hydrate
1 )概述
hydrate在react当中不算特别重要, 但是很多时候会用到的一个API- 这个 API 它主要作用就是在进入第一次渲染的时候,如果本身 dom 树上面已经有一个dom结构存在
- 是否可以去利用这一部分已经存在的dom,然后去避免掉在第一次渲染的时候
- 要去创建很多 dom 节点的一个过程,可以大大的提升第一次渲染的性能
- 看下 react 什么时候需要去执行
hydrate什么时候又不需要去执行它 - 在 ReactDOM.js 中找到 react 里面的两个渲染 API
- 一个是
hydrate另外一个是render - 它们接收的参数都是一样的
- 它们都调用同一个函数
legacyRenderSubtreeIntoContainer - 唯一的区别是它们传入的第4个参数不一样
- 一个是
2 )源码
定位到 packages/react-dom/src/client/ReactDOM.js#L627
hydrate(element: React$Node, container: DOMContainer, callback: ?Function) {// TODO: throw or warn if we couldn't hydrate?return legacyRenderSubtreeIntoContainer(null,element,container,true,callback,);
}render(element: React$Element<any>,container: DOMContainer,callback: ?Function,
) {return legacyRenderSubtreeIntoContainer(null,element,container,false,callback,);
}
对于 legacyRenderSubtreeIntoContainer 第4个参数 forceHydrate 表示是否强制融合
function legacyRenderSubtreeIntoContainer(parentComponent: ?React$Component<any, any>,children: ReactNodeList,container: DOMContainer,forceHydrate: boolean,callback: ?Function,
) {// TODO: Ensure all entry points contain this checkinvariant(isValidContainer(container),'Target container is not a DOM element.',);if (__DEV__) {topLevelUpdateWarnings(container);}// TODO: Without `any` type, Flow says "Property cannot be accessed on any// member of intersection type." Whyyyyyy.let root: Root = (container._reactRootContainer: any);if (!root) {// Initial mountroot = container._reactRootContainer = legacyCreateRootFromDOMContainer(container,forceHydrate,);if (typeof callback === 'function') {const originalCallback = callback;callback = function() {const instance = DOMRenderer.getPublicRootInstance(root._internalRoot);originalCallback.call(instance);};}// Initial mount should not be batched.DOMRenderer.unbatchedUpdates(() => {if (parentComponent != null) {root.legacy_renderSubtreeIntoContainer(parentComponent,children,callback,);} else {root.render(children, callback);}});} else {if (typeof callback === 'function') {const originalCallback = callback;callback = function() {const instance = DOMRenderer.getPublicRootInstance(root._internalRoot);originalCallback.call(instance);};}// Updateif (parentComponent != null) {root.legacy_renderSubtreeIntoContainer(parentComponent,children,callback,);} else {root.render(children, callback);}}return DOMRenderer.getPublicRootInstance(root._internalRoot);
}
- 在调用
legacyCreateRootFromDOMContainer这个方法的时候,会传入这个 forceHydrate 这个参数function legacyCreateRootFromDOMContainer(container: DOMContainer,forceHydrate: boolean, ): Root {// 在这个方法里面,首先它声明了一个参数叫 shouldHydrate,如果 forceHydrate 为 true, shouldHydrate 也一定为 true// 不是 true, 需要调用 `shouldHydrateDueToLegacyHeuristic` 来进行判断// 这也是目前在 react dom 环境中,即便使用了 render API,但仍然有可能会去执行 hydrate 的一个过程// 注意,只针对目前版本const shouldHydrate =forceHydrate || shouldHydrateDueToLegacyHeuristic(container);// First clear any existing content.if (!shouldHydrate) {let warned = false;let rootSibling;while ((rootSibling = container.lastChild)) {if (__DEV__) {if (!warned &&rootSibling.nodeType === ELEMENT_NODE &&(rootSibling: any).hasAttribute(ROOT_ATTRIBUTE_NAME)) {warned = true;warningWithoutStack(false,'render(): Target node has markup rendered by React, but there ' +'are unrelated nodes as well. This is most commonly caused by ' +'white-space inserted around server-rendered markup.',);}}container.removeChild(rootSibling);}}if (__DEV__) {if (shouldHydrate && !forceHydrate && !warnedAboutHydrateAPI) {warnedAboutHydrateAPI = true;lowPriorityWarning(false,'render(): Calling ReactDOM.render() to hydrate server-rendered markup ' +'will stop working in React v17. Replace the ReactDOM.render() call ' +'with ReactDOM.hydrate() if you want React to attach to the server HTML.',);}}// Legacy roots are not async by default.const isConcurrent = false;// 后续在创建 ReactRoot 的时候,传入了 shouldHydratereturn new ReactRoot(container, isConcurrent, shouldHydrate); }- 进入
shouldHydrateDueToLegacyHeuristicfunction shouldHydrateDueToLegacyHeuristic(container) {// 这里面我们拿到了rootElement 之后,我们首先判断的条件// 就是它是否存在, 以及它是否是一个普通的节点// 以及它是否有 `ROOT_ATTRIBUTE_NAME` 这个attribute// ROOT_ATTRIBUTE_NAME 的 值是 data-reactroot// 这个是在调用服务端渲染的API的时候,生成的HTML上面它的container节点上面会增加这个attribute// 这也是react服务端渲染的API帮助我们去在客户端去识别是否需要融合节点的一个帮助的attribute// 如果符合这个条件,React它就会猜测, 即便你调用的不是 Hydrate API// 它仍然猜测你是需要执行 hydrate,它的 shouldHydrate 就等于 trueconst rootElement = getReactRootElementInContainer(container);return !!(rootElement &&rootElement.nodeType === ELEMENT_NODE &&rootElement.hasAttribute(ROOT_ATTRIBUTE_NAME)); } - 进入
