简介
PrintStream继承了FilterOutputStream.是"装饰类"的一种,所以属于字节流体系中(与PrintStream相似的流PrintWriter继承于Writer,属于字符流体系中),为其他的输出流添加功能.使它们能够方便打印各种数据值的表示形式.此外,值得注意的是:
- 与其他流不同的是,PrintStream流永远不会抛出异常.因为做了try{}catch(){}会将异常捕获,出现异常情况会在内部设置标识,通过checkError()获取此标识.
- PrintStream流有自动刷新机制,例如当向PrintStream流中写入一个字节数组后自动调用flush()方法.
PrintStream流打印的字符通过平台默认的编码方式转换成字节,在写入的是字符,而不是字节的情况下,应该使用PrintWriter.PrintStream流中基本所有的print(Object obj)重载方法和println(Object obj)重载方法都是通过将对应数据先转换成字符串,然后调用write()方法写到底层输出流中.常见用到PrintStream流:System.out就被包装成PrintStream流,System.err也是PrintStream流,注意System.in不是PrintStream,是没有包装过的OutputStream.所以System.in不能直接使用.
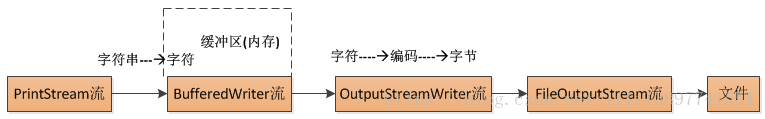
PrintStream流不是直接将数据写到文件的流,需要传入底层输出流out,而且要实现指定编码方式,需要中间流OutputStreamWriter,OutputStreamWriter流实现了字符流以指定编码方式转换成字节流.此外为了提高写入文件的效率,使用到了字符缓冲流BufferWriter.写入PrintStream流的数据怎么写到文件中.需要先了解一下数据读取和写入的流程.
1.数据从流写到文件过程
输出流----->缓冲流----->转化流----->文件流------>文件.
2.数据从文件到流的过程
文件----->文件流----->转化流----->缓冲流----->输入流.
那么从PrintStream流写到文件的过程是:
PrintStream介绍
1.构造方法
public PrintStream(OutputStream out) {}
public PrintStream(OutputStream out, boolean autoFlush) {}
public PrintStream(OutputStream out, boolean autoFlush, String encoding){}
public PrintStream(String fileName) {}
public PrintStream(String fileName, String csn){}
public PrintStream(File file){}
public PrintStream(File file, String csn){}
- 创建了默认编码方式的PrintStream流,字节输出流out作为PrintStream流的输出流,不自动刷新.
- 创建默认编码方式的PrintStream流,字节输出流out作为PrintStream流的输出流,传入是否自动刷新的参数autoFlush.
- 创建了指定编码名称encoding的PrintStream,字节输出流out作为PrintStream流的输出流.传入是否自动刷新的参数autoFlush.
- 创建了指定文件名称,默认字符编码方式的PrintStream流,FileOutputStream流作为PrintStream流的输出流.不自动刷新.
- 创建指定了文件名称和字符编码名称csn的PrintStream流,FileOutputStream作为PrintStream流的输出流.不自动刷新.
- 创建指定文件对象File和默认编码方式的PrintStream流,FileOutputStream作为PrintStream流的输出流.不自动刷新.
- 创建指定文件对象File和编码名称csn的PrintStream流,FileOutputStream作为PrintStream流的输出流.不自动刷新.
2.内部变量
private final boolean autoFlush;
private boolean trouble = false;
private Formatter formatter;
private BufferedWriter textOut;
private OutputStreamWriter charOut;
- autoFlush----是否自动刷新缓冲区.
- trouble----是否抛出异常的内部标识.当PrintStream流内部抛出异常时会捕获异常,然后将trouble的值设置成true.
- formatter----用于数据格式化的对象Formatter.
- textOut,charOut----PrintStream流本身不具备指定编码功能,BufferedWriter提供了缓冲数据的功能,而OutputStreamWriter提供了按照指定编码方法将字符转化成字节的功能.
