设计模式之模板方法模式:
定义一个操作中的算法的骨架,而将一些步骤延迟到子类中。模板方法使得子类可以不改变一个算法的结构即可重定义该算法的某些特定步骤。
简而言之就是:父类定义了骨架(调用哪些方法及其顺序),某些特定的方法由具体的子类来实现。
所以呢?在父类模板方法中是有两类方法的:
- 共同的方法:所有子类都必须用到的方法,类似于定义了一个框架,通常不用abstract而是final来修饰,防止子类重写,像下面的play方法
- 不同的方法:子类需要重写或者覆盖的方法,这种方法也分为两种:
1). 抽象方法:父类是抽象方法,子类必须实现的,如下面的startGame,endGame方法;
2). 钩子方法:父类中是一个空方法,子类继承的时候默认也是空的,这个方法有什么用呢?子类可以通过这个方法来自定义自己的其他一些步骤和过程,从而达到控制父类的目的。
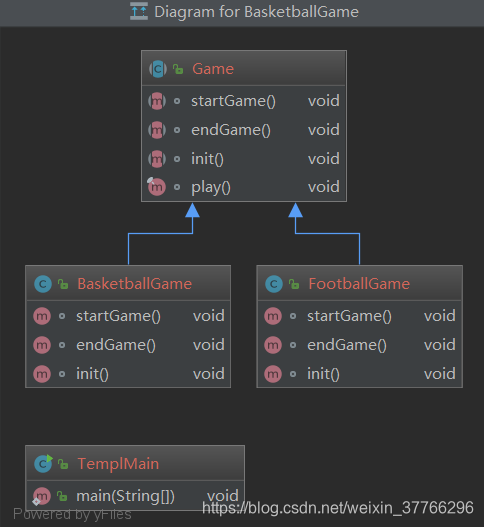
我们将创建一个定义操作的 Game 抽象类,其中,模板方法设置为 final,这样它就不会被重写。BasketballGame和 FootballGame 是扩展了 Game 的实体类,它们重写了抽象类的方法。
1. 创建抽象类Game:
public abstract class Game {abstract void startGame();abstract void endGame();abstract void init();final void play(){init();startGame();endGame();}
}
2. 创建扩展了上述类的实体类:
public class FootballGame extends Game {@Overridevoid startGame() {System.out.println("start football");}@Overridevoid endGame() {System.out.println("end football");}@Overridevoid init() {System.out.println("init football");}
}
public class BasketballGame extends Game {@Overridevoid startGame() {System.out.println("start basketball");}@Overridevoid endGame() {System.out.println("end basketball");}@Overridevoid init() {System.out.println("init basketball");}
}
3. 使用测试类测试:
public class TemplMain {public static void main(String[] args) {Game game = new FootballGame();//这样如果你想要改变其他球类,只需要换成下面这种形式,其他不用改变//Game game = new BasketballGame();game.play();}
}
再升级一下,举另一个例子:
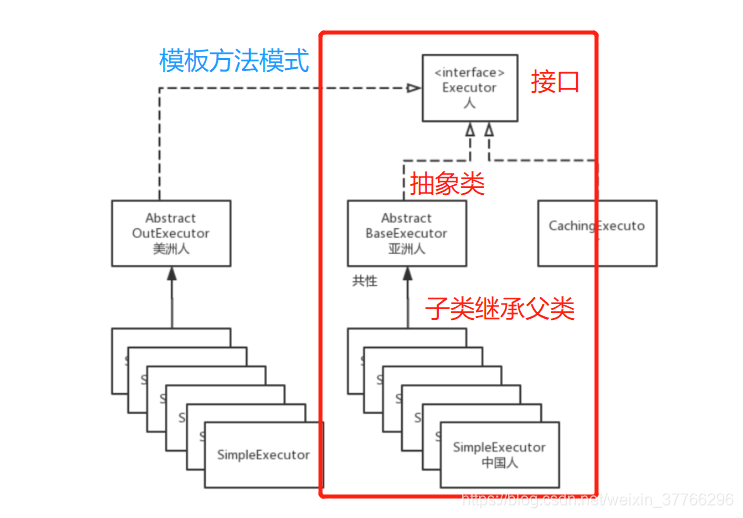
接口描述的是一种共性,一种动作action;
抽象类描述的是一个模板,一个特定的过程;
而子类则是可以根据自己的需要定制自己的过程。
不过,这样做的好处又是什么呢?
