文章参考Linux内核线程kernel thread详解 - 知乎
大概意思就是早期创建内核线程,是交由内核处理,由内核自己完成(感觉好像也不太对呢),创建一个内核线程比较麻烦,会导致内核阻塞。因此就诞生了工作队列以及现在的kthreadd 2号进程。这样我们在创建内核线程时,只需要将消息告诉它们,实际进行内核线程创建的任务有kthreadd完成,感觉类似一个下半部。
我环境使用的是kthreadd进行内核线程的创建
内核线程创建kthread_create
kthread_create-->kthread_create_on_node-->__kthread_create_on_node
#define kthread_create(threadfn, data, namefmt, arg...) \kthread_create_on_node(threadfn, data, NUMA_NO_NODE, namefmt, ##arg)可以看到这里只是将创建内核线程的任务加入了链表里面,然后唤醒kthreadd进行内核线程的创建
struct task_struct *__kthread_create_on_node(int (*threadfn)(void *data),void *data, int node,const char namefmt[],va_list args)
{DECLARE_COMPLETION_ONSTACK(done);struct task_struct *task;struct kthread_create_info *create = kmalloc(sizeof(*create),GFP_KERNEL);if (!create)return ERR_PTR(-ENOMEM);/* 被创建的内核线程的信息被存放到了create_info里面 */create->threadfn = threadfn;create->data = data;create->node = node;create->done = &done;spin_lock(&kthread_create_lock);/* 将create_info加入到链表中,然后唤醒kthreadd_task(2号进程)进行后续的内核线程创建 */list_add_tail(&create->list, &kthread_create_list);spin_unlock(&kthread_create_lock);wake_up_process(kthreadd_task);/** Wait for completion in killable state, for I might be chosen by* the OOM killer while kthreadd is trying to allocate memory for* new kernel thread.*//* 这里是等待内核线程创建完成,内核线程创建完成后会释放这样完成量函数kthread里面会释放这个completion*/if (unlikely(wait_for_completion_killable(&done))) {/** If I was SIGKILLed before kthreadd (or new kernel thread)* calls complete(), leave the cleanup of this structure to* that thread.*/if (xchg(&create->done, NULL))return ERR_PTR(-EINTR);/** kthreadd (or new kernel thread) will call complete()* shortly.*/wait_for_completion(&done);}/* 函数kthread里面会将result赋值为创建好的内核线程的task_struct */task = create->result;if (!IS_ERR(task)) {static const struct sched_param param = { .sched_priority = 0 };char name[TASK_COMM_LEN];/** task is already visible to other tasks, so updating* COMM must be protected.*/vsnprintf(name, sizeof(name), namefmt, args);set_task_comm(task, name);//这里设置内核线程的名字/** root may have changed our (kthreadd's) priority or CPU mask.* The kernel thread should not inherit these properties.*/sched_setscheduler_nocheck(task, SCHED_NORMAL, ¶m);set_cpus_allowed_ptr(task, cpu_all_mask);}kfree(create);return task;
}那2号进程kthreadd干了什么事情呢?
2号进程在rest_init里面创建,其处理函数为kthreadd
noinline void __ref rest_init(void)
{...............................pid = kernel_thread(kthreadd, NULL, CLONE_FS | CLONE_FILES);rcu_read_lock();kthreadd_task = find_task_by_pid_ns(pid, &init_pid_ns);rcu_read_unlock();
............................
