目录
- 目标
- 网络编程关注的问题
- 连接的建立
- 连接的断开
- 消息的到达
- 消息发送完毕
- 网络 IO 职责
- 检测 IO
- 检测 io剖析
- 操作 IO
- 阻塞IO 和 非阻塞IO
- IO 多路复用
- epoll
- 结构以及接口
- reactor编程
- 连接建立
- 连接断开
- 数据到达
- 数据发送完毕
- reactor 应用:后续补充源码解析
- 单 reacrtor
- 多 reactor(one eventloop per thread)
- 多线程
- 多进程
目标
- 明白网络模块要处理那些事情
- reactor 是怎么处理这些事情的
- reactor 如何封装的
- 网络模块与业务逻辑的关系
- 如何优化 reactor
网络编程关注的问题
连接的建立
分为两种:
服务端处理接收客户端的连接;
服务端作为客户端连接第三方服务(如数据库)
int clientfd = accept(listenfd, addr, sz);
// 举例为非阻塞io,阻塞io成功直接返回0;
int connectfd = socket(AF_INET, SOCK_STREAM, 0);
int ret = connect(connectfd, (struct sockaddr
*)&addr, sizeof(addr));
// ret == -1 && errno == EINPROGRESS 正在建立连接
// ret == -1 && errno = EISCONN 连接建立成功
连接的断开
分为两种:
主动断开
被动断开
// 主动关闭
close(fd);
shutdown(fd, SHUT_RDWR);
// 主动关闭本地读端,对端写段关闭
shutdown(fd, SHUT_RD);
// 主动关闭本地写端,对端读段关闭
shutdown(fd, SHUT_WR);// 被动:读端关闭
// 有的网络编程需要支持半关闭状态
int n = read(fd, buf, sz);
if (n == 0) {close_read(fd);// write()// close(fd);
}// 被动:写端关闭
int n = write(fd, buf, sz);
if (n == -1 && errno == EPIPE) {close_write(fd);// close(fd);
}
消息的到达
从缓冲区中读取数据
int n = read(fd, buf, sz);
if (n < 0) { // n == -1if (errno == EINTR || errno == EWOULDBLOCK)break;close(fd);
} else if (n == 0) {close(fd);
} else {// 处理 buf
}消息发送完毕
往缓冲区中写数据
int n = write(fd, buf, dz);
if (n == -1) {if (errno == EINTR || errno == EWOULDBLOCK) {return;}close(fd);
}网络 IO 职责
检测 IO
io 函数本身可以检测 io的状态;但是只能检测一个 fd对应的状态;
io 多路复用可以同时检测多个 io的状态;
区别:
io 函数可以检测具体的状态,io 多路复用只能检测出可读、可写、错误、断开等笼统的事件
检测 io剖析
io 函数和系统调用中都有用到 检测 io。主要功能就是检测 io 是否就绪,如果对应到 socket 网络通信来说每个函数检测的部分如下:
acccept();//检测全连接队列是否有数据://第 1 次握手:将数据放到半连接队列//第 3 次握手:将数据放入全连接队列connect();//检测是否收到 ACK,收到 ACK 就代表 IO 就绪,连接成功//第 2 次握手成功,就表示 client 连接成功read = 0; //检测 buf 是否含有 EOF 标记//关闭连接时,会往对应的缓冲区写入 EOF,读到 EOF 就会返回 0write //就是把数据写到 send_buf 缓冲区中,至于数据什么时候写,以什么形式写,何时到达对端,都是根绝协议栈来决定的操作 IO
只能使用 io 函数来进行操作;分为两种操作方式:
阻塞 io
非阻塞 io
阻塞IO 和 非阻塞IO
- 阻塞在网络线程
- 连接的 fd阻塞属性决定了 io函数是否阻塞
- 具体差异在:io 函数在数据未到达时是否立刻返回
// 默认情况下,fd 是阻塞的,设置非阻塞的方法如下;
int flag = fcntl(fd, F_GETFL, 0);
fcntl(fd, F_SETFL, flag | O_NONBLOCK);详细分析可以看I/O详解与五种网络I/O模型
IO 多路复用
io 多路复用只负责检测io,不负责操作 io
int n = epoll_wait(epfd, evs, sz, timeout);
timeout = -1 一直阻塞直到网络事件到达;
imeout = 0 不管是否有事件就绪立刻返回;
timeout = 1000 最多等待 1 s,如果1 s内没有事件触发则返回;
详细分析可以看I/O详解与五种网络I/O模型
epoll
结构以及接口
struct eventpoll {// ...struct rb_root rbr; // 管理 epoll 监听的事件struct list_head rdllist; // 保存着 epoll_wait
返回满⾜条件的事件// ...
