前言
目前用于**图像分割的**数据集,我目前接触到的用的比较多的有:
1 PASCAL VOC
2 COCO
3 YOLO
4 Halcon自己的格式(其实就是Halcon字典类型)
当前我涉及到计算机视觉中的数据集格式有,PASCAL VOC、COCO 和 YOLO 用于不同的目标检测和图像分割任务。以下是这三种数据集格式的介绍:
1. PASCAL VOC 格式:
PASCAL VOC(Visual Object Classes)是一个广泛使用的目标检测和图像分割数据集,其标注格式以XML文件的形式提供。以下是一个PASCAL VOC格式的示例(针对单个物体):
<annotation><folder>images</folder><filename>example.jpg</filename><source><database>PASCAL VOC</database></source><size><width>800</width><height>600</height><depth>3</depth></size><object><name>cat</name><pose>Unspecified</pose><truncated>0</truncated><difficult>0</difficult><bndbox><xmin>200</xmin><ymin>150</ymin><xmax>400</xmax><ymax>450</ymax></bndbox></object>
</annotation>
2. COCO 格式:
COCO(Common Objects in Context)是一个用于目标检测、分割和关键点估计的大规模数据集,其标注格式以JSON文件的形式提供。以下是一个COCO格式的示例(针对单个物体):
{"info": {},"images": [{"id": 1,"file_name": "example.jpg","width": 800,"height": 600,"depth": 3}],"annotations": [{"id": 1,"image_id": 1,"category_id": 1,"bbox": [200, 150, 200, 300],"area": 60000,"iscrowd": 0}],"categories": [{"id": 1,"name": "cat"}]
}
3. YOLO 格式:
YOLO(You Only Look Once)是一个目标检测算法,同时也有其特定的数据集格式。YOLO格式通常需要一个文本文件,其中每行描述了一张图像中的目标。以下是一个YOLO格式的示例(每行表示单个物体):
0 0.45 0.35 0.2 0.5
在此示例中,每行包含了类别索引和目标的归一化坐标信息(中心点坐标和宽高相对于图像尺寸的比例)。
请注意,这些示例仅为了演示目的,实际数据集文件可能包含更多图像和目标的标注信息。不同的数据集格式适用于不同的任务和算法,您在使用特定数据集时需要了解其相应的标注格式。
这几种格式,都是描述图片中的某个框框的位置,以及这个框框对应的类别。
背景
我现在手头有一个PASCAL VOC 格式的数据集,每张图片都有对应好的标记图片,我现在想用halcon去读取整个数据集。但是,halcon是有自己的标注工具的:MVTec Deep Learning Tool
有这个软件标注的图片,导出的数据集格式是:.hdict
那有没有办法,把 PASCAL VOC 直接转为 .hdict 格式呢?
PASCAL VOC 转 .hdict
PASCAL VOC 的格式类型,我们已经看到了,就是个XML解析这个XML不在话下,但是 .hdict这个文件是个二进制的文件,看不到其中的内容。
于是,我搜索全网,发现了一个 PASCAL VOC 转 .hdict 的一个halcon脚本,然后花了一块大洋买了下来,下载下来一看,问题不大,稍微改改果然能用:
*read_dict ('C:/Users/12820/Desktop/数据/分割.hdict', [], [], DictHandle)
* Image Acquisition 01: Code generated by Image Acquisition 01*read_dl_dataset_from_coco
*read_dlcreate_dict (NEWDictHandle1)
class_ids:=[0,1,2,3,4,5]
class_names:=['crazing', 'inclusion', 'patches', 'pitted_surface', 'rolled-in_scale', 'scratches']
image_dir:='images/'set_dict_tuple (NEWDictHandle1, 'class_ids', class_ids)
set_dict_tuple (NEWDictHandle1, 'class_names', class_names)
set_dict_tuple (NEWDictHandle1, 'image_dir', image_dir)list_files ('images/', ['files','follow_links','recursive'], ImageFiles)
tuple_regexp_select (ImageFiles, ['\\.(tif|tiff|gif|bmp|jpg|jpeg|jp2|png|pcx|pgm|ppm|pbm|xwd|ima|hobj)$','ignore_case'], ImageFiles)list_files ('labels/', ['files','follow_links','recursive'], xmladdress)
