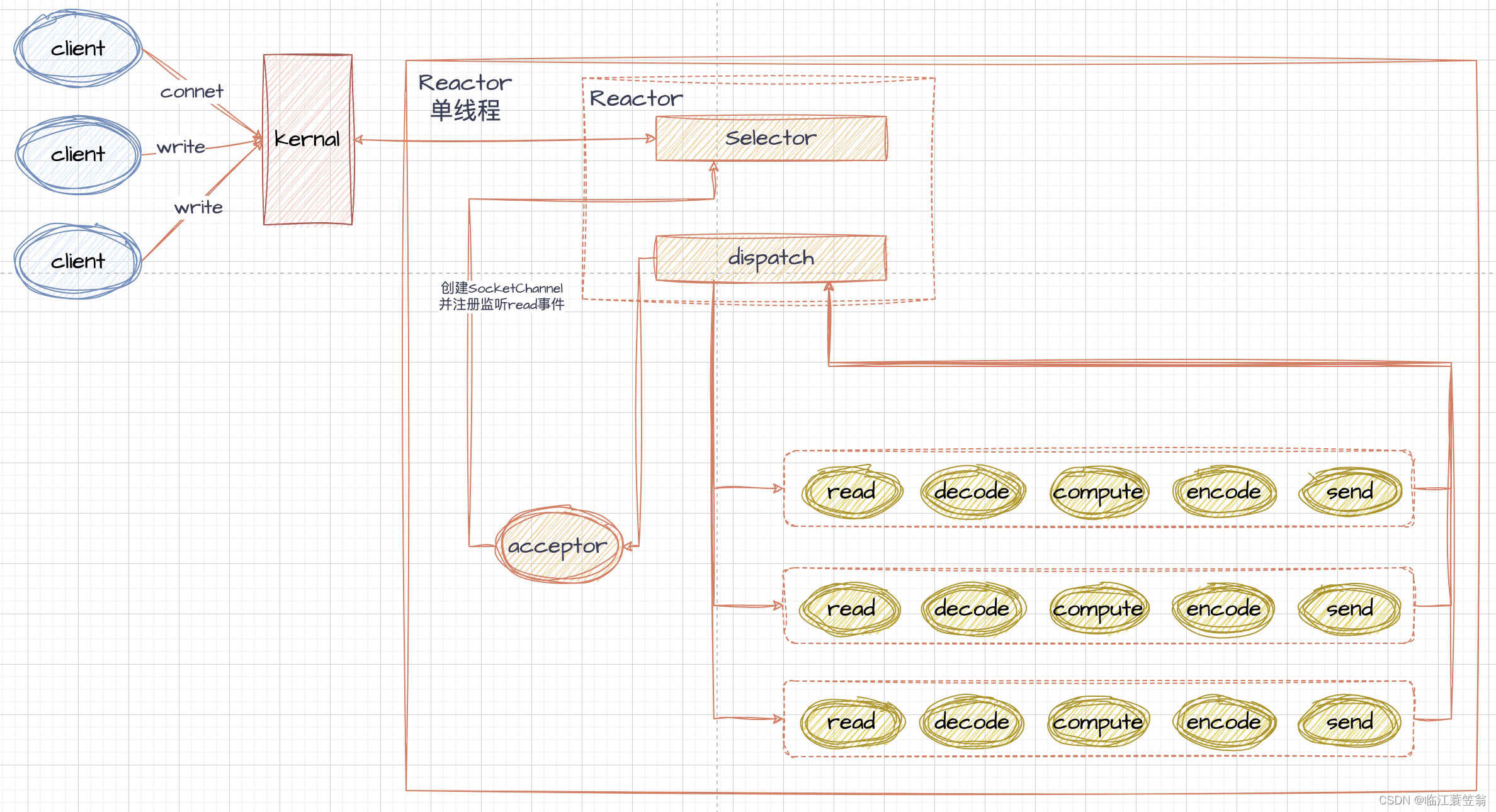
1.1 处理过程
- Reactor构建Selector,监控port的连接事件并注册到Selector,并添加连接事件处理方法Acceptor
- 有连接请求后,会触发Acceptor逻辑,会创建socketChannel并将此socketChannel的读事件注册到Reactor的Selector,并添加读事件处理方法Handle
- 如果有读请求,会触发Handle事件,进行业务处理
1.2 优缺点
一个线程需要处理连接请求、读写请求、业务处理,处理业务请求会想对较慢。需要等待业务处理完成,才能对其他请求进行处理。
单线程Reactor模型编程比较简单,比较适合业务处理可以快速完成的场景,比如Redis。
1.3 代码示例
Reactor代码:
static class Reactor implements Runnable {ServerSocketChannel serverSocketChannel;Selector selector;public Reactor(int port) {try {serverSocketChannel = ServerSocketChannel.open();selector = Selector.open();// 监听port端口serverSocketChannel.socket().bind(new InetSocketAddress(port));serverSocketChannel.configureBlocking(false);// 注册连接事件SelectionKey selectionKey = serverSocketChannel.