getReactRootElementInContainerfunction getReactRootElementInContainer(container: any) {if (!container) {return null;}// DOCUMENT_NODE 表示 window.document, 返回 documentElement 就是 html节点if (container.nodeType === DOCUMENT_NODE) {return container.documentElement;} else {return container.firstChild;} }- 这也是强烈不推荐在调用 render API 的时候传入 document 的原因
- 因为如果传入了document,那么它就会对整个HTML文档来进行一个调和的过程
- 如果我不需要一个融合的过程,它可能会直接把HTML里面所有的内容都删掉,那么这就很可能会导致一些问题了
- 所以在这里面,如果是你传入的是 document,它返回的是 documentElement,那就是HTML节点
- 如果它传入的不是 document, 就是这个 container.firstChild 节点
- 比如说传入的是root节点,root节点如果它没有子节点,它的firstChild 肯定就是一个 null这种情况
- 这时候肯定不需要融合的一个过程
- 进入
ReactRootfunction ReactRoot(container: Container,isConcurrent: boolean,hydrate: boolean, ) {const root = DOMRenderer.createContainer(container, isConcurrent, hydrate);this._internalRoot = root; }- 进入
createContainerexport function createContainer(containerInfo: Container,isConcurrent: boolean,hydrate: boolean, ): OpaqueRoot {return createFiberRoot(containerInfo, isConcurrent, hydrate); }- 进入
createFiberRootexport function createFiberRoot(containerInfo: any,isConcurrent: boolean,hydrate: boolean, ): FiberRoot {// Cyclic construction. This cheats the type system right now because// stateNode is any.const uninitializedFiber = createHostRootFiber(isConcurrent);let root;if (enableSchedulerTracing) {root = ({current: uninitializedFiber,containerInfo: containerInfo,pendingChildren: null,earliestPendingTime: NoWork,latestPendingTime: NoWork,earliestSuspendedTime: NoWork,latestSuspendedTime: NoWork,latestPingedTime: NoWork,didError: false,pendingCommitExpirationTime: NoWork,finishedWork: null,timeoutHandle: noTimeout,context: null,pendingContext: null,hydrate, // 注意这里挂载了nextExpirationTimeToWorkOn: NoWork,expirationTime: NoWork,firstBatch: null,nextScheduledRoot: null,interactionThreadID: unstable_getThreadID(),memoizedInteractions: new Set(),pendingInteractionMap: new Map(),}: FiberRoot);} else {root = ({current: uninitializedFiber,containerInfo: containerInfo,pendingChildren: null,earliestPendingTime: NoWork,latestPendingTime: NoWork,earliestSuspendedTime: NoWork,latestSuspendedTime: NoWork,latestPingedTime: NoWork,didError: false,pendingCommitExpirationTime: NoWork,finishedWork: null,timeoutHandle: noTimeout,context: null,pendingContext: null,hydrate, // 注意这里挂载了nextExpirationTimeToWorkOn: NoWork,expirationTime: NoWork,firstBatch: null,nextScheduledRoot: null,}: BaseFiberRootProperties);}uninitializedFiber.stateNode = root;// The reason for the way the Flow types are structured in this file,// Is to avoid needing :any casts everywhere interaction tracing fields are used.// Unfortunately that requires an :any cast for non-interaction tracing capable builds.// $FlowFixMe Remove this :any cast and replace it with something better.return ((root: any): FiberRoot); }- 把 hydrate 挂载上去,也就是告诉后续的流程,这一次渲染是需要 hydrate 的
- 进入
- 进入
- 设置了 root 上面的 hydrate 之后,在后续更新root的时候,比如在
updateHostRoot - 在它的更新流程当中会调用一个方法叫做
enterHydrationState这个方法
- 进入
定位到 packages/react-reconciler/src/ReactFiberBeginWork.js#L612
function updateHostRoot(current, workInProgress, renderExpirationTime) {// ... 跳过很多代码if ((current === null || current.child === null) &&root.hydrate &&enterHydrationState(workInProgress) // 注意这里) {// ... 跳过很多代码return workInProgress.child;
}
这个 enterHydrationState 方法标志着整个 react 应用的 hydrate 过程的一个开启
定位到 packages/react-reconciler/src/ReactFiberHydrationContext.js#L49
function enterHydrationState(fiber: Fiber): boolean {// supportsHydration 在 react dom 环境中是 写死的 trueif (!supportsHydration) {return false;}// 默认是 root, 也就是 ReactDOM.render 中的第2个参数const parentInstance = fiber.stateNode.containerInfo;// nextHydratableInstance 是一个全局变量nextHydratableInstance = getFirstHydratableChild(parentInstance);hydrationParentFiber = fiber;isHydrating = true;return true;
}
-
进入
getFirstHydratableChildexport function getFirstHydratableChild(parentInstance: Container | Instance, ): null | Instance | TextInstance {let next = parentInstance.firstChild;// Skip non-hydratable nodes.// 进入 while 循环while (next &&next.nodeType !== ELEMENT_NODE &&next.nodeType !== TEXT_NODE) {next = next.nextSibling; // 找到所有星弟节点}return (next: any); }- 找到 parentInstance 下面第一个 ELEMENT_NODE 或 TEXT_NODE
- 这其实是一些全局变量的初始化
- 因为调用这个方法,就代表着我们要正式开始执行 hydrate 的一个过程
- 因为 FiberRoot 对应的是挂载的那个节点, 它不是我们要渲染的APP里面的对应的节点
- 所以它并不是一个正式的流程里面的一部分,它只是标志着我们要开始了
-
开始了之后要做的是什么呢?
