目录
- 1. 相同的树
- 2. 另一棵树的子树
- 3. 翻转二叉树
- 4. 平衡二叉树
- 5. 对称二叉树
- 6. 二叉树构建与遍历
- 7. 二叉树的层序遍历
- 8. 二叉树的最近公共祖先
- 9. 从前序与中序遍历序列构造二叉树
- 10. 从中序与后序遍历序列构造二叉树
- 11. 根据二叉树创建字符串
- 12. 二叉树的前序遍历非递归实现
- 13. 二叉树的中序遍历非递归实现
- 14. 二叉树的后续遍历非递归实现
public class BinaryTree {class TreeNode{public int val;public TreeNode left;public TreeNode right;public TreeNode(int val) {this.val = val;}public TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {this.val = val;this.left = left;this.right = right;}}//穷举法构建二叉树public TreeNode creatBinaryTree(){TreeNode A = new TreeNode(1);TreeNode B = new TreeNode(2);TreeNode C = new TreeNode(3);TreeNode D = new TreeNode(4);TreeNode E = new TreeNode(5);TreeNode F = new TreeNode(6);TreeNode G = new TreeNode(7);TreeNode H = new TreeNode(8);A.left = B;A.right = C;B.left = D;B.right = E;C.left = F;C.right = G;E.right = H;TreeNode root = A;return root;}
}
1. 相同的树
相同的树
思路:从子问题的角度去考虑
- 首先,判断是否根结点处的结构相同,比如,两棵树的根结点是不是同时为空,或者一个为空另一个不为空,两个都不为空的四种情况,来判断结构
- 其次,当两棵树的根结点都不为空时,判断是否元素相同
- 最后,当元素相同时,判断两棵树根节点的左子树是否相同,右子树是否相同(递归)
class Solution {public boolean isSameTree(TreeNode p, TreeNode q) {if (p != null && q == null || p == null && q !=null) {//结构不一样return false;}//上述if语句没有进来,那么说明,要么两个都为空,要么两个都不是空if (p == null && q == null) {return true;}if (p.val != q.val) {return false;}//上述代码完成,走到这里,说明 p!=null && q!=null && p.val == q.valreturn isSameTree(p.left, q.left) && isSameTree(p.right, q.right);}
}
2. 另一棵树的子树
另一棵树的子树
思路:利用子问题递归解决
- 首先判断root是否为空
- 其次判断两棵树是否相同
- 然后判断root为根结点的树的左子树与之是否相同
- 最后判断root为根结点的树的右子树与之是否相同
class Solution {public boolean isSubtree(TreeNode root, TreeNode subRoot) {if (root == null) {return false;}if (isSameTree(root,subRoot)) {return true;}if (isSubtree(root.left, subRoot)){return true;}if (isSubtree(root.right, subRoot)){return true;}return false;}public boolean isSameTree(TreeNode p, TreeNode q) {if (p != null && q == null || p == null && q !=null) {//结构不一样return false;}//上述if语句没有进来,那么说明,要么两个都为空,要么两个都不是空if (p == null && q == null) {return true;}if (p.val != q.val) {return false;}//上述代码完成,走到这里,说明 p!=null && q!=null && p.val == q.valreturn isSameTree(p.left, q.left) && isSameTree(p.right, q.right);}
}
3. 翻转二叉树
翻转二叉树
- 将根结点处的左子树与右子树翻转
- 翻转左子树
- 翻转右子树
class Solution {public TreeNode invertTree(TreeNode root) {if (root == null) {return null;}TreeNode tmp = root.left;root.left = root.right;root.right = tmp; invertTree(root.left);invertTree(root.right);return root;}
}
4. 平衡二叉树
平衡二叉树
- 如果根结点为空,则为平衡二叉树
- 如果根结点不为空,求解左子树高度与右子树高度
- 如果根结点左右子树高度差大于1,则不为平衡二叉树
- 如果根结点左右子树高度差小于等于1,且左右子树均为平衡二叉树,则为平衡二叉树
public boolean isBalanced(TreeNode root) {if (root == null){return true;}int leftTreeHeight = getTreeHight(root.left);int rightTreeHeight = getTreeHight(root.right);int heightDifference = Math.abs(leftTreeHeight - rightTreeHeight);if(heightDifference > 1){return false;}else {return isBalanced(root.left) && isBalanced(root.right);}
