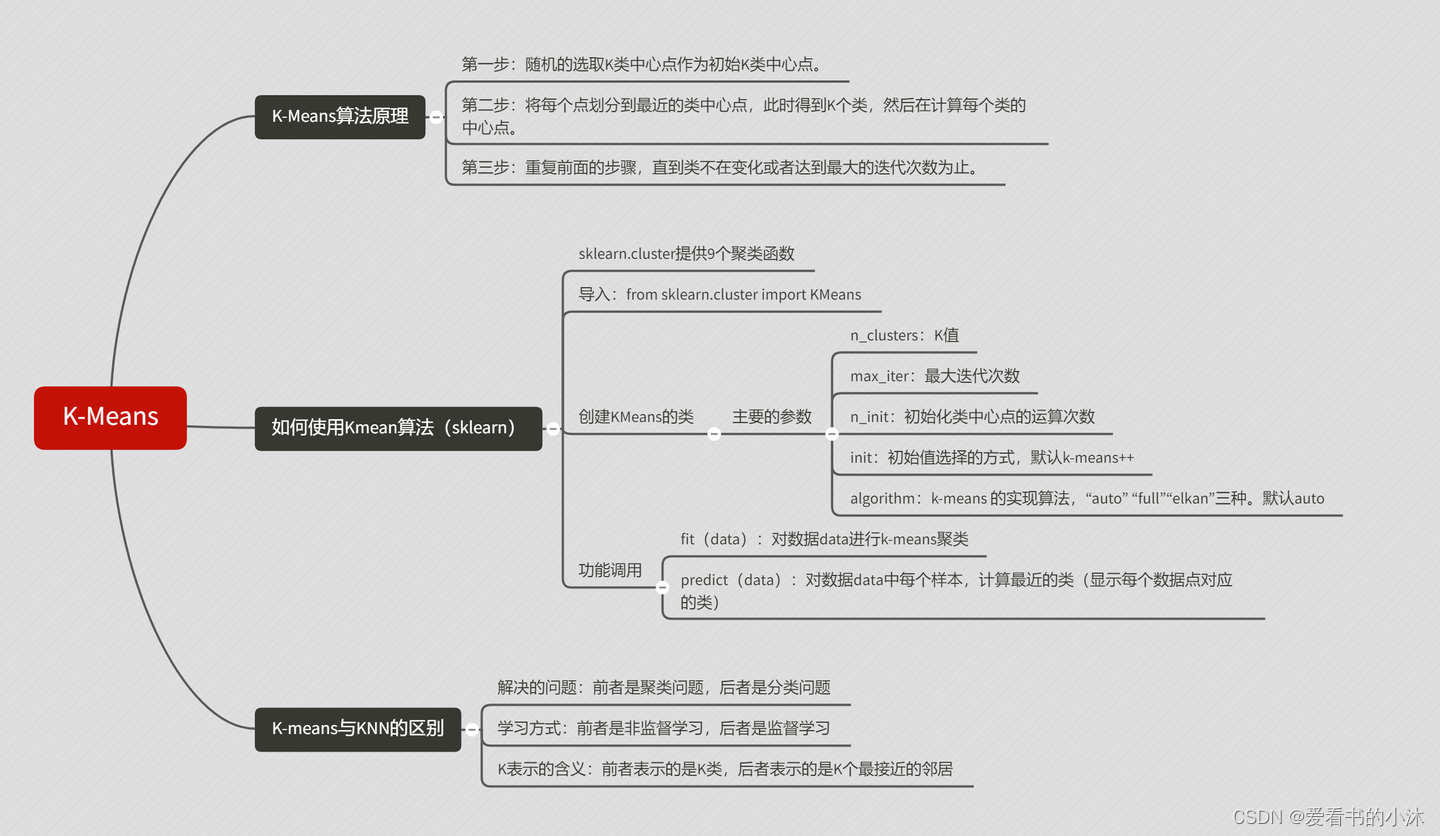
文章目录
- 1、简介
- 1.1 机器学习
- 1.2 K 均值聚类
- 1.2.1 聚类定义
- 1.2.2 K-Means定义
- 1.2.3 K-Means优缺点
- 1.2.4 K-Means算法步骤
- 2、测试
- 2.1 K-Means(Python)
- 2.2 K-Means(Sklearn)
- 2.2.1 例子1:数组分类
- 2.2.2 例子2:用户聚类分群
- 2.2.3 例子3:手写数字数据分类
- 2.2.4 例子4:鸢尾花数据分类
- 2.3 K-Means(nltk)
- 结语
1、简介
1.1 机器学习
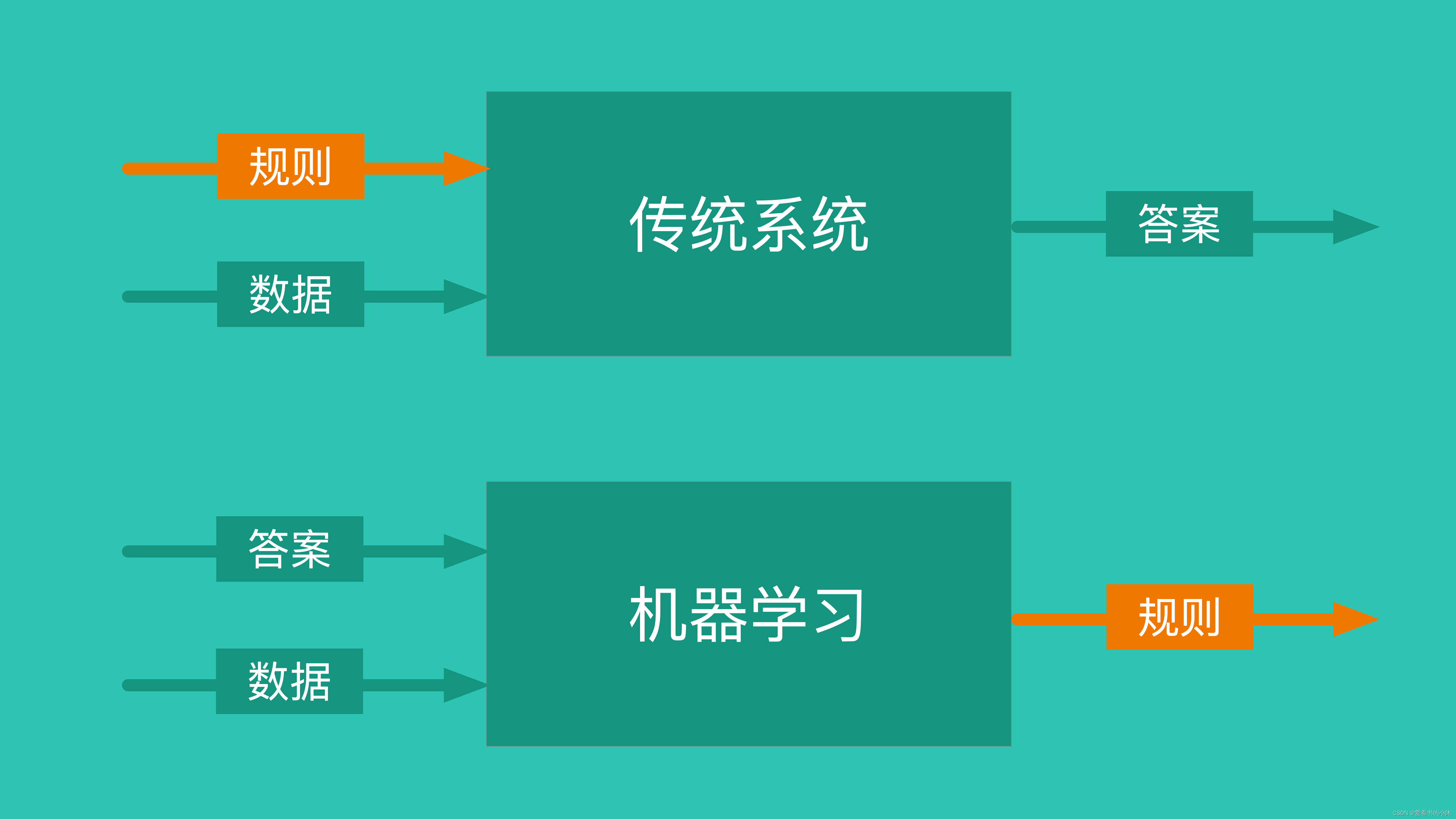
- 机器学习三要素:包括数据、模型、算法
- 机器学习三大任务方向:分类、回归、聚类
- 机器学习三大类训练方法:监督学习、非监督学习、强化学习
1.2 K 均值聚类
1.2.1 聚类定义
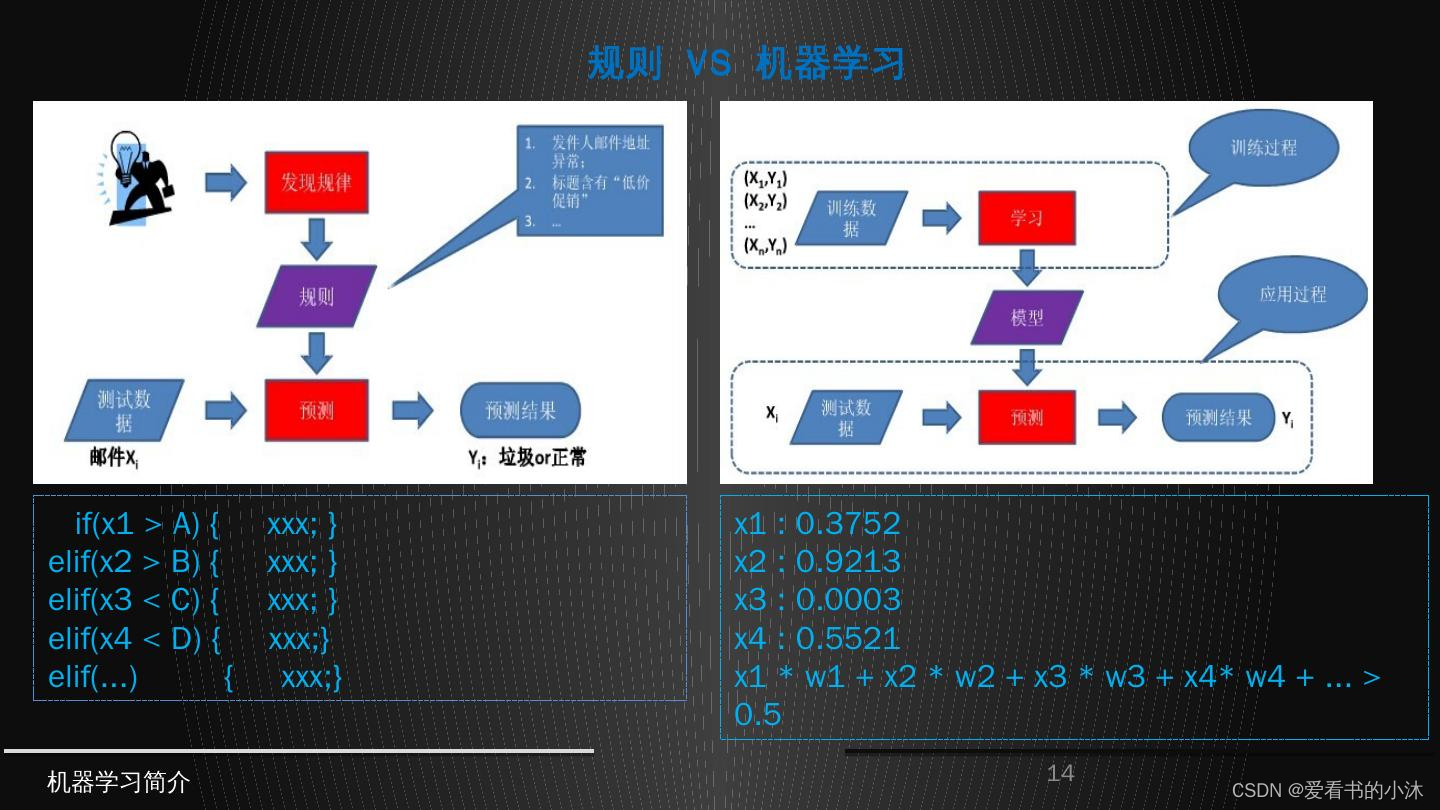
聚类是一种无监督学习任务,该算法基于数据的内部结构寻找观察样本的自然族群(即集群)。使用案例包括细分客户、新闻聚类、文章推荐等。
