godot游戏引擎是有2d光照的,用起来感觉还是很强大的,不知道他是怎么搞的,有时间看看他们怎么实现的。
之前一直以为cocos社区里面没有2d光照的实现,偶然看到2d实现的具体逻辑,现在整理如下,
一:实现原理
这里实现的2d光源是类似聚光灯的效果,是有一个衰减过程的,具体怎么个衰减法,还得用到我们学的数学知识就是线性衰减 y = -x + b,就是用它来模拟光照的衰减效果的,在光照半径范围内衰减的时候是一个值(根据距离进行衰减,该值的意义是对光照效果的贡献值),大于光照半径范围 光照贡献值急速的变为0.
1:需要哪些参数
模拟光照的参数,需要一个光源照射的半径范围r,光源锥形的角度r1,光源的强度indensity,光源的颜色 color,光源世界坐标,用来计算物体距离光源大小,以此来计算光照效果。
properties:alphaThreshold: { value: 0.5 }light_normal: { value: white }light_worldpos: { value: [255, 255, 255, 255], editor: { type: vec4 } } light_ambientColor: { value: [127, 127, 127, 127], editor: { type: color } }light_lightColor: { value: [255, 255, 255, 255], editor: { type: color } } light_radius: { value: 10.0 }light_halfRadius: { value: 0.5 }light_brightness: { value: 1.0 }uniform Constant {// 环境光模拟白天和黑夜vec4 light_ambientColor;// 光源颜色vec4 light_lightColor;// 光源世界坐标vec4 light_worldpos;// 光源半径float light_radius;// 光源角度半径 决定了光源锥形区域的宽度float light_halfRadius;// 光源的亮度float light_brightness;float light_unused;};光源的世界坐标可以通过外部脚本传入,定义一个节点挂在Light脚本来控制光源的世界坐标:
import { _decorator, Component, Node, Sprite, math, UITransform, Label, Vec2, Vec3, Vec4, Camera, view, Material, Texture2D, renderer, color, Color } from 'cc';
import { EDITOR } from 'cc/env';
const { ccclass, property, executeInEditMode } = _decorator;@ccclass('Light')
@executeInEditMode
export class Light extends Component {@property([Node])bodys_normal: Node[] = [];@property([Node])bodys: Node[] = [];@property(Material)eff: Material = null!;@property(Material)eff_normal: Material = null!;onLoad() {}start() {this.updateLight();}update() {this.updateLight();}getwpos(node2d: Node) {return node2d.worldPosition;}updateBody(target, lightPos) {// 更新uniformlet spr = target.getComponent(Sprite);// 灯光位置spr.getSharedMaterial(0).setProperty('light_worldpos', new Vec4(lightPos.x, lightPos.y, lightPos.z, 1));}updateLight() {// 光源位置let lightPos = this.getwpos(this.node)for (var idx in this.bodys_normal) {let node = this.bodys_normal[idx];if (null == node) return;this.updateBody(node, lightPos);}for (var idx in this.bodys) {let node = this.bodys[idx];if (null == node) return;this.updateBody(node, lightPos);}}
}
2:具体的一些细节
想要让光源产生效果,需要单独的给每个图片加上一个单独的材质,这样才能控制颜色的输出,这里使用时最新版本(3.8.x)的shader的结构:
// Copyright (c) 2017-2020 Xiamen Yaji Software Co., Ltd.