3.内部方法.
public void flush() {}
public void close() {}
public boolean checkError(){}
public void write(int b){}
public void write(byte buf[], int off, int len){}
public PrintStream printf(String format, Object ... args){}
public PrintStream printf(Locale l, String format, Object ... args){}
public PrintStream format(String format, Object ... args){}
public PrintStream format(Locale l, String format, Object ... args){}
public PrintStream append(CharSequence csq){}
public PrintStream append(CharSequence csq, int start, int end){}
public PrintStream append(char c){}
public void print(boolean b){}
public void print(char c) {}
public void print(int i) {}
public void print(long l) {}
public void print(float f) {}
public void print(double d) {}
public void print(char s[]) {}
public void print(String s) {}
public void print(Object obj) {}
public void println() {}
public void println(boolean x) {}
public void println(char x){}
public void println(int x) {}
public void println(long x) {}
public void println(float x) {}
public void println(double x) {}
public void println(char x[]) {}
public void println(String x) {}
public void println(Object x) {}
- flush()----刷新流,将缓冲的数据写到底层输出流中.
- close()—关闭流,释放关联的资源.
- checkError()—检查流中异常状态,如果PrintStream流中有异常抛出,返回true.
- write(int b)----将单个字节b写到PrintStream流中.
- write(byte buf[] ,int off,int len)----将字节数组buf中off位置开始,len个字节写到PrintStream流中.
- printf(String format, Object … args)----将数据args按照默认的Locale值和format格式进行格式化后写到PrintStream流中,方法执行等同于out.format(format, args)
- printf(Locale l, String format, Object … args)----将数据args根据Locale值和format格式进行格式化后写到PrintStream输出流中,方法执行等同于out.printf(l, format,args).
- format(String format, Object … args)----根据默认的Locale值和format格式来格式化数据args.
- format(Locale l, String format, Object … args)----将数据args根据Locale值和format格式进行格式化.
- append(CharSequence csq, int start, int end)----将字符序列csq中start(包含)位置到end(不包含)之间的子字符序列添加到PrintStream输出流中,此方法执行等同于out.print(csq.subSequence(start, end).toString()).
- append(char c)----将单个字符添加到PrintStream输出流中.此方法执行等同于out.print©.
其他的print(Object obj)的重载方法与println(Object obj)的重载方法总结如下,两个区别是println(Object obj)在写完数据后,会写入一个换行符.而这两类方法写入数据时都会先将数据转成字符串,然后调用底层输出流写到文件中(比如boolean类型的数据true,会先转成字符串"true").此两类方法都将写入数据转化成了字符串,所以实际调用的方法是write(String s).
| 修饰符 | 不写入换行的方法 | 写入换行的方法(写入数据+换行符) | 功能 |
|---|---|---|---|
| public | void print(boolean b){} | void println(boolean b){} | 将boolean类型数据对应字符串写到PrintStream流中 |
| public | void print(char c){} | void println(char c){} | 将char类型数据对应字符串写到PrintStream流中 |
| public | void print(int i) {} | void println(int i) {} | 将int类型数据对应字符串写到PrintStream流中 |
| public | void print(long l) {} | void println(long l) {} | 将long类型数据对应字符串写到PrintStream流中 |
| public | void print(float f) {} | void println(float f) {} | 将float类型数据对应字符串写到PrintStream流中 |
| public | void print(double d) {} | void println(double d) {} | 将double类型数据对应字符串写到PrintStream流中 |
| public | void print(char s[]) {} | void println(char s[]) {} | 将字符数组写到PrintStream流中 |
| public | void print(String s) {} | void println(String s) {} | 将字符串s写到PrintStream流中 |
| public | void print(Object obj) {} | void println(Object obj) {} | 将对象Obj对应字符串写到PrintStream流中 |
| public | - | void println() {} | 将换行符写到PrintStream流中 |
PrintStream案例