因为聚类是一种无监督学习(即数据没有标注),并且通常使用数据可视化评价结果。如果存在「正确的回答」(即在训练集中存在预标注的集群),那么分类算法可能更加合适。
依据算法原理,聚类算法可以分为基于划分的聚类算法(比如 K-means)、基于密度的聚类算法(比如DBSCAN)、基于层次的聚类算法(比如HC)和基于模型的聚类算法(比如HMM)。
1.2.2 K-Means定义
K 均值聚类是一种通用目的的算法,聚类的度量基于样本点之间的几何距离(即在坐标平面中的距离)。集群是围绕在聚类中心的族群,而集群呈现出类球状并具有相似的大小。聚类算法是我们推荐给初学者的算法,因为该算法不仅十分简单,而且还足够灵活以面对大多数问题都能给出合理的结果。
K-means是基于样本集合划分的聚类算法,是一种无监督学习。
1967年,J. MacQueen 在论文《 Some methods for classification and analysis of multivariate observations》中把这种方法正式命名为 K-means。
https://www.cs.cmu.edu/~bhiksha/courses/mlsp.fall2010/class14/macqueen.pdf

1.2.3 K-Means优缺点
优点:K 均值聚类是最流行的聚类算法,因为该算法足够快速、简单,并且如果你的预处理数据和特征工程十分有效,那么该聚类算法将拥有令人惊叹的灵活性。
缺点:该算法需要指定集群的数量,而 K 值的选择通常都不是那么容易确定的。另外,如果训练数据中的真实集群并不是类球状的,那么 K 均值聚类会得出一些比较差的集群。
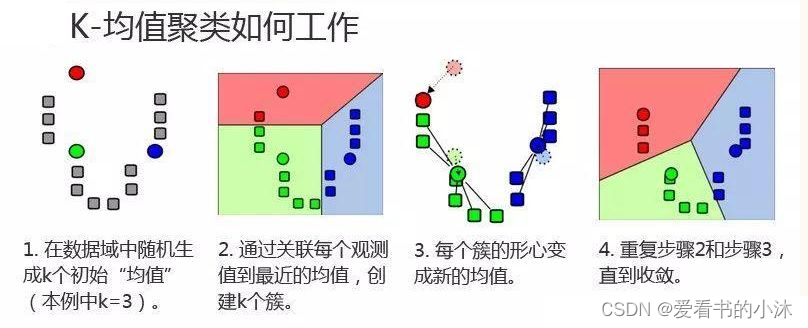
1.2.4 K-Means算法步骤
-
- 对于给定的一组数据,随机初始化K个聚类中心(簇中心)
-
- 计算每个数据到簇中心的距离(一般采用欧氏距离),并把该数据归为离它最近的簇。
-
- 根据得到的簇,重新计算簇中心。
-
- 对步骤2、步骤3进行迭代直至簇中心不再改变或者小于指定阈值。
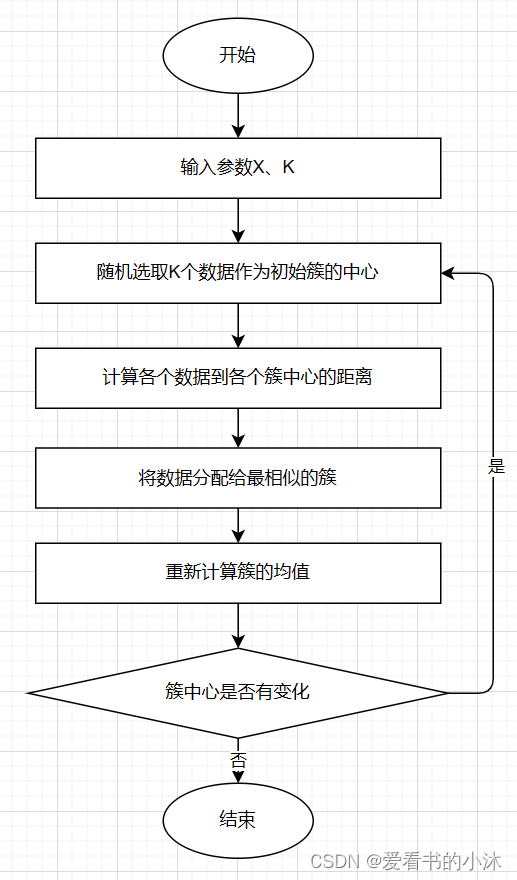
终止条件可以是:
没有(或最小数目)对象被重新分配给不同的聚类
没有(或最小数目)聚类中心再发生变化, 误差 平方和 局部最小。.
- 对步骤2、步骤3进行迭代直至簇中心不再改变或者小于指定阈值。
K-means聚类算法的主要步骤:
第一步:初始化聚类中心;
第二步:给聚类中心分配样本 ;
第三步:移动聚类中心 ;
第四步:停止移动。
注意:K-means算法采用的是迭代的方法,得到局部最优解.

