前言
上一篇文章跟大家分享了用NumSharp实现简单的线性回归,但是没有进行可视化,可能对拟合的过程没有直观的感受,因此今天跟大家介绍一下使用C#基于Scottplot进行可视化,当然Python的代码,我也会同步进行可视化。
Python代码进行可视化
Python代码用matplotlib做了可视化,我就不具体介绍了。
修改之后的python代码如下:
#The optimal values of m and b can be actually calculated with way less effort than doing a linear regression.
#this is just to demonstrate gradient descentimport numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from matplotlib.animation import FuncAnimation# y = mx + b
# m is slope, b is y-intercept
def compute_error_for_line_given_points(b, m, points):totalError = 0for i in range(0, len(points)):x = points[i, 0]y = points[i, 1]totalError += (y - (m * x + b)) ** 2return totalError / float(len(points))def step_gradient(b_current, m_current, points, learningRate):b_gradient = 0m_gradient = 0N = float(len(points))for i in range(0, len(points)):x = points[i, 0]y = points[i, 1]b_gradient += -(2/N) * (y - ((m_current * x) + b_current))m_gradient += -(2/N) * x * (y - ((m_current * x) + b_current))new_b = b_current - (learningRate * b_gradient)new_m = m_current - (learningRate * m_gradient)return [new_b, new_m]def gradient_descent_runner(points, starting_b, starting_m, learning_rate, num_iterations):b = starting_bm = starting_margs_data = []for i in range(num_iterations):b, m = step_gradient(b, m, np.array(points), learning_rate)args_data.append((b,m))return args_dataif __name__ == '__main__':points = np.genfromtxt("data.csv", delimiter=",")learning_rate = 0.0001initial_b = 0 # initial y-intercept guessinitial_m = 0 # initial slope guessnum_iterations = 10print ("Starting gradient descent at b = {0}, m = {1}, error = {2}".format(initial_b, initial_m, compute_error_for_line_given_points(initial_b, initial_m, points)))print ("Running...")args_data = gradient_descent_runner(points, initial_b, initial_m, learning_rate, num_iterations)b = args_data[-1][0]m = args_data[-1][1]print ("After {0} iterations b = {1}, m = {2}, error = {3}".format(num_iterations, b, m, compute_error_for_line_given_points(b, m, points)))data = np.array(points).reshape(100,2)x1 = data[:,0]y1 = data[:,1]x2 = np.linspace(20, 80, 100)y2 = initial_m * x2 + initial_bdata2 = np.array(args_data)b_every = data2[:,0]m_every = data2[:,1]# 创建图形和轴fig, ax = plt.subplots()line1, = ax.plot(x1, y1, 'ro')line2, = ax.plot(x2,y2)# 添加标签和标题plt.xlabel('x')plt.ylabel('y')plt.title('Graph of y = mx + b')# 添加网格plt.grid(True)# 定义更新函数def update(frame):line2.set_ydata(m_every[frame] * x2 + b_every[frame])ax.set_title(f'{frame} Graph of y = {m_every[frame]:.2f}x + {b_every[frame]:.2f}')# 创建动画
animation = FuncAnimation(fig, update, frames=len(data2), interval=500)# 显示动画
plt.show()实现的效果如下所示:
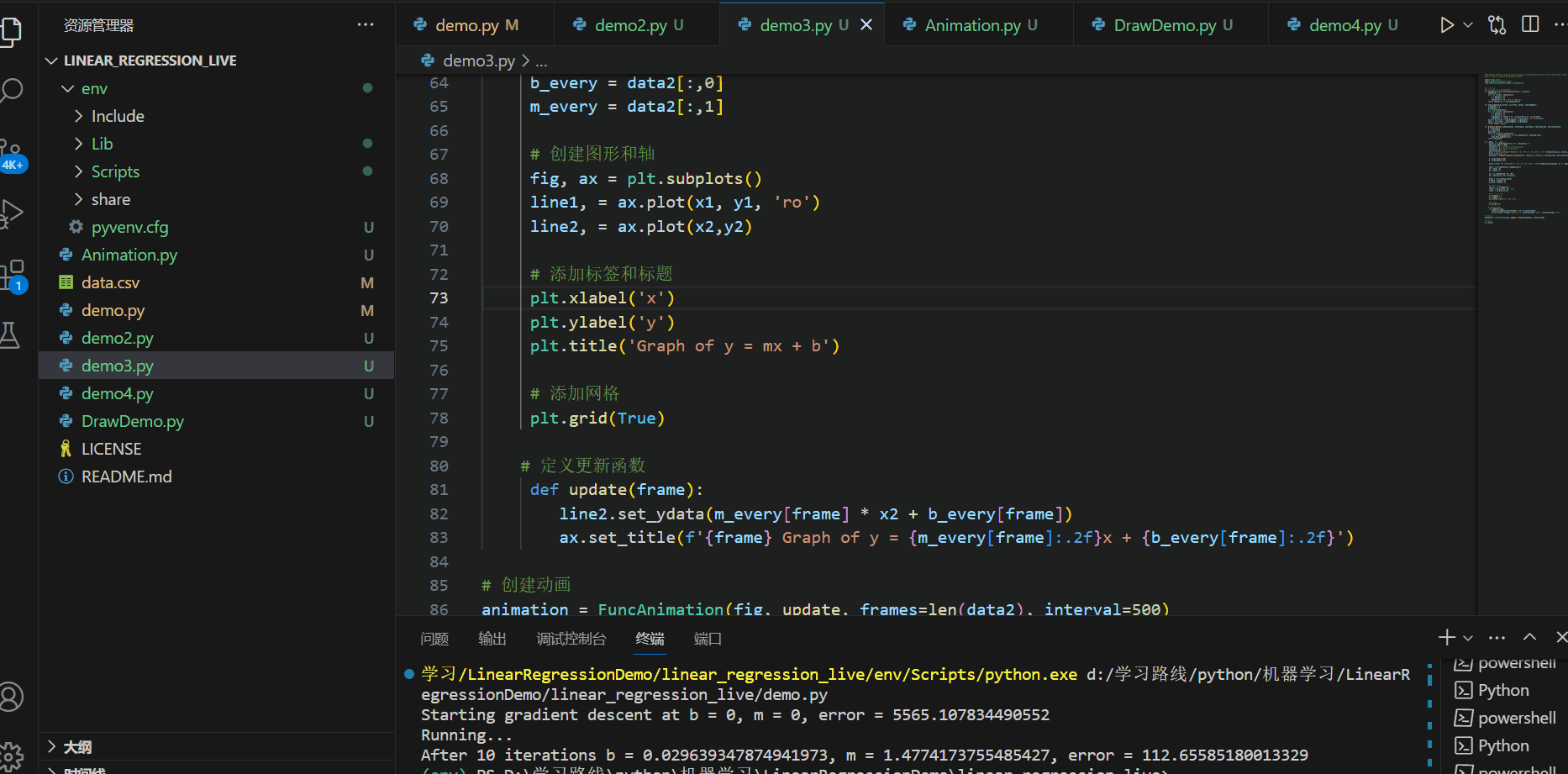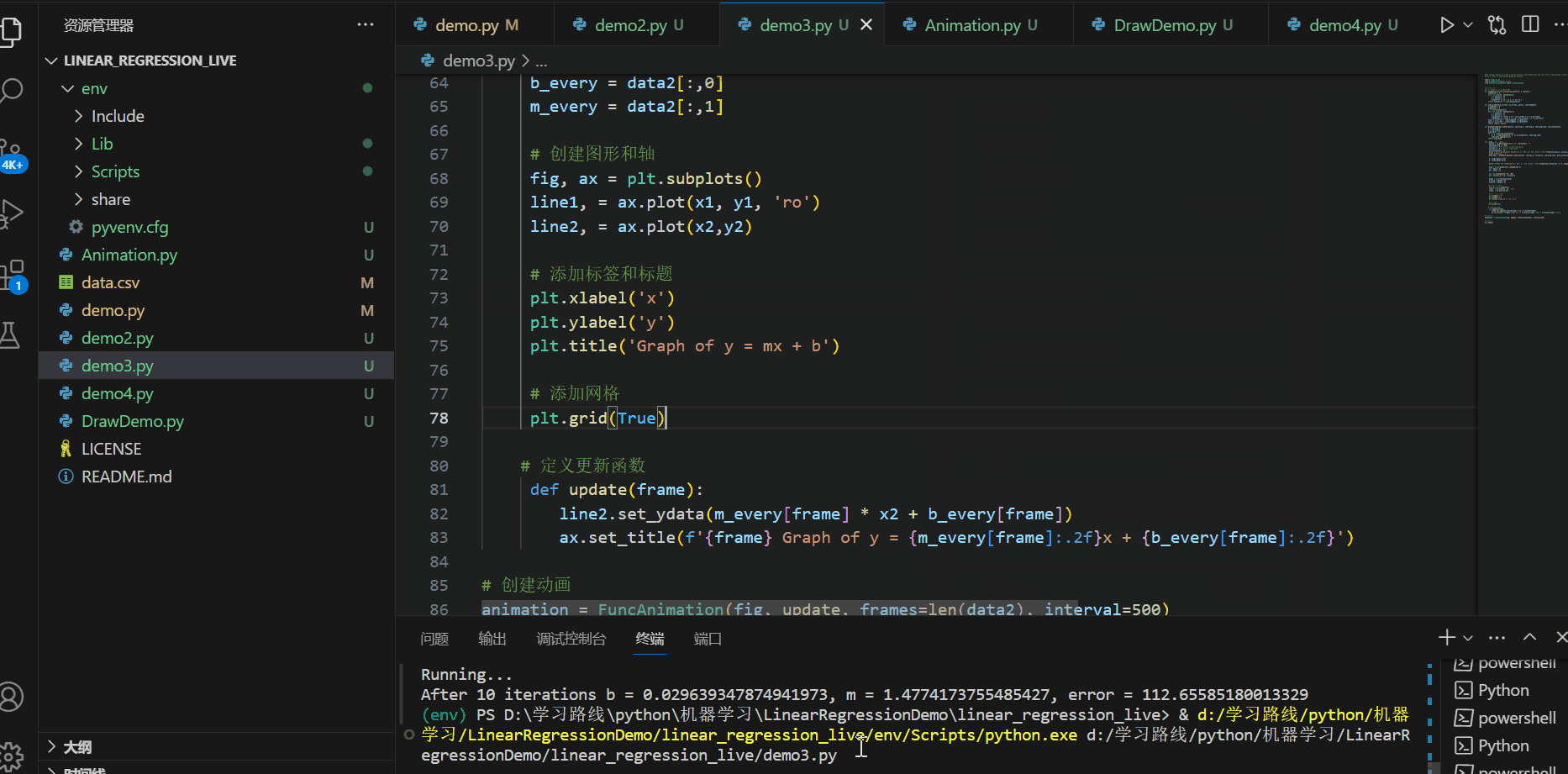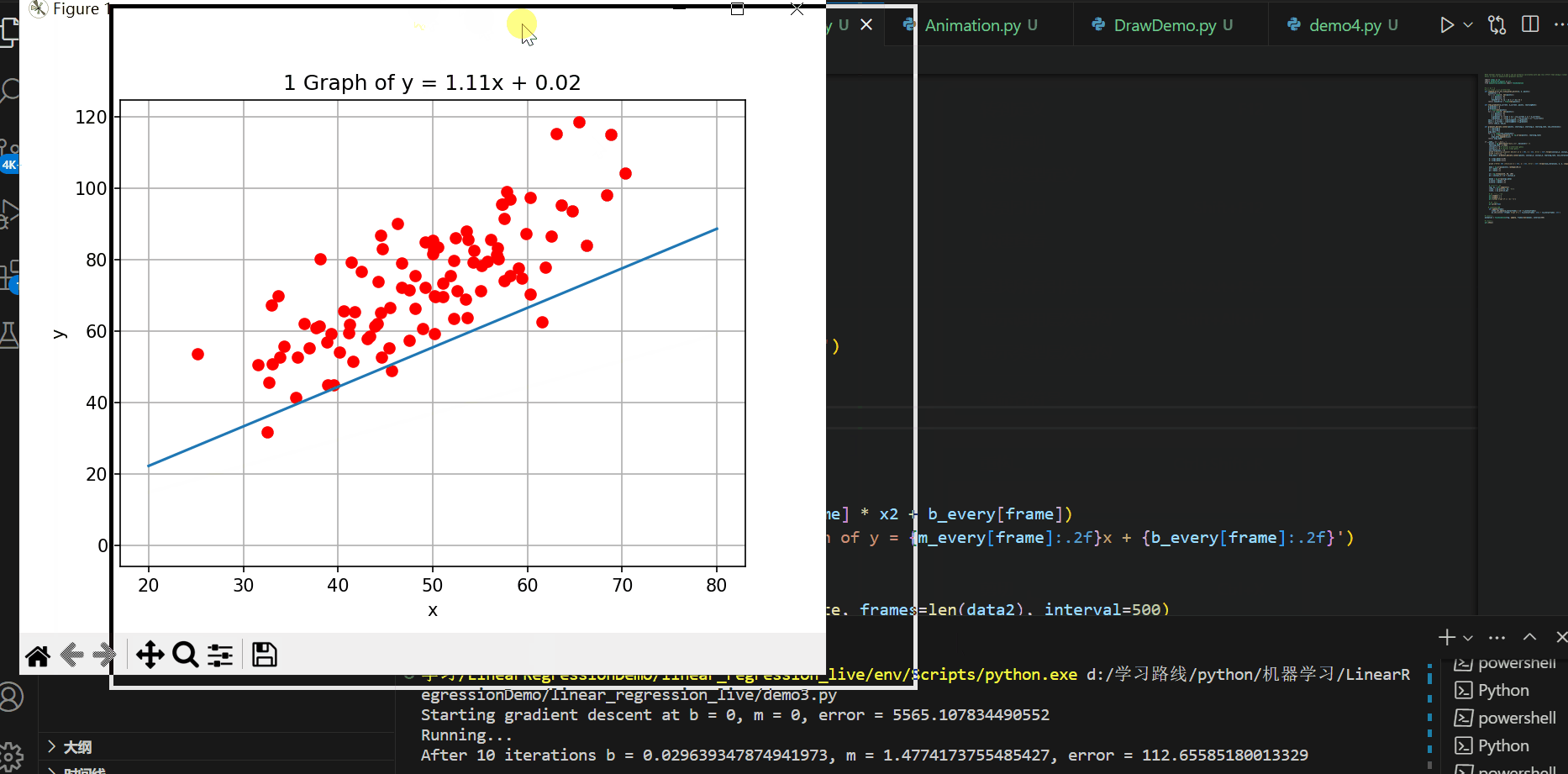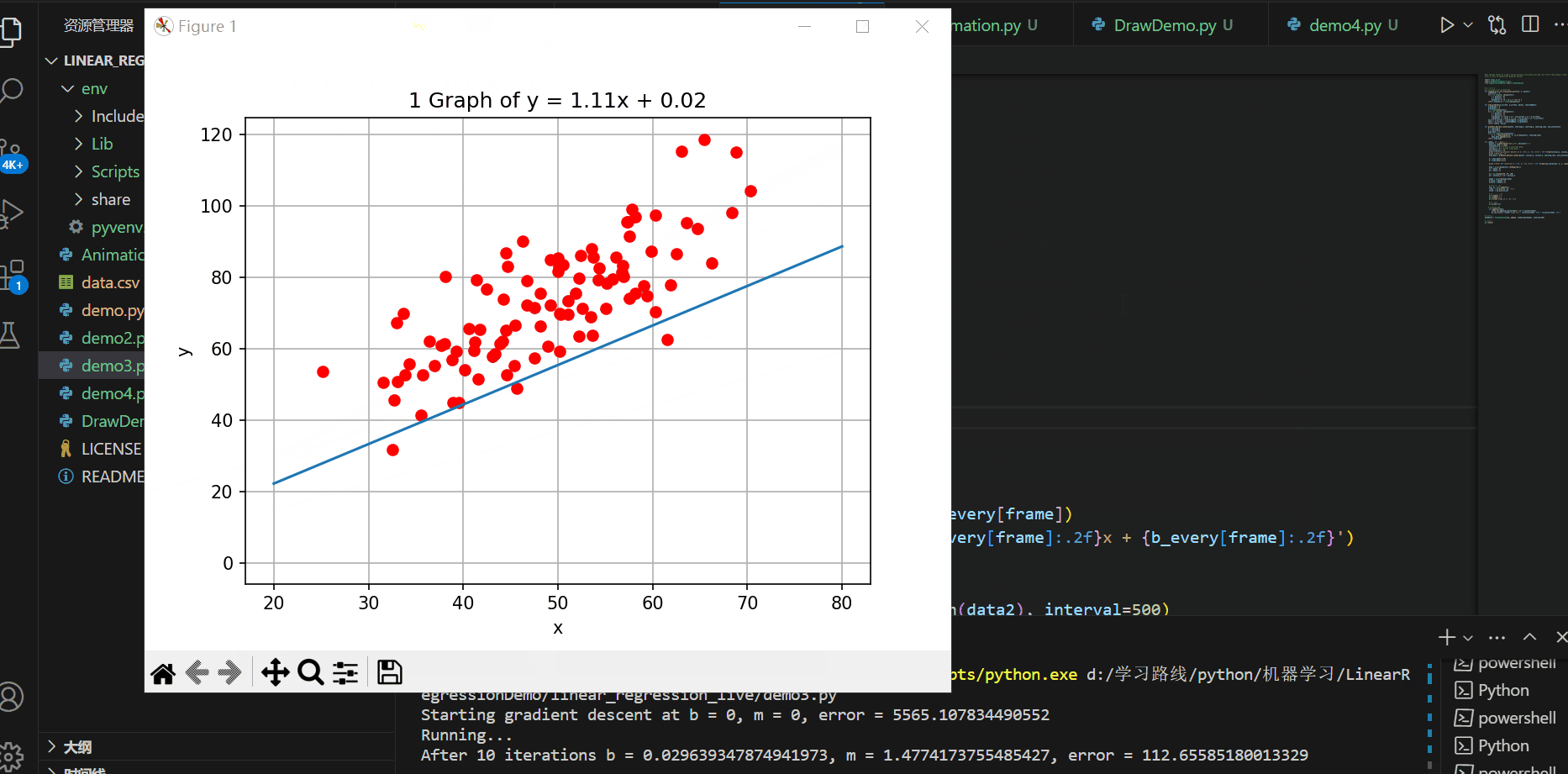
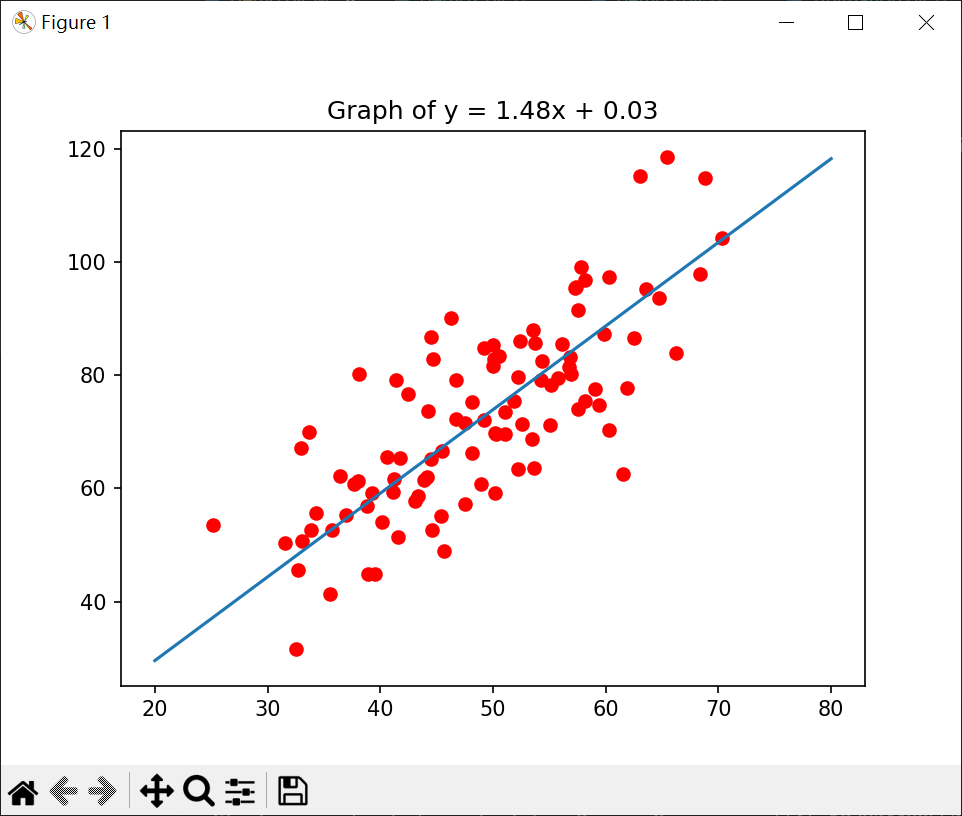
C#代码进行可视化
这是本文重点介绍的内容,本文的C#代码通过Scottplot进行可视化。
Scottplot简介
ScottPlot 是一个免费的开源绘图库,用于 .NET,可以轻松以交互方式显示大型数据集。
控制台程序可视化
首先我先介绍一下在控制台程序中进行可视化。
首先添加Scottplot包:
将上篇文章中的C#代码修改如下:
using NumSharp;namespace LinearRegressionDemo
{internal class Program{ static void Main(string[] args){ //创建double类型的列表List<double> Array = new List<double>();List<double> ArgsList = new List<double>();// 指定CSV文件的路径string filePath = "你的data.csv路径";// 调用ReadCsv方法读取CSV文件数据Array = ReadCsv(filePath);var array = np.array(Array).reshape(100,2);double learning_rate = 0.0001;double initial_b = 0;double initial_m = 0;double num_iterations = 10;Console.WriteLine($"Starting gradient descent at b = {initial_b}, m = {initial_m}, error = {compute_error_for_line_given_points(initial_b, initial_m, array)}");Console.WriteLine("Running...");ArgsList = gradient_descent_runner(array, initial_b, initial_m, learning_rate, num_iterations);double b = ArgsList[ArgsList.Count - 2];double m = ArgsList[ArgsList.Count - 1];Console.WriteLine($"After {num_iterations} iterations b = {b}, m = {m}, error = {compute_error_for_line_given_points(b, m, array)}");Console.ReadLine();var x1 = array[$":", 0];var y1 = array[$":", 1];var y2 = m * x1 + b;ScottPlot.Plot myPlot = new(400, 300);myPlot.AddScatterPoints(x1.ToArray<double>(), y1.ToArray<double>(), markerSize: 5);myPlot.AddScatter(x1.ToArray<double>(), y2.ToArray<double>(), markerSize: 0);myPlot.Title($"y = {m:0.00}x + {b:0.00}");myPlot.SaveFig("图片.png");}static List<double> ReadCsv(string filePath){List<double> array = new List<double>();try{// 使用File.ReadAllLines读取CSV文件的所有行string[] lines = File.ReadAllLines(filePath); // 遍历每一行数据foreach (string line in lines){// 使用逗号分隔符拆分每一行的数据string[] values = line.Split(',');// 打印每一行的数据foreach (string value in values){array.Add(Convert.ToDouble(value));} }}catch (Exception ex){Console.WriteLine("发生错误: " + ex.Message);}return array;}public static double compute_error_for_line_given_points(double b,double m,NDArray array){double totalError = 0;for(int i = 0;i < array.shape[0];i++){double x = array[i, 0];double y = array[i, 1];totalError += Math.Pow((y - (m*x+b)),2);}return totalError / array.shape[0];}public static double[] step_gradient(double b_current,double m_current,NDArray array,double learningRate){double[] args = new double[2];double b_gradient = 0;double m_gradient = 0;double N = array.shape[0];for (int i = 0; i < array.shape[0]; i++){double x = array[i, 0];double y = array[i, 1];b_gradient += -(2 / N) * (y - ((m_current * x) + b_current));m_gradient += -(2 / N) * x * (y - ((m_current * x) + b_current));}double new_b = b_current - (learningRate * b_gradient);double new_m = m_current - (learningRate * m_gradient);args[0] = new_b;args[1] = new_m;return args;}public static List<double> gradient_descent_runner(NDArray array, double starting_b, double