};
struct epitem {// ...struct rb_node rbn; // 红⿊树节点struct list_head rdllist; // 双向链表节点struct epoll_filefd ffd; // 事件句柄信息struct eventpoll *ep; // 指向所属的eventpoll对
象struct epoll_event event; // 注册的事件类型// ...
};
struct epoll_event {__uint32_t events; // epollin epollout
epollel(边缘触发)epoll_data_t data; // 保存 关联数据
};typedef union epoll_data {void *ptr;int fd;uint32_t u32;uint64_t u64;
}epoll_data_t;int epoll_create(int size);/**
op:
EPOLL_CTL_ADD
EPOLL_CTL_MOD
EPOLL_CTL_DELevent.events:
EPOLLIN 注册读事件
EPOLLOUT 注册写事件
EPOLLET 注册边缘触发模式,默认是水平触发
*/
int epoll_ctl(int epfd, int op, int fd, struct epoll_event* event);/**
events[i].events:
EPOLLIN 触发读事件
EPOLLOUT 触发写事件
EPOLLERR 连接发生错误
EPOLLRDHUP 连接读端关闭
EPOLLHUP 连接双端关闭
*/
int epoll_wait(int epfd, struct epoll_event*
events, int maxevents, int timeout);
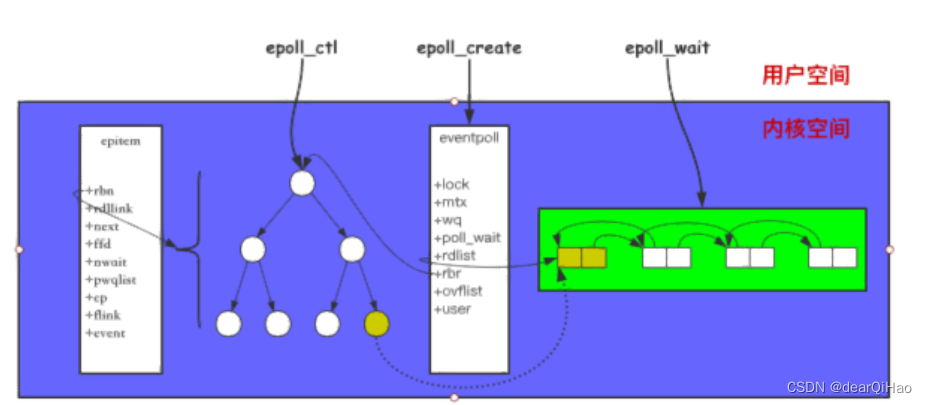
调用 epoll_create 会创建一个 epoll对象;
调用 epoll_ctl 添加到 epoll 中的事件都会与网卡驱动程序建立回调关系,相应事件触发是会调用回调函数(ep_poll_callback),将触发的事件拷贝到 rdlist 双向链表中;
调用 epoll_wait 将会把 rdlist 中就绪事件拷贝到用户态中;
reactor编程
reactor为什么要引入 IO多路复用?
Q: 什么是 IO 复用,IO 多路复用是否具有操作 具体连接的 IO功能?
A: IO 多路复用只有检测 IO 的功能,能检测多条连接是否 IO 就绪,但是不具备 IO 操作的功能,无法操作 IO 数据
Q: 为什么要把 IO 检测的功能丢给 IO 多路复用去做,而不是 IO 函数自己来做?
