文章目录
- openssl3.2 - 官方demo学习 - guide - tls-client-block.c
- 概述
- 记录问题
- server和client IP都为localhost
- server和client IP都为127.0.0.1
- 想到解决问题的方法1
- 想到解决问题的方法2
- 笔记
- END
openssl3.2 - 官方demo学习 - guide - tls-client-block.c
概述
tls 客户端
官方demo有问题, 无法建立客户端socket, 可以确认sSever没问题, 用tcping试过了.
启动server和Client时, 都用127.0.0.1是可以建立socket的, 可以通讯.
但是说IP不匹配, 以后再玩.(等自己做了靠谱的证书实验, 再继续验证这个官方demo)
记录问题
程序编译完, 做了2个脚本来实验.
分为2种情况记录
server和client IP都为localhost
@echo off
rem run_tls_server.cmd
echo tls server
set path=c:\openssl_3d2\bin;%path%
echo begin : %date% %time%
openssl s_server -www -accept localhost:23456 -cert servercert.pem -key serverkey.pem
echo end : %date% %time%
pause@echo off
echo run_tls_client.cmd
set path=c:\openssl_3d2\bin;%path%
echo begin : %date% %time%
set SSL_CERT_FILE=rootcert.pem
prj_template.exe localhost 23456
echo end : %date% %time%
pause先启动server的bat, 再启动client的bat
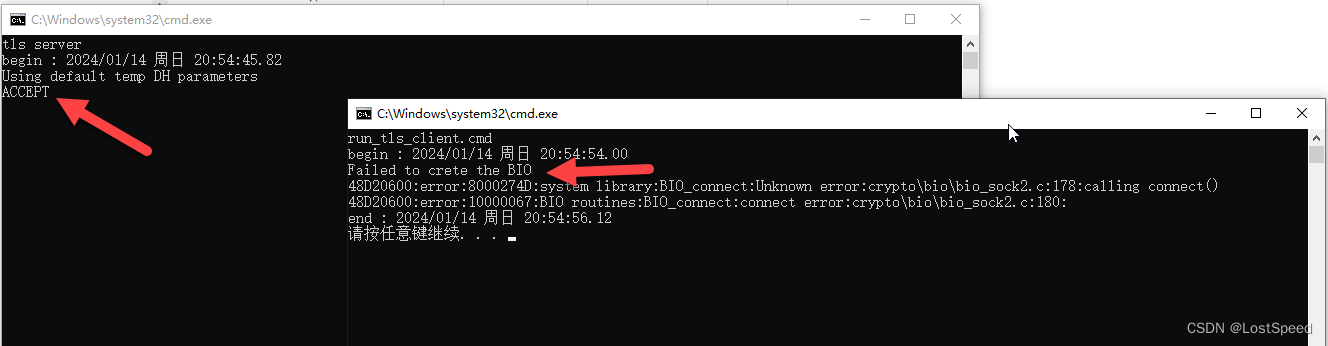
客户端报错信息显示建立socket失败.
服务器端一点反应没有, 说明客户端没连上服务器.
用tcping试试端口
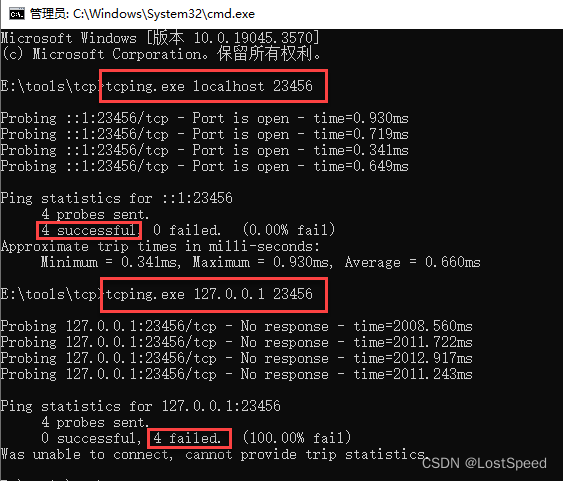
ping localhost 23456 时, 端口是能访问的.
ping 127.0.0.1 23456时, 端口是不能访问的.
说明客户端访问服务时, 用localhost要能访问才对.