starting_m, double learningRate,double num_iterations){double[] args = new double[2];List<double> argsList = new List<double>();args[0] = starting_b;args[1] = starting_m;for(int i = 0 ; i < num_iterations; i++) {args = step_gradient(args[0], args[1], array, learningRate);argsList.AddRange(args);}return argsList;}}
}然后得到的图片如下所示:
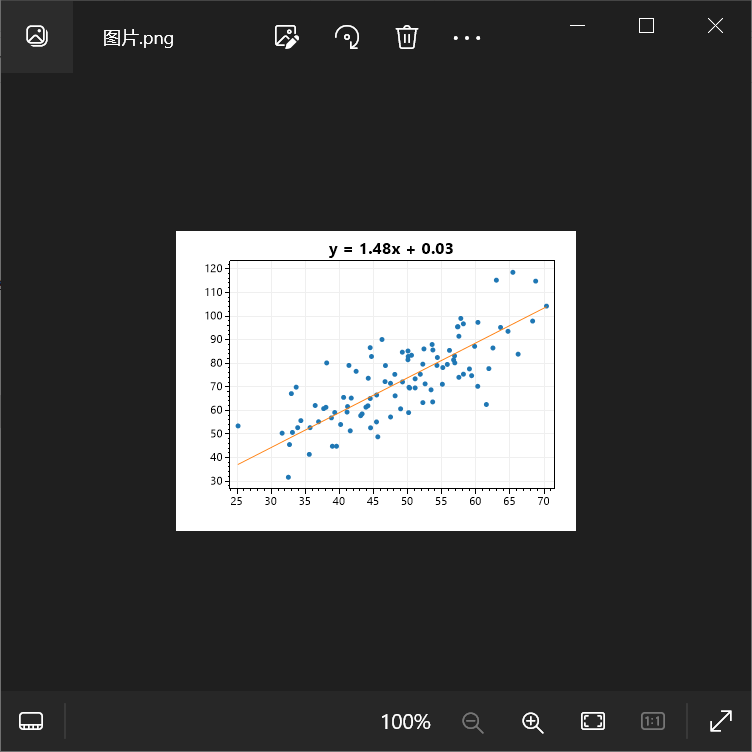
在以上代码中需要注意的地方:
var x1 = array[$":", 0];var y1 = array[$":", 1];
是在使用NumSharp中的切片,x1表示所有行的第一列,y1表示所有行的第二列。
当然我们不满足于只是保存图片,在控制台应用程序中,再添加一个 ScottPlot.WinForms包:
右键控制台项目选择属性,将目标OS改为Windows:
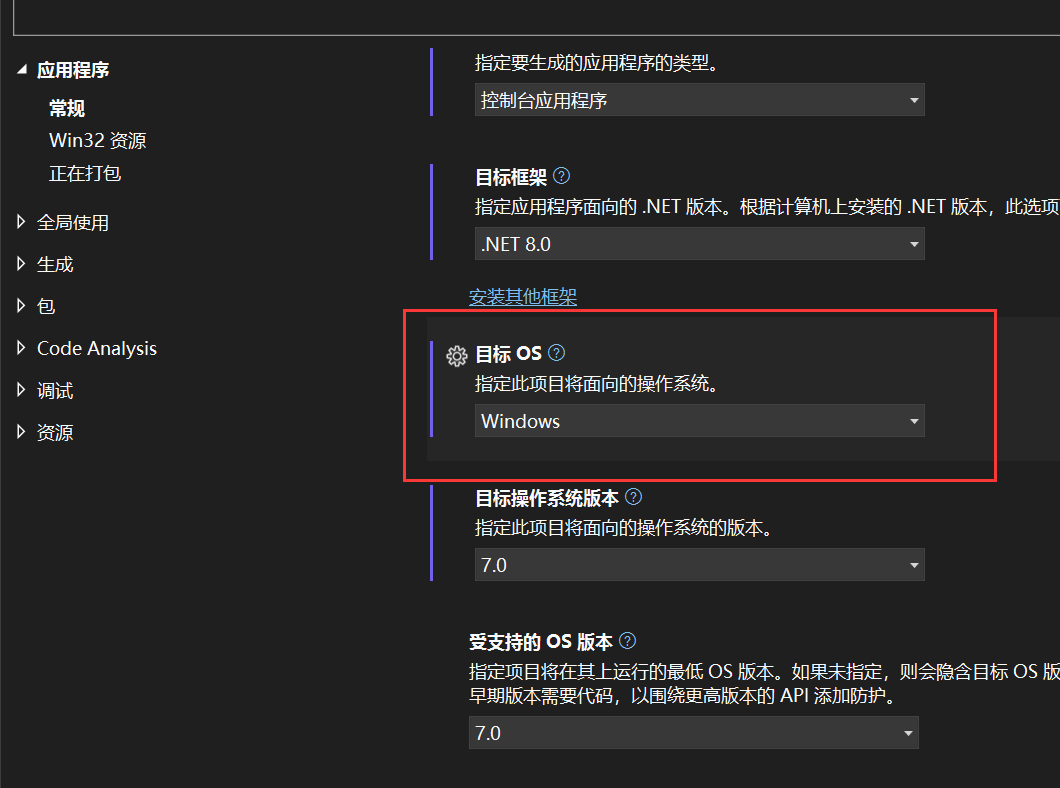
将上述代码中的
myPlot.SaveFig("图片.png");
修改为:
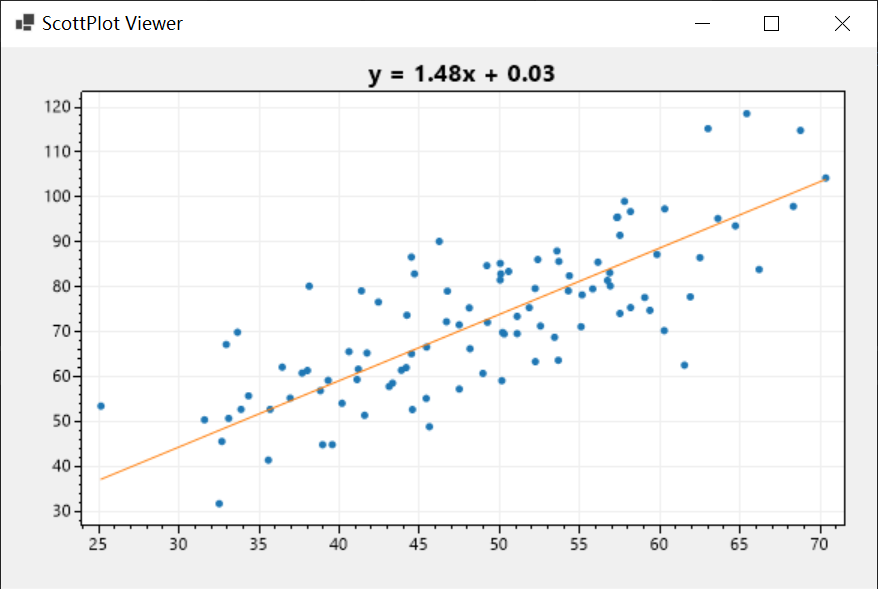
var viewer = new ScottPlot.FormsPlotViewer(myPlot);viewer.ShowDialog();
再次运行结果如下:
winform进行可视化
我也想像Python代码中那样画动图,因此做了个winform程序进行演示。
首先创建一个winform,添加ScottPlot.WinForms包,然后从工具箱中添加FormsPlot这个控件:
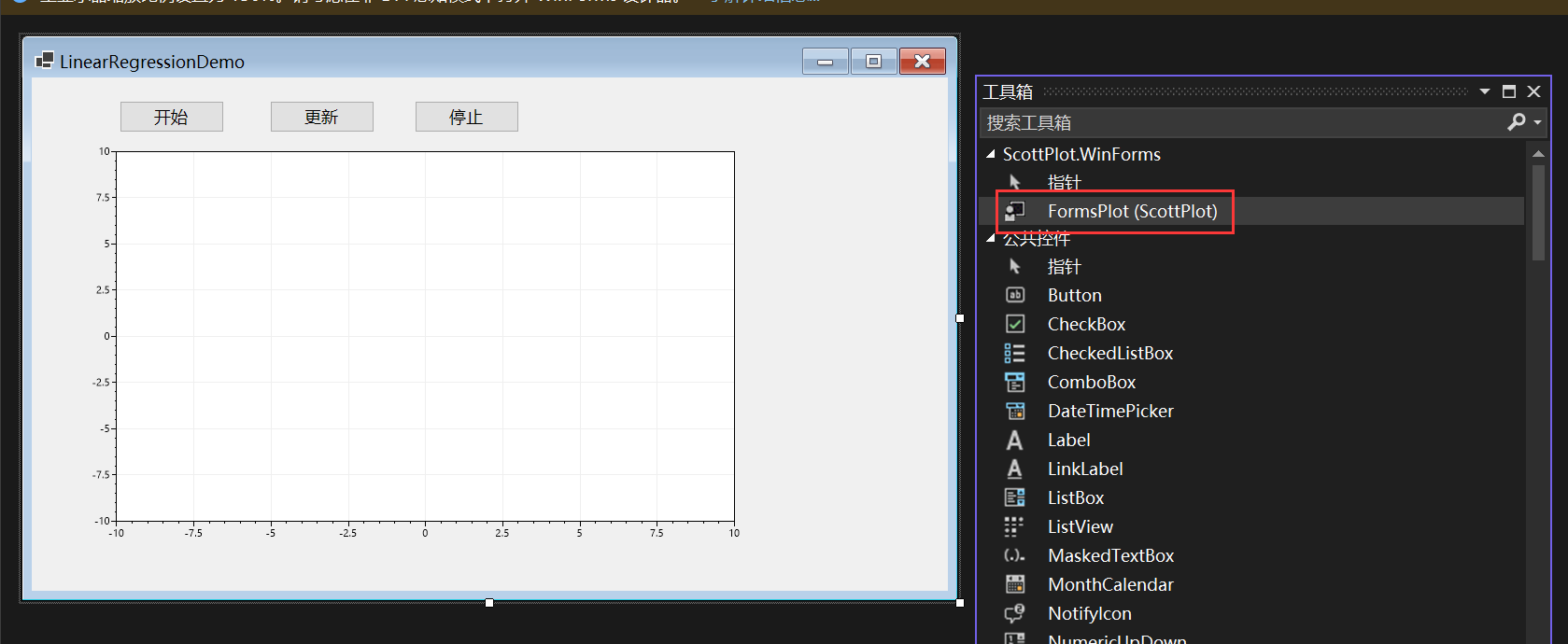
有两种方法实现,第一种方法用了定时器:
using NumSharp;
namespace WinFormDemo
{public partial class Form1 : Form{System.Windows.Forms.Timer updateTimer = new System.Windows.Forms.Timer();int num_iterations;int count = 0;NDArray? x1, y1, b_each, m_each;public Form1(){InitializeComponent();}private void button1_Click(object sender, EventArgs e){StartLinearRegression();}public void StartLinearRegression(){//创建double类型的列表List<double> Array = new List<double>();List<double> ArgsList = new List<double>();// 指定CSV文件的路径string filePath = "你的data.csv路径";// 调用ReadCsv方法读取CSV文件数据Array = ReadCsv(filePath);var array = np.array(Array).reshape(100, 2);double learning_rate = 0.0001;double initial_b = 0;double initial_m = 0;num_iterations = 10;ArgsList = gradient_descent_runner(array, initial_b, initial_m, learning_rate, num_iterations);x1 = array[$":", 0];y1 = array[$":", 1];var argsArr = np.array(ArgsList).reshape(num_iterations, 2);b_each = argsArr[$":", 0];m_each = argsArr[$":", 1];double b = b_each[-1];double m = m_each[-1];var y2 = m * x1 + b;formsPlot1.Plot.AddScatterPoints(x1.ToArray<double>(), y1.ToArray<double>(), markerSize: 5);//formsPlot1.Plot.AddScatter(x1.ToArray<double>(), y2.ToArray<double>(), markerSize: 0);formsPlot1.Render();}static List<double> ReadCsv(string filePath){List<double> array = new List<double>();try{// 使用File.ReadAllLines读取CSV文件的所有行string[] lines = File.ReadAllLines(filePath);// 遍历每一行数据foreach (string line in lines){// 使用逗号分隔符拆分每一行的数据string[] values = line.Split(',');// 打印每一行的数据foreach (string value in values){array.Add(Convert.ToDouble(value));}}}catch (Exception ex){Console.WriteLine("发生错误: " + ex.Message);}return array;}public static double compute_error_for_line_given_points(double b, double m, NDArray array){double totalError = 0;for (int i = 0; i < array.shape[0]; i++){double x = array[i, 0];double y = array[i, 1];totalError += Math.Pow((y - (m * x + b)), 2);}return totalError / array.shape[0];}public static double[] step_gradient(double b_current, double m_current, NDArray array, double learningRate){double[] args = new double[2];double b_gradient = 0;double m_gradient = 0;double N = array.shape[0];for (int i = 0; i < array.shape[0]; i++){double x = array[i, 0];double y = array[i, 1];b_gradient += -(2 / N) * (y - ((m_current * x) + b_current));m_gradient += -(2 / N) * x * (y - ((m_current * x) + b_current));}double new_b = b_current - (learningRate * b_gradient);double new_m = m_current - (learningRate * m_gradient);args[0] = new_b;args[1] = new_m;return args;}public static List<double> gradient_descent_runner(NDArray array, double starting_b, double starting_m, double learningRate, double num_iterations){double[] args = new double[2];List<double> argsList = new List<double>();args[0] = starting_b;args[1] = starting_m;for (int i = 0; i < num_iterations; i++){args = step_gradient(args[0], args[1], array, learningRate);argsList.AddRange(args);}return