文章目录
- 一、demo演示
- 二、原理分析
- 参考资料
一、demo演示
.section .data
message:.string "Hello, World!\n"
len = . - message.section .text
.globl _start
_start:# 调用 write() 函数输出 "Hello, World!"mov $1, %rax # 系统调用号为 1 表示 write()mov $1, %rdi # 文件描述符为 1 表示标准输出lea message(%rip), %rsi # 输出的字符串地址mov $len, %rdx # 输出的字符串长度syscall # 调用系统调用# 调用 exit() 函数退出程序mov $60, %rax # 系统调用号为 60 表示 exit()xor %rdi, %rdi # 返回值为 0syscall # 调用系统调用这段汇编代码是在标准输出上输出 “Hello, World!”,然后退出程序:
as -o hello.o hello.s
ld -o hello hello.o
# ./hello
Hello, World!
#include <unistd.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/wait.h>
#include <sys/ptrace.h>
#include <errno.h>
#include <sys/user.h>
#include <stdint.h>void fprint_wait_status(FILE *stream, int status)
{if( WIFSTOPPED(status) ) {fprintf(stream, "Child stopped: %d\n", WSTOPSIG(status));}if( WIFEXITED(status) ) {fprintf(stream, "Child exited: %d\n", WEXITSTATUS(status));}if( WIFSIGNALED(status) ) {fprintf(stream, "Child signaled: %d\n", WTERMSIG(status));}if( WCOREDUMP(status) ) {fprintf(stream, "Core dumped.\n");}
}int ptrace_instruction_pointer(int pid, uint64_t *rip)
{//获取指令指令的值struct user_regs_struct regs;if( ptrace(PTRACE_GETREGS, pid, NULL, (void*)®s) ) {fprintf(stderr, "Error fetching registers from child process: %s\n",strerror(errno));return -1;}if(rip)*rip = regs.rip;return 0;
}int singlestep(int pid)
{int retval, status;//通过ptrace发送单步调试的指令retval = ptrace(PTRACE_SINGLESTEP, pid, 0, 0);if( retval ) {return retval;}//阻塞在这里--等待子进程停止//子进程停止发送信号唤醒父进程 -- 父进程对子进程进行调试waitpid(pid, &status, 0);return status;
}int main(int argc, char ** argv)
{uint64_t rip;pid_t pid;int status;char *program;if (argc < 2) {fprintf(stderr, "Usage: %s elffile arg0 arg1 ...\n", argv[0]);exit(-1);}pid = fork();if( pid == -1 ) {fprintf(stderr, "Error forking: %s\n", strerror(errno));exit(-1);}if( pid == 0 ) {/* child */if( ptrace(PTRACE_TRACEME, 0, 0, 0) ) {fprintf(stderr, "Error setting TRACEME: %s\n", strerror(errno));exit(-1);}execvp(argv[1], argv + 1);} else {/* parent *///阻塞在这里--等待子进程停止waitpid(pid, &status, 0);fprint_wait_status(stderr,status);//WIFSTOPPED在处理子进程状态时判断子进程是否处于停止状态while( WIFSTOPPED(status) ) {if(ptrace_instruction_pointer(pid, &rip) ) {break;}fprintf(stderr, "RIP: %p\n", (void*)rip);status = singlestep(pid);}fprint_wait_status(stderr, status);fprintf(stderr, "Detaching\n");ptrace(PTRACE_DETACH, pid, 0, 0);}return 0;
}
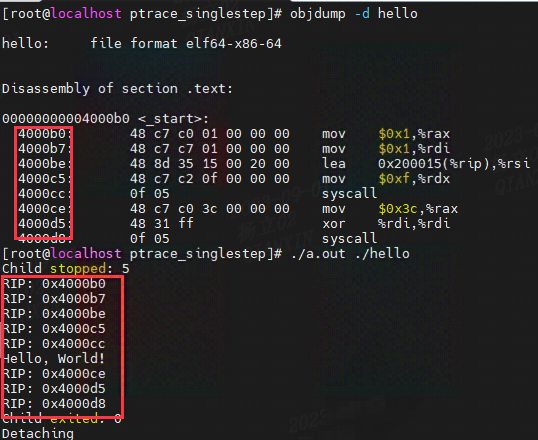
二、原理分析
PTRACE_SINGLESTEP:重新启动被跟踪进程,并在执行一条指令后停止。当使用PTRACE_SINGLESTEP选项时,被跟踪进程将在执行完一条指令后立即停止,以供跟踪进程进行单步调试或其他操作。
这个选项都会使被跟踪进程看起来好像是接收到了一个SIGTRAP信号而停止执行。跟踪进程可以在被跟踪进程停止时进行进一步的检查或操作。
以下是这个选项的使用方式:
ptrace(PTRACE_SINGLESTEP, pid, NULL, data);