这是不是官方demo有问题啊…
server和client IP都为127.0.0.1
@echo off
rem run_tls_server.cmd
echo tls server
set path=c:\openssl_3d2\bin;%path%
echo begin : %date% %time%
openssl s_server -www -accept 127.0.0.1:23456 -cert servercert.pem -key serverkey.pem
echo end : %date% %time%
pause@echo off
echo run_tls_client.cmd
set path=c:\openssl_3d2\bin;%path%
echo begin : %date% %time%
set SSL_CERT_FILE=rootcert.pem
prj_template.exe 127.0.0.1 23456
echo end : %date% %time%
pause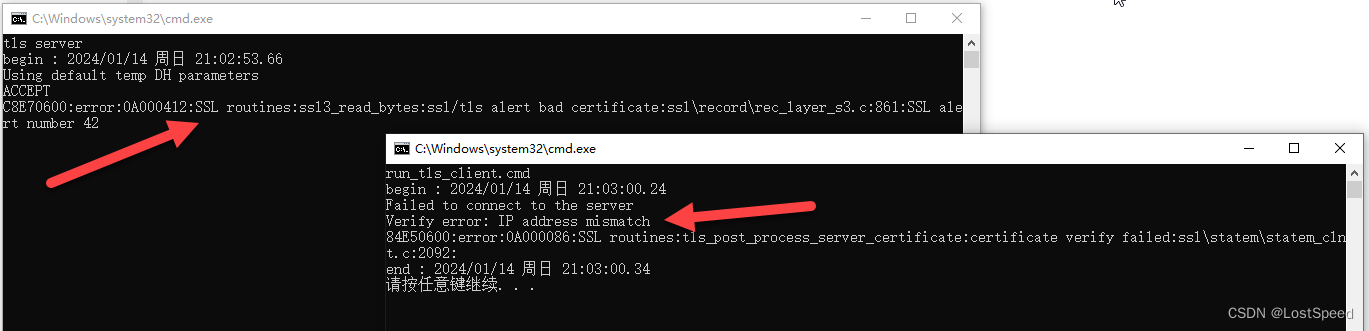
显示IP不匹配.
莫非只能用远程域名来访问? 不能用绝对IP来访问? 说不通啊.
只能先放这里, 等有头绪了再来尝试解决.
想到解决问题的方法1
我已经编译好了可以run的openssl.exe工程(openssl3.2 - 自己构建openssl.exe的VS工程(在编译完的源码版本上))