argsList;}private void button2_Click(object sender, EventArgs e){// 初始化定时器updateTimer.Interval = 1000; // 设置定时器触发间隔(毫秒)updateTimer.Tick += UpdateTimer_Tick;updateTimer.Start();}private void UpdateTimer_Tick(object? sender, EventArgs e){if (count >= num_iterations){updateTimer.Stop();}else{UpdatePlot(count);}count++;}public void UpdatePlot(int count){double b = b_each?[count];double m = m_each?[count];var y2 = m * x1 + b;formsPlot1.Plot.Clear();formsPlot1.Plot.AddScatterPoints(x1?.ToArray<double>(), y1?.ToArray<double>(), markerSize: 5);formsPlot1.Plot.AddScatter(x1?.ToArray<double>(), y2.ToArray<double>(), markerSize: 0);formsPlot1.Plot.Title($"第{count + 1}次迭代:y = {m:0.00}x + {b:0.00}");formsPlot1.Render();}private void button3_Click(object sender, EventArgs e){updateTimer.Stop();}private void Form1_Load(object sender, EventArgs e){}}
}简单介绍一下思路,首先创建List<double> argsList用来保存每次迭代生成的参数b、m,然后用
var argsArr = np.array(ArgsList).reshape(num_iterations, 2);
将argsList通过np.array()方法转化为NDArray,然后再调用reshape方法,转化成行数等于迭代次数,列数为2,即每一行对应一组参数值b、m。
b_each = argsArr[$":", 0];m_each = argsArr[$":", 1];
argsArr[$":", 0]表示每一行中第一列的值,也就是每一个b,argsArr[$":", 1]表示每一行中第二列的值。
double b = b_each[-1];double m = m_each[-1];
b_each[-1]用了NumSharp的功能表示b_each最后一个元素。
实现效果如下所示:
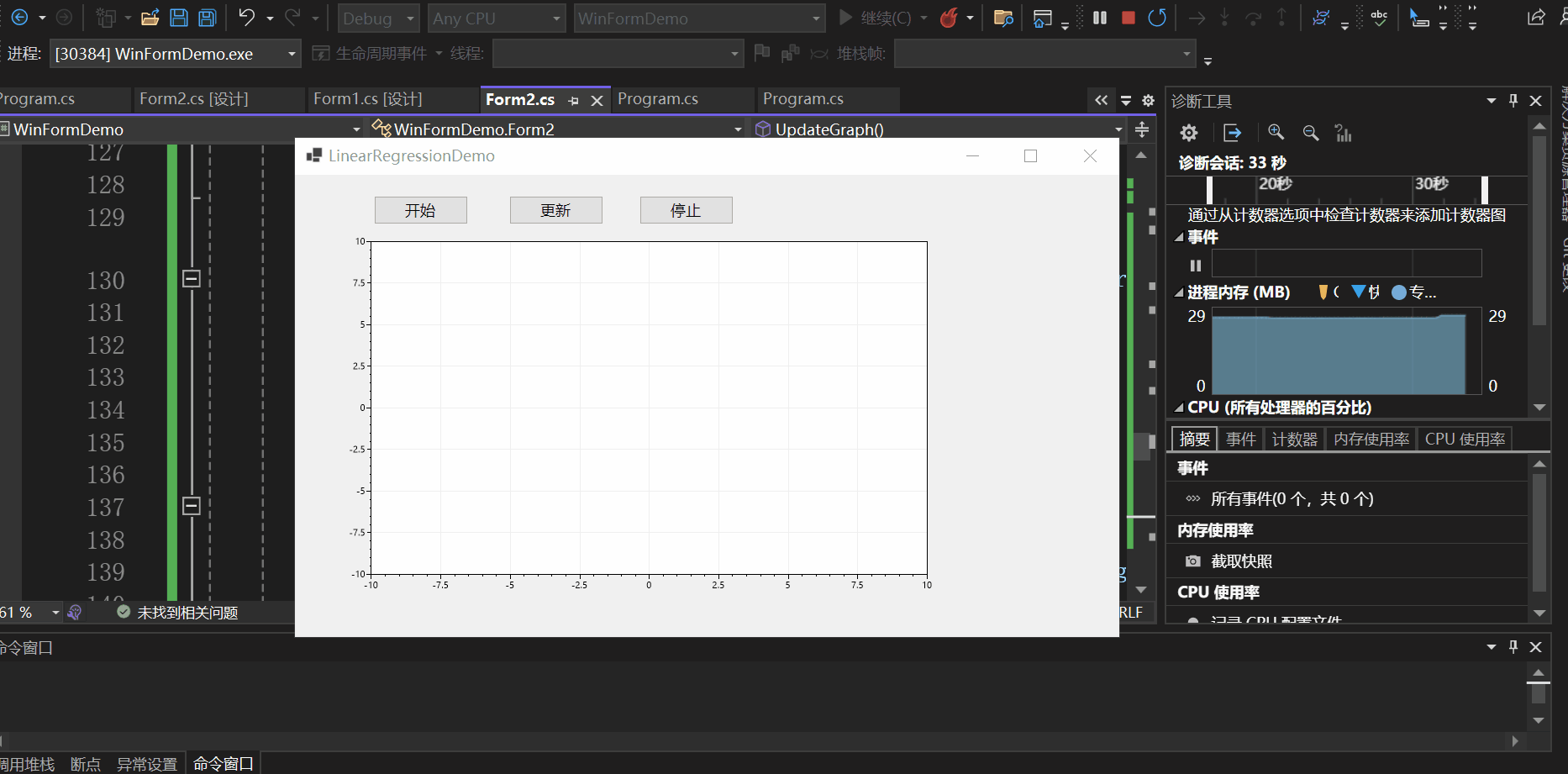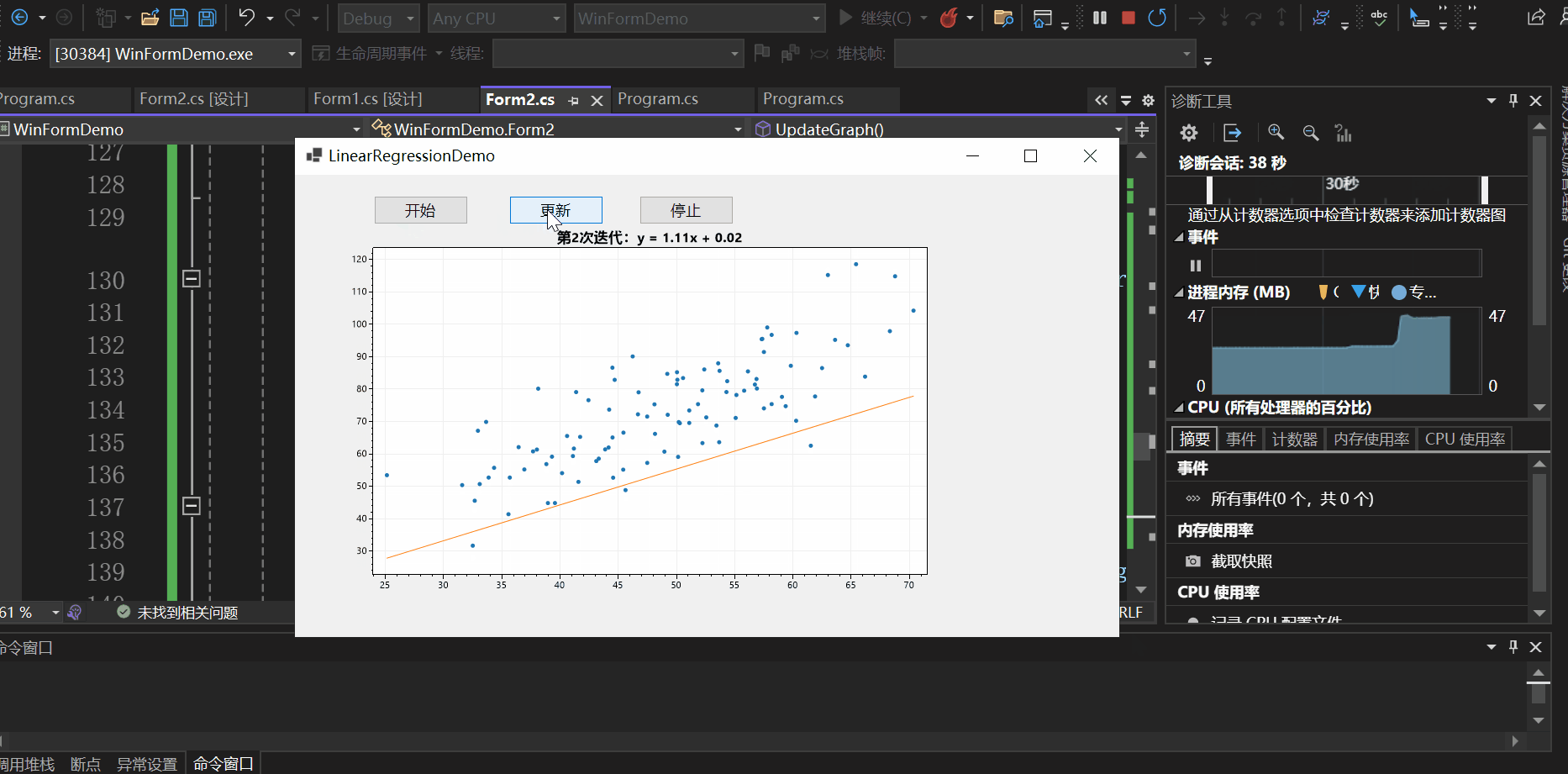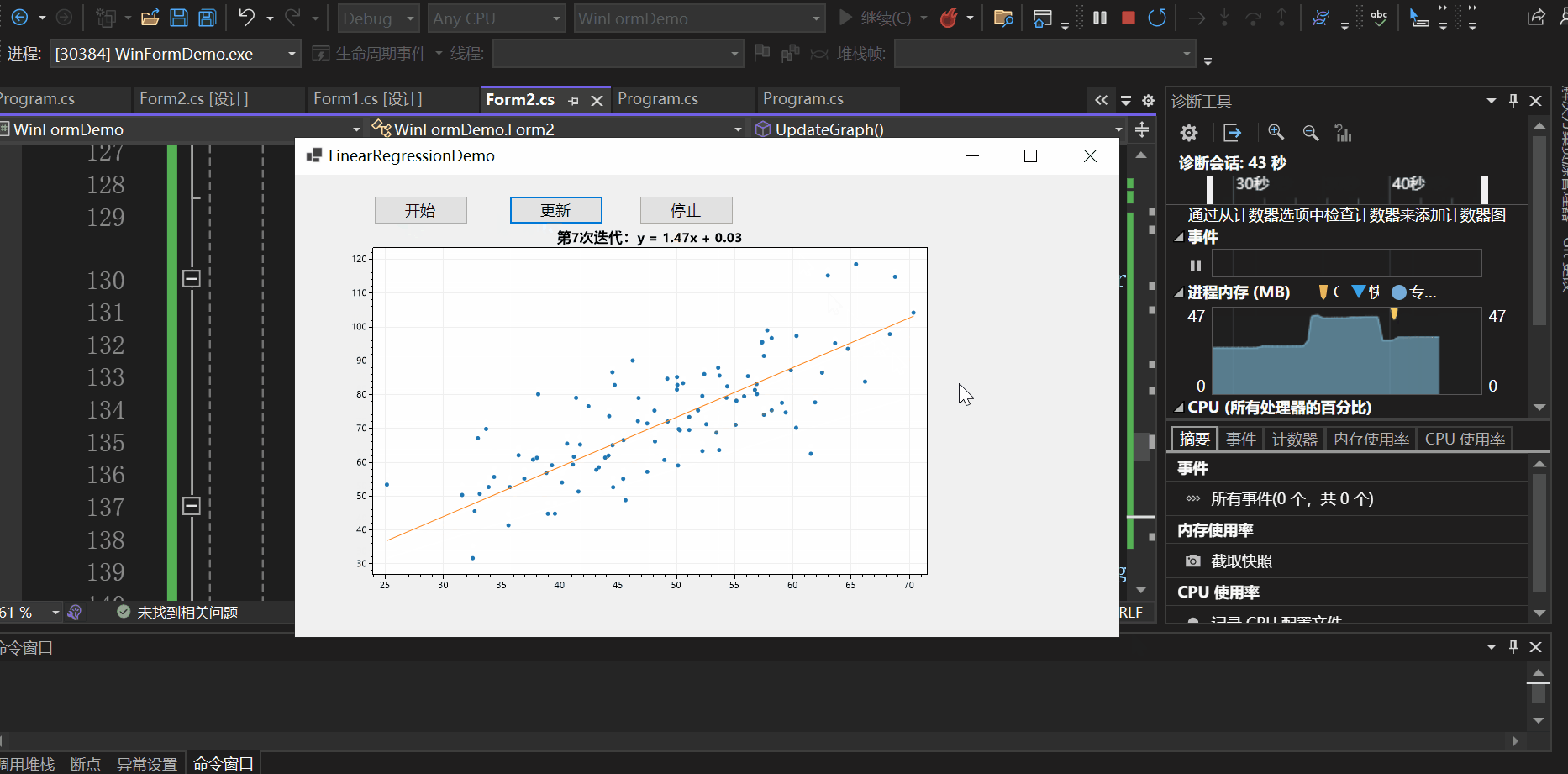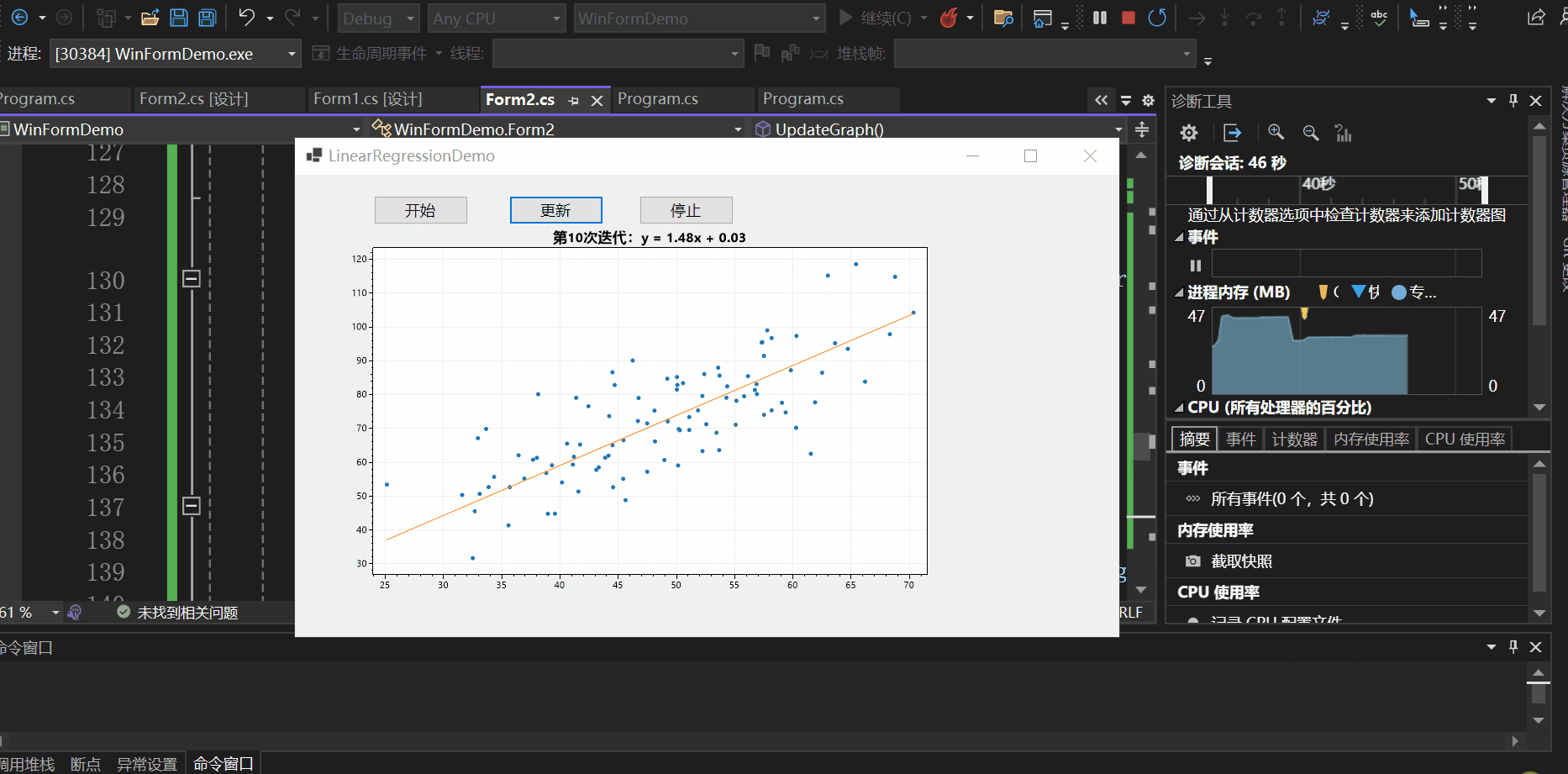

另一种方法可以通过异步实现:
using NumSharp;namespace WinFormDemo
{public partial class Form2 : Form{ int num_iterations;NDArray? x1, y1, b_each, m_each;public Form2(){InitializeComponent();}private void button1_Click(object sender, EventArgs e){StartLinearRegression();}public void StartLinearRegression(){//创建double类型的列表List<double> Array = new List<double>();List<double> ArgsList = new List<double>();// 指定CSV文件的路径string filePath = "你的data.csv路径";// 