pid是被跟踪进程的进程ID。
data参数如果非零,表示要发送给被跟踪进程的信号编号;如果为零,表示不发送任何信号。
在停止时,被跟踪进程会看起来好像是接收到了一个SIGTRAP信号。
原理图如下:

内核源码分析:
SYSCALL_DEFINE4(ptrace, long, request, long, pid, unsigned long, addr,unsigned long, data)
{//根据被跟踪进程的pid获取其struct task_struct结构体struct task_struct *child;child = ptrace_get_task_struct(pid);if (IS_ERR(child)) {ret = PTR_ERR(child);goto out;}//对被跟踪进程发起request请求arch_ptrace(child, request, addr, data);}
这是一个和处理器架构相关的函数:
long arch_ptrace(struct task_struct *child, long request,unsigned long addr, unsigned long data)
{ptrace_request(child, request, addr, data);
}
int ptrace_request(struct task_struct *child, long request,unsigned long addr, unsigned long data)
{#ifdef PTRACE_SINGLESTEPcase PTRACE_SINGLESTEP:#endifreturn ptrace_resume(child, request, data);
}
#ifdef PTRACE_SINGLESTEP
#define is_singlestep(request) ((request) == PTRACE_SINGLESTEP)static int ptrace_resume(struct task_struct *child, long request,unsigned long data)
{//设置单步调试标志if (is_singlestep(request){user_enable_single_step(child);}//唤醒子进程wake_up_state(child, __TASK_TRACED);}
void user_enable_single_step(struct task_struct *child)
{//这里传递的参数是0enable_step(child, 0);
}
user_enable_single_step 函数接受一个参数 child,表示要启用单步调试的任务结构体指针。该函数调用 enable_step 函数,并将 block 参数设置为 0,即不启用块步调试。这样,enable_step 函数将尝试启用任务的单步调试,而不启用块步调试。
/** Enable single or block step.*/
static void enable_step(struct task_struct *child, bool block)
{//传入的参数 block = 0/** Make sure block stepping (BTF) is not enabled unless it should be.* Note that we don't try to worry about any is_setting_trap_flag()* instructions after the first when using block stepping.* So no one should try to use debugger block stepping in a program* that uses user-mode single stepping itself.*/if (enable_single_step(child) && block)set_task_blockstep(child, true);else if (test_tsk_thread_flag(child, TIF_BLOCKSTEP))set_task_blockstep(child, false);
}
#define TIF_SINGLESTEP 4 /* reenable singlestep on user return*/#define X86_EFLAGS_TF 0x00000100 /* Trap Flag */#define TIF_FORCED_TF 24 /* true if TF in eflags artificially *//** Enable single-stepping. Return nonzero if user mode is not using TF itself.*/
static int enable_single_step(struct task_struct *child)
{struct pt_regs *regs = task_pt_regs(child);unsigned long oflags;/** If we stepped into a sysenter/syscall insn, it trapped in* kernel mode; do_debug() cleared TF and set TIF_SINGLESTEP.* If user-mode had set TF itself, then it's still clear from* do_debug() and we need to set it again to restore the user* state so we don't wrongly set TIF_FORCED_TF below.