目录
一、前言
二、AOP—快速入门
1.动态代理优化 :
2.问题分析 :
3.AOP—基本介绍 :
4.AOP—使用说明 :
5.AOP—入门案例 :
三、AOP—切入点表达式
1.基本说明 :
2.语法格式 :
3.注意事项 :
4.代码演示 :
四、AOP—切入点表达式的更多细节
1.JoinPoint :
1.1 简介
1.2 方法
1.3 演示
2.通知进阶 :
2.1 通过@AfterReturning获取方法的返回结果
2.2 通过@AfterThrowing获取异常信息
2.3 环绕通知
3.切入点表达式重用(@Pointcut) :
3.1 简介
3.2 实例
4.切面类执行顺序 :
4.1 简介
4.2 实例
5.基于XML配置AOP :
五、总结
一、前言
- 第五节内容,up主要和大家分享一下Spring AOP方面的内容;包括通知类型,切入表达式 和 基于XML配置AOP。
- 注意事项——①代码中的注释也很重要;②不要眼高手低,自己跟着敲一遍才真正有收获;③点击文章的侧边栏目录或者文章开头的目录可以进行跳转。
- 良工不示人以朴,up所有文章都会适时补充完善。大家如果有问题都可以在评论区进行交流或者私信up。感谢阅读!
二、AOP—快速入门
1.动态代理优化 :
“书接上回”,在动态代理一文最后,我们提出一个问题——假如将匿名内部类实现的invoke方法中的输出语句,都替换成方法,用一个方法直接切入,那不就既满足灵活性,又可以实现强大的功能吗?
那现在我们就来尝试一个简单的案例,我们自己定义一个简单的AOP类,并在该类中定义用于切入的静态方法(这么做可以达到降低耦合度的目的,而不是直接把方法定义在提供代理对象的类中);up以CyanAOP类为例,CyanAOP类代码如下 :
package com.cyan.spring.aop;import java.lang.reflect.Method;
import java.time.LocalDateTime;public class CyanAOP {//1. beforeNotice静态方法用于完成前置通知public static void beforeNotice(Method method, Object[] args) {//获取到当前传入的参数double n1 = (double) args[0];double n2 = (double) args[1];//获取当前方法名String name = method.getName();//Δ在运算方法执行前打印出运算日志System.out.println("运算日志————运算法则 = " + name + ",传入两个参数分别是 " + n1 + " 和 " + n2);}//2. returnNotice静态方法用于完成返回通知public static void returnNotice(Method method, Object result) {//获取当前方法名String name = method.getName();//Δ在运算方法执行后打印出运算日志System.out.println("运算日志————运算法则 = " + name + ",运算结果 = " + result);}//3.exceptionNotice静态方法用于完成异常通知public static void exceptionNotice(Method method) {System.out.println("异常日志————" + LocalDateTime.now() + ",方法" + method.getName() + "执行异常");}//4.afterNotice静态方法用于完成后置通知public static void afterNotice(Method method) {System.out.println("执行日志————" + method.getName() + "方法执行结束。");}
}
接着,在CalculatorProxyProvider类中调用CyanAOP类中的静态方法,取代原有的输出语句;
CalculatorProxyProvider类代码如下 :
package com.cyan.spring.aop;import java.lang.reflect.InvocationHandler;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
import java.lang.reflect.Proxy;public class CalculatorProxyProvider {private Calculator calculator;public CalculatorProxyProvider(Calculator calculator) {this.calculator = calculator;}/*底层仍然使用java.lang.reflect包下的Proxy类的newProxyInstance方法来获取代理对象。*/public Calculator getCalculatorProxy() {//1.获取newProxyInstance方法的第一个参数————类加载器ClassLoader classLoader = calculator.getClass().getClassLoader();//2.获取newProxyInstance方法的第二个参数————接口信息Class<?>[] interfaces = calculator.getClass().getInterfaces();//3.获取newProxyInstance方法的第三个参数————处理器对象//仍然借助匿名内部类来实现,并通过构造接口多态的形式做接收。InvocationHandler invocationHandler = new InvocationHandler() {@Overridepublic Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {//定义运算结果double result = 0.0;try {//Δ调用CyanAOP中的静态方法,实现前置通知CyanAOP.beforeNotice(method, args);//执行运算result = (double) method.invoke(calculator, args);System.out.println("result = " + result);//Δ调用CyanAOP中的静态方法,实现返回通知CyanAOP.returnNotice(method, result);//返回运算结果return result;} catch (Exception e) {//Δ调用CyanAOP中的静态方法,实现异常通知CyanAOP.exceptionNotice(method);throw new RuntimeException(e);} finally {//Δ调用CyanAOP中的静态方法,实现后置通知CyanAOP.afterNotice(method);}}};//4.调用newProxyInstance方法,得到代理对象Calculator instance = (Calculator) Proxy.newProxyInstance(classLoader, interfaces, invocationHandler);//5.返回获得的代理对象return instance;}
}
然后,在测试类中运行单元测试方法,测试动态代理是否生效,测试类TestCalculator代码如下 :
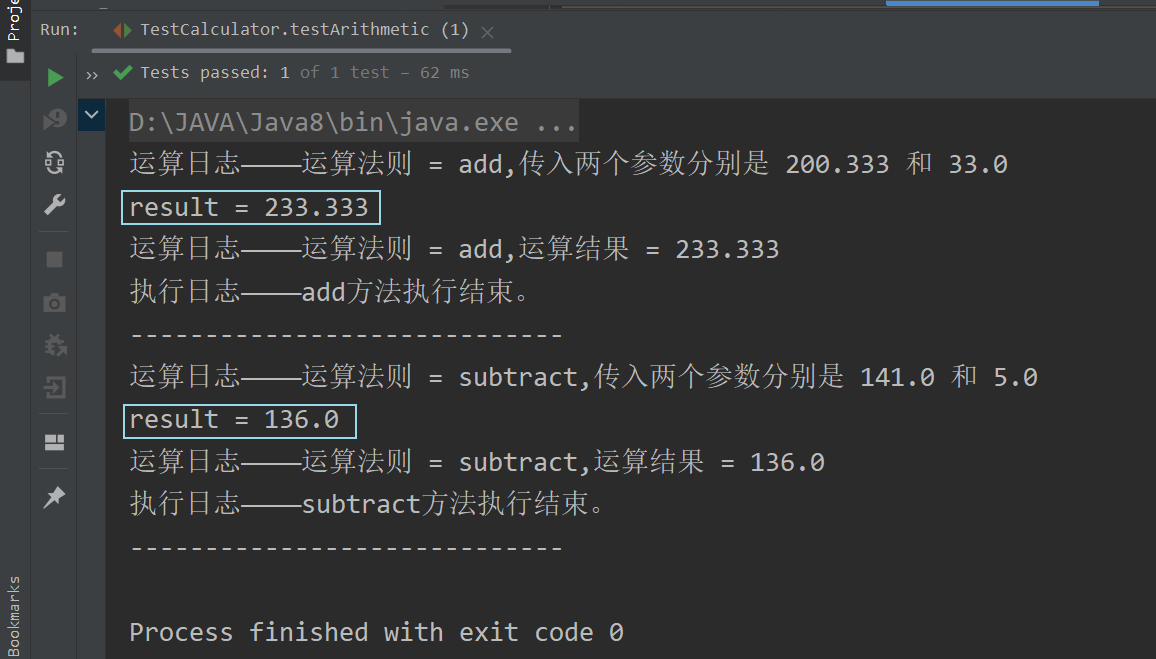
package com.cyan.spring.aop;import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;public class TestCalculator {@Testpublic void testArithmetic() {//1.构造接口多态Calculator calculator = new Calculator_Demo1();//2.传入需要被代理的对象CalculatorProxyProvider calculatorProxyProvider = new CalculatorProxyProvider(calculator);//3.获取代理对象Calculator calculatorProxy = calculatorProxyProvider.getCalculatorProxy();//4.通过代理对象调用实现类方法double addResult = calculatorProxy.add(200.333, 33);System.out.println("-----------------------------");double subtractResult = calculatorProxy.subtract(141, 5);System.out.println("-----------------------------");//double multiplyResult = calculatorProxy.multiply(11.11, 2);//System.out.println("-----------------------------");//double divideResult = calculatorProxy.divide(3917.0, 500.00);}
}
运行结果 :
2.问题分析 :
上文中我们通过自定义简单的AOP类,成功用较为灵活的“方法” 替换了 非常死板的“输出语句”。但是,新的问题出现了—— 这种改进方式依然不够灵活,功能依然弱鸡,并且复用性也比较差。
新的问题体现在哪里呢?
(1) 当前方案下,比如我们在测试类中调用了add方法和subtract方法,这俩个方法都受到了CyanAOP类中的静态方法的影响,但是,假如我们此时仅希望针对于add方法的控制,显然当前方案是做不到的。即,我们无法针对于某个或某些指定的方法进行控制,不够灵活。
(2) 当前方案下,CyanAOP类中定义的静态方法只是适用于Calculator接口和它的实现类;假如up此时又定义了其他的接口,那么CyanAOP类中定义的静态方法便无法满足新的需求。即,我们无法对于其他接口及其实现类进行切入控制,代码复用性差。
(3) 我们要明白,之所以存在以上问题,是由于当前方案缺少 “注解 + 反射机制” 的支持。
3.AOP—基本介绍 :
AOP : Aspect Oriented Programming,即面向切面编程。
我们知道,在传统的OOP中,某个类所定义的成员方法,只能被该类对象或该类的子类对象所调用;即我们先通过new关键字创建一个对象,亦可构成多态,然后通过 "对象." 的形式来调用类中的方法。
但是在AOP,我们是通过 “动态代理 + 反射” 的形式来调用类中的方法,那么类中的方法在执行过程中会被分为多个横切关注点,包括前置通知,返回通知,异常通知,后置通知。我们可以定义切面类,切面类中定义了用于切入的方法,通过注解配置,这些方法可以切入到任意支持AOP的类的任意方法的横切关注点。如下图所示 :