samples:=[]
for Index := 0 to |ImageFiles| - 1 by 1read_image (Image, ImageFiles[Index])open_file (xmladdress[Index], 'input', FileHandle)IsEof := falsebbox_row1:=[] bbox_col1:=[] bbox_row2:=[] bbox_col2:=[] bbox_label_id:=[]while (not(IsEof))fread_line (FileHandle, XmlElement, IsEof)if (IsEof)breakendiftuple_split (XmlElement, '<''>', Substrings)create_dict (image)if (Substrings[1]=='folder')floder:= Substrings[2] endif if (Substrings[1]=='filename')filename:= Substrings[2] endif *class_names:=['crazing', 'inclusion', 'patches', 'pitted_surface', 'rolled-in_scale', 'scratches']if (Substrings[1]=='name')if (Substrings[2]== class_names[0] )bbox_label_id:=[bbox_label_id,0]elseif (Substrings[2]==class_names[1])bbox_label_id:=[bbox_label_id,1]elseif (Substrings[2]==class_names[2])bbox_label_id:=[bbox_label_id,2]elseif (Substrings[2]==class_names[3])bbox_label_id:=[bbox_label_id,3]elseif (Substrings[2]==class_names[4])bbox_label_id:=[bbox_label_id,4]elseif (Substrings[2]==class_names[5])bbox_label_id:=[bbox_label_id,5]endifendifif (Substrings[1]=='xmin')bbox_col1:= [bbox_col1,Substrings[2]]tuple_number (bbox_col1, bbox_col1)endif if (Substrings[1]=='ymin')bbox_row1:= [bbox_row1,Substrings[2] ]tuple_number (bbox_row1, bbox_row1)endif if (Substrings[1]=='xmax')bbox_col2:=[bbox_col2, Substrings[2] ]tuple_number (bbox_col2, bbox_col2)endif if (Substrings[1]=='ymax')bbox_row2:=[bbox_row2, Substrings[2] ]tuple_number (bbox_row2, bbox_row2)endif endwhile* gen_rectangle1 (Rectangle,bbox_row1 , bbox_col1,bbox_row2 , bbox_col2)set_dict_tuple (image, 'image_id', Index+1)set_dict_tuple (image, 'image_file_name', floder+'/'+filename)set_dict_tuple (image, 'bbox_label_id', bbox_label_id)set_dict_tuple (image, 'bbox_row1', bbox_row1)set_dict_tuple (image, 'bbox_col1', bbox_col1)set_dict_tuple (image, 'bbox_row2', bbox_row2)set_dict_tuple (image, 'bbox_col2', bbox_col2)samples:=[samples,image]*stop()
endforset_dict_tuple (NEWDictHandle1, 'samples', samples)write_dict (NEWDictHandle1, '数据test.hdict', [], [])
看到最后一句:write_dict 才意识到,原来所谓的.hdict文件就是halcon里的字典格式啊!
虽然,这个脚本文件可以用,但是1800条数据转换下来,花费了将近半个小时,这能忍?
还有就是PASCAL VOC标注文件有点地方图片名称没带后缀导致,导入后图片无法在
Deep Learning Tool 中显示!所以,搞清楚原理之后,我还是自己写个工具才更省心啊:
HTuple NEWDict;