}kthreadd-->create_kthread-->kernel_thread
int kthreadd(void *unused)
{struct task_struct *tsk = current;/* Setup a clean context for our children to inherit. */set_task_comm(tsk, "kthreadd");ignore_signals(tsk);set_cpus_allowed_ptr(tsk, cpu_all_mask);set_mems_allowed(node_states[N_MEMORY]);current->flags |= PF_NOFREEZE;cgroup_init_kthreadd();/*其实就是一直检查kthread_create_list是否为空如果不为空,将不断的处理链表里面的任务处理,创建内核线程*/for (;;) {set_current_state(TASK_INTERRUPTIBLE);if (list_empty(&kthread_create_list))schedule();__set_current_state(TASK_RUNNING);spin_lock(&kthread_create_lock);while (!list_empty(&kthread_create_list)) {struct kthread_create_info *create;create = list_entry(kthread_create_list.next,struct kthread_create_info, list);list_del_init(&create->list);spin_unlock(&kthread_create_lock);create_kthread(create);spin_lock(&kthread_create_lock);}spin_unlock(&kthread_create_lock);}return 0;
}可以看到 内核线程的创建最终还是调用的kernel_thread。创建的内核线程会执行kthread,在函数kthread里面执行了我们设置的内核线程处理函数threadfun
static void create_kthread(struct kthread_create_info *create)
{int pid;#ifdef CONFIG_NUMAcurrent->pref_node_fork = create->node;
#endif/* We want our own signal handler (we take no signals by default). *//* 最终在kthread里面调用到我们设置的回调函数 */pid = kernel_thread(kthread, create, CLONE_FS | CLONE_FILES | SIGCHLD);if (pid < 0) {/* If user was SIGKILLed, I release the structure. */struct completion *done = xchg(&create->done, NULL);if (!done) {kfree(create);return;}create->result = ERR_PTR(pid);complete(done);}
}kthread运行线程处理函数
执行到这里,就算内核线程创建成功了.只不过它不会立即执行我们的threadfn(即创建内核线程时指定的函数),它会先释放completion,并让出cpu。这就是kthread_create后还需要wake_up_process的原因。
static int kthread(void *_create)
{/* Copy data: it's on kthread's stack */struct kthread_create_info *create = _create;int (*threadfn)(void *data) = create->threadfn;void *data = create->data;struct completion *done;struct kthread *self;int ret;self = kzalloc(sizeof(*self), GFP_KERNEL);set_kthread_struct(self);/* If user was SIGKILLed, I release the structure. *//* 将create->done赋值为NULL,并返回create->done原来的值 */done = xchg(&create->done, NULL);if (!done) {kfree(create);do_exit(-EINTR);}if (!self) {create->result = ERR_PTR(-ENOMEM);complete(done);do_exit(-ENOMEM);}self->data = data;init_completion(&self->exited);init_completion(&self->parked);/* 此时的current就已经是我们创建好的内核线程了 */current->vfork_done = &self->exited;/* OK, tell user we're spawned, wait for stop or wakeup */__set_current_state(TASK_UNINTERRUPTIBLE);//__kthread_create_on_node里面将result当做返回值的原因在这里体现create->result = current;/* 在这里释放的completion,__kthread_create_on_node才会继续往下走 */complete(done);/*可以看到内核线程创建完了会先让出cpu,并不会立即执行我们的线程处理函数这就是我们为什么需要wake_up_process的原因,需要wake之后,才会继续从这里执行然后走到我们的threadfn*/schedule();ret = -EINTR;/*这个检查,我怀疑就是导致kthread_stop表现出不同行为的原因*/if (!test_bit(KTHREAD_SHOULD_STOP, &self->flags)) {cgroup_kthread_ready();__kthread_parkme(self);/* 执行内核线程设置的处理函数 */ret = threadfn(data);}/* 可以看到如果threadfn执行完了,内核线程退出是do_exit */do_exit(ret);
}经过实际验证确实是kthread调用了complete(done);,kthread_create才能返回,否则__kthread_create_on_node会一直等待completion
测试代码如下
起了个定时器,定时器里面唤醒了一个内核线程.内核线程里面做了两个事情,一个是将comp_block设置为true,即跳过complete(done),另外一个是创建一个内核线程,看看是否会阻塞
struct task_struct *task;
struct timer_list timer;
/* 通过该变量控制是否是否completion */
extern bool comp_block;int kill_thread(void* a)
{/* 不释放completion,然后再看看kthread_create是否会阻塞 */comp_block = true;printk(KERN_EMERG "\r\n before create thread\n");kthread_create(test_thread, NULL, "test_task");printk(KERN_EMERG "\r\n after create thread\n");return;
}
void timer_work(unsigned long data)
{wake_up_process(task);return;
}static int smsc911x_init(struct net_device *dev)
{
...............................printk(KERN_EMERG "\r\n softlockup simulate, in_interrupt %u in_softirq %u, NR_CPUS %d\n", in_interrupt(), in_softirq(), NR_CPUS);timer.expires=jiffies+msecs_to_jiffies(20000);timer.function=timer_work;init_timer(&timer);add_timer(&timer);printk(KERN_EMERG "\r\n create thread\n"); task = kthread_create(kill_thread, NULL, "kill_task");printk(KERN_EMERG "\r\n create thread end\n");
....................................