给好启动server的参数和环境变量
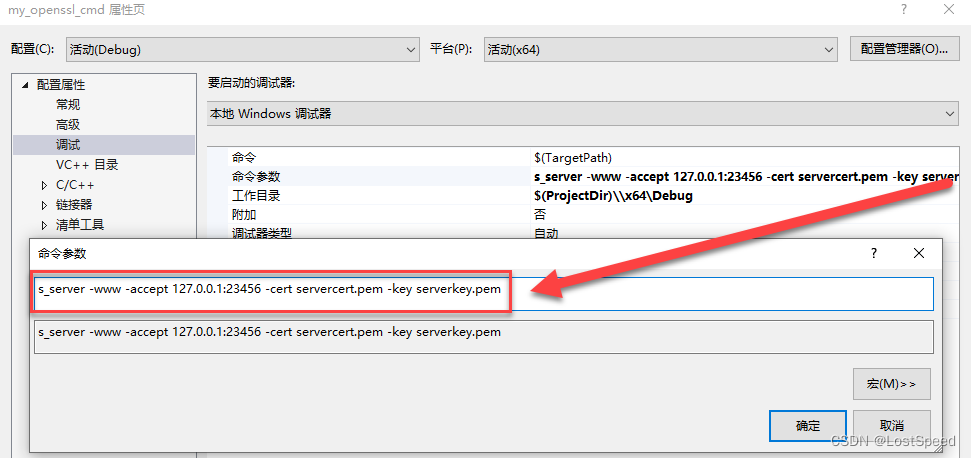
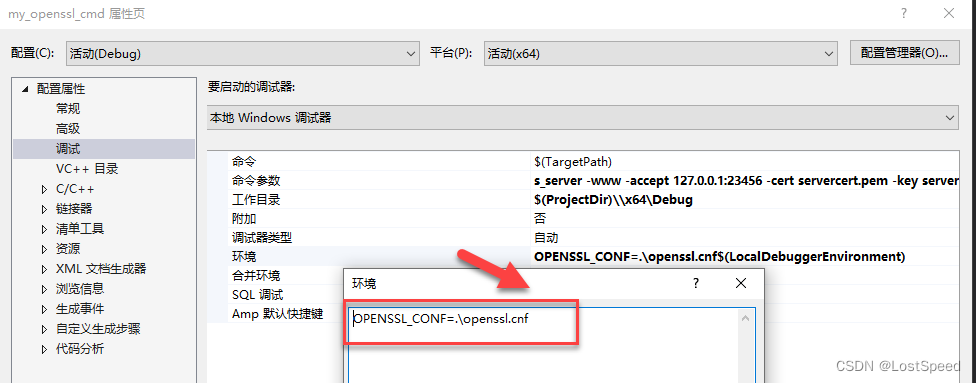
跑起来效果是一样的
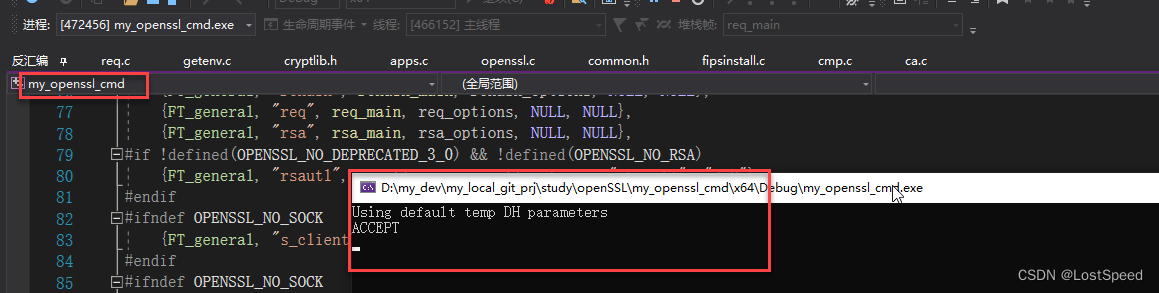
那么, 用127.0.0.1 23456 连上来的客户端, 如果有啥错误提示(e.g. IP不匹配), 那我可以在openssl.exe源码中单步查啊. 就知道为啥报错了.
想到解决问题的方法2
既然openssl.exe可以模拟一个服务, 那么也可以模拟一个客户端.
看了openssl.exe的实现, 确实有.
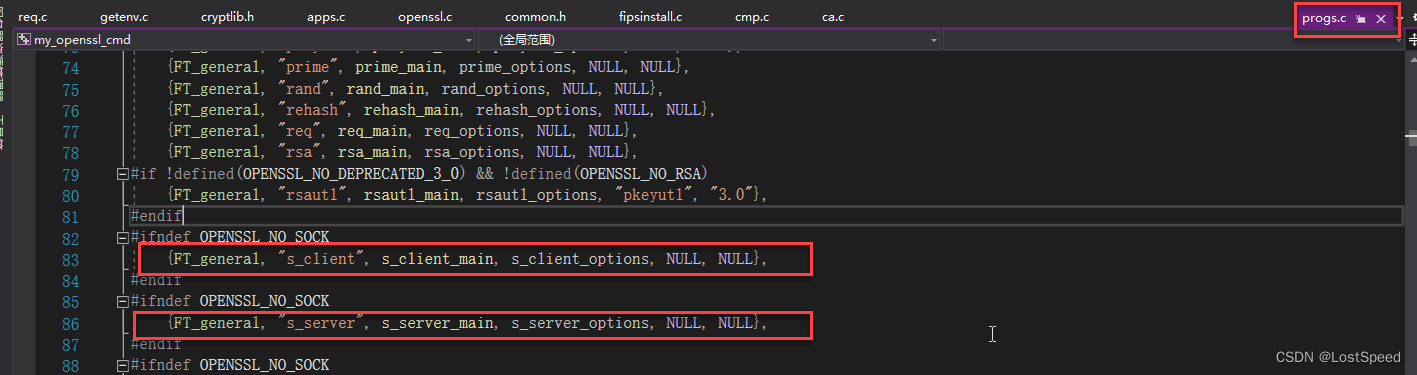
那我可以用openssl.exe模拟一个客户端,带着相同的参数跑起来, 如果正常, 我就移植(抄代码), 就实现了一个客户端.
等后续按照这2个思路试试.
openssl提供的demo不可能全部正确的, 前面已经发现了官方应用的demo实现有问题(e.g. openssl3.2 - 官方demo学习 - cms - cms_uncomp.c(官方应用实现错误, 需要修正)).
但是原版的openssl.exe实现是没有问题的(那么多openssl用户, 很多人都用openssl.exe直接来干活, 如果有啥bug, 早就修正了, 不可能埋雷).