4.AOP—使用说明 :
(1) 要想使用Spring 的AOP注解,需要导入以下几个jar包,如下图所示 :
此外,需要引入核心aspects.jar包,如下图所示 : (在Spring安装目录的libs目录下可以找到)
(2) 常用的用于声明通知方法的五大注解如下——
1> @Before : 前置通知;
2> @AfterReturning : 返回通知;
3> @AfterThrowing : 异常通知;
4> @After : 后置通知;
5> @Around : 环绕通知[可以将四个通知合并管理];
官方文档的解释如下 : (Spring Framework 6.1.2)
5.AOP—入门案例 :
需求 : 定义切面类CalculatorAspect,并在切面类中定义两个方法,利用通知注解, 将这两个方法分别切入到Calculator_Demo1类的add方法执行之前 和 执行之后,即分别作为前置通知 和 返回通知。PS : 需要在xml配置文件中配置注解扫描。
up先在aop.aspectJ包下拷贝/创建 这么几个类,如下图所示 :

Calculator接口代码如下 :
package com.cyan.spring.aop.aspectJ;/*** @author : Cyan_RA9* @version : 21.0*/
public interface Calculator {public abstract double add(double n1, double n2);public abstract double subtract(double n1, double n2);public abstract double multiply(double n1, double n2);public abstract double divide(double n1, double n2);
}
Calculator_Demo1类代码如下 :
package com.cyan.spring.aop.aspectJ;import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;@Component(value = "calculator01")
public class Calculator_Demo1 implements Calculator {@Overridepublic double add(double n1, double n2) {double result = n1 + n2;System.out.println("result = " + result);return result;}@Overridepublic double subtract(double n1, double n2) {double result = n1 - n2;System.out.println("result = " + result);return result;}@Overridepublic double multiply(double n1, double n2) {double result = n1 * n2;System.out.println("result = " + result);return result;}@Overridepublic double divide(double n1, double n2) {double result = -1;if (n2 != 0) { //分母不允许为0result = n1 / n2;}System.out.println("result = " + result);return result;}
}
切面类CalculatorAspect代码如下 : (注意看代码注释)
package com.cyan.spring.aop.aspectJ;import org.aspectj.lang.JoinPoint;
import org.aspectj.lang.Signature;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.After;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.AfterReturning;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Aspect;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Before;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;/*** 切面类 : CalculatorAspect*/
@Aspect //Aspect注解提供了底层切面编程的支撑
@Component //Component注解表示该类是一个组件
public class CalculatorAspect {/*(1) 通过配置@Before注解,将beforeAdvice方法切入到Calculator_Demo1的add方法执行之前,作为前置通知。(2) value = "execution(access_modifier return_type 全类名.方法名(形参声明))",表示将该方法切入到指定类的指定方法(注意方法重载)。(3) beforeAdvice方法即实际起作用的切入方法,其方法名不是唯一的,可以自行定义。(4) 切入方法的形参是JointPoint类对象,是AspectJ 切面框架在底层将相关参数打包成JointPoint传入的。(5) 此时的切面类相当于一个功能更加强大的CalculatorProxyProvider类。*/@Before(value = "execution(public double com.cyan.spring.aop.aspectJ.Calculator_Demo1.add(double, double))")public void beforeAdvice(JoinPoint joinPoint) {//1.通过连接点对象,得到方法参数Object[] args = joinPoint.getArgs();double n1 = (double) args[0];double n2 = (double) args[1];//2.通过连接点对象,得到方法签名对象Signature signature = joinPoint.getSignature();//3.