- 主要的集中在 HostComponent 以及 TextComponent
- 定位到 packages/react-reconciler/src/ReactFiberBeginWork.js#L685
- 找到
updateHostComponentfunction updateHostComponent(current, workInProgress, renderExpirationTime) {pushHostContext(workInProgress);if (current === null) {tryToClaimNextHydratableInstance(workInProgress);}const type = workInProgress.type;const nextProps = workInProgress.pendingProps;const prevProps = current !== null ? current.memoizedProps : null;let nextChildren = nextProps.children;const isDirectTextChild = shouldSetTextContent(type, nextProps);if (isDirectTextChild) {// We special case a direct text child of a host node. This is a common// case. We won't handle it as a reified child. We will instead handle// this in the host environment that also have access to this prop. That// avoids allocating another HostText fiber and traversing it.nextChildren = null;} else if (prevProps !== null && shouldSetTextContent(type, prevProps)) {// If we're switching from a direct text child to a normal child, or to// empty, we need to schedule the text content to be reset.workInProgress.effectTag |= ContentReset;}markRef(current, workInProgress);// Check the host config to see if the children are offscreen/hidden.if (renderExpirationTime !== Never &&workInProgress.mode & ConcurrentMode &&shouldDeprioritizeSubtree(type, nextProps)) {// Schedule this fiber to re-render at offscreen priority. Then bailout.workInProgress.expirationTime = Never;return null;}reconcileChildren(current,workInProgress,nextChildren,renderExpirationTime,);return workInProgress.child; }- 可以看到在 current 等于 null 的一个情况下,也就是初次渲染的情况下
- 它会调用一个方法叫做
tryToClaimNextHydratableInstance这么一个方法function tryToClaimNextHydratableInstance(fiber: Fiber): void {// 正在开始 hydrate 这里不会执行 跳过if (!isHydrating) {return;}// 这是刚在 enterHydrationState 找到的第一个合法的子节点let nextInstance = nextHydratableInstance;// 如果这个节点不存在, 说明我们当前正在更新的 HostComponent 是没有节点进行 hydrate 的流程的// 所以这个节点它是一个新增的节点,就是我们现在正在更新的这个 HostComponent,它是一个需要去新增的结点// 因为这个节点它已经找不到了,在 beginWork 这边更新完成之后,继续更新的是它的子节点,它本身已经不能找到跟它进行复用的一个节点了// 它的子节点就更不可能找到复用的子节点了, 所以到这边我们就可以停下来了// 对它的子树来说,就不需要再走 hydrate 的流程了,等到回过头来去更新它的兄弟节点的时候,又会重新开始这个 hydrate 的流程if (!nextInstance) {// Nothing to hydrate. Make it an insertion.insertNonHydratedInstance((hydrationParentFiber: any), fiber);isHydrating = false;hydrationParentFiber = fiber;return;}// 有可以 hydrate 节点的流程const firstAttemptedInstance = nextInstance;// 判断当前节点是否可以复用,这里是不可以复用if (!tryHydrate(fiber, nextInstance)) {// If we can't hydrate this instance let's try the next one.// We use this as a heuristic. It's based on intuition and not data so it// might be flawed or unnecessary.nextInstance = getNextHydratableSibling(firstAttemptedInstance);// 它又再去进行了一次 tryHydrate 为什么它这里要这么去做呢?// 它上面的注释向我们表明了它的一个用意// 如果发现这个节点它无法进行headict,我们尝试着去使用它的下一个兄弟节点// 这个尝试并不是基于数据分析得来的一个结果而纯粹是我作为一个开发者,直觉认为它可能会出现这样的一个情况// 所以这边的代码它并没有一个彻底的原理在里面,它只是出于开发者认为可能会出现这么一个情况// 而且加了这一段代码呢也没有太大的一个成本,所以就把它加进去了,可以防止一些很特意的情况出现了一个问题if (!nextInstance || !tryHydrate(fiber, nextInstance)) {// Nothing to hydrate. Make it an insertion.// 如果前后两次进行try的都不成功,说明我们当前的这个节点// 没有找到可以复用的那个原生的 dom 节点的,在没有找到的情况,我们就停止 hydrate 操作// 设置 isHydrating 为 false 代表着会继续向 hostComponent 的子节点去更新的过程中// 如果又遇到了新的 hostComponent,就不会走 hydrate 的一个流程insertNonHydratedInstance((hydrationParentFiber: any), fiber);isHydrating = false;hydrationParentFiber = fiber;return;}// We matched the next one, we'll now assume that the first one was// superfluous and we'll delete it. Since we can't eagerly delete it// we'll have to schedule a deletion. To do that, this node needs a dummy// fiber associated with it.deleteHydratableInstance((hydrationParentFiber: any),firstAttemptedInstance,);}// 可以复用,找下一个节点,child节点hydrationParentFiber = fiber;nextHydratableInstance = getFirstHydratableChild((nextInstance: any)); }insertNonHydratedInstance方法非常简单- 给fiber对象加上了 Placement 这个 SideEffect
- 因为它是一个需要去插入的节点
- 进入
tryHydratefunction tryHydrate(fiber, nextInstance) {switch (fiber.tag) {// 注意这里case HostComponent: {const type = fiber.type;const props = fiber.pendingProps;const instance = canHydrateInstance(nextInstance, type, props);if (instance !== null) {fiber.stateNode = (instance: Instance); // 注意,这里挂载到了 fiber.stateNode,在后续执行 hydrateInstance 时会直接使用return true;}return false;}// 注意这里case HostText: {const text = fiber.pendingProps;const textInstance = canHydrateTextInstance(nextInstance, text);if (textInstance !== null) {fiber.stateNode = (textInstance: TextInstance);return true;}return false;}default:return false;} }- 进入
