- 当子进程退出后,会给父进程发送一个17号SIGCHLD信号,父进程接收到17号信号后,进入信号处理函数调用waitpid函数回收僵尸进程
- 若多个子进程同时退出后,这是切回到父进程,此时父进程只会处理一个17号信号,其他17号信号会被屏蔽。所以17号信号处理函数中只调用一次waitpid函数,可能会造成僵尸进程回收不干净的问题。
- 如果成功回收到僵尸进程了,则再收一次,直到没有僵尸进程为止,结束循环
=0:没有僵尸进程,但是有活着的子进程,函数运行成功
=-1:没有僵尸进程,且没有子进程,函数运行失败。
17) SIGCHLD 当子进程退出后,父进程会收到该信号。该信号不会让进程退出。
想要简单的回收子进程,直接在父进程的某处wait(0)
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <dirent.h>
#include <errno.h>
#include <pthread.h>
#include <semaphore.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/ipc.h>
#include <sys/sem.h>
#include <sys/wait.h>
void callback(int sig){printf("触发 %d 信号\n",sig);pid_t wpid =wait(0);printf("wpid=%d\n",wpid);
}
int main(int argc, const char *argv[])
{//捕获17号信号if(signal(SIGCHLD,callback)==SIG_ERR){perror("signal");return -1;}printf("17号信息捕获成功\n");int i=0;while(i<20){if(fork()==0)//子进程{exit(0);//退出}i++;//只有父进程会执行i++}while(1) //不让父进程退出,不然僵尸进程会消失sleep(1);return 0;
}

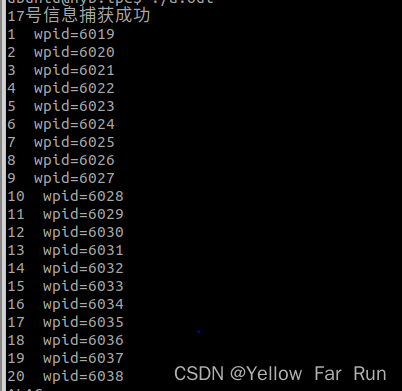
很明显没有捕获到20个僵尸进程
改进:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <dirent.h>
#include <errno.h>
#include <pthread.h>
#include <semaphore.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/ipc.h>
#include <sys/sem.h>
#include <sys/wait.h>
int count=0;
void callback(int sig){
// printf("触发 %d 信号\n",sig);
while(1){//当回收成功后,再收一次,直到回收失败//=-1,没有僵尸进程,也没有子进程//=0,没有僵尸进程,但是有子进程pid_t wpid =wait(0);if(wpid<=0)break;printf("%d wpid=%d\n",++count,wpid);
}
}
int main(int argc, const char *argv[])
{//捕获17号信号if(signal(SIGCHLD,callback)==SIG_ERR){perror("signal");return -1;}printf("17号信息捕获成功\n");int i=0;while(i<20){if(fork()==0)//子进程{exit(0);//退出}i++;//只有父进程会执行i++}while(1)sleep(1);return 0;
}
)



)





太阳能光伏推进大会暨展览会)




)