HOperatorSet.CreateDict(out NEWDict);List<int> class_ids = new List<int> { 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 };List<string> class_names = new List<string> { "crazing", "inclusion", "patches", "pitted_surface", "rolled-in_scale", "scratches" };string image_dir = "F:\\temp\\数据集格式转换测试\\images";//图片字典HTuple hv_image = new HTuple();HTuple hv_samples = new HTuple();HTuple hv_class_ids = new HTuple(class_ids.ToArray());HTuple hv_class_names = new HTuple(class_names.ToArray());HTuple hv_image_dir = new HTuple(image_dir);HOperatorSet.SetDictTuple(NEWDict, "class_ids", hv_class_ids);HOperatorSet.SetDictTuple(NEWDict, "class_names", hv_class_names);HOperatorSet.SetDictTuple(NEWDict, "image_dir", hv_image_dir);string[] imageFiles = Directory.GetFiles(image_dir, "*.*", SearchOption.AllDirectories);List<Dictionary<string, object>> samples = new List<Dictionary<string, object>>();int index = 0;string extension = "";foreach (string imagePath in imageFiles){HOperatorSet.CreateDict(out hv_image);string xmlPath = "D:/DATASET/yolo/NEU-DET/ANNOTATIONS/" + Path.GetFileNameWithoutExtension(imagePath) + ".xml";XDocument xdoc;using (StreamReader reader = new StreamReader(xmlPath)){string xmlContent = reader.ReadToEnd();xdoc = XDocument.Parse(xmlContent);// 现在可以使用xdoc进行XML解析操作}XElement xroot = xdoc.Root;//根节点List<int> bbox_label_ids = new List<int>();List<int> bbox_col1 = new List<int>();List<int> bbox_row1 = new List<int>();List<int> bbox_col2 = new List<int>();List<int> bbox_row2 = new List<int>();//----foldervar folder = xroot.Element("folder").Value;//----filenamevar filename = xroot.Element("filename").Value;if(Path.GetExtension(filename) != ""){extension = Path.GetExtension(filename);}else{if (extension != ""){filename += extension;}}//----获取object节点(一个xml中可能会有多个)var objectNodes = xroot.Descendants("object");foreach (var objectNode in objectNodes){//bndbox节点,包含xmin,ymin,xmax,ymaxXElement bndboxNode = objectNode.Element("bndbox");XElement xminNode = bndboxNode.Element("xmin");XElement yminNode = bndboxNode.Element("ymin");XElement xmaxNode = bndboxNode.Element("xmax");XElement ymaxNode = bndboxNode.Element("ymax");// 解析坐标值并添加到相应列表bbox_col1.Add(int.Parse(xminNode.Value));bbox_row1.Add(int.Parse(yminNode.Value));bbox_col2.Add(int.Parse(xmaxNode.Value));bbox_row2.Add(int.Parse(ymaxNode.Value));// 获取类别名称对应的编号,并添加到相应列表string className = objectNode.Element("name").Value;int id = class_names.IndexOf(className);bbox_label_ids.Add(id); }HOperatorSet.SetDictTuple(hv_image, "image_id", index + 1);HOperatorSet.SetDictTuple(hv_image, "image_file_name", (folder + "/") + filename);HOperatorSet.SetDictTuple(hv_image, "bbox_label_id", bbox_label_ids.ToArray());HOperatorSet.SetDictTuple(hv_image, "bbox_row1", bbox_row1.ToArray());HOperatorSet.SetDictTuple(hv_image, "bbox_col1", bbox_col1.ToArray());HOperatorSet.SetDictTuple(hv_image, "bbox_row2", bbox_row2.ToArray());HOperatorSet.SetDictTuple(hv_image, "bbox_col2", bbox_col2.ToArray());// hv_image添加到samplesusing (HDevDisposeHelper dh = new HDevDisposeHelper()){ HTuple ExpTmpLocalVar_samples = hv_samples.TupleConcat(hv_image);hv_samples.Dispose();hv_samples = ExpTmpLocalVar_samples; }index++;}HOperatorSet.SetDictTuple(NEWDict, "samples", hv_samples);HOperatorSet.WriteDict(NEWDict, "数据Csharp.hdict", new HTuple(), new HTuple());MessageBox.Show("转换完成");
这次使用XDocument方式解析,弹指间,转换就完成了!再次用Deep Learning Tool打开转换好的Csharp.hdict,这次就成功了
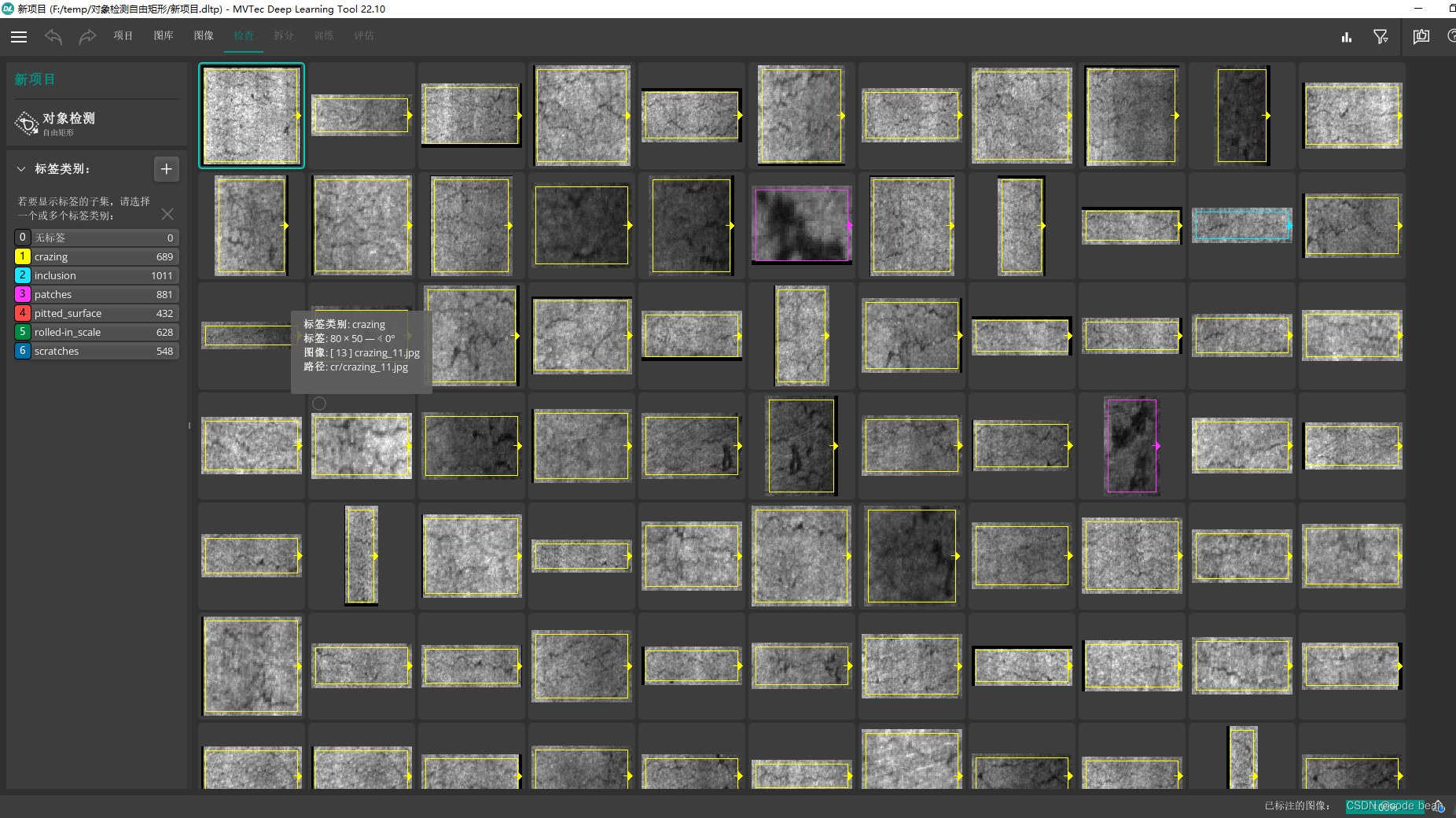
读取.hdict 格式的数据集
有了.hdict 这个格式的数据集,怎么用呢?
*读取数据集!!!这个就是深度学习工具标记的字典
read_dict (“xxxxx.hdict”, [], [], DLDataset)
应为它就是一个字典,所以直接使用read_dict就能读取数据集了!
还有,halcon除了自家的数据集之外,其实可以直接读取coco数据集:
read_dl_dataset_from_coco (FileExists, [], [], DLDataset1)
是不是很方便!
具体如何训练数据这些内容,后续持续输出,我们下一篇文件见!
附录
附送一个PASCAL VOC 转 YOLO的 python脚本!
import xml.etree.ElementTree as ET
import pickle
import os
from os import listdir, getcwd
from os.path import join
import globclasses = ["crazing", "inclusion", "patches", "pitted_surface", "rolled-in_scale", "scratches"]def convert(size, box):dw = 1./size[0]dh = 1./size[1]x = (box[0] + box[1])/2.0y = (box[2] + box[3])/2.0w = box[1] - box[0]h = box[3] - box[2]x = x*dww = w*dwy = y*dhh = h*dhreturn (x,y,w,h)def convert_annotation(image_name):in_file = open('./ANNOTATIONS/'+image_name[:-3]+'xml')out_file = open('./LABELS/'+image_name[:-3]+'txt','w')tree=ET.parse(in_file)root = tree.getroot()size = root.find('size')w = int(size.find('width').text)h = int(size.find('height').text)for obj in root.iter('object'):cls = obj.find('name').textif cls not in classes:print(cls)continuecls_id = classes.index(cls)xmlbox = obj.find('bndbox')b = (float(xmlbox.find('xmin').text), float(xmlbox.find('xmax').text), float(xmlbox.find('ymin').text), float(xmlbox.find('ymax').text))bb = convert((w,h), b)out_file.write(str(cls_id) + " " + " ".join([str(a) for a in bb]) + '\n')wd = getcwd()if __name__ == '__main__':for image_path in glob.glob("./IMAGES/*.jpg"):image_name = image_path.split('\\')[-1]#print(image_path)convert_annotation(image_name)



:flink概述,flink集群搭建,flink中执行任务,单节点、yarn运行模式,三种部署模式的具体实现)
![[当前就业]2023年8月25日-计算机视觉就业现状分析](http://pic.xiahunao.cn/[当前就业]2023年8月25日-计算机视觉就业现状分析)





)

)

)
event模块)


RGB屏幕 LTDC)