通过方法签名对象,获取到方法名String name = signature.getName();//Δ在运算方法执行前打印出运算日志System.out.println("运算日志————运算法则 = " + name + ",传入两个参数分别是 " + n1 + " 和 " + n2);}//returnAdvice方法,作为返回通知@AfterReturning(value = "execution(public double com.cyan.spring.aop.aspectJ.Calculator_Demo1.add(double, double))")public void returnAdvice(JoinPoint joinPoint) {//通过连接点对象,得到方法签名对象Signature signature = joinPoint.getSignature();//通过方法签名对象,获取到方法名String name = signature.getName();//获得方法参数Object[] args = joinPoint.getArgs();double result = (double) args[0] + (double) args[1];//Δ在运算方法执行后打印出运算日志System.out.println("运算日志————运算法则 = " + name + ",运算结果 = " + result);}//afterAdvice方法,作为后置通知@After(value = "execution(public double com.cyan.spring.aop.aspectJ.Calculator_Demo1.add(double, double))")public void afterAdvice(JoinPoint joinPoint) {//通过连接点对象,得到方法签名对象Signature signature = joinPoint.getSignature();//通过方法签名对象,获取到方法名String name = signature.getName();//Δ在运算方法最终执行完毕后打印出执行日志System.out.println("执行日志————" + name + "方法执行结束。");}
}
为了获取到bean对象,我们需要在xml配置文件中配置基于注解的组件扫描。up以beans_aop.xml类为例,代码如下 :
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop"xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/context https://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop https://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop.xsd"><!-- 配置自动扫描 --><context:component-scan base-package="com.cyan.spring.aop.aspectJ"/><!-- 开启基于注解的AOP功能,若不开启,不能实现切入[动态代理 + 反射调用] --><aop:aspectj-autoproxy/>
</beans>接着,我们仍在该包下定义一个测试类TestAspectJ,测试切面类中的方法是否成功切入到指定位置,TestAspectJ类代码如下 :
package com.cyan.spring.aop.aspectJ;import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;/*** @author : Cyan_RA9* @version : 21.0*/
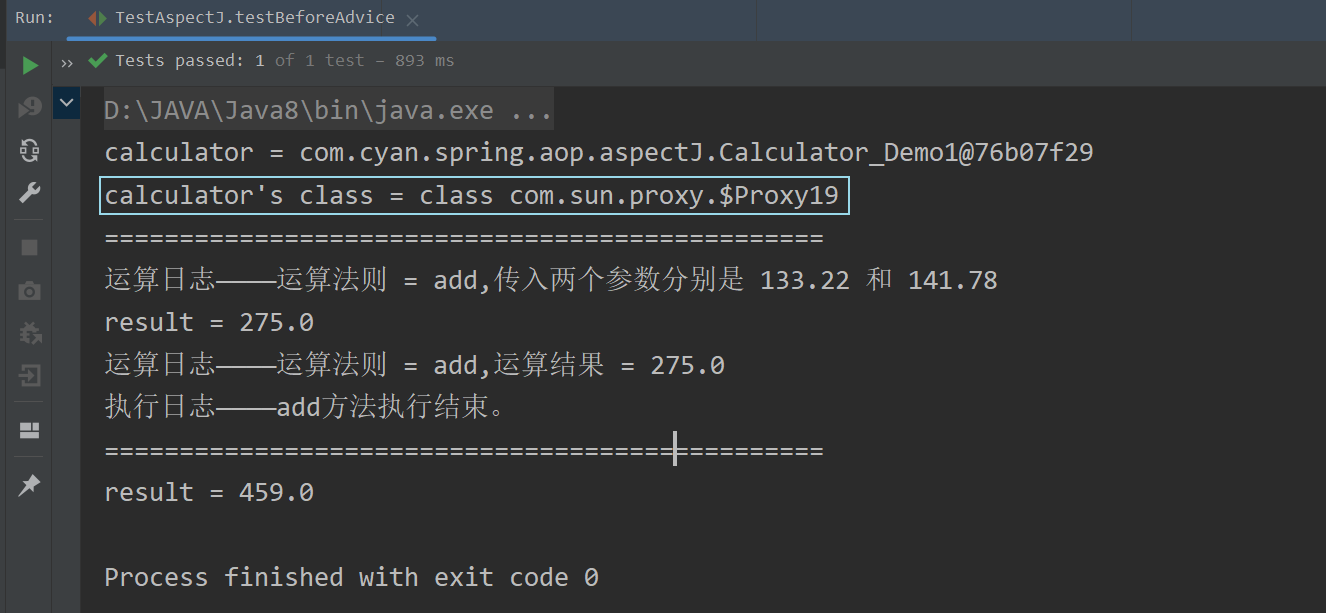
public class TestAspectJ {@Testpublic void testBeforeAdvice() {//1.获取IOC容器对象ApplicationContext ioc = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("beans_aop.xml");//2.通过接口类型来获取bean对象(实际获得的是代理对象,因此不能用实现类作为接收)//亦可以通过id来获取代理对象,同样需要使用接口类型来作接收Calculator calculator = ioc.getBean(Calculator.class);System.out.println("calculator = " + calculator);System.out.println("calculator's class = " + calculator.getClass());System.out.println("================================================");//3.通过得到的代理对象执行实现类中的方法calculator.add(133.22, 141.78);System.out.println("================================================");//4.调用其他方法,不会触发通知calculator.subtract(500, 41);}
}
运行结果 :
三、AOP—切入点表达式
1.基本说明 :
实际上,我们在上文 “AOP—入门案例” 中所用到的 “execution(public double com.cyan.spring.aop.aspectJ.Calculator_Demo1.add(double, double))” 就是一个切入点表达式。
其作用是——通过表达式的方式定位一个或多个具体的的连接点。
2.语法格式 :
(1) "execution(access_modifier return_type 全类名 方法名(形参列表))"
(2) Spring AOP的切入点表达式非常灵活,支持模糊配置。
eg1 : execution(* 全类名.*(..))——第一个 "*" 表示支持任意修饰符及返回值类型;第二个 "*" 表示支持该类中的任意方法;形参列表中的".."则表示可以匹配任意数量和类型的参数。(PS : 若目标类、接口与当前切面类在同一个包下,可以省略包名,只写类名)
eg2 : execution(public * 全类名.*(..))——表示支持该类中的所有公有的方法
eg3 : execution(public double 全类名.*(..))——表示支持该类中所有公有的且返回值为double的方法