public class PrintStreamDemo {public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {final String fileName = "D:\\java.txt";File file = new File(fileName);testPrintMethod(fileName, file);testOtherMethod(fileName,file);}private static void testOtherMethod(String fileName,File file) throws IOException {PrintStream ps = new PrintStream(fileName);ps.write("helloworld".getBytes());ps.println();ps.format("文件名称:%s", file.getName());ps.println();ps.write(0x41);ps.append("abcde");ps.close();}private static void testPrintMethod(final String fileName, File file) throws FileNotFoundException {PrintStream ps = new PrintStream(new FileOutputStream(fileName));ps.println('a');ps.println("hello");ps.println(2345);ps.print(3.1415);ps.println();//写入换行符.ps.printf("文件名称:%s,是否可读:%s", file.getName(),file.canRead());ps.println();ps.close();}
}
运行结果:
testPrintMethod结果:
testOtherMethod的结果:
PrintStream源码分析
public class PrintStream extends FilterOutputStream implements Appendable, Closeable
{//是否自动刷新缓冲区.private final boolean autoFlush;//是否抛出异常的内部标识.当PrintStream流内部抛出异常时会捕获异常,然后将trouble的值设置成true.private boolean trouble = false;//用于数据格式化的对象Formatter.private Formatter formatter;//OutputStreamWriter转化类,实现了编码方式,将字符转化字节.//BufferWriter实现了数据的缓冲.//输出流out是将内存中数据写到文件中./** 所以三个流的转化方式,将数据写到文件中的流程是:* 字符 缓冲 编码成字节 字节* PrintStream---->BufferWriter--->OutputStreamWriter---->FileOutputStream---->文件.* */private BufferedWriter textOut;private OutputStreamWriter charOut;//判断对象是否创建.private static <T> T requireNonNull(T obj, String message) {if (obj == null)throw new NullPointerException(message);return obj;}//根据字符编码名称返回Chatset对象.private static Charset toCharset(String csn)throws UnsupportedEncodingException{requireNonNull(csn, "charsetName");try {return Charset.forName(csn);} catch (IllegalCharsetNameException|UnsupportedCharsetException unused) {// UnsupportedEncodingException should be thrownthrow new UnsupportedEncodingException(csn);}}/*** 私有构造方法,创建的编码方式为charset的PrintStream,输出流out作为PrintStream流的输出流,* 传入是否自动刷新的参数autoFlush*/private PrintStream(boolean autoFlush, OutputStream out) {super(out);this.autoFlush = autoFlush;this.charOut = new OutputStreamWriter(this);this.textOut = new BufferedWriter(charOut);}private PrintStream(boolean autoFlush, OutputStream out, Charset charset) {super(out);this.autoFlush = autoFlush;this.charOut = new OutputStreamWriter(this, charset);this.textOut = new BufferedWriter(charOut);}private PrintStream(boolean autoFlush, Charset charset, OutputStream out)throws UnsupportedEncodingException{this(autoFlush, out, charset);}//创建了默认编码方式的PrintStream流,输出流out作为PrintStream流的输出流,不自动刷新.public PrintStream(OutputStream out) {this(out, false);}//创建默认编码方式的PrintStream流,输出流out作为PrintStream流的输出流,传入是否自动刷新的参数autoFlush.public PrintStream(OutputStream out, boolean autoFlush) {this(autoFlush, requireNonNull(out, "Null output stream"));}//创建了指定编码方式encoding的PrintStream,输出流out作为PrintStream流的输出流.传入是否自动刷新的参数autoFlush.public PrintStream(OutputStream out, boolean autoFlush, String encoding)throws UnsupportedEncodingException{this(autoFlush,requireNonNull(out, "Null output stream"),toCharset(encoding));}//创建了指定文件名称,默认字符编码方式的PrintStream流,FileOutputStream流作为PrintStream流的输出流.不自动刷新public PrintStream(String fileName) throws FileNotFoundException {this(false, new FileOutputStream(fileName));}//创建指定了文件名称和字符编码名称csn的PrintStream流,FileOutputStream作为PrintStream流的输出流.不自动刷新public PrintStream(String fileName, String csn)throws FileNotFoundException, UnsupportedEncodingException{this(false, toCharset(csn), new FileOutputStream(fileName));}//创建指定文件对象File和默认编码方式的PrintStream流,FileOutputStream作为PrintStream流的输出流.