- 将族群进行隔离,像上面的图一样,我们可以将不同种类的人,美洲人,亚洲人进行隔离,而不互相影响;
- 可以将一些日志和共性的动作很好的分离,规范子类的动作。
其实我们在一些框架,如spring,mybatis等都可以看到模板方法模式的影子,下面简单举一下例子:
像mybatis的Executor接口:
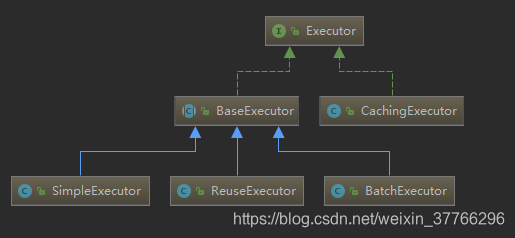
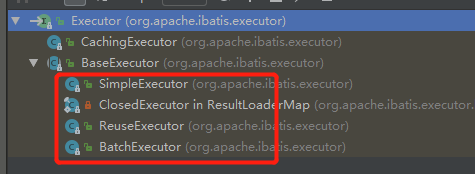
你就可以很明显的看到这种模式:
spring中的模板方法模式:
spring模板方法我来摘抄一些重点给大家看看:
下面的代码展示了Spring IOC容器初始化时运用到的模板方法模式。(截取部分关键代码)
1、首先定义一个接口ConfigurableApplicationContext,声明模板方法refresh
public interface ConfigurableApplicationContext extends ApplicationContext, Lifecycle, Closeable {/**声明了一个模板方法*/void refresh() throws BeansException, IllegalStateException;
}
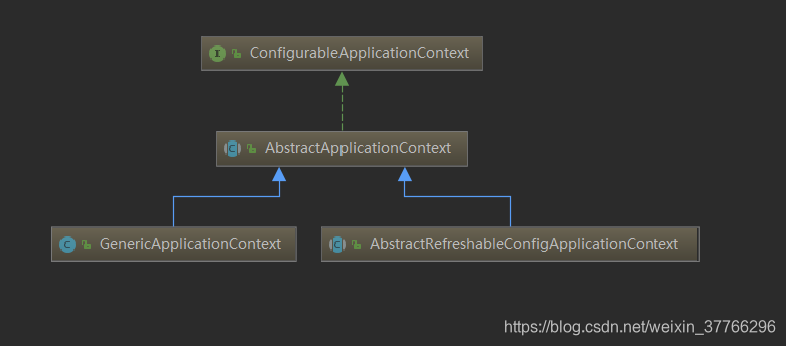
2、抽象类AbstractApplicationContext实现了接口,主要实现了模板方法refresh(这个方法很重要,是各种IOC容器初始化的入口)的逻辑:
public abstract class AbstractApplicationContext extends DefaultResourceLoaderimplements ConfigurableApplicationContext, DisposableBean {/**模板方法的具体实现*/public void refresh() throws BeansException, IllegalStateException {synchronized (this.startupShutdownMonitor) {// Prepare this context for refreshing.prepareRefresh();//注意这个方法是,里面调用了两个抽象方法refreshBeanFactory、getBeanFactory// Tell the subclass to refresh the internal bean factory.ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = obtainFreshBeanFactory();// Prepare the bean factory for use in this context.prepareBeanFactory(beanFactory);try {//注意这个方法是钩子方法,点进去父类看可以发现是空的// Allows post-processing of the bean factory in context subclasses.postProcessBeanFactory(beanFactory);// Invoke factory processors registered as beans in the context.invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(beanFactory);// Register bean processors that intercept bean creation.registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory);// Initialize message source for this context.initMessageSource();// Initialize event multicaster for this context.initApplicationEventMulticaster();//注意这个方法是钩子方法// Initialize other special beans in specific context subclasses.onRefresh();// Check for listener beans and register them.registerListeners();// Instantiate all remaining (non-lazy-init) singletons.finishBeanFactoryInitialization(beanFactory);// Last step: publish corresponding event.finishRefresh();}catch (BeansException ex) {// Destroy already created singletons to avoid dangling resources.destroyBeans();// Reset 'active' flag.cancelRefresh(ex);// Propagate exception to caller.throw ex;}}}
}
这里最主要有一个抽象方法obtainFreshBeanFactory、两个钩子方法postProcessBeanFactory和onRefresh,看看他们在类中的定义
看看获取Spring容器的抽象方法:
/**其实他内部只调用了两个抽象方法**/ protected ConfigurableListableBeanFactory obtainFreshBeanFactory() {refreshBeanFactory();ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = getBeanFactory();if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {logger.debug("Bean factory for " + getDisplayName() + ": " + beanFactory);}return beanFactory;}//上面两个方法就是下面这两个方法,可以看到他们都是抽象方法,等待具体的子类去实现protected abstract void refreshBeanFactory() throws BeansException, IllegalStateException;public abstract ConfigurableListableBeanFactory getBeanFactory() throws IllegalStateException;
3、具体实现的子类,实现了抽象方法getBeanFactory的子类有:
AbstractRefreshableApplicationContext:
public abstract class AbstractRefreshableApplicationContext extends AbstractApplicationContext {@Overridepublic final ConfigurableListableBeanFactory getBeanFactory() {synchronized (this.beanFactoryMonitor) {if (this.beanFactory == null) {throw new IllegalStateException("BeanFactory not initialized or already closed - " +"call 'refresh' before accessing beans via the ApplicationContext");}//这里的this.beanFactory在另一个抽象方法refreshBeanFactory的设置的return this.beanFactory;}}
}
GenericApplicationContext:
public class GenericApplicationContext extends AbstractApplicationContext implements BeanDefinitionRegistry {@Overridepublic final ConfigurableListableBeanFactory getBeanFactory() {//同样这里的this.beanFactory在另一个抽象方法中设置 return this.beanFactory;}
}
大家有空可以自己进去看看里面的源码!里面真是高深莫测!








、Class.class、getClass() 区别)









闪退导致EGit插件异常)