eg4 : execution(public double 全类名.*(double, ..))——表示支持该类中所有形参列表第一个参数为double类型,且后续参数可以是任意数量任意类型的,公有的返回值为double的方法。
eg5 : execution(double 全类名.*(double, double)——表示支持该类中所有形参列表为两个double类型,公有的且返回值为double类型的方法。
(3) 在AspectJ中,切入点表达式可以通过"&&","||","!"等操作符结合起来。
eg : execution(* *.add(int, ..)) || execution(* *.subtract(int, ..))——表示支持任意类中的任意访问修饰符和任意返回值类型的,且形参列表第一个参数为int类型的add 或 subtract方法。
3.注意事项 :
(1) 当切入点表达式直接指向了接口某个实现类的方法(非实现类特有方法),这时切入点表达式仅会对该实现类生效(动态代理 + 反射),即接口的其他实现类不会生效(不会得到代理对象,即使你以接口类型作为接收)。
(2) 当切入点表达式指向接口的方法时,切入表达式会对该接口的所有实现类生效。
(3) 切入点表达式也可以切入到没有实现接口的类的横切关注点中。(CGlib动态代理模式)
PS : JDK Proxy动态代理和CGlib动态代理的区别——
JDK动态代理是面向接口的,只能增强实现类中重写了接口中的方法。而CGlib是面向父类的,可以增强父类的所有方法。
JDK得到的对象是JDK代理对象实例,而CGlib得到的对象是被代理对象的子类。
4.代码演示 :
先来演示"注意事项"中的第一点,up新定义一个Calculator接口的实现类Calculator_Demo2类,代码如下 : (用@Component注解标记为组件,且给出了自定义的id值 = calculator02)
package com.cyan.spring.aop.aspectJ;import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;/*** @author : Cyan_RA9* @version : 21.0*/
@Component(value = "calculator02")
public class Calculator_Demo2 implements Calculator{@Overridepublic double add(double n1, double n2) {System.out.println("Calculator_Demo2");return 0;}@Overridepublic double subtract(double n1, double n2) {System.out.println("Calculator_Demo2");return 0;}@Overridepublic double multiply(double n1, double n2) {System.out.println("Calculator_Demo2");return 0;}@Overridepublic double divide(double n1, double n2) {System.out.println("Calculator_Demo2");return 0;}
}
切面类保持不变,即配置的切入表达式仍然直接指向了Calculator_Demo1类。
接着,up定义一个测试方法,代码如下 :
@Testpublic void testImplementationClass() {ApplicationContext ioc = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("beans_aop.xml");Calculator calculator01 = (Calculator) ioc.getBean("calculator01");Calculator calculator02 = (Calculator) ioc.getBean("calculator02");System.out.println("calculator01's class = " + calculator01.getClass());System.out.println("calculator02's class = " + calculator02.getClass());calculator01.add(2121, 212);System.out.println("===========================");calculator02.add(11, 635);}运行结果 :
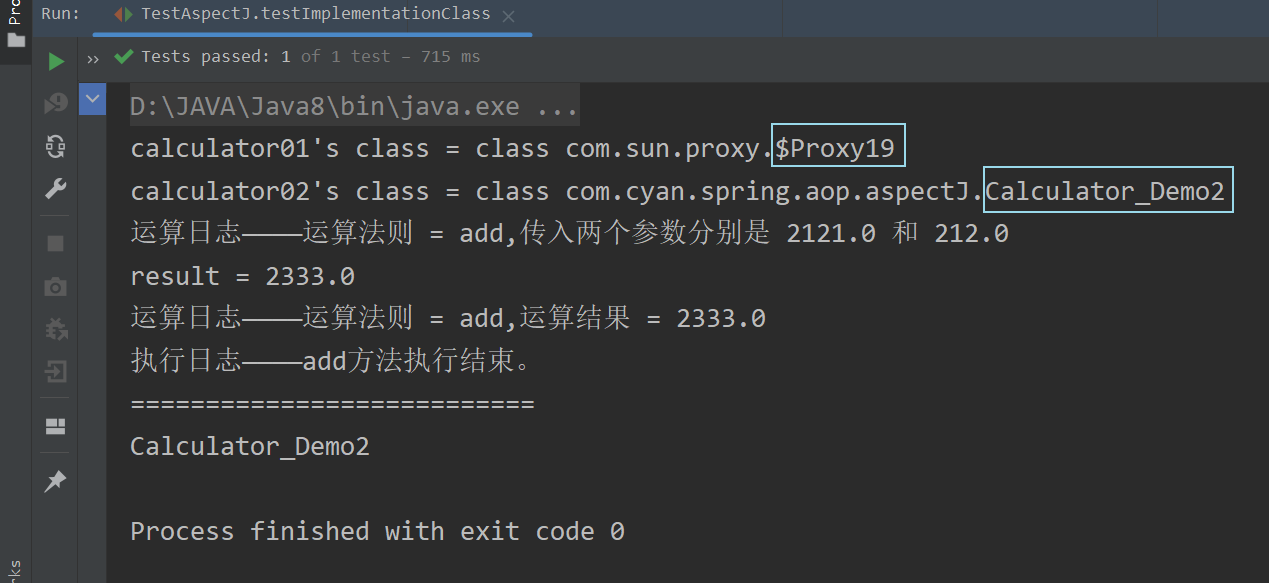
可以看到,只有Calculator_Demo1类成功得到了代理对象,且配置的切入点表达式也执行成功,而Calculator_Demo2类却仍然只是一个实现类对象。
注意,这时候,up将切面类中原来的@Before前置通知的代码注释掉,重新定义一个@Before前置通知,令切入表达式指向Calculator接口,代码如下 :
//配置到接口上@Before(value = "execution(public double com.cyan.spring.aop.aspectJ.Calculator.add(double, double))")public void beforeAdvice(JoinPoint joinPoint) {//1.通过连接点对象,得到方法参数Object[] args = joinPoint.getArgs();double n1 = (double) args[0];double n2 = (double) args[1];//2.通过连接点对象,得到方法签名对象Signature signature = joinPoint.getSignature();//3.通过方法签名对象,获取到方法名String name = signature.getName();//Δ在运算方法执行前打印出运算日志System.out.println("运算日志————运算法则 = " + name + ",传入两个参数分别是 " + n1 + " 和 " + n2);}这时,再次运行刚才的测试方法,会发现Calculator_Demo1类和Calculator_Demo2类都可以成功获得代理对象,并且配置的@Before前置通知也成功执行,运行结果如下图所示 :