调用ReadCsv方法读取CSV文件数据Array = ReadCsv(filePath);var array = np.array(Array).reshape(100, 2);double learning_rate = 0.0001;double initial_b = 0;double initial_m = 0;num_iterations = 10;ArgsList = gradient_descent_runner(array, initial_b, initial_m, learning_rate, num_iterations);x1 = array[$":", 0];y1 = array[$":", 1];var argsArr = np.array(ArgsList).reshape(num_iterations, 2);b_each = argsArr[$":", 0];m_each = argsArr[$":", 1];double b = b_each[-1];double m = m_each[-1];var y2 = m * x1 + b;formsPlot1.Plot.AddScatterPoints(x1.ToArray<double>(), y1.ToArray<double>(), markerSize: 5); formsPlot1.Render();}static List<double> ReadCsv(string filePath){List<double> array = new List<double>();try{// 使用File.ReadAllLines读取CSV文件的所有行string[] lines = File.ReadAllLines(filePath);// 遍历每一行数据foreach (string line in lines){// 使用逗号分隔符拆分每一行的数据string[] values = line.Split(',');// 打印每一行的数据foreach (string value in values){array.Add(Convert.ToDouble(value));}}}catch (Exception ex){Console.WriteLine("发生错误: " + ex.Message);}return array;}public static double compute_error_for_line_given_points(double b, double m, NDArray array){double totalError = 0;for (int i = 0; i < array.shape[0]; i++){double x = array[i, 0];double y = array[i, 1];totalError += Math.Pow((y - (m * x + b)), 2);}return totalError / array.shape[0];}public static double[] step_gradient(double b_current, double m_current, NDArray array, double learningRate){double[] args = new double[2];double b_gradient = 0;double m_gradient = 0;double N = array.shape[0];for (int i = 0; i < array.shape[0]; i++){double x = array[i, 0];double y = array[i, 1];b_gradient += -(2 / N) * (y - ((m_current * x) + b_current));m_gradient += -(2 / N) * x * (y - ((m_current * x) + b_current));}double new_b = b_current - (learningRate * b_gradient);double new_m = m_current - (learningRate * m_gradient);args[0] = new_b;args[1] = new_m;return