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_CONNECT);// 在连接事件上附加一个处理类selectionKey.attach(new Acceptor(selector, serverSocketChannel));} catch (IOException e) {System.out.println(e);}}@Overridepublic void run() {while (true) {try {selector.select();Set<SelectionKey> selectionKeys = selector.selectedKeys();Iterator<SelectionKey> iterator = selectionKeys.iterator();while (iterator.hasNext()) {SelectionKey selectionKey = iterator.next();dispatcher(selectionKey);iterator.remove();}} catch (Exception e) {}}}private void dispatcher(SelectionKey selectionKey) {Runnable runnable = (Runnable) selectionKey.attachment();runnable.run();}}
Acceptor与WorkHandle代码:
static class Acceptor implements Runnable {Selector selector;ServerSocketChannel serverSocketChannel;public Acceptor(Selector selector, ServerSocketChannel serverSocketChannel) {this.selector = selector;this.serverSocketChannel = serverSocketChannel;}@Overridepublic void run() {try {SocketChannel socketChannel = serverSocketChannel.accept();SelectionKey selectionKey = socketChannel.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_READ);selectionKey.attach(new WorkHandle(socketChannel));} catch (Exception e) {}}}static class WorkHandle implements Runnable {SocketChannel socketChannel;public WorkHandle(SocketChannel socketChannel) {this.socketChannel = socketChannel;}@Overridepublic void run() {try {ByteBuffer byteBuffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024);socketChannel.read(byteBuffer);socketChannel.write(ByteBuffer.wrap("message received".getBytes(StandardCharsets.UTF_8)));} catch (Exception e) {}}}
2.单Reactor多线程
单Reactor多线程主要是将业务处理进行多线程处理,其他操作还是由单线程处理。
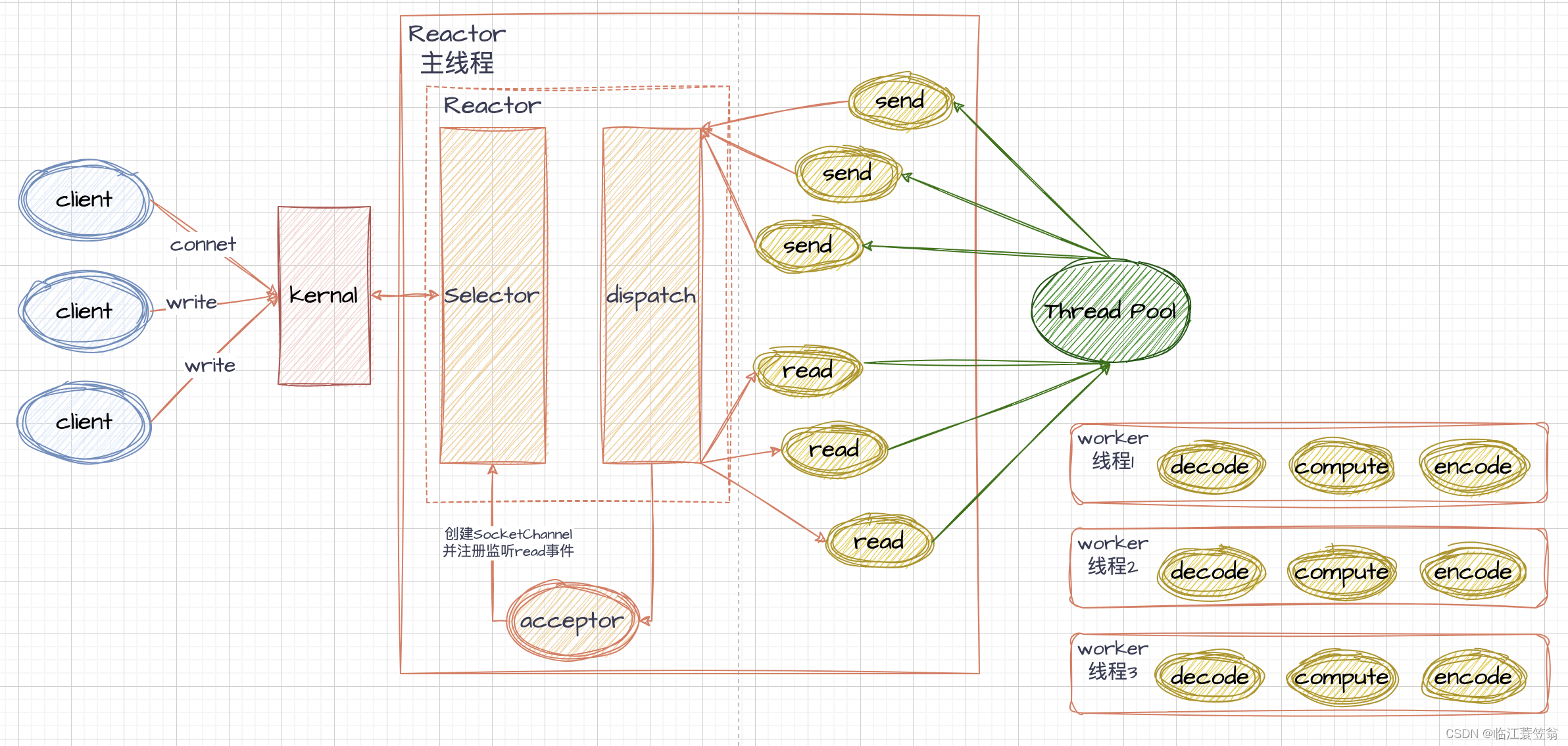
