使用Spring的AOP
- 一、AOP 的常用注解
- 1.切面类@Aspect
- 2.@Pointcut
- 3.前置通知@Before
- 4.后置通知@AfterReturning
- 5.环绕通知@Around
- 6.异常通知@AfterThrowing
- 7.最终通知@After
- 8.切面顺序@Order
- 9.启用自动代理@EnableAspectJAutoProxy
- 二、AOP注解方式开发
- 三、AOP 全注解开发
- 四、基于XML配置方式的AOP(了解)
- Spring 对
AOP的实现包括以下3种方式:- 第一种方式:Spring框架结合AspectJ框架实现的AOP,基于注解方式。
- 第二种方式:Spring框架结合AspectJ框架实现的AOP,基于XML方式。
- 第三种方式:Spring框架自己实现的AOP,基于XML方式。
- 实际开发种都是Spring + AspectJ来实现的AOP。
- 什么是AspectJ?(Eclipse组织的一个支持AOP的框架。AspectJ框架是独立于Spring框架之外的一个框架,Spring框架用了AspectJ)
- AspectJ项目起源于帕洛阿尔托(Palo Alto)研究中心(缩写为PARC)。该中心由Xerox集团资助,Gregor Kiczales领导,从1997年开始致力于AspectJ的开发,1998年第一次发布给外部用户,2001年发布1.0 release。为了推动AspectJ技术和社团的发展,PARC在2003年3月正式将AspectJ项目移交给了Eclipse组织,因为AspectJ的发展和受关注程度大大超出了PARC的预期,他们已经无力继续维持它的发展。
一、AOP 的常用注解
1.切面类@Aspect
-
@Aspect作用是把当前类标识为一个切面供容器读取。@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME) @Target({ElementType.TYPE}) public @interface Aspect {String value() default ""; }
2.@Pointcut
@Pointcut注解标注在方法上面,用来定义切入点。- 可以这样做:将切点表达式单独的定义出来,在需要的位置引入即可。
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME) @Target({ElementType.METHOD}) public @interface Pointcut {String value() default "";String argNames() default ""; }
3.前置通知@Before
@Before目标方法执行之前的通知@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME) @Target({ElementType.METHOD}) public @interface Before {String value();String argNames() default ""; }
4.后置通知@AfterReturning
@AfterReturning目标方法执行之后的通知@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME) @Target({ElementType.METHOD}) public @interface AfterReturning {String value() default "";String pointcut() default "";String returning() default "";String argNames() default ""; }
5.环绕通知@Around
@Around目标方法之前添加通知,同时目标方法执行之后添加通知。@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME) @Target({ElementType.METHOD}) public @interface Around {String value();String argNames() default ""; }
6.异常通知@AfterThrowing
@AfterThrowing发生异常之后执行的通知@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME) @Target({ElementType.METHOD}) public @interface AfterThrowing {String value() default "";String pointcut() default "";String throwing() default "";String argNames() default ""; }
7.最终通知@After
@After放在finally语句块中的通知@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME) @Target({ElementType.METHOD}) public @interface After {String value();String argNames() default ""; }
8.切面顺序@Order
- 我们知道,业务流程当中不一定只有一个切面,可能有的切面控制事务,有的记录日志,有的进行安全控制,如果多个切面的话,顺序如何控制:
可以使用@Order注解来标识切面类,为@Order注解的value指定一个整数型的数字,数字越小,优先级越高。@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME) @Target({ElementType.TYPE, ElementType.METHOD, ElementType.FIELD}) @Documented public @interface Order {/*** The order value.* <p>Default is {@link Ordered#LOWEST_PRECEDENCE}.* @see Ordered#getOrder()*/int value() default Ordered.LOWEST_PRECEDENCE; }
9.启用自动代理@EnableAspectJAutoProxy
- 开启自动代理之后,凡事带有@Aspect注解的bean都会生成代理对象。
@Target(ElementType.TYPE) @Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME) @Documented @Import(AspectJAutoProxyRegistrar.class) public @interface EnableAspectJAutoProxy {boolean proxyTargetClass() default false;boolean exposeProxy() default false; }
二、AOP注解方式开发
-
注意:本文使用了
log4j2日志,如果不知道可以看我的博客 ===> Spring对IoC的实现中的第一个Spring程序 -
注意本文也使用了
junit进行单元测试。 -
使用
Spring+AspectJ的AOP需要引入的依赖如下:<!--spring的核心依赖 aop core beans jcl expression 等--> <dependency><groupId>org.springframework</groupId><artifactId>spring-context</artifactId><version>6.1.4</version> </dependency> <!-- AOP 依赖的AspectJ --> <dependency><groupId>org.springframework</groupId><artifactId>spring-aspects</artifactId><version>6.1.4</version> </dependency> -
Spring配置文件中添加context命名空间和aop命名空间
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop"xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsdhttp://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsdhttp://www.springframework.org/schema/aop http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop.xsd"></beans> -