最后来演示一下注意事项3——即CGlib动态代理的使用。
up新定义一个Cat类,代码如下 :
package com.cyan.spring.aop.aspectJ;import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;@Component(value = "cat01")
public class Cat {public void eat() {System.out.println("Cat love to eat meat.");}
}
然后,再新定义一个切面类,CatAspect类代码如下 :
package com.cyan.spring.aop.aspectJ;import org.aspectj.lang.JoinPoint;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Aspect;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Before;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;@Aspect
@Component
public class CatAspect {@Before(value = "execution(public * Cat.*(..))")public void beforeEat(JoinPoint joinPoint) {System.out.println("猫猫吃饭前也要洗手捏~");}
}
最后,再定义一个简单的测试类,测试CGlib动态代理是否生效,CatTest类代码如下 :
package com.cyan.spring.aop.aspectJ;import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;public class CatTest {@Testpublic void testCGlib() {ApplicationContext ioc = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("beans_aop.xml");Cat cat01 = (Cat) ioc.getBean("cat01");System.out.println("cat01's class = " + cat01.getClass());cat01.eat();}
}
运行结果 :

可以看到,切面类中定义的前置通知成功执行!
四、AOP—切入点表达式的更多细节
1.JoinPoint :
1.1 简介
JoinPoint,即连接点对象,通过该对象可以获取到调用的Method的签名,即方法签名对象Signature。
1.2 方法
//(1) 获取方法名
joinPoint.getSignature().getName();
//(2) 获取简单类名
joinPoint.getSignature().getDeclaringType().getSimpleName();
//(3) 获取全类名
joinPoint.getSignature().getDeclaringTypeName();
//(4) 获取访问权限修饰符(int类型)
joinPoint.getSignature().getModifiers();
//(5) 获取方法的参数,用数组作接收。
Object[] args = joinPoint.getArgs();
//(6) 获取被代理的对象
joinPoint.getTarget();
//(7) 获取代理对象本身
joinPoint.getThis();
1.3 演示
我们就在刚才的CatAspect中测试这些方法,CatAspect类代码如下 :
package com.cyan.spring.aop.aspectJ;import org.aspectj.lang.JoinPoint;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Aspect;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Before;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;@Aspect
@Component
public class CatAspect {@Before(value = "execution(public * Cat.*(..))")public void beforeEat(JoinPoint joinPoint) {System.out.println("猫猫吃饭前也要洗手捏~");String name = joinPoint.getSignature().getName();String simpleName = joinPoint.getSignature().getDeclaringType().getSimpleName();String declaringTypeName = joinPoint.getSignature().getDeclaringTypeName();int modifiers = joinPoint.getSignature().getModifiers();Object[] args = joinPoint.getArgs();Object target = joinPoint.getTarget();Object aThis = joinPoint.getThis();System.out.println("-----------------------------------------------");System.out.println("name = " + name);System.out.println("simpleName = " + simpleName);System.out.println("declaringTypeName = " + declaringTypeName);System.out.println("modifiers = " + modifiers);System.out.println("args = " + args);System.out.println("target = " + target);System.out.println("aThis = " + aThis.getClass());System.out.println("-----------------------------------------------");}
}
运行结果 :