}bool comp_block = false;
static int kthread(void *_create)
{
.............................../* OK, tell user we're spawned, wait for stop or wakeup */__set_current_state(TASK_UNINTERRUPTIBLE);create->result = current;if (false == comp_block){complete(done);}schedule();
..........................................
}
效果展示 :可以看到并未打印kthread_create后面的log,并且内核线程kill_task也是一直无法退出
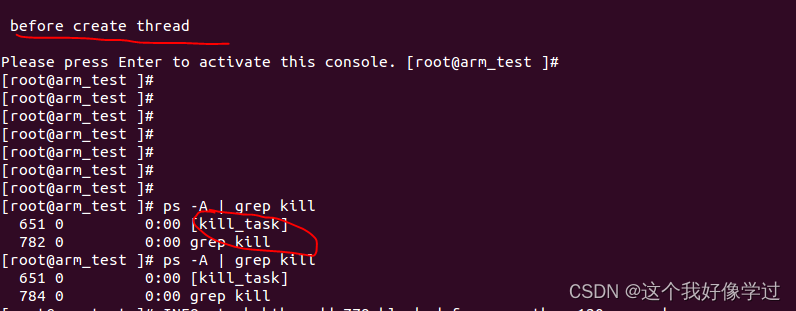
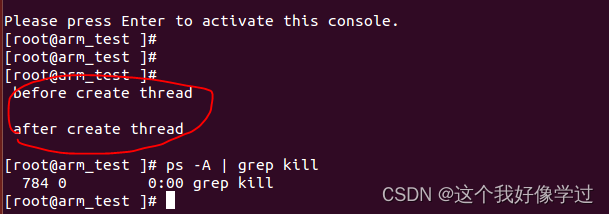
如果定时器里面不设置comp_block的值,即正常释放completion,log如下
内核线程退出kthread_stop
kthread_stop:只是告诉内核线程应该退出了,但是要不要退出,还需要看内核线程处理函数是否检查该消息,并且检查到以后还必须主动退出。
1、设置内核线程为KTHREAD_SHOULD_STOP,当内核线程的处理函数用kthread_should_stop检查标记时,能感知到该事件(如果内核线程一直不检查,那么即使调用了kthread_stop也是没有用的)
2、重新唤醒内核线程,如何内核线程没有运行,那么也是无法感知到这个事件的
3、等待completion释放
int kthread_stop(struct task_struct *k)
{struct kthread *kthread;int ret;trace_sched_kthread_stop(k);get_task_struct(k);kthread = to_kthread(k);set_bit(KTHREAD_SHOULD_STOP, &kthread->flags);kthread_unpark(k);wake_up_process(k);wait_for_completion(&kthread->exited);ret = k->exit_code;put_task_struct(k);trace_sched_kthread_stop_ret(ret);return ret;
}wait_for_completion(&kthread->exited);
这个是在哪里释放的呢?
exited其实就是vfork_done,
static int kthread(void *_create)
{
........................................self->data = data;init_completion(&self->exited);init_completion(&self->parked);/* 此时的current就已经是我们创建好的内核线程了 */current->vfork_done = &self->exited;..............................do_exit(ret);
}那么vfork_done是在哪里释放的呢?
do_exit-->exit_mm-->exit_mm_release-->mm_release
static void mm_release(struct task_struct *tsk, struct mm_struct *mm)
{
.................................../** All done, finally we can wake up parent and return this mm to him.* Also kthread_stop() uses this completion for synchronization.*/if (tsk->vfork_done)complete_vfork_done(tsk);
}






)
眼影)

)



)
:文件管理-文件目录命令)