A: 主要是为了提升性能,因为在大部分情况下,大会部分连接是没有交互的。
提升性能的原因如下,就 IO 是否阻塞的情况进行分析:
- 阻塞 IO :若 IO 有自己检测,那么就代表每条 连接需要一条线程来处理
- 非阻塞 IO :每个 IO 都需要调用 while 循环在应用层检测
reactor 把对 IO 的处理转换成对事件的处理:
- 注册 IO 就绪事件,注册到 IO 多路复用之中。注册具体事件时,会绑定一个回调函数,当事件发生时调用该回调函数,并在回调函数中操作具体的 IO
- epoll_wait 收集事件,处理事件(通常是封装为事件循环)
reactor中用到了 IO 多路复用 和 非阻塞 IO,他们分别用到了 IO的哪种功能?
- IO 多路复用 :检测 IO
- 非阻塞 IO:操作 IO
reactor 为什么要搭配非阻塞 IO?
- 多线程环境:将一个 listen放到多个 epoll中处理,如果此时有三个县城响应了,但是只会有一个线程抢到执行权,其余的线程就会一直被阻塞
- 边缘触发:读事件出发时,如果 read 在一次事件中把 read_buf 读空后再 read,就会阻塞线程
- 用select产生的bug:当一个数据到达时,select会报告读事件,但是数据可能没有通过校验和检测——所以该事件会被丢弃。但此时 select 已经上报读事件了,此时如果用的是阻塞 IO 去读,就会造成阻塞线程
Q: 是不是 IO 多路复用一定要搭配 非阻塞 IO?
A: 不一定:例如 MySQL
连接建立
// 一、处理客户端的连接
// 1. 注册监听 listenfd 的读事件
struct epoll_event ev;
ev.events |= EPOLLIN;
epoll_ctl(efd, EPOLL_CTL_ADD, listenfd, &ev);
// 2. 当触发 listenfd 的读事件,调用 accept 接收新的连
接
int clientfd = accept(listenfd, addr, sz);
struct epoll_event ev;
ev.events |= EPOLLIN;
epoll_ctl(efd, EPOLL_CTL_ADD, clientfd, &ev);
// 二、处理连接第三方服务
// 1. 创建 socket 建立连接
int connectfd = socket(AF_INET, SOCK_STREAM, 0);
connect(connectfd, (struct sockaddr *)&addr,
sizeof(addr));
// 2. 注册监听 connectfd 的写事件
struct epoll_event ev;
ev.events |= EPOLLOUT;
epoll_ctl(efd, EPOLL_CTL_ADD, connectfd, &ev);
// 3. 当 connectfd 写事件被触发,连接建立成功
if (status == e_connecting && e->events &
EPOLLOUT) {status == e_connected;// 这里需要把写事件关闭epoll_ctl(epfd, EPOLL_CTL_DEL, connectfd,
NULL);
}连接断开
if (e->events & EPOLLRDHUP) {// 读端关闭close_read(fd);close(fd);
}
if (e->events & EPOLLHUP) {// 读写端都关闭close(fd);
}数据到达
// reactor 要用非阻塞io
// select
if (e->events & EPOLLIN) {while (1) {int n = read(fd, buf, sz);if (n < 0) {if (errno == EINTR)continue;if (errno == EWOULDBLOCK)break;close(fd);} else if (n == 0) {close_read(fd);// close(fd);}// 业务逻辑了}
}
数据发送完毕
int n = write(fd, buf, dz);
if (n == -1) {if (errno == EINTR)continue;if (errno == EWOULDBLOCK) {struct epoll_event ev;ev.events = EPOLLOUT;epoll_ctl(epfd, EPOLL_CTL_ADD, fd, &ev);return;}close(fd);
}
// ...
if (e->events & EPOLLOUT) {int n = write(fd, buf, sz);//...if (n == sz) {epoll_ctl(epfd, EPOLL_CTL_DEL, fd, NULL);}
}reactor 应用:后续补充源码解析
The reactor design pattern is an event handling pattern
(事件处理模式)for handling service requests delivered
concurrently to a service handler by one or more inputs
(处理一个或多个并发传递到服务端的服务请求). The service
handler then demultiplexes the incoming requests and
dispatches them synchronously (同步)to the associated
request handlers.