canHydrateInstance// packages/react-dom/src/client/ReactDOMHostConfig.js#L462 export function canHydrateInstance(instance: Instance | TextInstance,type: string,props: Props, ): null | Instance {if (instance.nodeType !== ELEMENT_NODE ||type.toLowerCase() !== instance.nodeName.toLowerCase() // 它们标签名不一样) {return null; // 这种情况,节点不能复用}// This has now been refined to an element node.return ((instance: any): Instance); // 可以复用并返回 } - 进入
canHydrateTextInstanceexport function canHydrateTextInstance(instance: Instance | TextInstance,text: string, ): null | TextInstance {if (text === '' || instance.nodeType !== TEXT_NODE) {// Empty strings are not parsed by HTML so there won't be a correct match here.return null;}// This has now been refined to a text node.return ((instance: any): TextInstance); } - 主要是上述
HostComponent和HostText的处理过程 - 这个方法主要是判断节点是否可以被复用
- 比如在 HostComponent 中来帮助我们判断正在更新的这个 hostcomponent
- 它跟随着 hydrate 的流程一步一步走下来,正处于的那一个原本 dom 树中存在的那个节点
- 它是否可以被复用这么的一个判断
- 如果
tryHydrate是 true 的,就不符合这个条件,就继续向下去找下一个节点了- 就通过调用
getFirstHydratableChild - 因为按照正常的beginWork的逻辑,接下去要进入的节点是目前正在更新的这个 HostComponent 的child的节点
- 在它的child节点上面一直往下去找, 进入这个方法
export function getFirstHydratableChild(parentInstance: Container | Instance, ): null | Instance | TextInstance {let next = parentInstance.firstChild;// Skip non-hydratable nodes.while (next &&next.nodeType !== ELEMENT_NODE &&next.nodeType !== TEXT_NODE) {next = next.nextSibling;}return (next: any); }
- 就通过调用
- 而如果
tryHydrate是 false 的- 这里面并没有直接终止 hydrate 的流程,而是去找到了它的 nextHydratableSibling
- 调用
getNextHydratableSibling进入它export function getNextHydratableSibling(instance: Instance | TextInstance, ): null | Instance | TextInstance {// 获取当前节点的下一个兄弟节点let node = instance.nextSibling;// Skip non-hydratable nodes.// 去遍历兄弟节点, 找到一个符合需求的那么一个节点while (node &&node.nodeType !== ELEMENT_NODE &&node.nodeType !== TEXT_NODE) {node = node.nextSibling;}return (node: any); }
- 可见
getNextHydratableSibling和getFirstHydratableChild基本上差不多- 只不过一个是遍历的它的兄弟节点,一个是遍历它的子节点当中的兄弟节点
- 进入
- 这边在beginWork的流程中,updateHostComponent,它继续执行的更新的是向下它的子节点
- 如果在我们更新当前节点的时候都没有找到一个可以复用的 dom 节点
- 它的子节点根本不可能找到一个可以复用的节点来进行对应, 这是很明显的一个情况
- react在上述工作进行了跳过 hydrate 的一个流程,让后续的代码就不需要去进行一个判断之类的操作了
- 也节省了一些性能的损耗
- 这就是在 beginWork 当中去执行了 tryToClaimNextHydratableInstance 这个方法
- 它的主要目的是判断我们当前的 hostcomponent 是否有可以复用的这个节点
- 然后去继续往下找,直到找到 beginWork 的一侧子树被 hydrate 完之后
- 后续就要进入 completeUnitOfWork 了
- 这样对一侧的子树的更新已经完成了
- 在后续执行 completeUnitOfWork 的时候,要去真正的创建dom节点了
- 对于 hostcomponent,是需要去创建 instance
- 对于 hydrate 的一个流程,就不需要去创建 instance,而是需要去复用原本 dom 就已经存在的这个 instance
-
在 beginWork 的流程当中,去判断更新的一个 HostComponent
-
是否可以从 hydrate 的 dom 节点当中去找到一个可以复用的节点
-
如果不能找到,就对这节点以及它的子树停止一个 hydrate 的流程,然后设置一些全局变量
-
接下去走的流程是在 completeUnitOfWork
定位到 packages/react-reconciler/src/ReactFiberCompleteWork.js#L540
进入 completeWork
function completeWork(current: Fiber | null,workInProgress: Fiber,renderExpirationTime: ExpirationTime,
): Fiber | null {const newProps = workInProgress.pendingProps;switch (workInProgress.tag) {case IndeterminateComponent:break;case LazyComponent:break;case SimpleMemoComponent:case FunctionComponent:break;case ClassComponent: {const Component = workInProgress.type;if (isLegacyContextProvider(Component)) {popLegacyContext(workInProgress);}break;}case HostRoot: {popHostContainer(workInProgress);popTopLevelLegacyContextObject(workInProgress);const fiberRoot = (workInProgress.stateNode: FiberRoot);if (fiberRoot.pendingContext) {fiberRoot.context = fiberRoot.pendingContext;fiberRoot.pendingContext = null;}if (current === null || current.child === null) {// If we hydrated, pop so that we can delete any remaining children// that weren't hydrated.popHydrationState(workInProgress);// This resets the hacky state to fix isMounted before committing.// TODO: Delete this when we delete isMounted and findDOMNode.workInProgress.effectTag &= ~Placement;}updateHostContainer(workInProgress);break;}case HostComponent: {popHostContext(workInProgress);const rootContainerInstance = getRootHostContainer();const type = workInProgress.type;if (current !== null && workInProgress.stateNode != null) {updateHostComponent(current,workInProgress,type,newProps,rootContainerInstance,);if (current.ref !== workInProgress.ref) {markRef(workInProgress);}} else {if (!newProps) {invariant(workInProgress.stateNode !