args;}public static List<double> gradient_descent_runner(NDArray array, double starting_b, double starting_m, double learningRate, double num_iterations){double[] args = new double[2];List<double> argsList = new List<double>();args[0] = starting_b;args[1] = starting_m;for (int i = 0; i < num_iterations; i++){args = step_gradient(args[0], args[1], array, learningRate);argsList.AddRange(args);}return argsList;}private void Form2_Load(object sender, EventArgs e){}public async Task UpdateGraph(){for (int i = 0; i < num_iterations; i++){double b = b_each?[i];double m = m_each?[i];var y2 = m * x1 + b;formsPlot1.Plot.Clear();formsPlot1.Plot.AddScatterPoints(x1?.ToArray<double>(), y1?.ToArray<double>(), markerSize: 5);formsPlot1.Plot.AddScatter(x1?.ToArray<double>(), y2.ToArray<double>(), markerSize: 0);formsPlot1.Plot.Title($"第{i + 1}次迭代:y = {m:0.00}x + {b:0.00}");formsPlot1.Render();await Task.Delay(1000);}}private async void button2_Click(object sender, EventArgs e){await UpdateGraph();}}
}点击更新按钮开始执行异步任务:
private async void button2_Click(object sender, EventArgs e){await UpdateGraph();}
public async Task UpdateGraph(){for (int i = 0; i < num_iterations; i++){double b = b_each?[i];double m = m_each?[i];var y2 = m * x1 + b;formsPlot1.Plot.Clear();formsPlot1.Plot.AddScatterPoints(x1?.ToArray<double>(), y1?.ToArray<double>(), markerSize: 5);formsPlot1.Plot.AddScatter(x1?.ToArray<double>(), y2.ToArray<double>(), markerSize: 0);formsPlot1.Plot.Title($"第{i + 1}次迭代:y = {m:0.00}x + {b:0.00}");formsPlot1.Render();await Task.Delay(1000);}
实现效果如下:
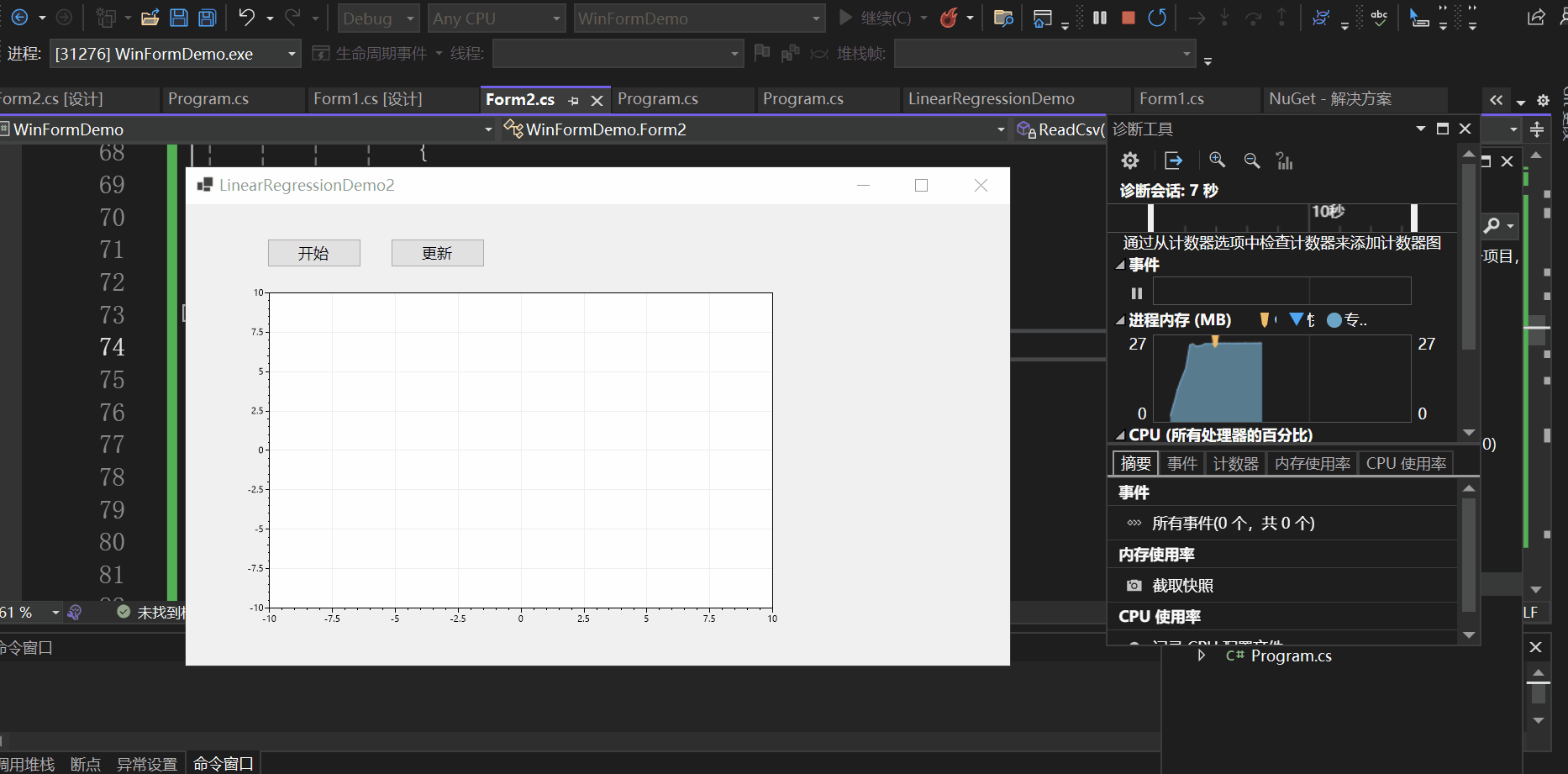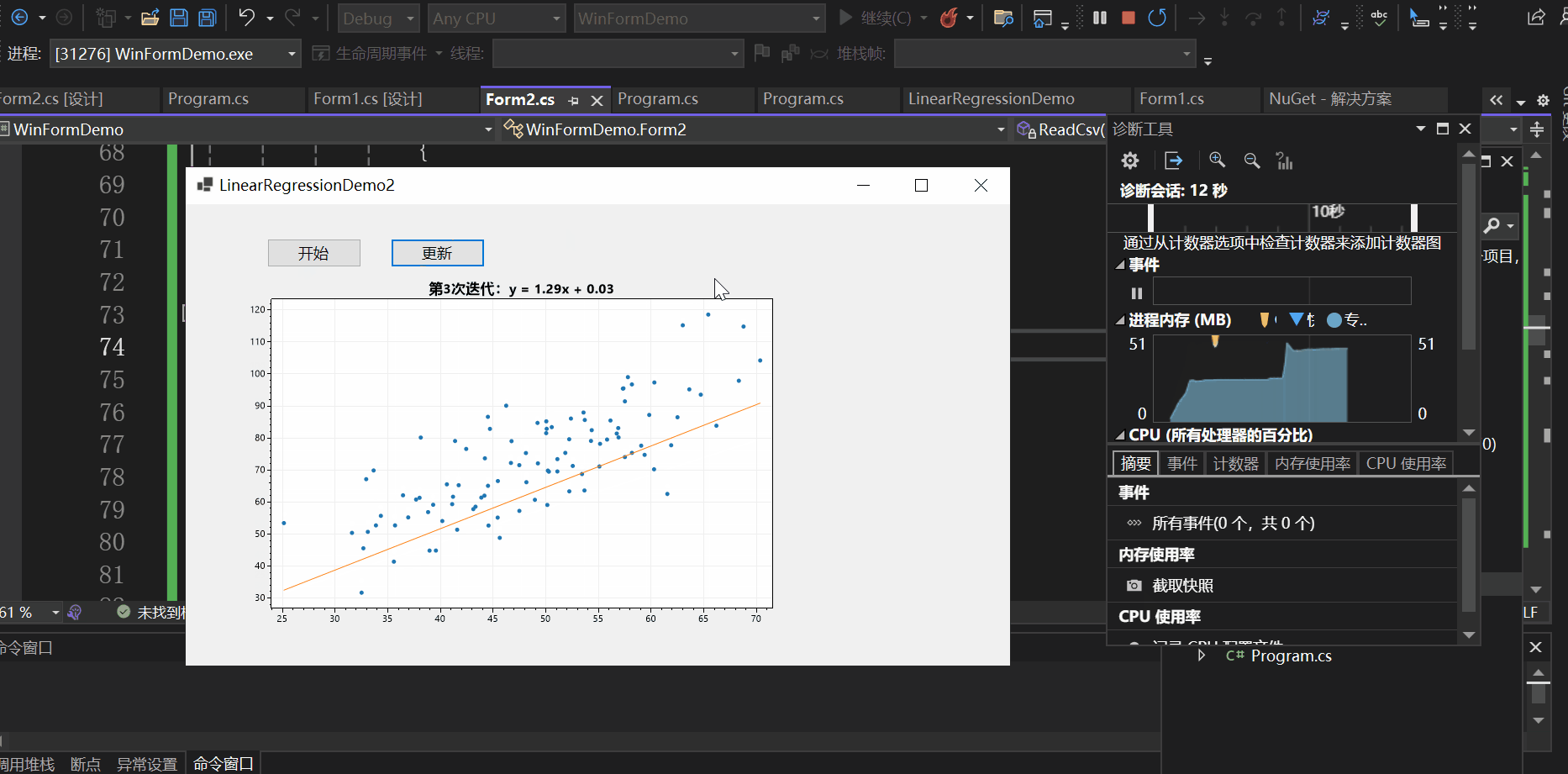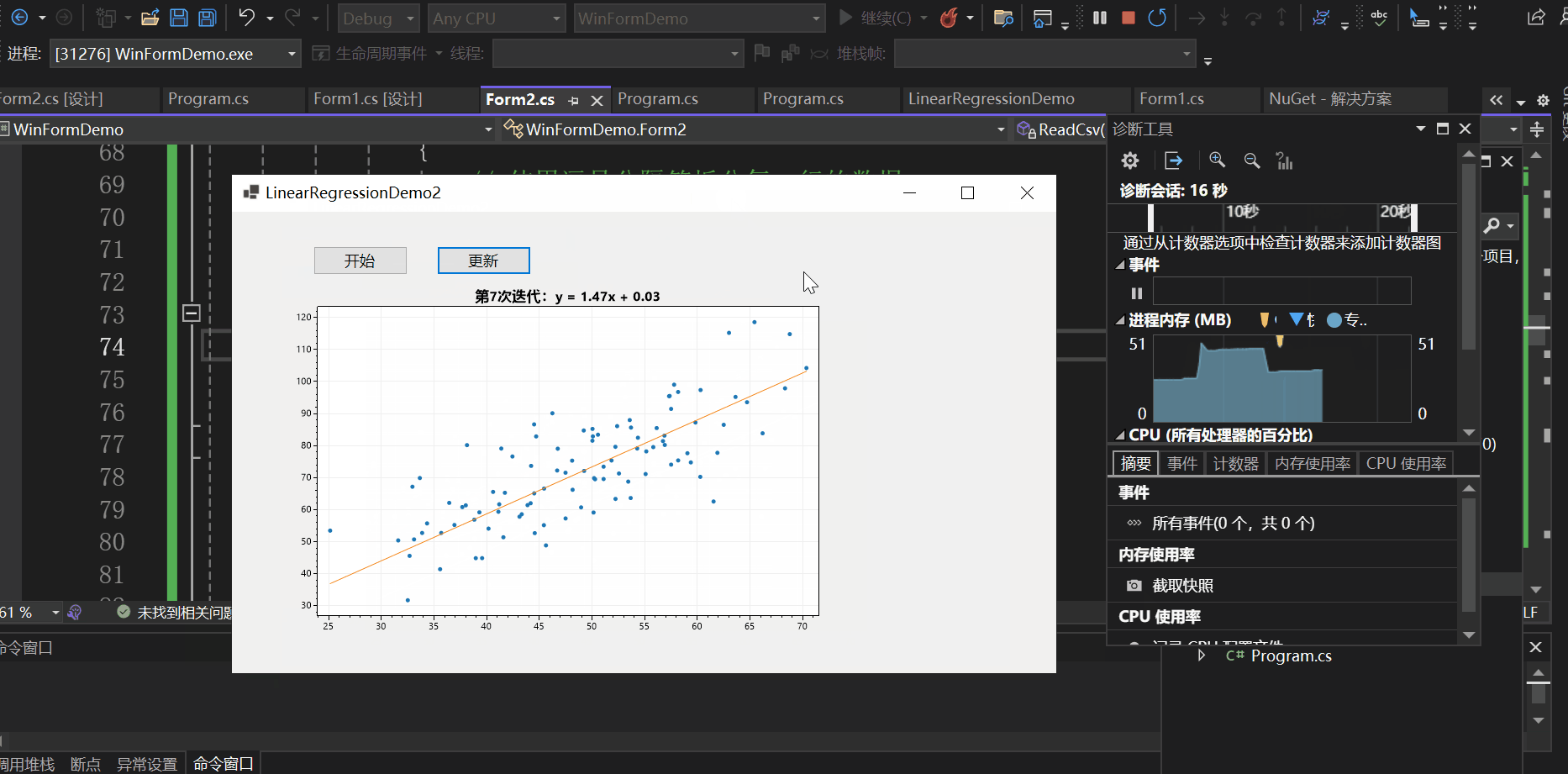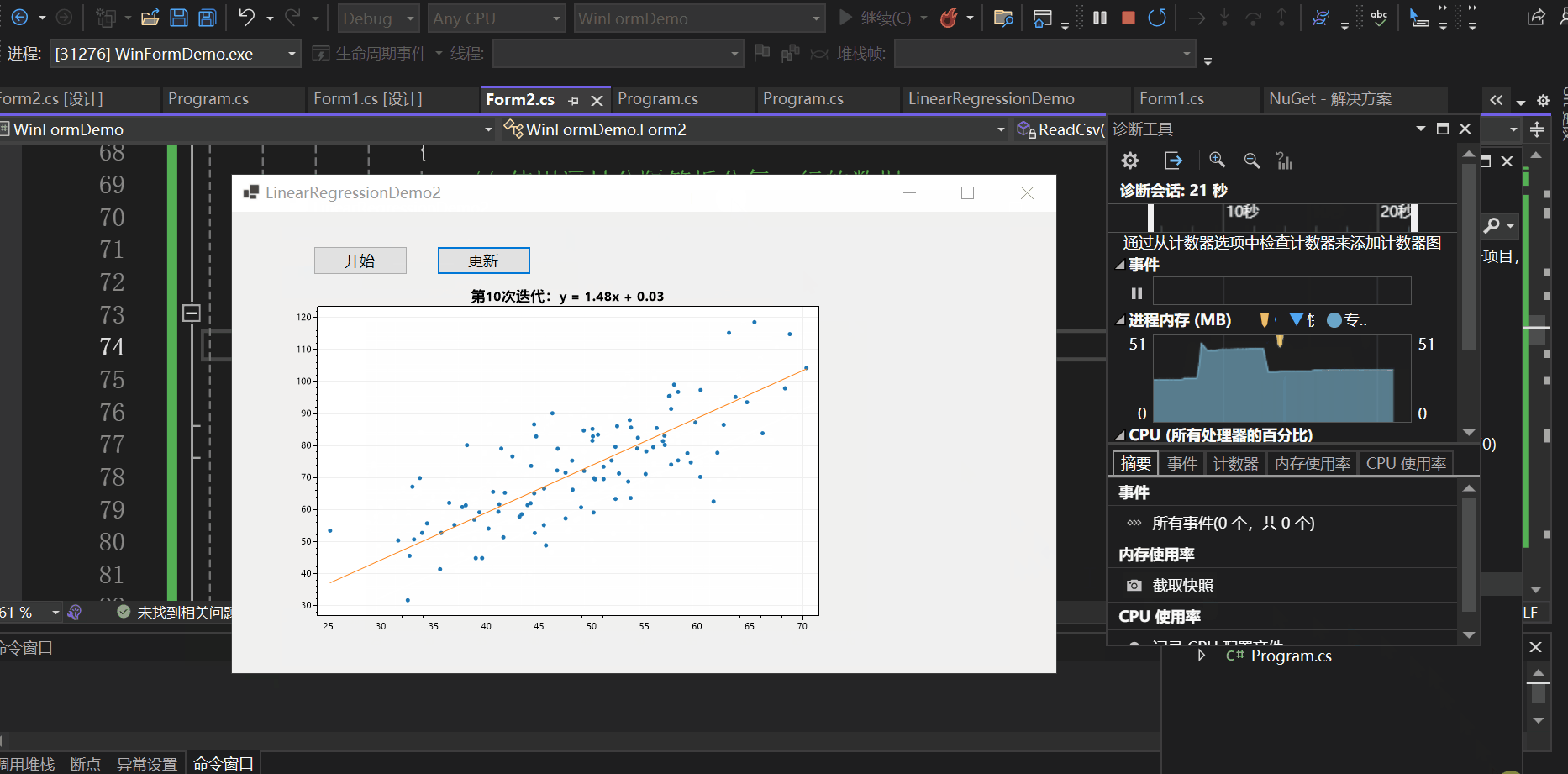
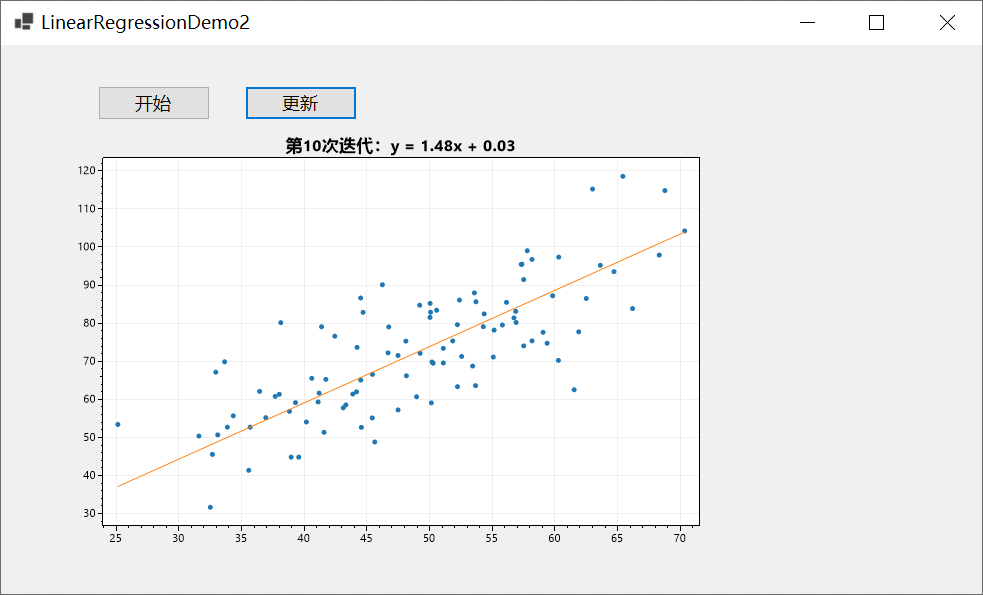
总结
本文以一个控制台应用与一个winform程序为例向大家介绍了C#如何基于ScottPlot进行数据可视化,并介绍了实现动态绘图的两种方式,一种是使用定时器,另一种是使用异步操作,希望对你有所帮助。



)

QT概述)

)

)
)







分析)
)