2、测试
2.1 K-Means(Python)
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-
import numpy as np
from matplotlib import pyplotclass K_Means(object):# k是分组数;tolerance‘中心点误差’;max_iter是迭代次数def __init__(self, k=2, tolerance=0.0001, max_iter=300):self.k_ = kself.tolerance_ = toleranceself.max_iter_ = max_iterdef fit(self, data):self.centers_ = {}for i in range(self.k_):self.centers_[i] = data[i]for i in range(self.max_iter_):self.clf_ = {}for i in range(self.k_):self.clf_[i] = []# print("质点:",self.centers_)for feature in data:# distances = [np.linalg.norm(feature-self.centers[center]) for center in self.centers]distances = []for center in self.centers_:# 欧拉距离# np.sqrt(np.sum((features-self.centers_[center])**2))distances.append(np.linalg.norm(feature - self.centers_[center]))classification = distances.index(min(distances))self.clf_[classification].append(feature)# print("分组情况:",self.clf_)prev_centers = dict(self.centers_)for c in self.clf_:self.centers_[c] = np.average(self.clf_[c], axis=0)# '中心点'是否在误差范围optimized = Truefor center in self.centers_:org_centers = prev_centers[center]cur_centers = self.centers_[center]if np.sum((cur_centers - org_centers) / org_centers * 100.0) > self.tolerance_:optimized = Falseif optimized:breakdef predict(self, p_data):distances = [np.linalg.norm(p_data - self.centers_[center]) for center in self.centers_]index = distances.index(min(distances))return indexif __name__ == '__main__':x = np.array([[1, 2], [1.5, 1.8], [5, 8], [8, 8], [1, 0.6], [9, 11]])k_means = K_Means(k=2)k_means.fit(x)print(k_means.centers_)for center in k_means.centers_:pyplot.scatter(k_means.centers_[center][0], k_means.centers_[center][1], marker='*', s=150)for cat in k_means.clf_:for point in k_means.clf_[cat]:pyplot.scatter(point[0], point[1], c=('r' if cat == 0 else 'b'))predict = [[2, 1], [6, 9]]for feature in predict:cat = k_means.predict(predict)pyplot.scatter(feature[0], feature[1], c=('r' if cat == 0 else 'b'), marker='x')pyplot.show()
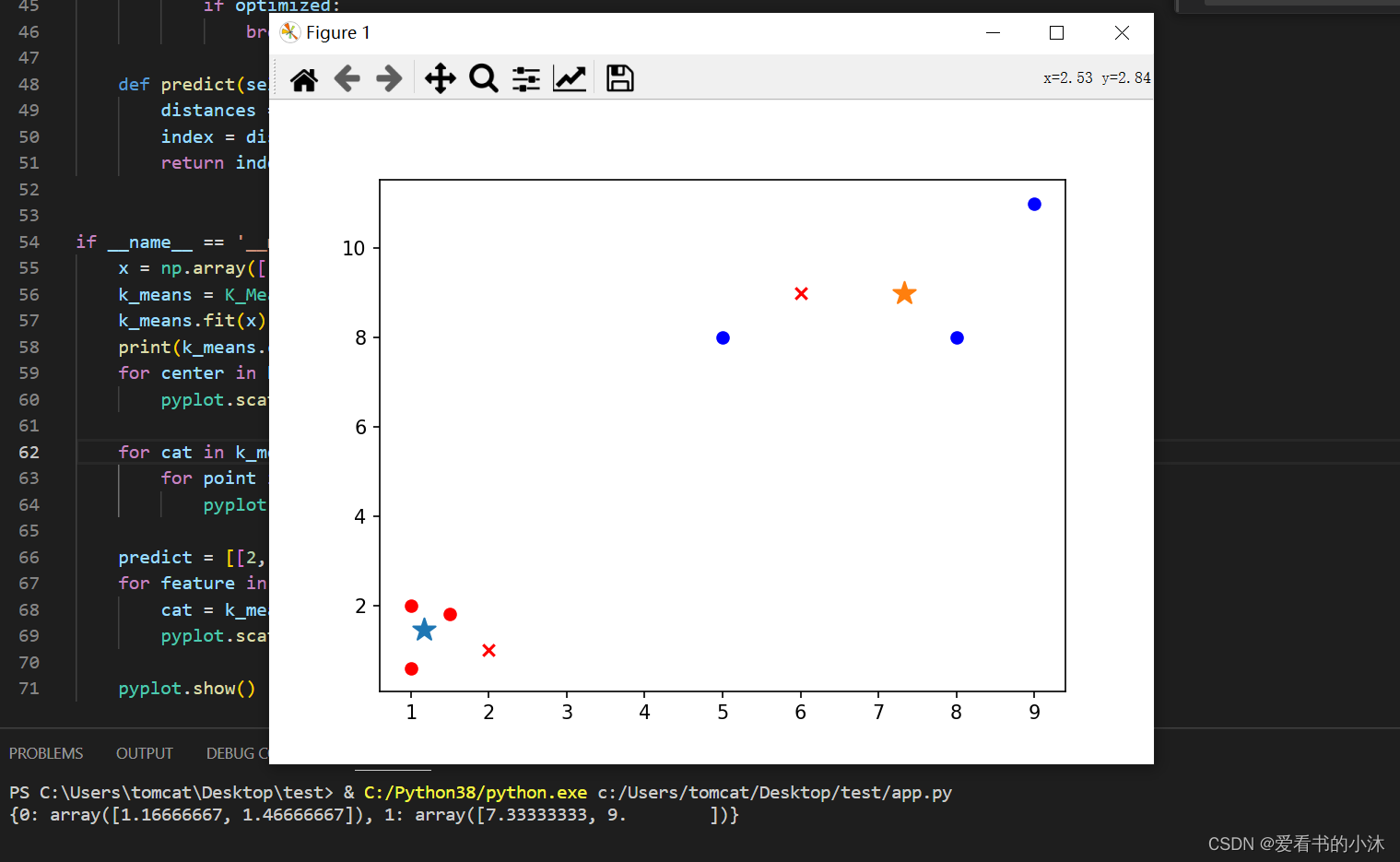
*是两组数据的”中心点”;x是预测点分组。
2.2 K-Means(Sklearn)
http://scikit-learn.org/stable/modules/clustering.html#k-means
2.2.1 例子1:数组分类
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-
import numpy as np
from matplotlib import pyplot