2.通知进阶 :
2.1 通过@AfterReturning获取方法的返回结果
在使用@AfterReturning注解配置“返回通知”时,可以在配置切入点表达式后,额外通过returning = "表示返回结果的变量"来定义方法的返回结果,但需要在切入方法的形参列表中,同时也额外定义一个相同名称的变量。如下图所示 :
我们可以定义一个单元测试方法,测试方法的返回结果是否成功传递到了result变量中,代码如下 :
//返回通知获取方法的运行结果@Testpublic void testReturningResult() {ApplicationContext ioc = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("beans_aop.xml");Calculator calculator = ioc.getBean("calculator01", Calculator.class);System.out.println("calculator's class = " + calculator.getClass());calculator.add(11.5, 141);}运行结果 :

2.2 通过@AfterThrowing获取异常信息
在使用@AfterThrowing注解配置“返回通知”时,可以在配置切入点表达式后,额外通过throwing= "表示异常信息的变量"来定义方法的异常信息,但需要在切入方法的形参列表中,同时也额外定义一个相同名称的变量(注意变量的类型)。如下图所示 :
我们可以在Calculator_Demo2类的add方法中,故意制造一个算术异常,如下图所示 :

然后,定义一个单元测试方法,测试“异常通知”是否成功获取了异常信息。代码如下 :
//异常通知获取方法的异常信息@Testpublic void testExceptionInfo() {ApplicationContext ioc = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("beans_aop.xml");Calculator calculator = ioc.getBean("calculator02", Calculator.class);System.out.println("calculator's class = " + calculator.getClass());calculator.add(11.5, 141);}运行结果 :

2.3 环绕通知
环绕通知可以将四个通知合并管理,它可以完成其他四个通知的功能(前置通知,返回通知,异常通知,后置通知)。
我们新定义一个切面类CalculatorAspect_EX,用于配置环绕通知;为了防止之前配置的其他通知对测试结果造成干扰,up把之前定义的切面类CalculatorAspect类先给注释掉了。
CalculatorAspect_EX类代码如下 :
package com.cyan.spring.aop.aspectJ;import org.aspectj.lang.ProceedingJoinPoint;
import org.aspectj.lang.Signature;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.*;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;import java.time.LocalDateTime;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.List;/*** 切面类 : CalculatorAspect_EX*/
@Aspect //Aspect注解提供了底层切面编程的支撑
@Component //Component注解表示该类是一个组件
public class CalculatorAspect_EX {//定义一个切入方法,用于实现“环绕通知”@Around(value = "execution(* Calculator_Demo1.add(..))")public Object aroundAdvice(ProceedingJoinPoint proceedingJoinPoint) {//定义方法的返回结果Object result = null;//通过连接点对象获取方法签名对象Signature signature = proceedingJoinPoint.getSignature();//通过方法签名对象获取方法名String methodName = signature.getName();//try-catch-finally结构try {//1.完成前置通知的任务Object[] args = proceedingJoinPoint.getArgs();List<Object> objects = Arrays.asList(args);System.out.println("(Around~)运算日志————运算法则 = " + methodName + ",传入的参数是 " + objects);//!!!//在环绕通知中,需要通过proceed()方法来执行目标方法result = proceedingJoinPoint.proceed();//2.完成返回通知的任务System.out.println("(Around~)运算日志————运算法则 = " + methodName + ",运算结果 = " + result);} catch (Throwable throwable) {//3.完成异常通知的任务System.out.println("(Around~)异常日志————" + LocalDateTime.now() + ",方法" + methodName + "执行异常");System.out.println("(Around~)异常信息如下————\n" + throwable);} finally {//4.完成后置通知的任务System.out.println("(Around~)执行日志————" + methodName + "方法执行结束。");}return result; }
}
然后,up再定义一个单元测试方法,用于测试环绕通知是否生效,代码如下 :
//环绕通知测试@Testpublic void testAroundAdvice() {ApplicationContext ioc = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("beans_aop.xml");Calculator calculator = ioc.getBean("calculator01", Calculator.class);System.out.println("calculator's class = " + calculator.getClass());calculator.add(150, 255.5);}运行结果 :