== null,'We must have new props for new mounts. This error is likely ' +'caused by a bug in React. Please file an issue.',);// This can happen when we abort work.break;}const currentHostContext = getHostContext();// TODO: Move createInstance to beginWork and keep it on a context// "stack" as the parent. Then append children as we go in beginWork// or completeWork depending on we want to add then top->down or// bottom->up. Top->down is faster in IE11.let wasHydrated = popHydrationState(workInProgress);if (wasHydrated) {// TODO: Move this and createInstance step into the beginPhase// to consolidate.if (prepareToHydrateHostInstance(workInProgress,rootContainerInstance,currentHostContext,)) {// If changes to the hydrated node needs to be applied at the// commit-phase we mark this as such.markUpdate(workInProgress);}} else {let instance = createInstance(type,newProps,rootContainerInstance,currentHostContext,workInProgress,);appendAllChildren(instance, workInProgress, false, false);// Certain renderers require commit-time effects for initial mount.// (eg DOM renderer supports auto-focus for certain elements).// Make sure such renderers get scheduled for later work.if (finalizeInitialChildren(instance,type,newProps,rootContainerInstance,currentHostContext,)) {markUpdate(workInProgress);}workInProgress.stateNode = instance;}if (workInProgress.ref !== null) {// If there is a ref on a host node we need to schedule a callbackmarkRef(workInProgress);}}break;}case HostText: {let newText = newProps;if (current && workInProgress.stateNode != null) {const oldText = current.memoizedProps;// If we have an alternate, that means this is an update and we need// to schedule a side-effect to do the updates.updateHostText(current, workInProgress, oldText, newText);} else {if (typeof newText !== 'string') {invariant(workInProgress.stateNode !== null,'We must have new props for new mounts. This error is likely ' +'caused by a bug in React. Please file an issue.',);// This can happen when we abort work.}const rootContainerInstance = getRootHostContainer();const currentHostContext = getHostContext();let wasHydrated = popHydrationState(workInProgress);if (wasHydrated) {if (prepareToHydrateHostTextInstance(workInProgress)) {markUpdate(workInProgress);}} else {workInProgress.stateNode = createTextInstance(newText,rootContainerInstance,currentHostContext,workInProgress,);}}break;}case ForwardRef:break;case SuspenseComponent: {const nextState = workInProgress.memoizedState;if ((workInProgress.effectTag & DidCapture) !== NoEffect) {// Something suspended. Re-render with the fallback children.workInProgress.expirationTime = renderExpirationTime;// Do not reset the effect list.return workInProgress;}const nextDidTimeout = nextState !== null;const prevDidTimeout = current !== null && current.memoizedState !== null;if (current !== null && !nextDidTimeout && prevDidTimeout) {// We just switched from the fallback to the normal children. Delete// the fallback.// TODO: Would it be better to store the fallback fragment on// the stateNode during the begin phase?const currentFallbackChild: Fiber | null = (current.child: any).sibling;if (currentFallbackChild !== null) {// Deletions go at the beginning of the return fiber's effect listconst first = workInProgress.firstEffect;if (first !== null) {workInProgress.firstEffect = currentFallbackChild;currentFallbackChild.nextEffect = first;} else {workInProgress.firstEffect = workInProgress.lastEffect = currentFallbackChild;currentFallbackChild.nextEffect = null;}currentFallbackChild.effectTag = Deletion;}}// The children either timed out after previously being visible, or// were restored after previously being hidden. Schedule an effect// to update their visiblity.if (//nextDidTimeout !== prevDidTimeout ||// Outside concurrent mode, the primary children commit in an// inconsistent state, even if they are hidden. So if they are hidden,// we need to schedule an effect to re-hide them, just in case.((workInProgress.effectTag & ConcurrentMode) === NoContext &&nextDidTimeout)) {workInProgress.effectTag |= Update;}break;}case Fragment:break;case Mode:break;case Profiler:break;case HostPortal:popHostContainer(workInProgress);updateHostContainer(workInProgress);break;case ContextProvider:// Pop provider fiberpopProvider(workInProgress);break;case ContextConsumer:break;case MemoComponent:break;case IncompleteClassComponent: {// Same as class component case. I put it down here so that the tags are// sequential to ensure this switch is compiled to a jump table.const Component = workInProgress.type;if (isLegacyContextProvider(Component)) {popLegacyContext(workInProgress);}break;}default:invariant(false,'Unknown unit of work tag. This error is likely caused by a bug in ' +'React. Please file an issue.',);}return null;