from sklearn.cluster import KMeansif __name__ == '__main__':x = np.array([[1, 2], [1.5, 1.8], [5, 8], [8, 8], [1, 0.6], [9, 11]])# 把上面数据点分为两组(非监督学习)clf = KMeans(n_clusters=2)clf.fit(x) # 分组centers = clf.cluster_centers_ # 两组数据点的中心点labels = clf.labels_ # 每个数据点所属分组print(centers)print(labels)for i in range(len(labels)):pyplot.scatter(x[i][0], x[i][1], c=('r' if labels[i] == 0 else 'b'))pyplot.scatter(centers[:,0],centers[:,1],marker='*', s=100)# 预测predict = [[2,1], [6,9]]label = clf.predict(predict)for i in range(len(label)):pyplot.scatter(predict[i][0], predict[i][1], c=('r' if label[i] == 0 else 'b'), marker='x')pyplot.show()
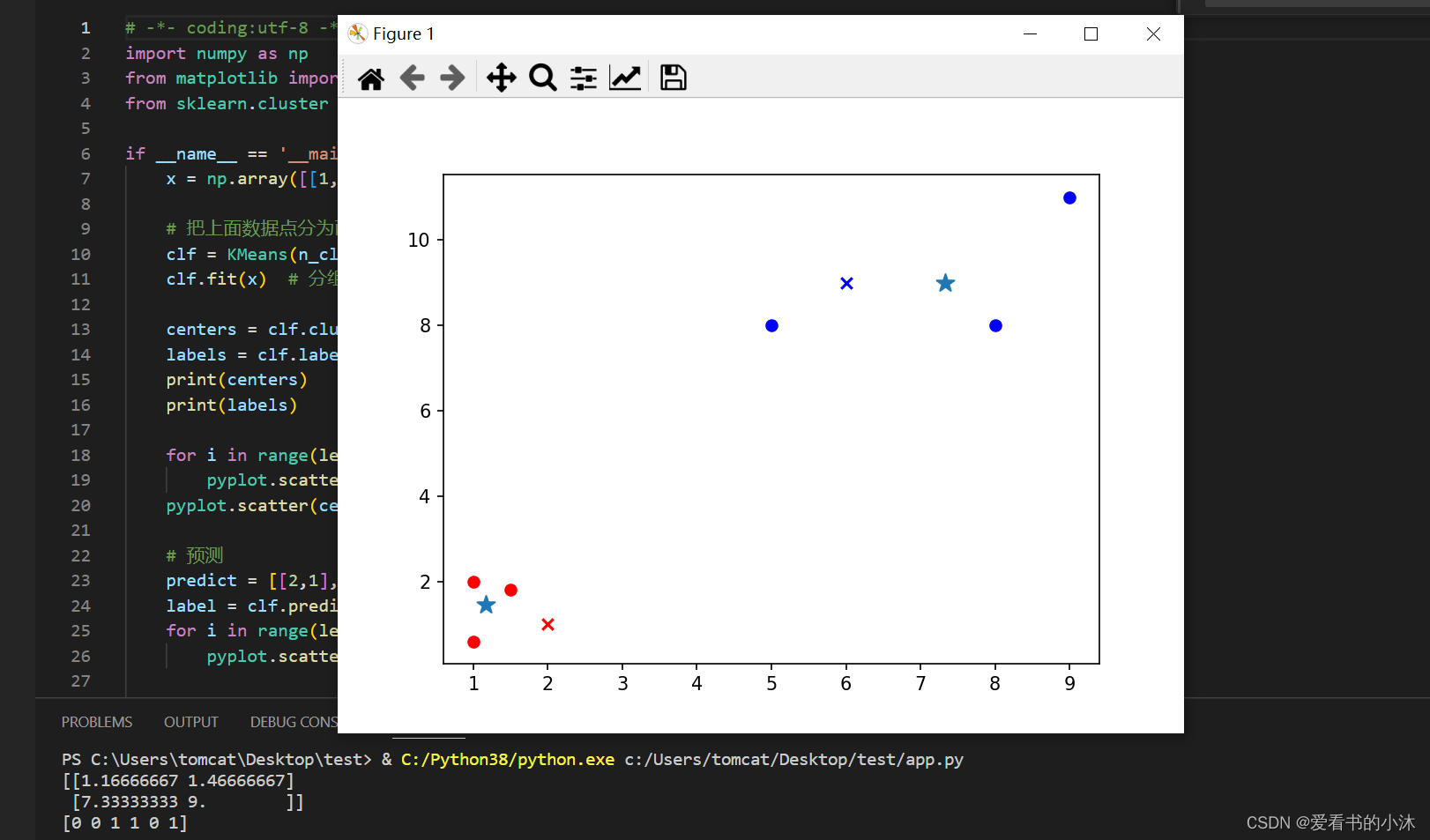
2.2.2 例子2:用户聚类分群
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-
import numpy as np
from sklearn.cluster import KMeans
from sklearn import preprocessing
import pandas as pd# 加载数据
df = pd.read_excel('titanic.xls')
df.drop(['body', 'name', 'ticket'], 1, inplace=True)
df.fillna(0, inplace=True) # 把NaN替换为0# 把字符串映射为数字,例如{female:1, male:0}
df_map = {}
cols = df.columns.values
for col in cols:if df[col].dtype != np.int64 and df[col].dtype != np.float64:temp = {}x = 0for ele in set(df[col].values.tolist()):if ele not in temp:temp[ele] = xx += 1df_map[df[col].name] = tempdf[col] = list(map(lambda val: temp[val], df[col]))# 将每一列特征标准化为标准正太分布
x = np.array(df.drop(['survived'], 1).astype(float))
x = preprocessing.scale(x)
clf = KMeans(n_clusters=2)
clf.fit(x)# 计算分组准确率
y = np.array(df['survived'])
correct = 0
for i in range(len(x)):predict_data = np.array(x[i].astype(float))predict_data = predict_data.reshape(-1, len(predict_data))predict = clf.predict(predict_data)if predict[0] == y[i]:correct += 1print(correct * 1.0 / len(x))
2.2.3 例子3:手写数字数据分类
"""
===========================================================
A demo of K-Means clustering on the handwritten digits data
===========================================================
"""# %%
# Load the dataset
# ----------------
#
# We will start by loading the `digits` dataset. This dataset contains
# handwritten digits from 0 to 9. In the context of clustering, one would like
# to group images such that the handwritten digits on the image are the same.import numpy as npfrom sklearn.datasets import load_digitsdata, labels = load_digits(return_X_y=True)
(n_samples, n_features), n_digits = data.shape, np.unique(labels).sizeprint(f"# digits: {n_digits}; # samples: {n_samples}; # features {n_features}")# %%
