引言
上一篇博客《XML模板解析————Dom4j解析xml案例分析》简单讲解了关于xml模板的解析,使用到了dom4j,这篇文章其实算是个姊妹篇,都是对于目前工作中的一些任务,如xml、json相互解析所涉及到的知识。
但是相对于xml而言,我更希望通过这篇博客能够稍微全面的学习一下jackson。因为之前用过的相关类库是国产的fastjson,虽然简单的操作还可以,但是最近发现远比jackson的功能还是差远了。虽然fastjson在性能方面上较为优秀,但是jackson本身非常稳定,并且功能相当齐全,历史也较为久远,而且jackson也是Spring Boot对于json解析的默认推荐。如果你的项目是Spring Boot,不需要引入任何的额外配置即可完成对json的处理操作,真是又强大,又好用。
一、ObjectMapper类
ObjectMapper类是Jackson库的主要类。它提供了一些功能将Java对象匹配JSON结构,反之亦然。它使用JsonParser和JsonGenerator的实例实现JSON实际的读/写。
ObjectMapper是可以反复使用的对象。
二、JSON字符串转POJO对象
@Testpublic void jsonStrToJavaBean() throws JsonParseException, JsonMappingException, IOException {String stuJsonStr = "{\"name\" : \"Tom\", \"age\" : 25}";ObjectMapper mapper = new ObjectMapper();Student stu = mapper.readValue(stuJsonStr, Student.class);System.out.println(stu);String stuStr = mapper.writeValueAsString(stu);System.out.println(stuStr);}执行结果:
com.group.coursesystem.util.JsonTest$Student@167fdd33
{"name":"Tom","age":25}三、对象序列化
对象序列化指的是将POJO对象保存到文件中,文件以".json"结尾,并且要能够从json文件中读出对象。
将对象序列化到json文件中:
@Testpublic void convertBeanAndJsonFile() throws JsonGenerationException, JsonMappingException, IOException {ObjectMapper mapper = new ObjectMapper();Student stu = new Student("Milly", 23);mapper.writeValue(new File(stu.getName() + ".json"), stu);}执行结果:
![]()
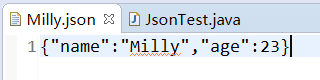
将json文件读出到Bean中:
@Testpublic void jsonFileToBean() throws JsonParseException, JsonMappingException, IOException {ObjectMapper mapper = new ObjectMapper();Student stu = mapper.readValue(new File("Milly.json"), Student.class);System.out.println(stu);}执行结果:
[name = Milly, age = 23]
四、数据绑定
Jackson数据绑定分为简单数据绑定和完全数据绑定。
4.1 简单数据绑定
简单数据绑定是指JSON映射到Java核心数据类型,如String 、Map、List等。
| JSON类型 | Java类型 |
| object | LinkedHashMap<String,Object> |
| array | ArrayList<Object> |
| string | String |
| complete number | Integer, Long or BigInteger |
| fractional number | Double / BigDecimal |
| true | false | Boolean |
| null | null |
示例代码:
@Testpublic void simpleDataBind() throws JsonGenerationException, JsonMappingException, IOException {ObjectMapper mapper = new ObjectMapper();boolean isStudent = true;int[] nums = {1, 3, 5, 7, 9};Student Jerry = new Student("Jerry", 26);Map<String, Student> stuMap = new HashMap<>();stuMap.put("studentObj", Jerry);Map<String, Object> dataMap = new HashMap<>();dataMap.put("studentName", Jerry.getName());dataMap.put("studentAge", Jerry.getAge());dataMap.put("Jerry", Jerry);dataMap.put("stuMap", stuMap);dataMap.put("nums", nums);dataMap.put("isStudent", isStudent);// -----------------序列化为json文件------------------mapper.writeValue(new File("dataMap.json"), dataMap);// -------------------从json文件中读出各个对象----------------Map<String, Object> readDataMap = mapper.readValue(new File("dataMap.json"), Map.class);System.out.println(readDataMap);System.out.println(readDataMap.get("Jerry"));System.out.println(readDataMap.get("stuMap"));System.out.println(readDataMap.get("nums"));System.out.println(readDataMap.get("isStudent"));}执行结果:
dataMap.json文件内容(原始形式为排列成一行,下图为原数据手动格式化后的结果):
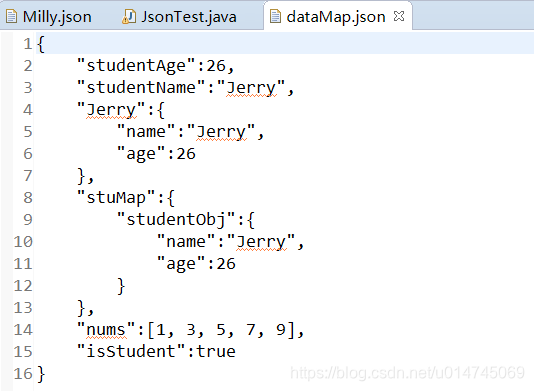
控制台输出:

4.2 完全数据绑定
完全数据绑定指JSON映射到任何Java对象。
参考二、三节。

、Class.class、getClass() 区别)









闪退导致EGit插件异常)