}
- 在 completeWork 中,对于 HostComponent 的一个更新
- current,它等于 null 的情况在这里, 会先去执行一个方法叫做 popHydrationState
- 这个方法就是我们开始要去准备复用这个节点的流程了
function popHydrationState(fiber: Fiber): boolean {// 这里直接跳过,不会执行if (!supportsHydration) {return false;}if (fiber !== hydrationParentFiber) {// We're deeper than the current hydration context, inside an inserted// tree.return false;}if (!isHydrating) {// If we're not currently hydrating but we're in a hydration context, then// we were an insertion and now need to pop up reenter hydration of our// siblings.popToNextHostParent(fiber);isHydrating = true;return false;}const type = fiber.type;// If we have any remaining hydratable nodes, we need to delete them now.// We only do this deeper than head and body since they tend to have random// other nodes in them. We also ignore components with pure text content in// side of them.// TODO: Better heuristic.if (fiber.tag !== HostComponent ||(type !== 'head' &&type !== 'body' &&!shouldSetTextContent(type, fiber.memoizedProps))) {let nextInstance = nextHydratableInstance;while (nextInstance) {deleteHydratableInstance(fiber, nextInstance);nextInstance = getNextHydratableSibling(nextInstance);}}popToNextHostParent(fiber);nextHydratableInstance = hydrationParentFiber? getNextHydratableSibling(fiber.stateNode): null;return true; }- 关于
fiber !== hydrationParentFiber如下图解释
- 关于
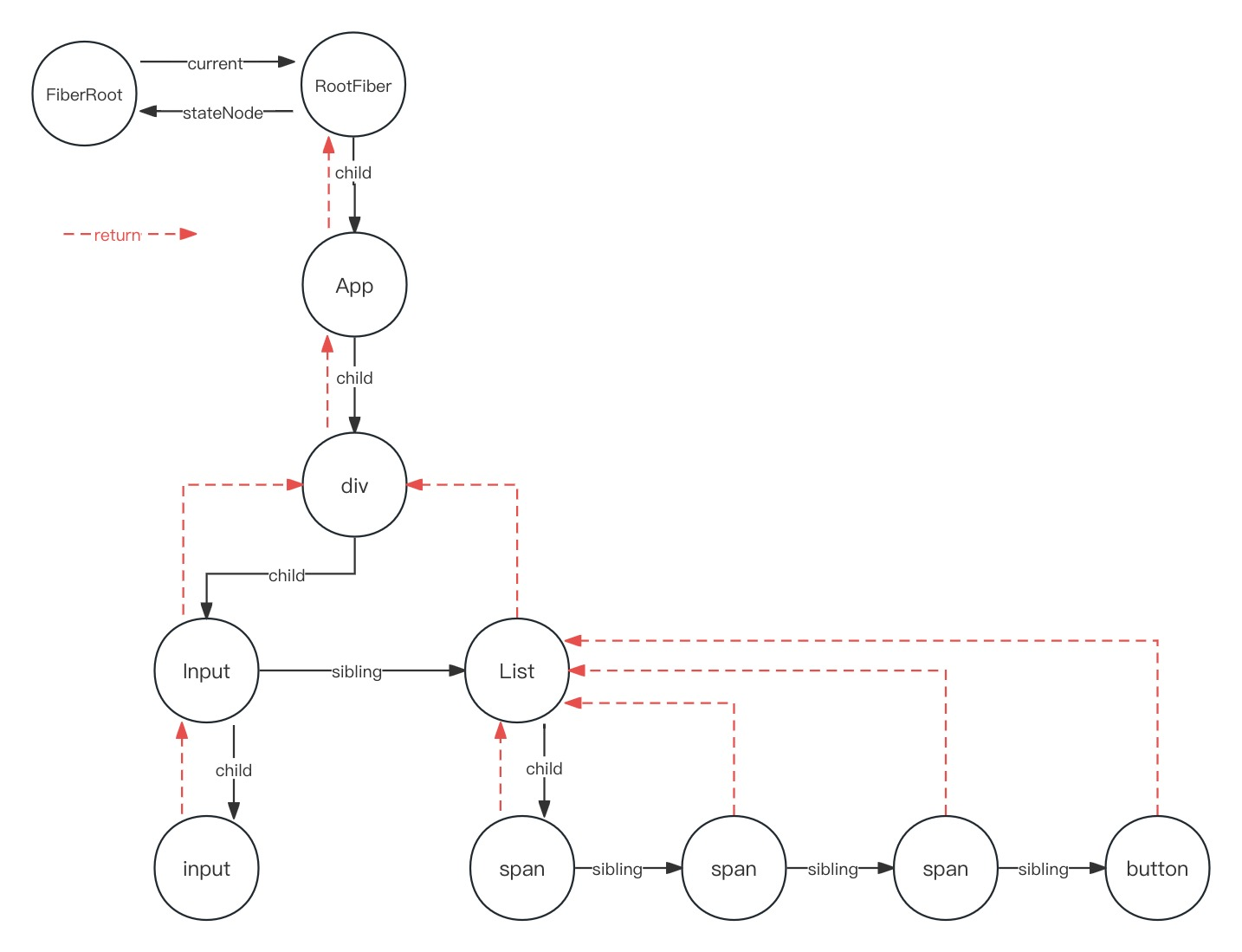
- 在这张图里面,其中有 div, input, span和 button 这几个是原生的dom节点
- 在第一次渲染的时候,要去尝试执行 hydrate 的, 先回到 beginWork 的流程
- 在 beginWork 当中,调用了
tryToClaimNextHydratableInstance的时候, - 在
enterHydrationState的里面,设置了这些初始化的变量function enterHydrationState(fiber: Fiber): boolean {// supportsHydration 在 react dom 环境中是 写死的 trueif (!supportsHydration) {return false;}// 默认是 root, 也就是 ReactDOM.render 中的第2个参数const parentInstance = fiber.stateNode.containerInfo;// nextHydratableInstance 是一个全局变量nextHydratableInstance = getFirstHydratableChild(parentInstance);hydrationParentFiber = fiber;isHydrating = true;return true; } - 然后,它的 nextHydratableInstance 是等于
getFirstHydratableChild(parentInstance) - 对于这张图里面的情况,它找到的它第一个可以使用的节点,它肯定是 div 这个节点
- 也就是说执行了这个
enterHydrationState方法之后,这个变量它变成了 div - 然后这个
hydrationParentFiber是目前传进来的 fiber,也就是这个 RootFiber - 等到在div这个节点更新的时候,我们会执行这个
tryToClaimNextHydratableInstance方法 - 执行这个方法的时候,
if (!tryHydrate(fiber, nextInstance)) {}, 这个 tryHydrate 是成功的 - 成功了之后会设置
hydrationParentFiber = fiber;这里的fiber就是当前fiber, 也就是 div 所对应的fiber - 而
nextHydratableInstance是上图的 input,因为div要找到它一侧的子节点 - 对于这个div节点来说,input span和button都是它的子节点,第一个符合条件的就是input
- 找到这个input之后,我们对于 beginWork 中的
updateHostComponent,也就是这个input节点的时候,我们又会去执行这个方法 - 继续执行这个方法之后,我们的 hydrationParentFiber 变成了 input,然后 nextHydratableInstance 变成null了,因为没有子节点了
export function getFirstHydratableChild(parentInstance: Container | Instance, ): null | Instance | TextInstance {let next = parentInstance.firstChild; // 这时候是 null// Skip non-hydratable nodes.// 跳过 while 循环while (next &&next.nodeType !== ELEMENT_NODE &&next.nodeType !== TEXT_NODE) {next = next.nextSibling; // 找到所有星弟节点}return (next: any); // 最终 return null } - 到这里为止,我们的 beginWork 已经从一侧子树更新完了
- 这个时候要对 input 执行 completeUnitOfWork
- 那么 completeUnitOfWork 它首先执行的是 popHydrationState, 再次回到这个方法
function popHydrationState(fiber: Fiber): boolean {// 这里直接跳过,不会执行if (!supportsHydration) {return false;}// 这个条件肯定是不符合的, 两者是相等的if (fiber !== hydrationParentFiber) {// We're deeper than the current hydration context, inside an inserted// tree.return false;}if (!isHydrating) {// If we're not currently hydrating but we're in a hydration context, then// we were an insertion and now need to pop up reenter hydration of our// siblings.popToNextHostParent(fiber);isHydrating = true;return false;}const type = fiber.type;// If we have any remaining hydratable nodes, we need to delete them now.// We only do this deeper than head and body since they tend to have random// other nodes in them. We also ignore components with pure text content in// side of them.// TODO: Better heuristic.if (fiber.tag !== HostComponent ||(type !== 'head' &&type !== 'body' &&!shouldSetTextContent(type, fiber.memoizedProps))) {let nextInstance = nextHydratableInstance;while (nextInstance) {deleteHydratableInstance(fiber, nextInstance);nextInstance = getNextHydratableSibling(nextInstance);}}popToNextHostParent(fiber);nextHydratableInstance = hydrationParentFiber? getNextHydratableSibling(fiber.stateNode): null;return true;} if (fiber !== hydrationParentFiber) {}这个条件不符合,目前两者相等- 那么这个条件什么时候会符合呢?