# Define our evaluation benchmark
# -------------------------------
#
# We will first our evaluation benchmark. During this benchmark, we intend to
# compare different initialization methods for KMeans. Our benchmark will:
#
# * create a pipeline which will scale the data using a
# :class:`~sklearn.preprocessing.StandardScaler`;
# * train and time the pipeline fitting;
# * measure the performance of the clustering obtained via different metrics.
from time import timefrom sklearn import metrics
from sklearn.pipeline import make_pipeline
from sklearn.preprocessing import StandardScalerdef bench_k_means(kmeans, name, data, labels):"""Benchmark to evaluate the KMeans initialization methods.Parameters----------kmeans : KMeans instanceA :class:`~sklearn.cluster.KMeans` instance with the initializationalready set.name : strName given to the strategy. It will be used to show the results in atable.data : ndarray of shape (n_samples, n_features)The data to cluster.labels : ndarray of shape (n_samples,)The labels used to compute the clustering metrics which requires somesupervision."""t0 = time()estimator = make_pipeline(StandardScaler(), kmeans).fit(data)fit_time = time() - t0results = [name, fit_time, estimator[-1].inertia_]# Define the metrics which require only the true labels and estimator# labelsclustering_metrics = [metrics.homogeneity_score,metrics.completeness_score,metrics.v_measure_score,metrics.adjusted_rand_score,metrics.adjusted_mutual_info_score,]results += [m(labels, estimator[-1].labels_) for m in clustering_metrics]# The silhouette score requires the full datasetresults += [metrics.silhouette_score(data,estimator[-1].labels_,metric="euclidean",sample_size=300,)]# Show the resultsformatter_result = ("{:9s}\t{:.3f}s\t{:.0f}\t{:.3f}\t{:.3f}\t{:.3f}\t{:.3f}\t{:.3f}\t{:.3f}")print(formatter_result.format(*results))# %%
# Run the benchmark
# -----------------
#
# We will compare three approaches:
#
# * an initialization using `k-means++`. This method is stochastic and we will
# run the initialization 4 times;
# * a random initialization. This method is stochastic as well and we will run
# the initialization 4 times;
# * an initialization based on a :class:`~sklearn.decomposition.PCA`
# projection. Indeed, we will use the components of the
# :class:`~sklearn.decomposition.PCA` to initialize KMeans. This method is
# deterministic and a single initialization suffice.
from sklearn.cluster import KMeans
from sklearn.decomposition import PCAprint(82 * "_")
print("init\t\ttime\tinertia\thomo\tcompl\tv-meas\tARI\tAMI\tsilhouette")kmeans = KMeans(init="k-means++", n_clusters=n_digits, n_init=4, random_state=0)
bench_k_means(kmeans=kmeans, name="k-means++", data=data, labels=labels)kmeans = KMeans(init="random", n_clusters=n_digits, n_init=4, random_state=0)
bench_k_means(kmeans=kmeans, name="random", data=data, labels=labels)pca = PCA(n_components=n_digits).fit(data)
kmeans = KMeans(init=pca.components_, n_clusters=n_digits, n_init=1)
bench_k_means(kmeans=kmeans, name="PCA-based", data=data, labels=labels)print(82 * "_")# %%
# Visualize the results on PCA-reduced data
# -----------------------------------------
#
# :class:`~sklearn.decomposition.PCA` allows to project the data from the
# original 64-dimensional space into a lower dimensional space. Subsequently,
# we can use :class:`~sklearn.decomposition.PCA` to project into a
# 2-dimensional space and plot the data and the clusters in this new space.
import matplotlib.pyplot as pltreduced_data = PCA(n_components=2).fit_transform(data)