* If enable_single_step() was used last and that is what* set TIF_SINGLESTEP, then both TF and TIF_FORCED_TF are* already set and our bookkeeping is fine.*/if (unlikely(test_tsk_thread_flag(child, TIF_SINGLESTEP)))regs->flags |= X86_EFLAGS_TF;/** Always set TIF_SINGLESTEP - this guarantees that* we single-step system calls etc.. This will also* cause us to set TF when returning to user mode.*/// 设置子进程的thread_info实例的flags字段对应的标志位为TIF_SINGLESTEPset_tsk_thread_flag(child, TIF_SINGLESTEP);oflags = regs->flags;/* Set TF on the kernel stack.. */regs->flags |= X86_EFLAGS_TF;/** ..but if TF is changed by the instruction we will trace,* don't mark it as being "us" that set it, so that we* won't clear it by hand later.** Note that if we don't actually execute the popf because* of a signal arriving right now or suchlike, we will lose* track of the fact that it really was "us" that set it.*/if (is_setting_trap_flag(child, regs)) {clear_tsk_thread_flag(child, TIF_FORCED_TF);return 0;}/** If TF was already set, check whether it was us who set it.* If not, we should never attempt a block step.*/if (oflags & X86_EFLAGS_TF)return test_tsk_thread_flag(child, TIF_FORCED_TF);set_tsk_thread_flag(child, TIF_FORCED_TF);return 1;
}
enable_single_step 函数,用于启用单步调试模式。以下是代码说明:
(1)调用 task_pt_regs 宏获取子进程任务的struct pt_regs:
struct pt_regs 是一个在Linux内核中用于保存进程或线程上下文中寄存器值的数据结构。
它定义了一个包含了各种寄存器的成员的结构体,用于保存任务在进行上下文切换时的寄存器状态,以及在进行异常处理或调试时用于保存当前执行指令的上下文信息。
struct pt_regs {unsigned long r15;unsigned long r14;unsigned long r13;unsigned long r12;unsigned long rbp;unsigned long rbx;
/* arguments: non interrupts/non tracing syscalls only save up to here*/unsigned long r11;unsigned long r10;unsigned long r9;unsigned long r8;unsigned long rax;unsigned long rcx;unsigned long rdx;unsigned long rsi;unsigned long rdi;unsigned long orig_rax;
/* end of arguments */
/* cpu exception frame or undefined */unsigned long rip;unsigned long cs;unsigned long eflags;unsigned long rsp;unsigned long ss;
/* top of stack page */
};
struct pt_regs *regs = task_pt_regs(child);
struct thread_struct {/* Cached TLS descriptors: */struct desc_struct tls_array[GDT_ENTRY_TLS_ENTRIES];unsigned long sp0;unsigned long sp;......
};struct task_struct {
/* CPU-specific state of this task */struct thread_struct thread;
}#define task_pt_regs(tsk) ((struct pt_regs *)(tsk)->thread.sp0 - 1)
将 tsk 的内核栈指针减去 1,然后将结果转换为 struct pt_regs* 类型的指针。
在给定的宏定义中,将任务的内核栈指针 (tsk)->thread.sp0 减去 1 的目的是将指针向前移动一个偏移量,使其指向寄存器上下文结构体 pt_regs 的起始位置。
在x86架构中,寄存器上下文结构体 pt_regs 被存储在任务的内核栈的顶部。所以,通过将内核栈指针减去 1,指针将移动到 pt_regs 结构体的位置。这种偏移一般是由于栈的增长方向的约定造成的。在x86架构中,栈从高地址向低地址增长,而栈顶部位于较高的地址。因此,为了指向位于栈顶的 pt_regs 结构体,需要将栈指针减去 1。
函数检查任务的 TIF_SINGLESTEP 线程标志。这里用 unlikely 修饰表示这是一个小概率事件。