所以参照openssl.exe的客户端实现, 是绝对没问题的.
笔记
/*!\file tls-client-block.c\note openssl3.2 - 官方demo学习 - guide - tls-client-block.ctls 客户端官方demo有问题, 无法建立客户端socket, 可以确认sSever没问题, 用tcping试过了.启动server和Client时, 都用127.0.0.1是可以建立socket的, 可以通讯.但是说证书不匹配, 以后再玩.
*//** Copyright 2023 The OpenSSL Project Authors. All Rights Reserved.** Licensed under the Apache License 2.0 (the "License"). You may not use* this file except in compliance with the License. You can obtain a copy* in the file LICENSE in the source distribution or at* https://www.openssl.org/source/license.html*//** NB: Changes to this file should also be reflected in* doc/man7/ossl-guide-tls-client-block.pod*/#include <string.h>/* Include the appropriate header file for SOCK_STREAM */
#ifdef _WIN32 /* Windows */
# include <winsock2.h>
#else /* Linux/Unix */
# include <sys/socket.h>
#endif#include <openssl/bio.h>
#include <openssl/ssl.h>
#include <openssl/err.h>#include "my_openSSL_lib.h"/* Helper function to create a BIO connected to the server */
static BIO *create_socket_bio(const char *hostname, const char *port, int family)
{int sock = -1;BIO_ADDRINFO *res;const BIO_ADDRINFO *ai = NULL;BIO *bio;/** Lookup IP address info for the server.*/if (!BIO_lookup_ex(hostname, port, BIO_LOOKUP_CLIENT, family, SOCK_STREAM, 0,&res))return NULL;/** Loop through all the possible addresses for the server and find one* we can connect to.*/for (ai = res; ai != NULL; ai = BIO_ADDRINFO_next(ai)) {/** Create a TCP socket. We could equally use non-OpenSSL calls such* as "socket" here for this and the subsequent connect and close* functions. But for portability reasons and also so that we get* errors on the OpenSSL stack in the event of a failure we use* OpenSSL's versions of these functions.*/sock = BIO_socket(BIO_ADDRINFO_family(ai), SOCK_STREAM, 0, 0);if (sock == -1)continue;/* Connect the socket to the server's address */if (!BIO_connect(sock, BIO_ADDRINFO_address(ai), BIO_SOCK_NODELAY)) {BIO_closesocket(sock);sock = -1;continue;}/* We have a connected socket so break out of the loop */break;}/* Free the address information resources we allocated earlier */BIO_ADDRINFO_free(res);/* If sock is -1 then we've been unable to connect to the server */if (sock == -1)return NULL;/* Create a BIO to wrap the socket */bio = BIO_new(BIO_s_socket());if (bio == NULL) {BIO_closesocket(sock);return NULL;}/** Associate the newly created BIO with the underlying socket. By* passing BIO_CLOSE here the socket will be automatically closed when* the BIO is freed. Alternatively you can use BIO_NOCLOSE, in which* case you must close the socket explicitly when it is no longer* needed.*/BIO_set_fd(bio, sock, BIO_CLOSE);return bio;
}/** Simple application to send a basic HTTP/1.0 request to a server and* print the response on the screen.*/
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{SSL_CTX *ctx = NULL;SSL *ssl = NULL;BIO *bio = NULL;int res = EXIT_FAILURE;int ret;const char *request_start = "GET / HTTP/1.0\r\nConnection: close\r\nHost: ";const char *request_end = "\r\n\r\n";size_t written, readbytes;char buf[160];char *hostname, *port;int argnext = 1;int ipv6 = 0;if (argc < 3) {printf("Usage: tls-client-block [-6] hostname port\n");goto end;}if (!strcmp(argv[argnext], "-6")) {if (argc < 4) {printf("Usage: tls-client-block [-6] hostname port\n");goto end;}ipv6 = 1;argnext++;}hostname = argv[argnext++];port = argv[argnext];/** Create an SSL_CTX which we can use to create SSL objects from. We* want an SSL_CTX for creating clients so we use TLS_client_method()* here.*/ctx = SSL_CTX_new(TLS_client_method());if (ctx == NULL) {printf("Failed to create the SSL_CTX\n");goto end;}/** Configure the client to abort the handshake if certificate* verification fails. Virtually all clients should do this unless you* really know what you are doing.*/SSL_CTX_set_verify(ctx, SSL_VERIFY_PEER, NULL);/* Use the default trusted certificate store */if (!SSL_CTX_set_default_verify_paths(ctx)) {printf("Failed to set the default trusted certificate store\n");goto end;}/** TLSv1.1 or earlier are deprecated by IETF and are generally to be* avoided if possible. We require a minimum TLS version of TLSv1.2.