第一步:定义目标类以及目标方法
package com.gdb.service;import org.slf4j.Logger; import org.slf4j.LoggerFactory; import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;//目标类 @Service public class OrderService {private static final Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(OrderService.class);//目标方法public void detail() {logger.info("正在打印订单详情......");} } -
第二步:编写切面类
package com.gdb.aspect;import org.aspectj.lang.ProceedingJoinPoint; import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.*; import org.slf4j.Logger; import org.slf4j.LoggerFactory; import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;//切面类(通知+切点 = 切面) @Aspect @Component public class MyAspect {private static final Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(MyAspect.class);//这是需要增强的代码(通知)@Before("execution(* com.gdb.service..* (..))") // com.gdb.service包下的所有方法public void beforeAdvice() {logger.info("前置通知执行了");}@AfterReturning("execution(* com.gdb.service..* (..))") // com.gdb.service包下的所有方法,public void afterReturningAdvice() {logger.info("后置通知执行了");}@Around("execution(* com.gdb.service..* (..))") // com.gdb.service包下的所有方法,public void aroundAdvice(ProceedingJoinPoint proceedingJoinPoint) throws Throwable {logger.info("前置环绕通知执行了");proceedingJoinPoint.proceed(); // 执行目标方法logger.info("后置环绕通知执行了");}@AfterThrowing("execution(* com.gdb.service..* (..))") // com.gdb.service包下的所有方法,public void afterThrowingAdvice() {logger.info("异常通知执行了");}@After("execution(* com.gdb.service..* (..))") // com.gdb.service包下的所有方法,public void afterAdvice() {logger.info("最终通知执行了");} } -
第三步:在配置文件中启动包扫描启用自动代理
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop"xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsdhttp://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsdhttp://www.springframework.org/schema/aop http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop.xsd"><!--开启组件扫描--><context:component-scan base-package="com.gdb"/><!--开启自动代理--><aop:aspectj-autoproxy proxy-target-class="false"/><!--<aop:aspectj-autoproxy proxy-target-class="true"/> 开启自动代理之后,凡事带有@Aspect注解的bean都会生成代理对象。proxy-target-class="true" 表示采用cglib动态代理。proxy-target-class="false" 表示采用jdk动态代理。默认值是false。即使写成false,当没有接口的时候,也会自动选择cglib生成代理类。--> </beans> -
第四步:编写测试程序
@Test public void test(){ApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("spring.xml");OrderService orderService = applicationContext.getBean("orderService", OrderService.class);orderService.detail(); } -
第五步:执行结果
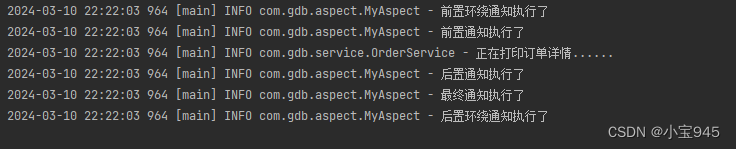
- 通过上面的执行结果就可以判断他们的执行顺序了,这里不再赘述。
-
第六步:结果中没有异常通知,这是因为目标程序执行过程中没有发生异常。我们尝试让目标方法发生异常:
package com.gdb.service;import org.slf4j.Logger; import org.slf4j.LoggerFactory; import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;@Service public class OrderService {private static final Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(OrderService.class);public void detail() {logger.info("正在打印订单详情......");throw new RuntimeException();} } -
第七步:执行结果:
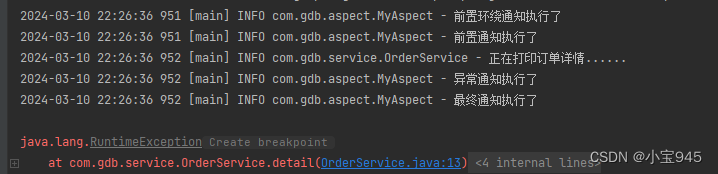
- 通过测试得知,当发生异常之后,最终通知也会执行,因为最终通知
@After会出现在finally语句块中。出现异常之后,后置通知和环绕通知的结束部分不会执行。
- 通过测试得知,当发生异常之后,最终通知也会执行,因为最终通知
-
优化使用切点表达式:
- 上面编写的切面类的缺点是:
- 第一:切点表达式重复写了多次,没有得到复用。
- 第二:如果要修改切点表达式,需要修改多处,难维护。
- 上面编写的切面类的缺点是:
-
可以这样做:将切点表达式单独的定义出来,在需要的位置引入即可。