- 就是之前在
tryToClaimNextHydratableInstance的时候 - 去执行 tryHydrate 比如说执行对于 div 的一个 tryHydrate,发现找不到对应的节点可以复用
- 那么这个时候我们设置的 hydrationParentFiber 是 div, 然后停止了 hydrate
- 这个时候更新到input节点的时候,是不会执行这个
tryToClaimNextHydratableInstance的方法 - 执行到头部的
if (!isHydrating)之后,它就直接 return 了,后面的逻辑是完全不会执行到的 - 所以这个时候 hydrationParentFiber 仍然是 div
- 所以对 input 执行 completeUnitOfWork 的时候,
if (fiber !== hydrationParentFiber) {}它们这个就不会相等了 - 就直接return false 就可以了,因为它不能被复用
- 就是之前在
- 接下来
if (!isHydrating) {}什么情况下它会是 false 呢?- 就是说在之前
tryToClaimNextHydratableInstance的时候,if (!tryHydrate(fiber, nextInstance)) {}, 它是不成功的这么一个情况 - 这个时候 isHydrating 就会变成false,但是要注意的是如果它能执行到这条代码说明,在这一个节点上发现它是不能复用的
- 而所有不能复用的节点都是它或者它的子节点,所以它的父节点是可以复用的
- 接下去要执行 completeUnitOfWork 的是 div,这时候就要设置 isHydrating 为 true 了
- 同时,这边它就执行了
popToNextHostParent这个方法function popToNextHostParent(fiber: Fiber): void {let parent = fiber.return;while (parent !== null &&parent.tag !== HostComponent &&parent.tag !== HostRoot) {parent = parent.return;}hydrationParentFiber = parent; } - 它就是往它的父链上面去找,第一个是 HostComponent 或者是 HostRoot 的节点就可以了
- 就是说在之前
- 在
if (!isHydrating) {}这边最后 return false- 因为它本身它这个节点是不能被 hydrate 的
- 然后在以上3个 if 条件都不符合的情况下, 说明我们这个节点是可以复用的
- 可以复用的情况,做了什么事情呢?
if (fiber.tag !== HostComponent || (type !== 'head' && type !== 'body' && !shouldSetTextContent(type, fiber.memoizedProps))) {}- 它判断了是否等于body,head,并且
shouldSetTextContent这个方法export function shouldSetTextContent(type: string, props: Props): boolean {return (type === 'textarea' ||type === 'option' ||type === 'noscript' ||typeof props.children === 'string' ||typeof props.children === 'number' ||(typeof props.dangerouslySetInnerHTML === 'object' &&props.dangerouslySetInnerHTML !== null &&props.dangerouslySetInnerHTML.__html != null)); }- 它其实就是判断了一下是否是input相关的标签
- 符合上述if这个时候,就是一个 HostText
- 既然它是一个 HostText,如果当前这边的正在要被 hydrate 的这个节点它存在的话就是不合理的
- 因为要是把当前节点都替换成纯文字的, 所以在这里,它直接把所有的节点都给它删除了,就执行这个
deleteHydratableInstancefunction deleteHydratableInstance(returnFiber: Fiber,instance: HydratableInstance, ) {// 跳过if (__DEV__) {// ... 忽略}// 创建一个待删除的fiber节点const childToDelete = createFiberFromHostInstanceForDeletion();childToDelete.stateNode = instance;childToDelete.return = returnFiber;childToDelete.effectTag = Deletion; // 注意这里// This might seem like it belongs on progressedFirstDeletion. However,// these children are not part of the reconciliation list of children.// Even if we abort and rereconcile the children, that will try to hydrate// again and the nodes are still in the host tree so these will be// recreated.if (returnFiber.lastEffect !== null) {returnFiber.lastEffect.nextEffect = childToDelete;returnFiber.lastEffect = childToDelete;} else {returnFiber.firstEffect = returnFiber.lastEffect = childToDelete;} }- 其实这边做法是比较奇怪的一个做法
- 单独去创建了一个fiber对象,然后给这个fiber对象指定了
effectTag是Deletion - 就是我们要通过这个删除节点,也要放到
commitRoot里面去做 - 这个节点,在真正的react应用当中,它是没有对应的fiber节点的,它只是在dom当中存在
- 为了要删除它,需要单独去为它创建一个fiber对象,然后把它挂到 returnFiber 的 effect的链上
- 最终在
commitRoot的时候能够执行到这个effect,然后对它执行一个删除的操作,最终把dom节点删除 - 这样做的目的,是为了统一整个react更新的流程,所以单独这么去做的一个事情
- 这是对 HostText 的一个处理,接下去就执行
popToNextHostParent - 因为接下去要执行 completeWork 的是它的 parent 上面的 host 节点
- 然后 一个三目运算,成立,通过
getNextHydratableSibling是找它的兄弟节点 - 如果不成立,返回 null
- 这边为什么要这么做呢?