如果该标志已设置,说明在内核模式下发生了 sysenter/syscall 指令,do_debug() 函数已经清除了 TF(Trap Flag)并设置了 TIF_SINGLESTEP 标志。但如果用户模式自己设置了 TF 标志,那么 TF 仍然被 do_debug() 清除,因此需要重新设置 TF 标志来恢复用户模式的状态,以避免错误地设置 TIF_FORCED_TF。
(2)函数使用 set_tsk_thread_flag 函数将任务的 TIF_SINGLESTEP 线程标志设置为真,以确保在系统调用等情况下仍能进行单步调试。
(3)保存当前子进程寄存器 flags 的值到 oflags 变量中。
(4)在内核栈上设置 TF 标志,即将 TF 标志设置为 1。
(5)如果要执行的指令改变了 TF 标志的值,说明不是由我们自己设置的,所以不应该将其标记为 “us” 设置的,以免后续手动清除该标志。如果发生这种情况,函数通过 clear_tsk_thread_flag 函数清除 TIF_FORCED_TF 标志,并返回 0。
(6)如果 TF 标志已经设置,并且之前设置 TF 的不是我们自己,说明我们不应该尝试 block step ,因此返回 0。
(7)如果 TF 标志之前未设置,函数使用 set_tsk_thread_flag 函数将任务的 TIF_FORCED_TF 标志设置为真,并返回 1。
struct thread_info {__u32 flags;
}
/** flag set/clear/test wrappers* - pass TIF_xxxx constants to these functions*/static inline void set_ti_thread_flag(struct thread_info *ti, int flag)
{set_bit(flag, (unsigned long *)&ti->flags);
}
#define task_thread_info(task) ((struct thread_info *)(task)->stack)
// arch/x86/include/asm/thread_info.h/** thread information flags* - these are process state flags that various assembly files* may need to access* - pending work-to-be-done flags are in LSW* - other flags in MSW* Warning: layout of LSW is hardcoded in entry.S*/#define TIF_SINGLESTEP 4 /* reenable singlestep on user return*/
// include/linux/sched.h/* set thread flags in other task's structures* - see asm/thread_info.h for TIF_xxxx flags available*/
static inline void set_tsk_thread_flag(struct task_struct *tsk, int flag)
{set_ti_thread_flag(task_thread_info(tsk), flag);
}其中上述的代码我们需要关心的是:
/** Enable single-stepping. Return nonzero if user mode is not using TF itself.*/
static int enable_single_step(struct task_struct *child)
{/** Always set TIF_SINGLESTEP - this guarantees that* we single-step system calls etc.. This will also* cause us to set TF when returning to user mode.*/set_tsk_thread_flag(child, TIF_SINGLESTEP);
}
在使用PTRACE_SINGLESTEP时,将在被跟踪进程的task_struct中,设置struct thread_info成员flags设置为TIF_SINGLESTEP标志。这只是设置被跟踪进程的thread_info实例的flags字段对应的标志位。
在该标志被设置后,内核在恢复被跟踪进程的正常工作前,只需要用wake_up_state唤醒被跟踪进程即可。
进程设置该标志后,对于x86_64处理器会在每条指令执行后生成一个调试异常:
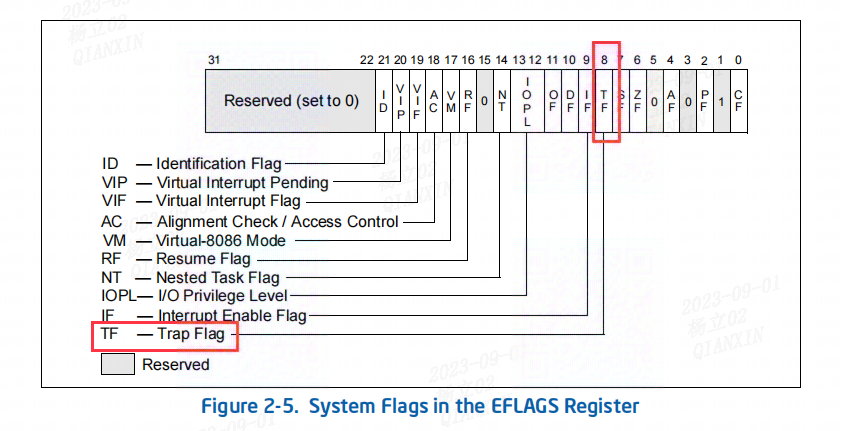
在 x86 架构中,TRAP(Trap Flag,陷阱标志)位于 EFLAGS 寄存器的第 8 位(bit 8)。该位用于启用或禁用单步调试模式。下面是关于 TRAP 位的解释:
当 TRAP 位被设置为 1 时,即启用单步调试模式,处理器会在每条指令执行后生成一个调试异常。这样可以在每条指令执行后检查程序的执行状态,实现逐指令调试。单步调试模式允许程序的执行被暂停以进行调试操作。
当 TRAP 位被清除为 0 时,即禁用单步调试模式,处理器不会生成调试异常,程序会正常连续执行,无需逐条指令地暂停。
如果一个应用程序使用 POPF、POPFD 或 IRET 指令设置 TF(Trap Flag)标志,那么在执行这些指令后的下一条指令之后会生成一个调试异常。这意味着程序可以通过设置 TF 标志来实现在指令级别上的单步调试。
TRAP 位用于控制处理器是否在每条指令执行后生成调试异常,从而实现单步调试。通过设置或清除 TF 标志,程序可以启用或禁用单步调试模式,并在需要时触发调试异常以进行调试操作。
参考资料
Linux 3.10.0







)




)