可以看到,通过环绕通知,成功达到了“前置通知”,“返回通知”,“后置通知”的效果。
3.切入点表达式重用(@Pointcut) :
3.1 简介
我们在之前定义的切面类CalculatorAspect类中定义了多个切入点表达式,但是我们发现这样一个问题——多个切入点表达式都指向了相同的类的相同方法,未免有些冗余的感觉,能不能想办法将这些切入点表达式进行复用,以提高使用效率呢?
为了统一管理切入点表达式,我们可以使用切入点表达式重用技术(使用@Pointcut注解)。其使用格式如下图所示 :
3.2 实例
需求 : 我们就在原来的CalculatorAspect切面类中进行修改,要求通过@Pointcut注解配置一个切入点表达式,然后对该表达式重用,完成前置通知和返回通知。
实现 : 首先,为防止对输出结果造成干扰,up先将上文“环绕通知”中定义的CalculatorAspect_EX切面类注释掉。然后在CalculatorAspect类中进行配置,代码如下 :
package com.cyan.spring.aop.aspectJ;import org.aspectj.lang.JoinPoint;
import org.aspectj.lang.Signature;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.*;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;import java.time.LocalDateTime;/*** 切面类 : CalculatorAspect*/
@Aspect //Aspect注解提供了底层切面编程的支撑
@Component //Component注解表示该类是一个组件
public class CalculatorAspect {/*切入点表达式重用*/@Pointcut(value = "execution(public double Calculator_Demo1.add(..))")public void myPointcut() {}//@Before(value = "execution(public double com.cyan.spring.aop.aspectJ.Calculator.add(double, double))")@Before(value = "myPointcut()")public void beforeAdvice(JoinPoint joinPoint) {//1.通过连接点对象,得到方法参数Object[] args = joinPoint.getArgs();double n1 = (double) args[0];double n2 = (double) args[1];//2.通过连接点对象,得到方法签名对象Signature signature = joinPoint.getSignature();//3.通过方法签名对象,获取到方法名String name = signature.getName();//Δ在运算方法执行前打印出运算日志System.out.println("运算日志————运算法则 = " + name + ",传入两个参数分别是 " + n1 + " 和 " + n2);}//returnAdvice方法,作为返回通知//@AfterReturning(value = "execution(* Calculator_Demo1.add(double, double))", returning = "result")@AfterReturning(value = "myPointcut()", returning = "result")public void returnAdvice(JoinPoint joinPoint, Object result) {//通过连接点对象,得到方法签名对象Signature signature = joinPoint.getSignature();//通过方法签名对象,获取到方法名String name = signature.getName();//获得方法参数Object[] args = joinPoint.getArgs();//double result = (double) args[0] + (double) args[1];//Δ在运算方法执行后打印出运算日志System.out.println("运算日志————运算法则 = " + name + ",运算结果 = " + result);}}
接着,仍然在测试类TestAspectJ中定义一个单元测试方法,测试切入表达式重用是否成功,代码如下 :
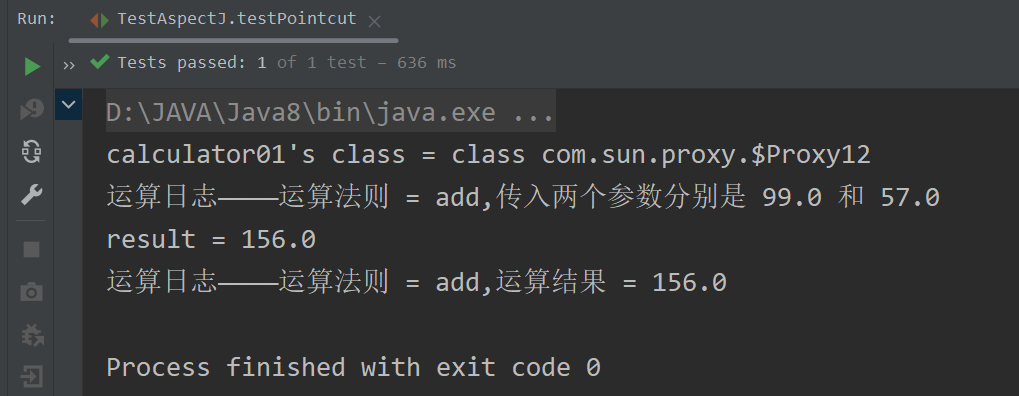
//切入表达式重用测试@Testpublic void testPointcut() {ApplicationContext ioc = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("beans_aop.xml");Calculator calculator01 = ioc.getBean("calculator01", Calculator.class);System.out.println("calculator01's class = " + calculator01.getClass());calculator01.add(11, 22);}运行结果 :

