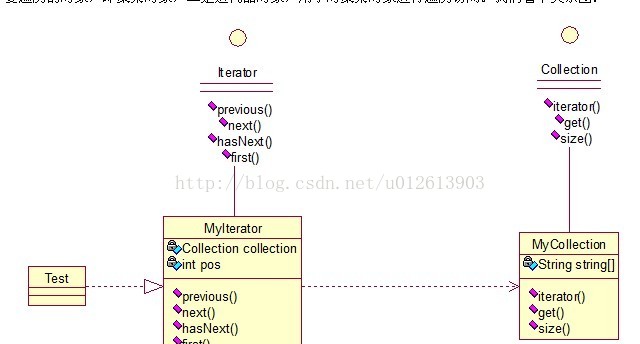
顾名思义,迭代器模式就是顺序访问聚集中的对象,一般来说,集合中非常常见,如果对集合类比较熟悉的话,理解本模式会十分轻松。这句话包含两层意思:一是需要遍历的对象,即聚集对象,二是迭代器对象,用于对聚集对象进行遍历访问。我们看下关系图:
public interface Collection {
public Iterator iterator();
/*取得集合元素*/
public Object get(int i);
/*取得集合大小*/
public int size();
}
- public interface Iterator {
- //前移
- public Object previous();
- //后移
- public Object next();
- public boolean hasNext();
- //取得第一个元素
- public Object first();
- }
- public class MyCollection implements Collection {
- public String string[] = {"A","B","C","D","E"};
- @Override
- public Iterator iterator() {
- return new MyIterator(this);
- }
- @Override
- public Object get(int i) {
- return string[i];
- }
- @Override
- public int size() {
- return string.length;
- }
- }
- public class MyIterator implements Iterator {
- private Collection collection;
- private int pos = -1;
- public MyIterator(Collection collection){
- this.collection = collection;
- }
- @Override
- public Object previous() {
- if(pos > 0){
- pos--;
- }
- return collection.get(pos);
- }
- @Override
- public Object next() {
- if(pos<collection.size()-1){
- pos++;
- }
- return collection.get(pos);
- }
- @Override
- public boolean hasNext() {
- if(pos<collection.size()-1){
- return true;
- }else{
- return false;
- }
- }
- @Override
- public Object first() {
- pos = 0;
- return collection.get(pos);
- }
- }
- public class Test {
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- Collection collection = new MyCollection();
- Iterator it = collection.iterator();
- while(it.hasNext()){
- System.out.println(it.next());
- }
- }
- }





)





)


)