kmeans = KMeans(init="k-means++", n_clusters=n_digits, n_init=4)
kmeans.fit(reduced_data)# Step size of the mesh. Decrease to increase the quality of the VQ.
h = 0.02 # point in the mesh [x_min, x_max]x[y_min, y_max].# Plot the decision boundary. For that, we will assign a color to each
x_min, x_max = reduced_data[:, 0].min() - 1, reduced_data[:, 0].max() + 1
y_min, y_max = reduced_data[:, 1].min() - 1, reduced_data[:, 1].max() + 1
xx, yy = np.meshgrid(np.arange(x_min, x_max, h), np.arange(y_min, y_max, h))# Obtain labels for each point in mesh. Use last trained model.
Z = kmeans.predict(np.c_[xx.ravel(), yy.ravel()])# Put the result into a color plot
Z = Z.reshape(xx.shape)
plt.figure(1)
plt.clf()
plt.imshow(Z,interpolation="nearest",extent=(xx.min(), xx.max(), yy.min(), yy.max()),cmap=plt.cm.Paired,aspect="auto",origin="lower",
)plt.plot(reduced_data[:, 0], reduced_data[:, 1], "k.", markersize=2)
# Plot the centroids as a white X
centroids = kmeans.cluster_centers_
plt.scatter(centroids[:, 0],centroids[:, 1],marker="x",s=169,linewidths=3,color="w",zorder=10,
)
plt.title("K-means clustering on the digits dataset (PCA-reduced data)\n""Centroids are marked with white cross"
)
plt.xlim(x_min, x_max)
plt.ylim(y_min, y_max)
plt.xticks(())
plt.yticks(())
plt.show()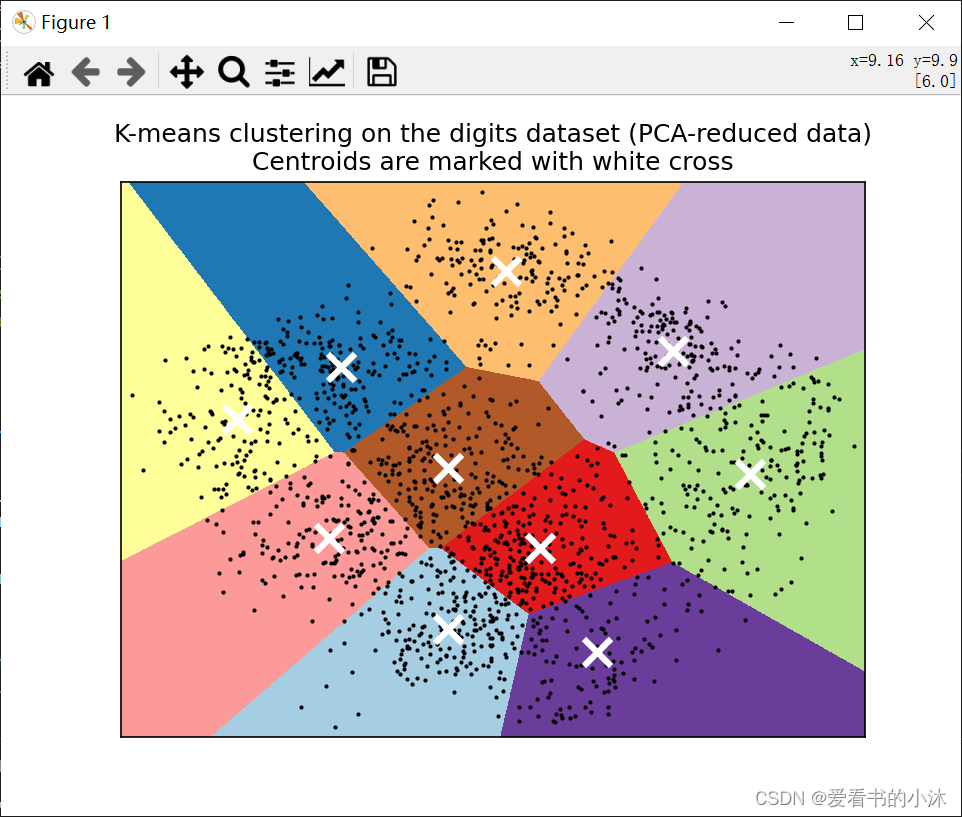
2.2.4 例子4:鸢尾花数据分类
import timeimport pandas as pd
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
from numpy import nonzero, array
from sklearn.cluster import KMeans
from sklearn.metrics import f1_score, accuracy_score, normalized_mutual_info_score, rand_score, adjusted_rand_score
from sklearn.preprocessing import LabelEncoder
from sklearn.decomposition import PCA# 数据保存在.csv文件中
iris = pd.read_csv("datasets/data/Iris.csv", header=0) # 鸢尾花数据集 Iris class=3
# wine = pd.read_csv("datasets/data/wine.csv") # 葡萄酒数据集 Wine class=3
# seeds = pd.read_csv("datasets/data/seeds.csv") # 小麦种子数据集 seeds class=3
# wdbc = pd.read_csv("datasets/data/wdbc.csv") # 威斯康星州乳腺癌数据集 Breast Cancer Wisconsin (Diagnostic) class=2
# glass = pd.read_csv("datasets/data/glass.csv") # 玻璃辨识数据集 Glass Identification class=6
df = iris # 设置要读取的数据集
# print(df)columns = list(df.columns) # 获取数据集的第一行,第一行通常为特征名,所以先取出
features = columns[:len(columns) - 1] # 数据集的特征名(去除了最后一列,因为最后一列存放的是标签,不是数据)
dataset = df[features] # 预处理之后的数据,去除掉了第一行的数据(因为其为特征名,如果数据第一行不是特征名,可跳过这一步)
attributes = len(df.columns) - 1 # 属性数量(数据集维度)
original_labels = list(df[columns[-1]]) # 原始标签def initialize_centroids(data, k):# 从数据集中随机选择k个点作为初始质心centers = data[np.random.choice(data.shape[0], k, replace=False)]return centersdef get_clusters(data, centroids):# 计算数据点与质心之间的距离,并将数据点分配给最近的质心distances = np.linalg.norm(data[:, np.newaxis] - centroids, axis=2)cluster_labels = np.argmin(distances, axis=1)return cluster_labelsdef update_centroids(data, cluster_labels, k):# 计算每个簇的新质心,即簇内数据点的均值new_centroids = np.array([data[cluster_labels == i].mean(axis=0) for i in range(k)])return new_centroidsdef k_means(data, k, T, epsilon):start = time.time() # 开始时间,计时# 初始化质心centroids = initialize_centroids(data, k)t = 0while t <= T:# 分配簇cluster_labels = get_clusters(data, centroids)# 更新质心new_centroids = update_centroids(data, cluster_labels, k)# 检查收敛条件if np.linalg.norm(new_centroids - centroids) < epsilon:breakcentroids = new_centroidsprint("第", t, "次迭代")t += 1print("用时:{0}".format(time.time() - start))return cluster_labels, centroids# 计算聚类指标