4.切面类执行顺序 :
4.1 简介
(1) 若多个切面类中定义的切入方法指向了同一个横切关注点,可以通过@Order(value=n)注解来控制切面类执行的优先级,其中,n的值越小,则该切面类执行的优先级越高。PS : 注意,是org.springframework.core.annotation包下的@Order注解。
(2) 多个切面类的执行顺序,其实和FilterChain过滤器链的执行顺序是十分相似的,即后调用的先执行完毕,如下图所示 :
4.2 实例
新定义一个切面类——CalculatorAspect2类,并修改该切面类中前置通知和返回通知的输出信息,以和CalculatorAspect切面类作区分。CalculatorAspect2类代码如下 :
package com.cyan.spring.aop.aspectJ;import org.aspectj.lang.JoinPoint;
import org.aspectj.lang.Signature;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.AfterReturning;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Aspect;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Before;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;@Aspect
@Component
public class CalculatorAspect2 {//前置通知@Before(value = "execution(public double com.cyan.spring.aop.aspectJ.Calculator.add(double, double))")public void beforeAdvice(JoinPoint joinPoint) {//1.通过连接点对象,得到方法参数Object[] args = joinPoint.getArgs();double n1 = (double) args[0];double n2 = (double) args[1];//2.通过连接点对象,得到方法签名对象Signature signature = joinPoint.getSignature();//3.通过方法签名对象,获取到方法名String name = signature.getName();//Δ在运算方法执行前打印出运算日志System.out.println("(2)运算日志————运算法则 = " + name + ",传入两个参数分别是 " + n1 + " 和 " + n2);}//返回通知@AfterReturning(value = "execution(* Calculator_Demo1.add(double, double))", returning = "result")public void returnAdvice(JoinPoint joinPoint, Object result) {//通过连接点对象,得到方法签名对象Signature signature = joinPoint.getSignature();//通过方法签名对象,获取到方法名String name = signature.getName();//获得方法参数Object[] args = joinPoint.getArgs();//double result = (double) args[0] + (double) args[1];//Δ在运算方法执行后打印出运算日志System.out.println("(2)运算日志————运算法则 = " + name + ",运算结果 = " + result);}
}
这时,若我们运行测试方法(切入表达式重用中定义的测试方法),会发现两个切面类的切入方法同时生效,运行结果如下图所示 :

可以看到,当前是旧的切面类先生效;现在,我们给两个切面类都配置上@Order注解,如下图所示 :

可以看到,此时新配置的切面类CalculatorAspect2的执行优先级更高;这时我们重新运行测试方法,运行结果如下 :
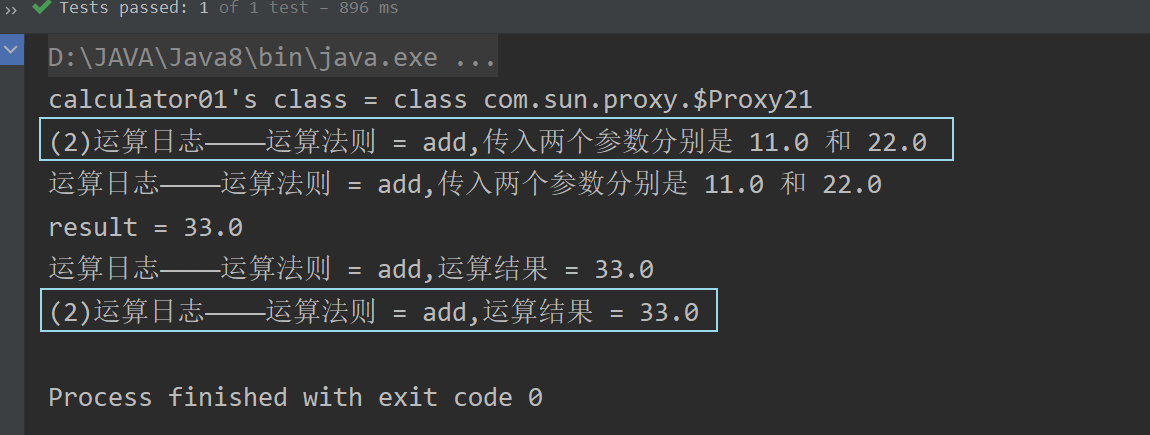
可以看到,果然是CalculatorAspect2切面类先执行。
5.基于XML配置AOP :
到现在为止,我们一直都在使用“基于注解配置AOP”的形式,那么基于XML又怎么配置AOP呢?
up将原先的beans_aop.xml配置文件进行修改,将注解扫描的代码注释掉,并在该配置文件中基于XML配置AOP,beans_aop.xml代码如下 :
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop"xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/context https://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop https://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop.xsd"><!-- 配置自动扫描 --><!--<context:component-scan base-package="com.cyan.spring.aop.aspectJ"/>--><!-- 开启基于注解的AOP功能,若不开启,不能实现切入[动态代理 + 反射调用] --><!--<aop:aspectj-autoproxy/>--><!--配置实现类对象(被代理对象)--><bean class="com.cyan.spring.aop.aspectJ.Calculator_Demo1" id="calculator01"/><!--配置切面类--><bean class="com.cyan.spring.aop.aspectJ.CalculatorAspect" id="aspect01"/><!--XML配置AOP--><aop:config><!-- 先配置切入点(联系之前的“切入点表达式重用”) --><aop:pointcut id="myPointcut" expression="execution(public double *.add(..))"/><!-- 再指定切面类 --><aop:aspect ref="aspect01" order="3"><!-- 表示将该类中的beforeAdvice方法切入到myPointcut指向的横切关注点上,并作为前置通知 --><aop:before method="beforeAdvice" pointcut-ref="myPointcut"/><!-- 方法的返回结果保存在result变量中 --><aop:after-returning method="returnAdvice" pointcut-ref="myPointcut" returning="result"/><!-- 方法的异常信息保存在exception变量中 --><aop:after-throwing method="throwingAdvice" pointcut-ref="myPointcut" throwing="exception"/></aop:aspect></aop:config>
</beans>重新运行测试方法,会发现依然成功,如下图所示 :
五、总结
- 🆗,以上就是Spring系列博文第五小节的全部内容了。
- 总结一下,我们先从“动态代理的优化”引出,自己定义了一个AOP类进行模拟,进行问题分析后(不够灵活,复用性差);又通过一个入门案例了解了AOP——通知注解的使用。接着,我们又详细介绍了AOP——切入点表达式,包括它的基本使用,注意事项和更多细节;最后,我们又简单介绍了基于XML方式配置AOP。
- 下一节内容——Spring 手动实现Spring底层机制,我们不见不散😆。感谢阅读!
System.out.println("END--------------------------------------------------");












)

 API(1688.item_search_img)在电商中的前景)

)




)