不自动刷新.public PrintStream(File file) throws FileNotFoundException {this(false, new FileOutputStream(file));}//创建指定文件对象File和编码名称csn的PrintStream流,FileOutputStream作为PrintStream流的输出流.不自动刷新.public PrintStream(File file, String csn)throws FileNotFoundException, UnsupportedEncodingException{// ensure charset is checked before the file is openedthis(false, toCharset(csn), new FileOutputStream(file));}//确保流没有关闭.private void ensureOpen() throws IOException {if (out == null)throw new IOException("Stream closed");}//刷新流,调用flush()会将缓冲数据写到底层输出流中.public void flush() {synchronized (this) {try {ensureOpen();out.flush();}catch (IOException x) {trouble = true;}}}private boolean closing = false; /* To avoid recursive closing *///关闭流,释放关联资源.public void close() {synchronized (this) {if (! closing) {closing = true;try {textOut.close();out.close();}catch (IOException x) {trouble = true;}textOut = null;charOut = null;out = null;}}}//刷新流,检查异常状态,如果底层输出流抛出异常,将会返回true.public boolean checkError() {if (out != null)flush();if (out instanceof java.io.PrintStream) {PrintStream ps = (PrintStream) out;return ps.checkError();}return trouble;}//设置流的异常状态.protected void setError() {trouble = true;}//清除流的异常状态protected void clearError() {trouble = false;}//将单个字节b写到PrintStream流中.public void write(int b) {try {synchronized (this) {ensureOpen();out.write(b);if ((b == '\n') && autoFlush)out.flush();}}catch (InterruptedIOException x) {Thread.currentThread().interrupt();}catch (IOException x) {trouble = true;}}//将字节数组buf中off位置开始,len个字节写到PrintStream流中.public void write(byte buf[], int off, int len) {try {synchronized (this) {ensureOpen();out.write(buf, off, len);if (autoFlush)out.flush();}}catch (InterruptedIOException x) {Thread.currentThread().interrupt();}catch (IOException x) {trouble = true;}}/**下面对于的字符操作的私有方法会时时刷新缓冲,保持跟底层输出流一样效率*///将字符数组buf写到PrintStream流中.private void write(char buf[]) {try {synchronized (this) {ensureOpen();textOut.write(buf);textOut.flushBuffer();charOut.flushBuffer();if (autoFlush) {for (int i = 0; i < buf.length; i++)if (buf[i] == '\n')out.flush();}}}catch (InterruptedIOException x) {Thread.currentThread().interrupt();}catch (IOException x) {trouble = true;}}//将字符串s写到PrintStream流中.private void write(String s) {try {synchronized (this) {ensureOpen();textOut.write(s);textOut.flushBuffer();charOut.flushBuffer();if (autoFlush && (s.indexOf('\n') >= 0))out.flush();}}catch (InterruptedIOException x) {Thread.currentThread().interrupt();}catch (IOException x) {trouble = true;}}//将换行符写到PrintStream流中private void newLine() {try {synchronized (this) {ensureOpen();textOut.newLine();textOut.flushBuffer();charOut.flushBuffer();if (autoFlush)out.flush();}}catch (InterruptedIOException x) {Thread.currentThread().interrupt();}catch (IOException x) {trouble = true;}}//将boolean类型数据对应的字符串"true"或者"false"写到PrintStream流中,实际调用write()方法public void print(boolean b) {write(b ? "true" : "false");}//将char类型数据对应字符串写到PrintStream流中,实际调用write()方法public void print(char c) {write(String.valueOf(c));}//将int类型数据对应的字符串写到PrintStream流中,实际调用write()方法.public void print(int i) {write(String.valueOf(i));}//将long类型数据对应的字符串写到PrintStream流中,实际调用write()方法.public void print(long l) {write(String.valueOf(l));}//将float类型数据对应的字符串写到PrintStream流中,实际调用write()方法.public void print(float f) {write(String.valueOf(f));}//将doule类型数据对应的字符串写到PrintStream流中,实际调用write()方法.public void print(double d) {write(String.valueOf(d));}//将字符数组写到PrintStream流中,实际调用write()方法.public void print(char s[]) {write(s);}//将字符串s写到PrintStream流中,s为null,将会写入"null",实际调用write()方法.public void print(String s) {if (s == null) {s = "null";}write(s);}//将对象obj对应的字符串写到PrintStream流中,实际调用write()方法.public void print(Object obj) {write(String.valueOf(obj));}//将换行符写到PrintStream流中.