package com.gdb.aspect;import org.aspectj.lang.ProceedingJoinPoint; import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.*; import org.slf4j.Logger; import org.slf4j.LoggerFactory; import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;@Aspect @Component public class MyAspect {private static final Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(MyAspect.class);@Pointcut("execution(* com.gdb.service..* (..))")public void pointcut() {}@Before("pointcut()") // com.gdb.service包下的所有方法public void beforeAdvice() {logger.info("前置通知执行了");}@AfterReturning("pointcut()") // com.gdb.service包下的所有方法,public void afterReturningAdvice() {logger.info("后置通知执行了");}@Around("pointcut()") // com.gdb.service包下的所有方法,public void aroundAdvice(ProceedingJoinPoint proceedingJoinPoint) throws Throwable {logger.info("前置环绕通知执行了");proceedingJoinPoint.proceed();logger.info("后置环绕通知执行了");}@AfterThrowing("pointcut()") // com.gdb.service包下的所有方法,public void afterThrowingAdvice() {logger.info("异常通知执行了");}@After("pointcut()") // com.gdb.service包下的所有方法,public void afterAdvice() {logger.info("最终通知执行了");} } -
使用@Pointcut注解来定义独立的切点表达式。
-
注意这个@Pointcut注解标注的方法随意,只是起到一个能够让@Pointcut注解编写的位置。
三、AOP 全注解开发
- 第一步:
就是编写一个类,在这个类上面使用大量注解来代替spring的配置文件,spring配置文件消失了,如下:package com.gdb.config;import org.springframework.context.annotation.ComponentScan; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration; import org.springframework.context.annotation.EnableAspectJAutoProxy;@Configuration // 配置类 @ComponentScan("com.gdb") @EnableAspectJAutoProxy(proxyTargetClass = false) public class SpringConfig { } - 第二步:测试程序也变化了
@Test public void test() {AnnotationConfigApplicationContext applicationContext = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(SpringConfig.class);OrderService orderService = applicationContext.getBean("orderService", OrderService.class);orderService.detail(); } - 第三步:执行结果
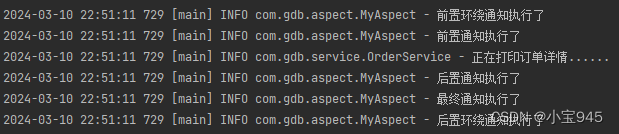
四、基于XML配置方式的AOP(了解)
- 第一步:编写目标类
package com.gdb.service;import org.slf4j.Logger;
import org.slf4j.LoggerFactory;public class OrderService {private static final Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(OrderService.class);public void detail() {logger.info("正在打印订单详情......");}
}
- 第二步:编写切面类,并且编写通知
package com.gdb.aspect;import org.aspectj.lang.ProceedingJoinPoint;
import org.slf4j.Logger;
import org.slf4j.LoggerFactory;public class MyAspect {private static final Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(MyAspect.class);public void beforeAdvice() {logger.info("前置通知执行了");}public void afterReturningAdvice() {logger.info("后置通知执行了");}public void aroundAdvice(ProceedingJoinPoint proceedingJoinPoint) throws Throwable {logger.info("前置环绕通知执行了");proceedingJoinPoint.proceed();logger.info("后置环绕通知执行了");}public void afterThrowingAdvice() {logger.info("异常通知执行了");}public void afterAdvice() {logger.info("最终通知执行了");}
}
- 第三步:编写spring配置文件
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop"xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsdhttp://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsdhttp://www.springframework.org/schema/aop http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop.xsd"><bean id="myAspect" class="com.gdb.aspect.MyAspect"/><bean id="orderService" class="com.gdb.service.OrderService"/><!--aop配置--><aop:config><!--切点表达式--><aop:pointcut id="p" expression="execution(* com.gdb.service..* (..))"/><!--切面--><aop:aspect ref="myAspect"><!--切面=通知 + 切点--><aop:before method="beforeAdvice" pointcut-ref="p"/><aop:after-returning method="afterReturningAdvice" pointcut-ref="p"/><aop:around method="aroundAdvice" pointcut-ref="p"/><aop:after-throwing method="afterThrowingAdvice" pointcut-ref="p"/><aop:after method="afterAdvice" pointcut-ref="p"/></aop:aspect></aop:config>
</beans>
- 第四步:编写测试程序
@Test
public void test() {ClassPathXmlApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("spring.xml");OrderService orderService = applicationContext.getBean("orderService", OrderService.class);orderService.detail();
}
- 第四步:执行结果
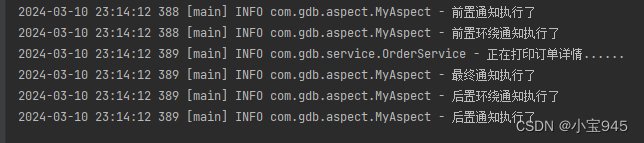
通过结果可以看出来顺序和前面的不一样了,我感觉是配置文件中的顺序有关系,由于主要都是使用注解的方式。



![[uni-app ] createAnimation锚点旋转 及 二次失效问题处理](http://pic.xiahunao.cn/[uni-app ] createAnimation锚点旋转 及 二次失效问题处理)

等级考试试卷(一级))


)
)



)
)
概念和例题)


)
-java+ selenium自动化测试- quit和close的区别(详解教程))