}//用于求解树的高度
public int getTreeHight(TreeNode root){if(root == null){return 0;}if(root.left == null && root.right == null){return 1;}int leftHeight = getTreeHight(root.left);int rightHeight = getTreeHight(root.right);return Math.max(leftHeight, rightHeight) + 1;
}
5. 对称二叉树
对称二叉树
- 根结点如果为空,则为对称二叉树
- 根结点如果不为空:
- 判断左结点与右结点在结构上是否对称
- 判断左结点与右节点在数值上是否对称
- 递归判断左子树与右子树是否对称
public class IsSymmetric {public boolean isSymmetric(TreeNode root) {if (root == null){return true;}return isSymmetricChild(root.left,root.right);}public boolean isSymmetricChild(TreeNode treeLeft, TreeNode treeRight) {//1.判断结构上是否对称if (treeLeft == null && treeRight != null || treeLeft != null && treeRight == null){return false;}if (treeLeft == null && treeRight == null){return true;}//2.判断数值上是否对称if (treeLeft.val != treeRight.val){return false;}//3.递归进行判断return isSymmetricChild(treeLeft.left, treeRight.right) && isSymmetricChild(treeLeft.right, treeRight.left);}
}
6. 二叉树构建与遍历
二叉树构建与遍历
利用二叉树前序遍历生成的字符串构建二叉树:
- 构建根结点
- 构建左子树
- 构建右子树
class TreeNode {public char val;public TreeNode left;public TreeNode right;public TreeNode() {}public TreeNode(char val) {this.val = val;}public TreeNode(char val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {this.val = val;this.left = left;this.right = right;}
}
import java.util.Scanner;public class BinaryTreeConstructionAndTraversal {//二叉树构建private static int i = 0;private static TreeNode BinaryTreeConstruction (String str){if (str == null){return null;}TreeNode root = null;if (str.charAt(i) != '#') {root = new TreeNode(str.charAt(i));i++;root.left = BinaryTreeConstruction(str);root.right = BinaryTreeConstruction(str);}else {i++;}return root;}//中序遍历private static void inOrder (TreeNode root){if (root == null){return;}inOrder(root.left);System.out.print(root.val + " ");inOrder(root.right);}public static void main(String[] args) {Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);while (scanner.hasNextLine()){String str = scanner.nextLine();TreeNode root = BinaryTreeConstruction(str);inOrder(root);}}
}
7. 二叉树的层序遍历
二叉树的层序遍历
将一层的元素加入顺序表当中,再将这些顺序表加入新的顺序表当中
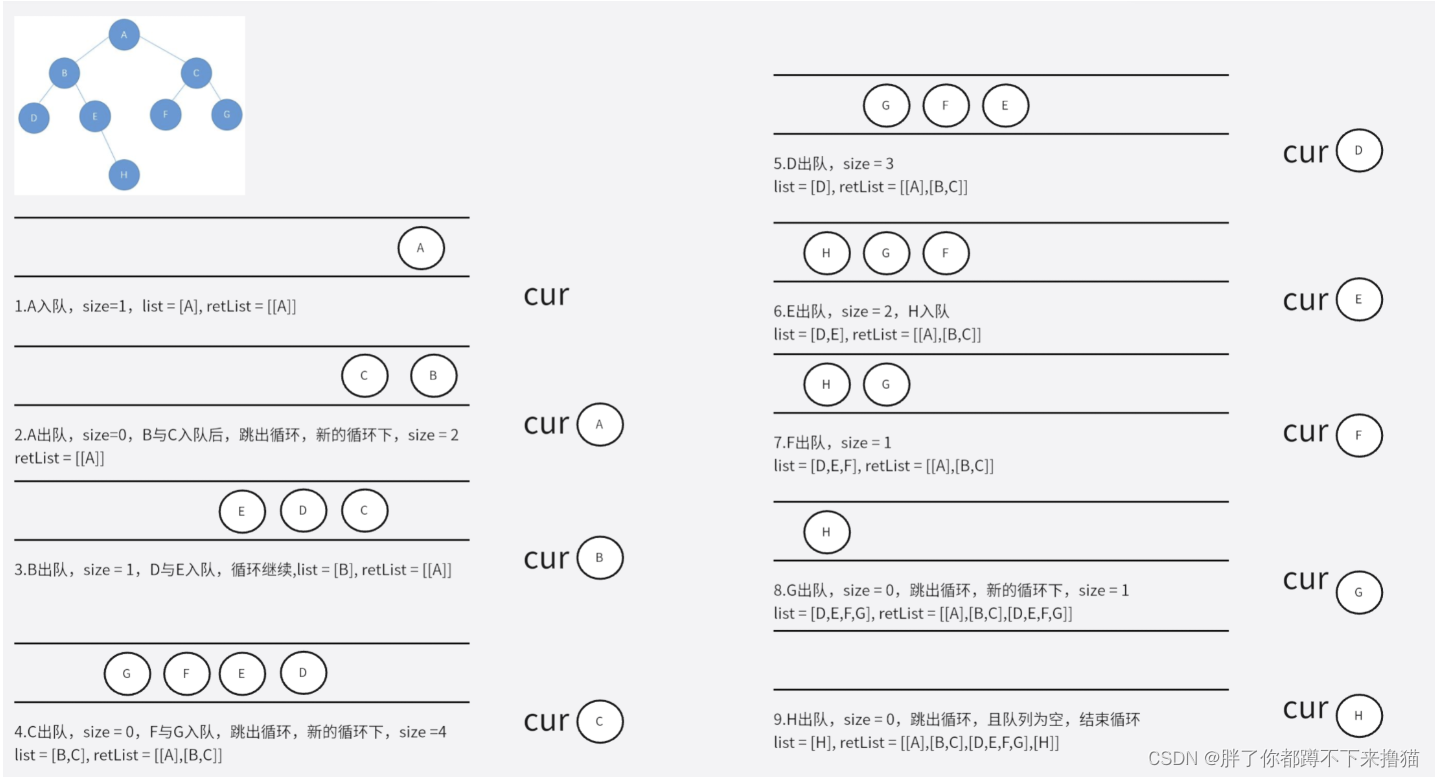
public List<List<Character>> levelOrder(TreeNode root){List<List<Character>> retList = new ArrayList<>();if (root == null){return retList;}Queue<TreeNode> queue = new LinkedList<>();queue.offer(root);while (!queue.isEmpty()){int size = queue.size();List<Character> list = new ArrayList<>();while (size != 0){TreeNode cur = queue.poll();list.add(cur.val);size--;if (cur.left != null){queue.offer(cur.left);}if (cur.right != null){queue.offer(cur.right);}}retList.add(list);}return retList;
}
8. 二叉树的最近公共祖先
二叉树的最近公共祖先
方法一:
- 先判断p或者q 是不是 root当中的一个