用于终止当前行(换行符由系统定义)public void println() {newLine();}//将boolean类型数据对应的字符串+换行符写到PrintStream流中,实际调用print()-->write()public void println(boolean x) {synchronized (this) {print(x);newLine();}}//将char类型单个字符对应字符串+换行符写到PrintStream流中,实际调用print()-->write()public void println(char x) {synchronized (this) {print(x);newLine();}}//将int类型数据对应的字符串+换行符写到PrintStream流中,实际调用print()-->write()public void println(int x) {synchronized (this) {print(x);newLine();}}//将long类型数据对应的字符串+换行符写到PrintStream流中,实际调用print()-->write()public void println(long x) {synchronized (this) {print(x);newLine();}}//将float类型数据对应的字符串+换行符写到PrintStream流中,实际调用print()-->write()public void println(float x) {synchronized (this) {print(x);newLine();}}//将double类型数据对应的字符串+换行符写到PrintStream流中,实际调用print()-->write()public void println(double x) {synchronized (this) {print(x);newLine();}}//将字符数组+换行符写到PrintStream流中,实际调用print()-->write()public void println(char x[]) {synchronized (this) {print(x);newLine();}}//将字符串+换行符写到PrintStream流中,实际调用print()-->write()public void println(String x) {synchronized (this) {print(x);newLine();}}//将对象x对应的字符串+换行符写到PrintStream流中,实际调用print()-->write().public void println(Object x) {String s = String.valueOf(x);synchronized (this) {print(s);newLine();}}//将数据args按照默认的Locale值和format格式进行格式化后写到PrintStream流中.//方法执行等同于out.format(format, args)public PrintStream printf(String format, Object ... args) {return format(format, args);}//将数据args根据Locale值和format格式进行格式化后写到PrintStream输出流中//方法执行等同于out.printf(l, format,args)public PrintStream printf(Locale l, String format, Object ... args) {return format(l, format, args);}//根据默认的Locale值和format格式来格式化数据args写到PrintStream输出流中.public PrintStream format(String format, Object ... args) {try {synchronized (this) {ensureOpen();if ((formatter == null)|| (formatter.locale() != Locale.getDefault()))formatter = new Formatter((Appendable) this);formatter.format(Locale.getDefault(), format, args);}} catch (InterruptedIOException x) {Thread.currentThread().interrupt();} catch (IOException x) {trouble = true;}return this;}//将数据args根据Locale值和format格式进行格式化后写到PrintStream输出流中.public PrintStream format(Locale l, String format, Object ... args) {try {synchronized (this) {ensureOpen();if ((formatter == null)|| (formatter.locale() != l))formatter = new Formatter(this, l);formatter.format(l, format, args);}} catch (InterruptedIOException x) {Thread.currentThread().interrupt();} catch (IOException x) {trouble = true;}return this;}//将字符序列csq添加到PrintStream输出流中,此方法执行等同于 out.print(csq.toString())public PrintStream append(CharSequence csq) {if (csq == null)print("null");elseprint(csq.toString());return this;}//将字符序列csq中start(包含)位置到end(不包含)之间的子字符序列添加到PrintStream输出流中//此方法执行等同于out.print(csq.subSequence(start, end).toString())public PrintStream append(CharSequence csq, int start, int end) {CharSequence cs = (csq == null ? "null" : csq);write(cs.subSequence(start, end).toString());return this;}//将单个字符添加到PrintStream输出流中.此方法执行等同于out.print(c)public PrintStream append(char c) {print(c);return this;}
}
总结
PrintStream继承自OutputStream,属于字节流的一种,方法包含写入单个字节和字节数组的方法.相似流有PrintWriter,继承自Writer()方法,属于字符流的一种.PrintWriter流中没有写入字节的方法,而有写入单个字符和字符数组的方法.








求解三阶微分方程)




)