CCEffect %{techniques:- passes:- vert: light-vs:vertfrag: light-fs:fragdepthStencilState:depthTest: falsedepthWrite: falseblendState:targets:- blend: trueblendSrc: src_alphablendDst: one_minus_src_alphablendDstAlpha: one_minus_src_alpharasterizerState:cullMode: noneproperties:alphaThreshold: { value: 0.5 }light_normal: { value: white }light_worldpos: { value: [255, 255, 255, 255], editor: { type: vec4 } } light_ambientColor: { value: [127, 127, 127, 127], editor: { type: color } }light_lightColor: { value: [255, 255, 255, 255], editor: { type: color } } light_radius: { value: 10.0 }light_halfRadius: { value: 0.5 }light_brightness: { value: 1.0 }
}%CCProgram light-vs %{precision highp float;#include <builtin/uniforms/cc-global>#if USE_LOCAL#include <builtin/uniforms/cc-local>#endif#if SAMPLE_FROM_RT#include <common/common-define>#endifin vec3 a_position;in vec2 a_texCoord;in vec4 a_color;out vec4 color;out vec2 uv0;out vec4 object_position;vec4 vert () {vec4 pos = vec4(a_position, 1);// 不适用mvp矩阵计算成世界坐标,因为如果屏幕是横屏的时候,转成世界坐标后,x轴会出现拉伸。// 这里使用的是UI的坐标系,参考light.ts获取世界坐标的代码。object_position = pos;#if USE_LOCALpos = cc_matWorld * pos;#endif#if USE_PIXEL_ALIGNMENTpos = cc_matView * pos;pos.xyz = floor(pos.xyz);pos = cc_matProj * pos;#elsepos = cc_matViewProj * pos;#endifuv0 = a_texCoord;#if SAMPLE_FROM_RTCC_HANDLE_RT_SAMPLE_FLIP(uv0);#endifcolor = a_color;return pos;}
}%CCProgram light-fs %{precision highp float;#include <builtin/internal/embedded-alpha>#include <builtin/internal/alpha-test>in vec4 color;in vec4 object_position;#if USE_TEXTUREin vec2 uv0;#pragma builtin(local)layout(set = 2, binding = 11) uniform sampler2D cc_spriteTexture;#endif// 是否使用2d法线#if USE_2D_NORMALuniform sampler2D light_normal;#endif#if USE_2D_LIGHTuniform Constant {// 环境光模拟白天和黑夜vec4 light_ambientColor;// 光源颜色vec4 light_lightColor;// 光源世界坐标vec4 light_worldpos;// 光源半径float light_radius;// 光源角度半径 决定了光源锥形区域的宽度float light_halfRadius;// 光源的亮度float light_brightness;float light_unused;};/*** 亮度计算, 按照距离远近衰减, 采取内外光圈叠加方式, 按照世界坐标计算 (0.0 ~ 1.0)* @param dist 距离 (0.0 ~ 1.0)* @param cutoff_r 外光圈半径 (> 0.0) 光源的截止半径 超过这个半径区域不再受到关照的影响* @param half_r 内光圈半径, 使用cutoffRadius的半径占比 (0.0 ~ 1.0) 光源的角度半径,决定了光源锥形区域的宽度*/float light_bright(float dist, float cutoff_r, float half_r) {// 截距float intercept = cutoff_r * half_r;// dx_1 = 1 / (2 * intercept) => y = 1 / 2x; 双曲线 近处float dx_1 = 0.5 / intercept;// dx_2曲线和dx_1曲线对称,对称中心是(cutoff_r / 2,1 / cutoff_r) 远处float dx_2 = 0.5 / (cutoff_r - intercept);float offset = 0.5 + intercept * dx_2;// 近处 慢慢衰减float falloffTermNear = clamp((1.0 - dist * dx_1), 0.0, 1.0);// 远处 远离光源的时候迅速减小到0float falloffTermFar = clamp((offset - dist * dx_2), 0.0, 1.0);// 当dist > intercept 的时候 => 1 dist < intercept => 0float falloffSelect = step(intercept, dist);// 计算光源对某一个点的照明贡献 距离衰减因子 dist < intercept => fallofftTermNear 近距离因子 dist > intercept => 远距离因子float falloffTerm = (1.0 - falloffSelect) * falloffTermNear + falloffSelect * falloffTermFar;return falloffTerm;}/*** 计算灯光的颜色值* @param dist 物体距离光源的距离, 世界单位 (> 0.0)* @param radius 光源半径,世界单位 (> 0.0)*/vec3 light_diffuse (float dist, float radius) { // 计算像素点所在光圈位置的亮度float falloffTerm = light_bright(dist, radius, light_halfRadius);// falloffTerm 为亮度值, light_lightColor 为灯光颜色return falloffTerm * vec3(light_lightColor);}/*** 计算光照颜色* @param object_position 物体坐标, 世界坐标* @param object_vertex_normal 顶点的法线向量, 归一化*/vec3 light_color(vec3 col) {// 计算光线方向, 这个方式不能直接用,打个比方纹理是正方形的,而世界坐标可能是长方形的(GL的坐标固定在-1.0到1.0之间, 而屏幕不一定是正方形)vec4 object_direction = object_position - light_worldpos;// 计算物体与灯光的距离float object_dist = length(vec3(object_direction));// 开启这个可以测试// object_dist = length(uv0 - 0.5);// 计算物体与灯光的的距离, 占用直径的百分比float object_dist_normal = object_dist / (light_radius * 2.0);// 获取灯光漫反射颜色vec3 diffuse = light_diffuse(object_dist_normal, light_radius);#if USE_2D_NORMAL// 获取法向量vec3 normal = texture(light_normal, uv0).rgb;normal = normal * 2.0 - 1.0;// 计算光照反射系数,向量点积float normalDot = max(0.0, dot(normal, -normalize(vec3(object_direction.x, object_direction.y, -60))));// 反射光 * 法向量衰减 + 环境光 return col * (diffuse * light_brightness * normalDot + vec3(light_ambientColor));#else// 反射光 * 法向量衰减 + 环境光 (没有法线的情况下需要 0.5 衰减)return col * (diffuse * light_brightness + vec3(light_ambientColor));#endif }/*** 计算光照颜色* @param object_position 物体坐标, 世界坐标* @param object_vertex_normal 顶点的法线向量, 