- 左子树当中查找p或者q(先查找到p就返回p,先查找到q就返回q)
- 右子树当中查找p或者q(先查找到p就返回p,先查找到q就返回q)
- 整体判断:
- 左子树和右子树中都查找到了,则最近公共祖先为root
- 如果左子树中没有查找到,则最近的公共祖先为右子树中查找到的
- 如果右子树中没有查找到,则最近的公共祖先为左子树中查找到的
public TreeNode lowestCommonAncestor(TreeNode root, TreeNode p, TreeNode q) {if (root == null) {return null;}if (p == root || q == root) {return root;}TreeNode left = lowestCommonAncestor(root.left, p, q);TreeNode right = lowestCommonAncestor(root.right, p, q);if (left != null && right != null) {return root;}if (left == null) {return right;}return left;
}
方法二:
-
求解p、q各自路径
-
求解路径的相交点(大小做差,出栈)
public TreeNode lowestCommonAncestor(TreeNode root, TreeNode p, TreeNode q){Stack<TreeNode> stackp = new Stack<>();Stack<TreeNode> stackq = new Stack<>();int sizep = 0;int sizeq = 0;if (getPath(root, p, stackp)){sizep = stackp.size();}if (getPath(root, q, stackq)){sizeq = stackq.size();}int sizepq = sizep - sizeq;if (sizepq > 0){for (int i = 0; i < sizepq; i++) {stackp.pop();}}else {for (int i = 0; i < Math.abs(sizepq); i++) {stackq.pop();}}while (stackp.peek() != stackq.peek()){stackp.pop();stackq.pop();}return stackp.peek();
}
找到二叉树中node的所在路径
- 判断是否为空
- 判断是否等于node
- 该结点入栈
- 判断左子树是否存在路径
- 判断右子树是否存在路径
- 都不存在说明该结点不在路径上,出栈
public boolean getPath(TreeNode root, TreeNode node, Stack<TreeNode> stack){if (root == null){return false;}if (root == node){return true;}stack.push(root);boolean flgLeft = getPath(root.left, node, stack);if (flgLeft){return true;}boolean flgRight = getPath(root.right, node, stack);if (flgRight){return true;}stack.pop();return false;
}
9. 从前序与中序遍历序列构造二叉树
从前序与中序遍历序列构造二叉树
- 创建根节点
- 在中序遍历的字符串当中 找到当前根节点的下标
- 分别创建左子树和右子树
public int preIndex;
public TreeNode buildTree(int[] preorder, int[] inorder) {return buildTreeChild(preorder, inorder, 0, inorder.length - 1);
}private TreeNode buildTreeChild(int[] preorder, int[] inorder, int inBegin, int inEnd) {if (inBegin > inEnd) {return null;}// 1、创建根节点TreeNode root = new TreeNode(preorder[preIndex]);// 2. 在中序遍历的字符串当中 找到当前根节点的下标int rootIndex = findRootIndex(inorder,inBegin,inEnd,preorder[preIndex]);preIndex++;// F// 3. 分别创建左子树和右子树root.left = buildTreeChild(preorder, inorder, inBegin, rootIndex - 1);root.right = buildTreeChild(preorder, inorder, rootIndex + 1, inEnd);return root;
}private int findRootIndex(int[] inorder, int inBegin, int inEnd, int key) {for (int i = inBegin; i <= inEnd; i++) {if (inorder[i] == key) {return i;}}return -1;
}
10. 从中序与后序遍历序列构造二叉树
从中序与后序遍历序列构造二叉树
- 创建根节点
- 在中序遍历的字符串当中 找到当前根节点的下标
- 分别创建右子树和左子树
public int postIndex;
public TreeNode buildTree(int[] inorder,int[] postorder) {postIndex = postorder.length - 1;return buildTreeChild(postorder, inorder, 0, inorder.length - 1);