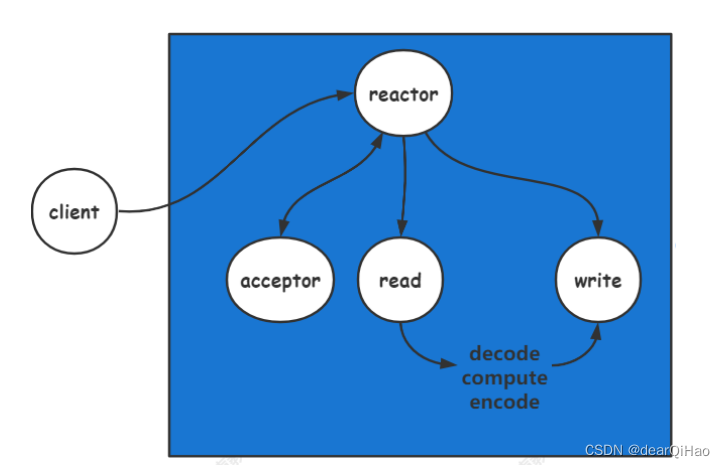
单 reacrtor
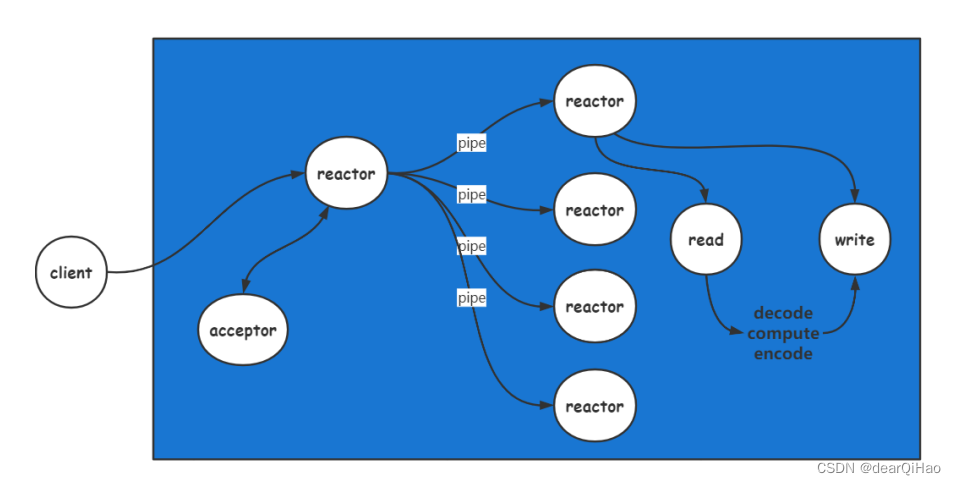
多 reactor(one eventloop per thread)
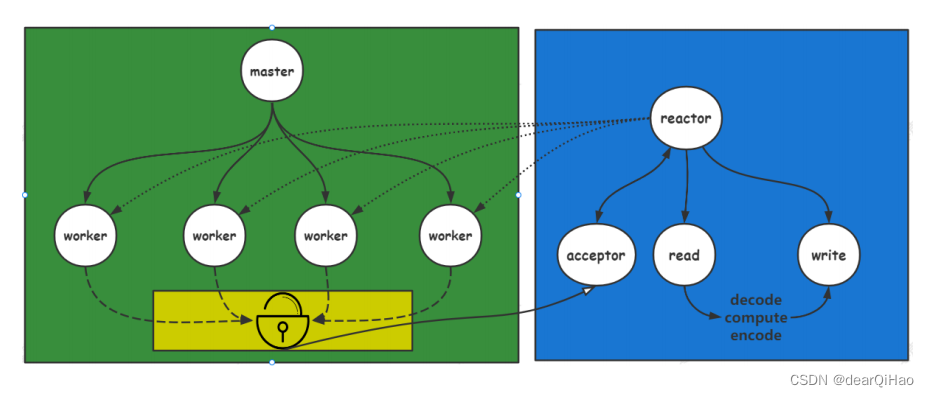
多线程
多进程

:HBase 对接 Hive)

附教程)






面试题 54:二叉搜索树的第 k 大节点)







![LSTM的记忆能力实验 [HBU]](http://pic.xiahunao.cn/LSTM的记忆能力实验 [HBU])