归一化*/vec4 light_dist() {}#endifvec4 frag () {vec4 o = vec4(1, 1, 1, 1);#if USE_TEXTUREo *= CCSampleWithAlphaSeparated(cc_spriteTexture, uv0);#if IS_GRAYfloat gray = 0.2126 * o.r + 0.7152 * o.g + 0.0722 * o.b;o.r = o.g = o.b = gray;#endif#endifo *= color;ALPHA_TEST(o);#if USE_2D_LIGHTreturn vec4(light_color(vec3(o)), o.a);#elsereturn o;#endif}
}%
主要的核心方法:light_bright,这个方法是用来计算光照贡献值的。
其中intercept = cutoff_r * half_r 是设定了一个阙值,当dist < intercept的时候用什么样的衰减方式,当dist > intercept的时候用什么样的衰减方式,
那么 float dx_1 = 0.5 / intercept 该怎么理解呢,这个得结合falloffTermNear,falloffTermFar来理解,就好比v = s / t,总的衰减总数是1,前半部分(dist < intercept)占了0.5,那么后半部分就是1 - 0.5,我还是画一张图来理解吧,每衰减 1需要消耗的值就是 dx_1,这个dx_1可以理解为衰减的速率,也就是下面代码中出现的斜率,也就是衰减速度。那么dx_1讲清楚了,自然而然dx_2你也是理解的
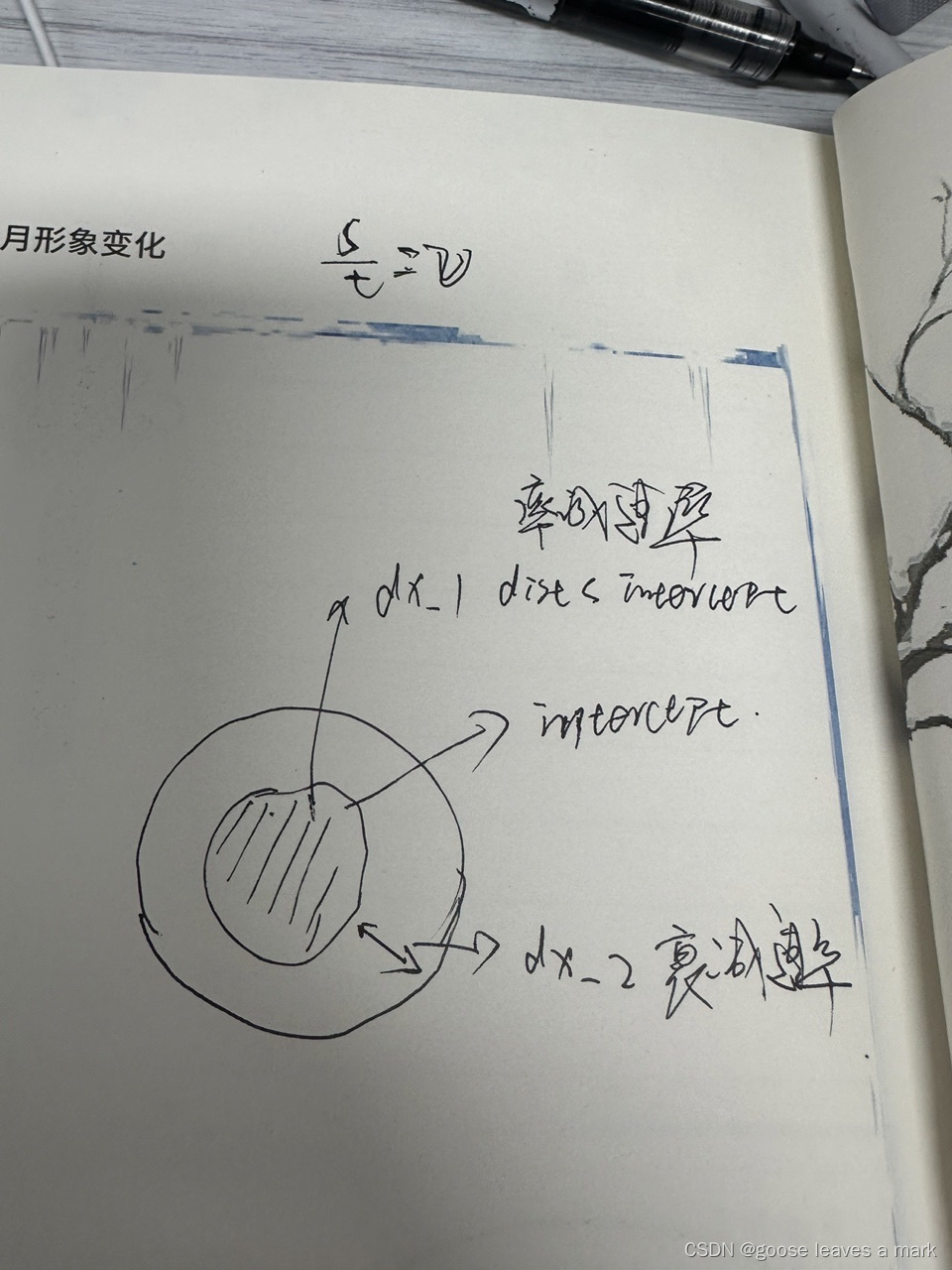
这里还有一个点就是offset什么意思,offset指的就是当dist = intercept的时候怎么保证两个衰减过程衔接的非常自然呢,咱们可以列一个公式看看
1 - dist * dx_1 = offset - dist * dx_2,很容易我们解方程就能够知道 offset = 0.5 + intercept * dx_2;
最后根据dist来计算对光照的影响程度就可以了,
/*** 亮度计算, 按照距离远近衰减, 采取内外光圈叠加方式, 按照世界坐标计算 (0.0 ~ 1.0)* @param dist 距离 (0.0 ~ 1.0)* @param cutoff_r 外光圈半径 (> 0.0) 光源的截止半径 超过这个半径区域不再受到关照的影响* @param half_r 内光圈半径, 使用cutoffRadius的半径占比 (0.0 ~ 1.0) 光源的角度半径,决定了光源锥形区域的宽度*/float light_bright(float dist, float cutoff_r, float half_r) {// 截距float intercept = cutoff_r * half_r;// dx_1 = 1 / (2 * intercept) => y = 1 / 2x; 双曲线 近处float dx_1 = 0.5 / intercept;// dx_2曲线和dx_1曲线对称,对称中心是(cutoff_r / 2,1 / cutoff_r) 远处float dx_2 = 0.5 / (cutoff_r - intercept);// 用在两种衰减过程中的阙值出的矫正保证颜色渐变的连贯 计算过程是 1 - dist * dx_1 = offset - dist * dx_2 可以反算出来 offset = 0.5 + intercept * dx_2float offset = 0.5 + intercept * dx_2;// 近处 慢慢衰减 线性衰减float falloffTermNear = clamp((1.0 - dist * dx_1), 0.0, 1.0);// 远处 远离光源的时候迅速减小到0float falloffTermFar = clamp((offset - dist * dx_2), 0.0, 1.0);// 当dist > intercept 的时候 => 1 dist < intercept => 0float falloffSelect = step(intercept, dist);// 计算光源对某一个点的照明贡献 距离衰减因子 dist < intercept => fallofftTermNear 近距离因子 dist > intercept => 远距离因子float falloffTerm = (1.0 - falloffSelect) * falloffTermNear + falloffSelect * falloffTermFar;return falloffTerm;}讲解到这里希望你能够理解光源产生的过程。
下面贴下原文的链接:
cocos creator 2D关照
我只是把不容易理解的部分给讲一下,希望对你有帮助。



)







)