- 首先它返回 null 是可以理解的,因为它这个节点已经没有父节点了
- 在父链上已经没有找到可以去被 hydrate 的节点
- 那么说明这个节点它就是一个 FiberRoot,这个 null 肯定是可以的
- 如果有的话,为什么要去找它的兄弟节点呢?
- 因为如果有兄弟节点,在 completeUnitOfWork 的过程当中,说明它也应该存在当前节点是有兄弟节点的
- 有兄弟节点,就在 completeUnitOfWork 中, 是会返回这个兄弟节点
- 并对这个兄弟节点执行 beginWork 这个流程
- 所以在这种情况下,肯定是要走这个流程的,它就去找它的兄弟节点
- 如果这边是没有兄弟节点,它就变成null了,这也是没有任何问题的
- 在唯一一个要使用到 nextHydratableInstance 的地方是删除它的节点
- 因为它是 null 就不会进入到 while循环,它也没有任何的关系
- 如果是 null 会不会对后面的流程有影响呢?
- 接着在
completeWork当中,wasHydrated是 true 之后 - 会调用一个方法叫做
prepareToHydrateHostInstancefunction prepareToHydrateHostInstance(fiber: Fiber,rootContainerInstance: Container,hostContext: HostContext, ): boolean {if (!supportsHydration) {invariant(false,'Expected prepareToHydrateHostInstance() to never be called. ' +'This error is likely caused by a bug in React. Please file an issue.',);}const instance: Instance = fiber.stateNode; // fiber.stateNode 一开始就已经被挂载了, 这时候是 nullconst updatePayload = hydrateInstance(instance, // nullfiber.type,fiber.memoizedProps,rootContainerInstance, // hostRoot 对应的 containerhostContext,fiber,);// TODO: Type this specific to this type of component.fiber.updateQueue = (updatePayload: any);// If the update payload indicates that there is a change or if there// is a new ref we mark this as an update.if (updatePayload !== null) {return true;}return false; }- 进入
hydrateInstanceexport function hydrateInstance(instance: Instance, type: string,props: Props,rootContainerInstance: Container,hostContext: HostContext,internalInstanceHandle: Object, ): null | Array<mixed> {precacheFiberNode(internalInstanceHandle, instance);// TODO: Possibly defer this until the commit phase where all the events// get attached.updateFiberProps(instance, props);let parentNamespace: string;if (__DEV__) {const hostContextDev = ((hostContext: any): HostContextDev);parentNamespace = hostContextDev.namespace;} else {parentNamespace = ((hostContext: any): HostContextProd);}return diffHydratedProperties(instance,type,props,parentNamespace,rootContainerInstance,); }- 这个
precacheFiberNode在之前执行finalizeInitialChildren内部,也会执行这个方法- 就是在 node 上面挂载了 fiber 的一个引用
- 之后执行
updateFiberProps就是通过不同的节点来执行了一些属性export function updateFiberProps(node, props) {node[internalEventHandlersKey] = props; } - 接下去是重点,
return diffHydratedProperties- 这个方法其实它就是对比了原生的dom节点上面的属性,以及在 react 渲染中拿到的 props 它们之间的一个情况
- 然后,它也会生成一个 updatePayload
- 在 prepareToHydrateHostInstance 里面, 去执行 hydrateInstance 的时候
- 它返回的是一个 updatepayload,并且设置到了 fiber.updateQueen 上面
- 最终它就直接return是true还是false了,以此来判断是否这个节点要更新
- 这个就跟之前的更新流程是非常相似的,它通过 updateQueen 去记录了这个dom节点,它需要更新的属性
- 最终在 commitRoot 的阶段,会把这些更新都应用到这个 dom 节点上面
- 源码,参考: packages/react-dom/src/client/ReactDOMComponent.js#L834
- 它跟 updateProperties 唯一的区别是
- 这个node,它本身也是由react来创建的,已经存储了一些信息了
- 而 hydrate 它的一个流程当中的这个dom节点不是react创建的
- 所以它的对比过程可能会稍微更复杂一点,那其实也是差不多的
- 比如,要去绑定事件,验证 props
- 对应每一个props 去判断一下在原生的那个节点上面是否存在
- 如果有存在,它就不加到 updatePayload
- 如果不存在,那都加进去,所以其实就是这么一些流程
- 这些代码非常的长是跟dom操作相关性比较大的一些内容
- 这些是涉及到 dom 操作的内容,都是比较基础的内容,不涉及react核心
- 这个
- 进入
- 在最初的
tryHydrate中,已经执行fiber.stateNode = (instance: Instance) - 这里,fiber.stateNode 已经被赋值了其上
canHydrateInstance得到的 instance, 也即是从dom节点上找到的instance - 在后续
hydrateInstance中的 instance 参数就是 fiber.stateNode,不需要使用在popHydrationState中的 nextHydratableInstance 属性了 - 所以, 在上边
popHydrationState的时候,nextHydratableInstance 最终拿到是 null 也没有任何关系- 因为这个节点是可以 hydrate 的
- 它的节点已经对应拿到了
- 这个 nextHydratableInstance 只是一个标识的量
- 接着在
- 以上,在 beginWork 复用了这个节点之后
- 并且已经进行了
diffHydratedProperties了 - 说明我们这个节点已经复用成功了
- 之后就是走后面的 commitRoot 流程等内容了



![[晓理紫]CCF系列会议截稿时间订阅](http://pic.xiahunao.cn/[晓理紫]CCF系列会议截稿时间订阅)








-INNER JOIN和OUTER JOIN的区别)

 还不会写 Stable Diffusion (SD) 绘画提示词?没关系,ChatGPT帮你搞定)