2.1 处理机制
从整体架构图可知,整个处理机制与Reactor单线程模式基本一致。单个线程还是需要负责处理连接和读写请求,但是业务处理会提交到线程池进行处理。
2.2 优缺点
此模型不会因为业务处理相对较慢,而导致IO请求出现等待的情况。但是由于Reactor既要负责连接请求还需要负责读写请求。一个客户端一般只有一次连接请求,但是会有多次读写请求。如果有频繁的读请求,单个线程处理可能会导致无法及时处理其他读请求。
3.主从Reactor
主从Reactor模型主要是利用一个主Reactor监控连接请求就绪、一个或者多个子Reactor监控读请求就绪,业务请求还是通过线程池处理。
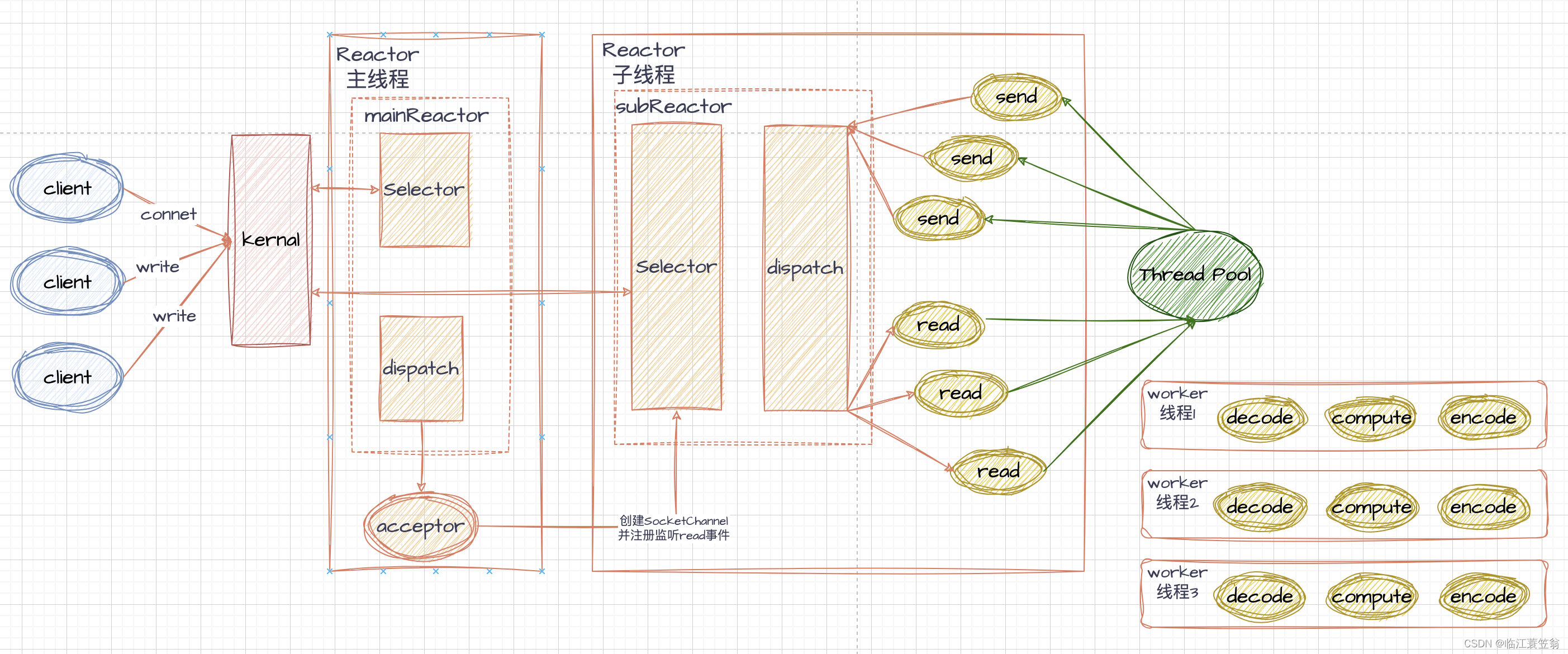
3.1 处理机制
从整体架构图可知,整个处理机制与Reactor多线程模式基本一致。单个线程负责处理连接请求,一个或者多个线程负责处理读写请求,业务处理会提交到线程池进行处理。
3.2 优缺点
此模型逻辑处理相对比较复杂。但是由于将连接请求还需要读写请求进行了拆分处理,可以很好的支持频繁的读写请求场景。
参考链接
1.Reactor模型


![[蓝桥杯 2015 省 B] 生命之树](http://pic.xiahunao.cn/[蓝桥杯 2015 省 B] 生命之树)









)
![P8680 [蓝桥杯 2019 省 B] 特别数的和 Python](http://pic.xiahunao.cn/P8680 [蓝桥杯 2019 省 B] 特别数的和 Python)
![洛谷 [传智杯 #5 初赛] B-莲子的机械动力学](http://pic.xiahunao.cn/洛谷 [传智杯 #5 初赛] B-莲子的机械动力学)



?)
Module Error (from ./node_modules/eslint-loader/index.js))