}private TreeNode buildTreeChild(int[] postorder, int[] inorder, int inBegin, int inEnd) {if (inBegin > inEnd) {return null;}// 1、创建根节点TreeNode root = new TreeNode(postorder[postIndex]);// 2. 在中序遍历的字符串当中 找到当前根节点的下标int rootIndex = findRootIndex(inorder, inBegin, inEnd, postorder[postIndex]);postIndex--;// F// 3. 分别创建右子树和左子树root.right = buildTreeChild(postorder, inorder, rootIndex + 1, inEnd);root.left = buildTreeChild(postorder, inorder, inBegin, rootIndex - 1);return root;
}private int findRootIndex(int[] inorder, int inBegin, int inEnd, int key) {for (int i = inBegin; i <= inEnd; i++) {if (inorder[i] == key) {return i;}}return -1;
}
11. 根据二叉树创建字符串
根据二叉树创建字符串
-
判断根结点是否为空,当根结点不为空时(前序遍历)
-
将根结点加入字符串中
-
判断左结点
-
如果根结点的左结点不为空
- 加入"("
- 构建左子树字符串
- 加入")"
-
如果根结点的左结点为空,但右节点不为空,需要将为空的左结点表示出来:
- 加入"()"
-
如果左右结点均为空,无需操作
-
-
判断右节点
- 如果根结点的右结点不为空
- 加入"("
- 构建右子树字符串
- 加入")"
- 如果根结点的右结点不为空
public String tree2str(TreeNode root) {StringBuilder stringBuilder = new StringBuilder();tree2str2(root,stringBuilder);return stringBuilder.toString();
}private void tree2str2(TreeNode root, StringBuilder stringBuilder){if (root == null){return;}stringBuilder.append(root.val);if (root.left != null) {stringBuilder.append("(");tree2str2(root.left, stringBuilder);stringBuilder.append(")");}else if (root.right != null){stringBuilder.append("()");}else {}if (root.right != null){stringBuilder.append("(");tree2str2(root.right, stringBuilder);stringBuilder.append(")");}}
12. 二叉树的前序遍历非递归实现
二叉树的前序遍历非递归实现
public List<Integer> preorderTraversal(TreeNode root){List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>();Stack<TreeNode> stack = new Stack<>();if (root == null){return list;}TreeNode cur = root;while (cur!=null || !stack.isEmpty()){while (cur != null){stack.push(cur);list.add(cur.val);cur = cur.left;}TreeNode top = stack.pop();cur = top.right;}return list;
}
13. 二叉树的中序遍历非递归实现
二叉树的中序遍历非递归实现
public List<Integer> inorderTraversal(TreeNode root){List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>();Stack<TreeNode> stack = new Stack<>();if (root == null){return list;}TreeNode cur = root;while (cur!=null || !stack.isEmpty()){while (cur != null){stack.push(cur);cur = cur.left;}TreeNode top = stack.pop();list.add(top.val);cur = top.right;}return list;
}
14. 二叉树的后续遍历非递归实现
二叉树的后续遍历非递归实现
public List<Integer> postorderTraversal(TreeNode root){List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>();Stack<TreeNode> stack = new Stack<>();if (root == null){return list;}TreeNode cur = root;TreeNode prev = null;//用于判断该结点是否入过栈while (cur!=null || !stack.isEmpty()){while (cur != null){stack.push(cur);cur = cur.left;}TreeNode top = stack.peek();//元素弹出条件:上述条件保障了该节点的左子树为空,只要保证该节点右子树为空或者在上一次被弹出过if (top.right == null || top.right == prev){top = stack.pop();list.add(top.val);prev = top;}else {cur = top.right;}}return list;
}













》笔记3.7)

)
-- 视图存储方式触发器)