*/if (!SSL_CTX_set_min_proto_version(ctx, TLS1_2_VERSION)) {printf("Failed to set the minimum TLS protocol version\n");goto end;}/* Create an SSL object to represent the TLS connection */ssl = SSL_new(ctx);if (ssl == NULL) {printf("Failed to create the SSL object\n");goto end;}/** Create the underlying transport socket/BIO and associate it with the* connection.*/bio = create_socket_bio(hostname, port, ipv6 ? AF_INET6 : AF_INET);if (bio == NULL) {printf("Failed to crete the BIO\n");goto end;}SSL_set_bio(ssl, bio, bio);/** Tell the server during the handshake which hostname we are attempting* to connect to in case the server supports multiple hosts.*/if (!SSL_set_tlsext_host_name(ssl, hostname)) {printf("Failed to set the SNI hostname\n");goto end;}/** Ensure we check during certificate verification that the server has* supplied a certificate for the hostname that we were expecting.* Virtually all clients should do this unless you really know what you* are doing.*/if (!SSL_set1_host(ssl, hostname)) {printf("Failed to set the certificate verification hostname");goto end;}/* Do the handshake with the server */if (SSL_connect(ssl) < 1) {printf("Failed to connect to the server\n");/** If the failure is due to a verification error we can get more* information about it from SSL_get_verify_result().*/if (SSL_get_verify_result(ssl) != X509_V_OK)printf("Verify error: %s\n",X509_verify_cert_error_string(SSL_get_verify_result(ssl)));goto end;}/* Write an HTTP GET request to the peer */if (!SSL_write_ex(ssl, request_start, strlen(request_start), &written)) {printf("Failed to write start of HTTP request\n");goto end;}if (!SSL_write_ex(ssl, hostname, strlen(hostname), &written)) {printf("Failed to write hostname in HTTP request\n");goto end;}if (!SSL_write_ex(ssl, request_end, strlen(request_end), &written)) {printf("Failed to write end of HTTP request\n");goto end;}/** Get up to sizeof(buf) bytes of the response. We keep reading until the* server closes the connection.*/while (SSL_read_ex(ssl, buf, sizeof(buf), &readbytes)) {/** OpenSSL does not guarantee that the returned data is a string or* that it is NUL terminated so we use fwrite() to write the exact* number of bytes that we read. The data could be non-printable or* have NUL characters in the middle of it. For this simple example* we're going to print it to stdout anyway.*/fwrite(buf, 1, readbytes, stdout);}/* In case the response didn't finish with a newline we add one now */printf("\n");/** Check whether we finished the while loop above normally or as the* result of an error. The 0 argument to SSL_get_error() is the return* code we received from the SSL_read_ex() call. It must be 0 in order* to get here. Normal completion is indicated by SSL_ERROR_ZERO_RETURN.*/if (SSL_get_error(ssl, 0) != SSL_ERROR_ZERO_RETURN) {/** Some error occurred other than a graceful close down by the* peer.*/printf ("Failed reading remaining data\n");goto end;}/** The peer already shutdown gracefully (we know this because of the* SSL_ERROR_ZERO_RETURN above). We should do the same back.*/ret = SSL_shutdown(ssl);if (ret < 1) {/** ret < 0 indicates an error. ret == 0 would be unexpected here* because that means "we've sent a close_notify and we're waiting* for one back". But we already know we got one from the peer* because of the SSL_ERROR_ZERO_RETURN above.*/printf("Error shutting down\n");goto end;}/* Success! */res = EXIT_SUCCESS;end:/** If something bad happened then we will dump the contents of the* OpenSSL error stack to stderr. There might be some useful diagnostic* information there.*/if (res == EXIT_FAILURE)ERR_print_errors_fp(stderr);/** Free the resources we allocated. We do not free the BIO object here* because ownership of it was immediately transferred to the SSL object* via SSL_set_bio(). The BIO will be freed when we free the SSL object.*/SSL_free(ssl);SSL_CTX_free(ctx);return res;
}
:磁盘管理、分区、格式化)


:页面和自定义组件生命周期)


: 损失函数loss function)


)








