1. 前言
软件设计模式定义了一组类和它们之间的关系,它们相互作用用以解决软件开发过程中面临的常见问题。由于验证工程师所做工作的重要部分包括使用面向对象语言(如SystemVerilog)进行编码,因此许多遇到的挑战都适合应用特定的设计模式来解决。将它们应用到代码中,有助于代码的可重用性和可维护性,从而提高了整体代码质量。本文介绍备忘录(亦称: 快照、Snapshot、Memento)在验证环境中的使用,来对设计逻辑中实现的特性进行建模。
2. 备忘录
备忘录模式是一种行为设计模式, 允许在不暴露对象实现细节的情况下保存和恢复对象之前的状态。在软件开发环境中,它在应用程序中提供了撤销机制,促进了数据的隐藏,并且不违背封装原则。在验证环境中,它可以用来对需要“恢复的场景”进行建模。举个例子,如下图所示,比如Arm CPU运行在状态pstate1下,这时候突然来了个中断导致它切换到状态pstate2,中断可能嵌套,继续切换到状态pstate3、pstate4、pstate5等等,中断处理结束后,需要返回到之前的运行状态。因此在中断切换状态时需要保存当前的CPU状态信息,这样才能在中断处理完成后,根据历史保存的CPU状态信息切换回来。备忘录模式提供了很好的建模方式。
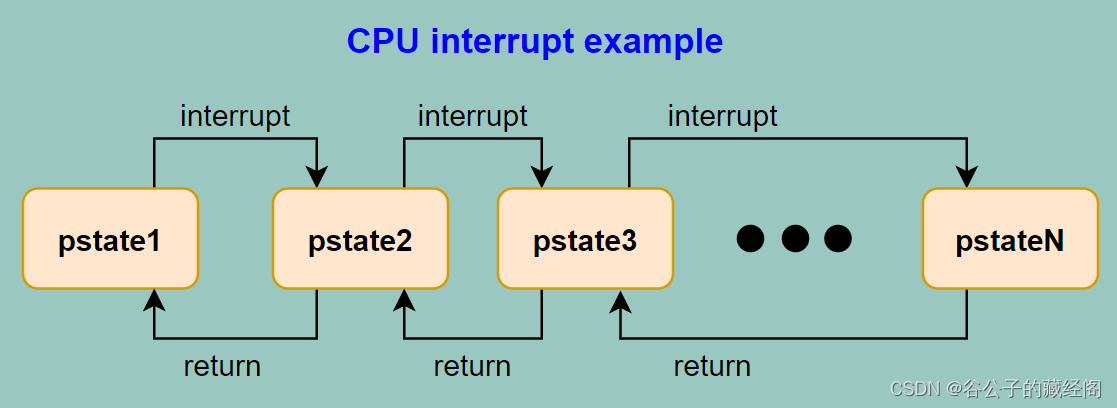
备忘录模式提供了三个主要组件:
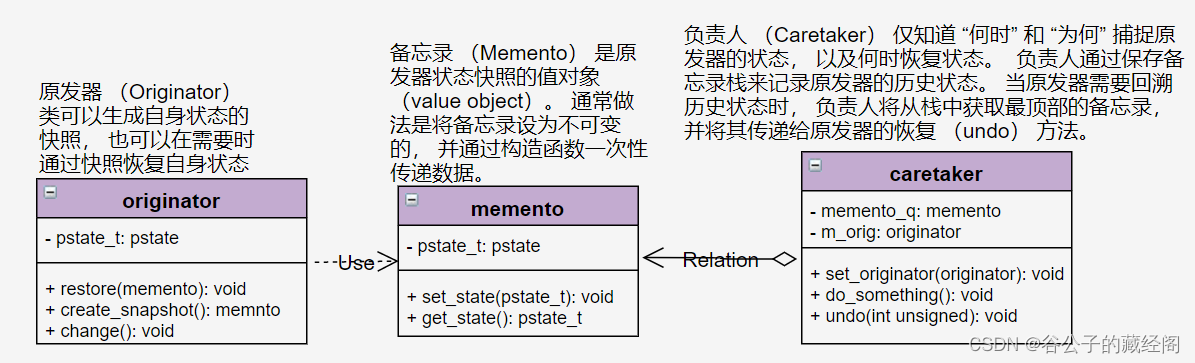
Memento:表示要保存和恢复的内容的容器类,在上图示例中Memento类包含pstate的状态和相应的get/set方法。
Originator:使用Memento类来保存当前的状态。它类似于这里CPU的角色。
Caretaker:请求Originator保存状态,且它直到所有保存的状态,并且可以请求恢复到历史的某个状态。
下图使用UML类图提供了上述三者之间的图形化关系,如何看懂UML类图大家可以自行搜索下资料。
3. 参考代码
CPU处理中断进入和返回状态的参考代码如下:
typedef struct packed {bit [3:0] nzcv;bit [1:0] currentel;bit tco;
} pstate_t;class memento extends uvm_object;`uvm_object_utils (memento)local pstate_t pstate;function new (string name = "memento");super.new(name);endfunction : newfunction void set_pstate(pstate_t _pstate);this.pstate = _pstate;endfunction : set_pstatefunction pstate_t get_pstate();return pstate;endfunction : get_pstateendclass : mementoclass originator extends uvm_object;`uvm_object_utils (originator)local pstate_t pstate;function new (string name = "originator");super.new(name);endfunction : newfunction void change();pstate = $random();endfunction : changefunction memento create_snapshot();memento m_memento = memento::type_id::create("m_memento");m_memento.set_pstate(pstate);`uvm_info("[snapshot pstate:]", $psprintf("nzcv:'b%b, currentel:'b%b, tco:'b%b", pstate.nzcv, pstate.currentel, pstate.tco), UVM_LOW)return m_memento;endfunctionfunction void restore (memento _snapshot);pstate = _snapshot.get_pstate();`uvm_info("[restore