def clustering_indicators(labels_true, labels_pred):if type(labels_true[0]) != int:labels_true = LabelEncoder().fit_transform(df[columns[len(columns) - 1]]) # 如果数据集的标签为文本类型,把文本标签转换为数字标签f_measure = f1_score(labels_true, labels_pred, average='macro') # F值accuracy = accuracy_score(labels_true, labels_pred) # ACCnormalized_mutual_information = normalized_mutual_info_score(labels_true, labels_pred) # NMIrand_index = rand_score(labels_true, labels_pred) # RIARI = adjusted_rand_score(labels_true, labels_pred)return f_measure, accuracy, normalized_mutual_information, rand_index, ARI# 绘制聚类结果散点图
def draw_cluster(dataset, centers, labels):center_array = array(centers)if attributes > 2:dataset = PCA(n_components=2).fit_transform(dataset) # 如果属性数量大于2,降维center_array = PCA(n_components=2).fit_transform(center_array) # 如果属性数量大于2,降维else:dataset = array(dataset)# 做散点图label = array(labels)plt.scatter(dataset[:, 0], dataset[:, 1], marker='o', c='black', s=7) # 原图# plt.show()colors = np.array(["#FF0000", "#0000FF", "#00FF00", "#FFFF00", "#00FFFF", "#FF00FF", "#800000", "#008000", "#000080", "#808000","#800080", "#008080", "#444444", "#FFD700", "#008080"])# 循换打印k个簇,每个簇使用不同的颜色for i in range(k):plt.scatter(dataset[nonzero(label == i), 0], dataset[nonzero(label == i), 1], c=colors[i], s=7, marker='o')# plt.scatter(center_array[:, 0], center_array[:, 1], marker='x', color='m', s=30) # 聚类中心plt.show()if __name__ == "__main__":k = 3 # 聚类簇数T = 100 # 最大迭代数n = len(dataset) # 样本数epsilon = 1e-5# 预测全部数据# labels, centers = k_means(np.array(dataset), k, T, epsilon)clf = KMeans(n_clusters=k, max_iter=T, tol=epsilon)clf.fit(np.array(dataset)) # 分组centers = clf.cluster_centers_ # 两组数据点的中心点labels = clf.labels_ # 每个数据点所属分组# print(labels)F_measure, ACC, NMI, RI, ARI = clustering_indicators(original_labels, labels) # 计算聚类指标print("F_measure:", F_measure, "ACC:", ACC, "NMI", NMI, "RI", RI, "ARI", ARI)# print(membership)# print(centers)# print(dataset)draw_cluster(dataset, centers, labels=labels)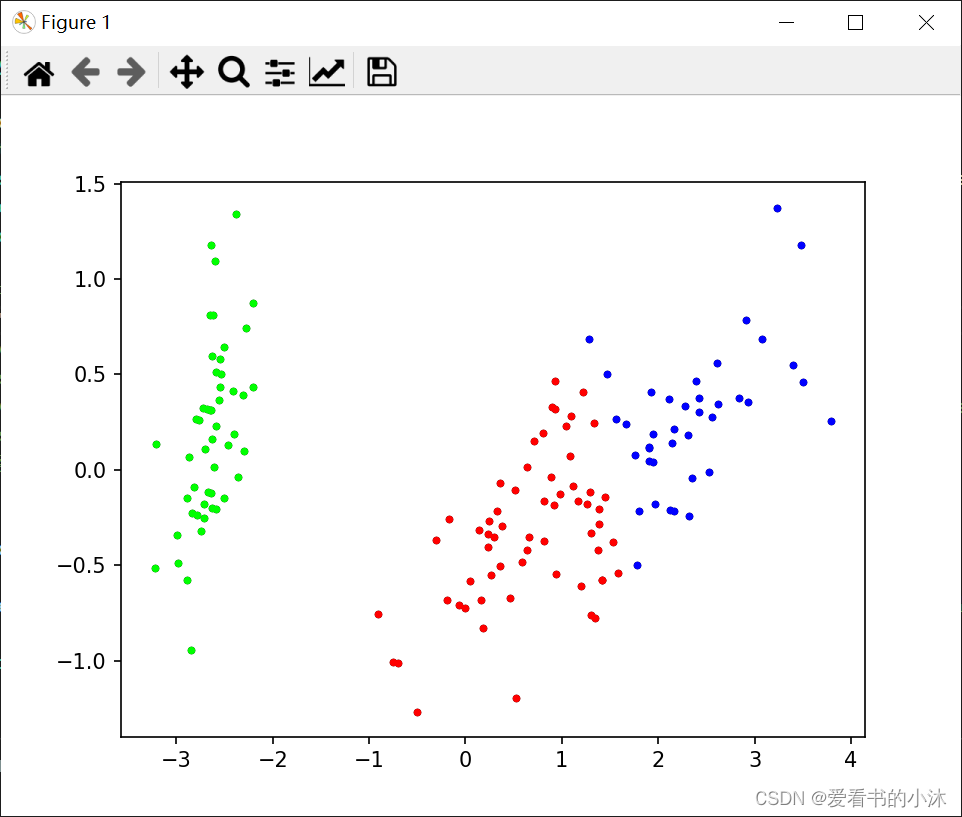
2.3 K-Means(nltk)
https://www.nltk.org/api/nltk.cluster.kmeans.html
K-means 聚类器从 k 个任意选择的均值开始,然后分配 具有最接近均值的聚类的每个向量。然后,它会重新计算 每个簇的均值,作为簇中向量的质心。这 重复该过程,直到群集成员身份稳定下来。这是一个 爬坡算法,可能收敛到局部最大值。因此, 聚类通常以随机的初始均值重复,并且大多数 选择常见的输出均值。
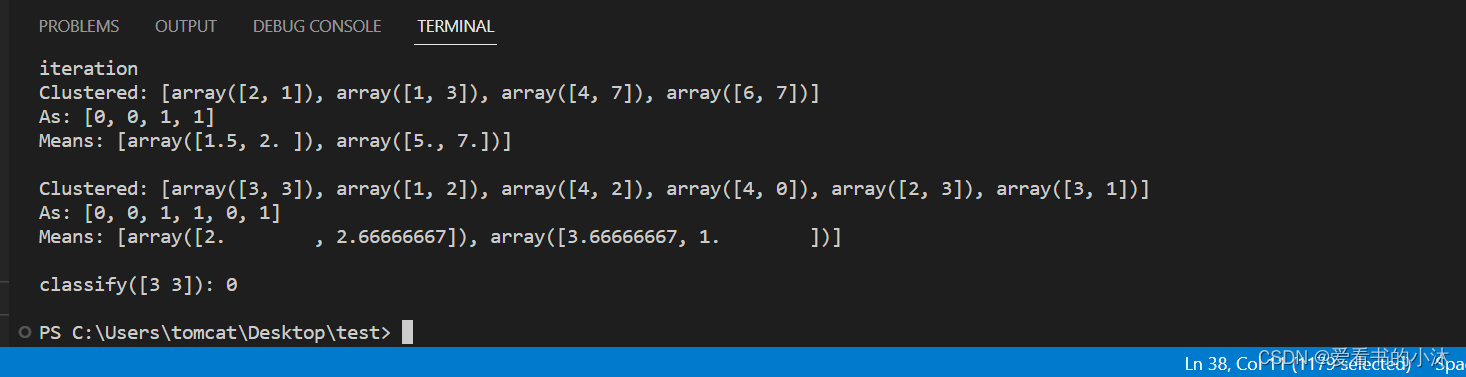
def demo():# example from figure 14.9, page 517, Manning and Schutzeimport numpyfrom nltk.cluster import KMeansClusterer, euclidean_distancevectors = [numpy.array(f) for f in [[2, 1], [1, 3], [4, 7], [6, 7]]]means = [[4, 3], [5, 5]]clusterer = KMeansClusterer(2, euclidean_distance, initial_means=means)clusters = clusterer.cluster(vectors, True, trace=True)print("Clustered:", vectors)print("As:", clusters)print("Means:", clusterer.means())print()vectors = [numpy.array(f) for f in [[3, 3], [1, 2], [4, 2], [4, 0], [2, 3], [3, 1]]]# test k-means using the euclidean distance metric, 2 means and repeat# clustering 10 times with random seedsclusterer = KMeansClusterer(2, euclidean_distance, repeats=10)clusters = clusterer.cluster(vectors, True)print("Clustered:", vectors)print("As:", clusters)print("Means:", clusterer.means())print()# classify a new vectorvector = numpy.array([3, 3])print("classify(%s):" % vector, end=" ")print(clusterer.classify(vector))print()if __name__ == "__main__":demo()
结语
如果您觉得该方法或代码有一点点用处,可以给作者点个赞,或打赏杯咖啡;╮( ̄▽ ̄)╭
如果您感觉方法或代码不咋地//(ㄒoㄒ)//,就在评论处留言,作者继续改进;o_O???
如果您需要相关功能的代码定制化开发,可以留言私信作者;(✿◡‿◡)
感谢各位大佬童鞋们的支持!( ´ ▽´ )ノ ( ´ ▽´)っ!!!

并在Pycharm中配置)

)
: Doris Join类型 - Colocation Join)










)


![[verilog] 免费开源的 verilog 仿真工具:icarus verilog](http://pic.xiahunao.cn/[verilog] 免费开源的 verilog 仿真工具:icarus verilog)