pstate:]", $psprintf("nzcv:'b%b, currentel:'b%b, tco:'b%b", pstate.nzcv, pstate.currentel, pstate.tco), UVM_LOW)endfunction : restoreendclass : originatorclass caretaker extends uvm_object;`uvm_object_utils (caretaker)local memento memento_q[$];local originator m_orig;function new (string name = "caretaker");super.new(name);endfunction : newfunction void set_originator(originator _m_orig);m_orig = _m_orig;endfunction : set_originatorfunction void dosomething();memento_q.push_back(m_orig.create_snapshot);m_orig.change();endfunction : dosomethingfunction void undo(int unsigned _index);if (_index > memento_q.size() || memento_q.size() == 0 ) $fatal;m_orig.restore(memento_q[_index]);endfunction : undoendclass : caretaker模拟测试代码如下:
class monitor;function void test();caretaker m_caretaker = caretaker::type_id::create("m_caretaker");originator m_originator = originator::type_id::create("m_originator");m_caretaker.set_originator(m_originator);m_caretaker.dosomething(); // snapshot0m_caretaker.dosomething(); // snapshot1m_caretaker.dosomething(); // snapshot2m_caretaker.dosomething(); // snapshot3m_caretaker.undo(1);m_caretaker.dosomething(); // snapshot4m_caretaker.undo(3);endfunction : testendclass : monitor输出仿真结果如下:
[[snapshot pstate:]] nzcv:'b0000, currentel:'b00, tco:'b0
[[snapshot pstate:]] nzcv:'b0100, currentel:'b10, tco:'b0
[[snapshot pstate:]] nzcv:'b0000, currentel:'b00, tco:'b1
[[snapshot pstate:]] nzcv:'b0001, currentel:'b00, tco:'b1
[[restore pstate:]] nzcv:'b0100, currentel:'b10, tco:'b0
[[snapshot pstate:]] nzcv:'b0100, currentel:'b10, tco:'b0
[[restore pstate:]] nzcv:'b0001, currentel:'b00, tco:'b1在提供的示例中,保存和恢复动作是由中断进入和中断退出事件触发的。在UVM中,事件由监视器(monitor)发出的,该监视器观察中断接口并使用Memento设计模式。该例子支持保存和恢复多个CPU状态。遇到中断时,caretaker的do_something()函数在开始时就把当前的pstate存储到memento里,然后进行其它的中断处理动作,相当于备份了历史状态。如果中断结束了,caretaker的undo()函数可以指定返回到哪个历史状态。
下次给大家分享下设计模式中责任链模式(Chain of Responsibility)在芯片验证中的应用。













-线程)



)


