前言
最近有些读者私信我说希望后面多分享spring方面的文章,这样能够在实际工作中派上用场。正好我对spring源码有过一定的研究,并结合我这几年实际的工作经验,把spring中我认为不错的知识点总结一下,希望对您有所帮助。
一 如何获取spring容器对象
1.实现BeanFactoryAware接口
@Service
public class PersonService implements BeanFactoryAware {private BeanFactory beanFactory;@Overridepublic void setBeanFactory(BeanFactory beanFactory) throws BeansException {this.beanFactory = beanFactory;}public void add() {Person person = (Person) beanFactory.getBean("person");}
}
实现BeanFactoryAware接口,然后重写setBeanFactory方法,就能从该方法中获取到spring容器对象。
2.实现ApplicationContextAware接口
@Service
public class PersonService2 implements ApplicationContextAware {private ApplicationContext applicationContext;@Overridepublic void setApplicationContext(ApplicationContext applicationContext) throws BeansException {this.applicationContext = applicationContext;}public void add() {Person person = (Person) applicationContext.getBean("person");}}
实现ApplicationContextAware接口,然后重写setApplicationContext方法,也能从该方法中获取到spring容器对象。
3.实现ApplicationListener接口
@Service
public class PersonService3 implements ApplicationListener<ContextRefreshedEvent> {private ApplicationContext applicationContext;@Overridepublic void onApplicationEvent(ContextRefreshedEvent event) {applicationContext = event.getApplicationContext();}public void add() {Person person = (Person) applicationContext.getBean("person");}}
实现ApplicationListener接口,需要注意的是该接口接收的泛型是ContextRefreshedEvent类,然后重写onApplicationEvent方法,也能从该方法中获取到spring容器对象。
此外,不得不提一下Aware接口,它其实是一个空接口,里面不包含任何方法。
它表示已感知的意思,通过这类接口可以获取指定对象,比如:
通过BeanFactoryAware获取BeanFactory
通过ApplicationContextAware获取ApplicationContext
通过BeanNameAware获取BeanName等
Aware接口是很常用的功能,目前包含如下功能:

二 如何初始化bean
spring中支持3种初始化bean的方法:
xml中指定init-method方法
使用@PostConstruct注解
实现InitializingBean接口
第一种方法太古老了,现在用的人不多,具体用法就不介绍了。
1.使用@PostConstruct注解
@Service
public class AService {@PostConstructpublic void init() {System.out.println("===初始化===");}
}
在需要初始化的方法上增加@PostConstruct注解,这样就有初始化的能力。
2.实现InitializingBean接口
@Service
public class BService implements InitializingBean {@Overridepublic void afterPropertiesSet() throws Exception {System.out.println("===初始化===");}
}
实现InitializingBean接口,重写afterPropertiesSet方法,该方法中可以完成初始化功能。
这里顺便抛出一个有趣的问题:init-method、PostConstruct 和 InitializingBean 的执行顺序是什么样的?
决定他们调用顺序的关键代码在AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory类的initializeBean方法中。

这段代码中会先调用BeanPostProcessor的postProcessBeforeInitialization方法,而PostConstruct是通过InitDestroyAnnotationBeanPostProcessor实现的,它就是一个BeanPostProcessor,所以PostConstruct先执行。
而invokeInitMethods方法中的代码:

决定了先调用InitializingBean,再调用init-method。
所以得出结论,他们的调用顺序是:

三 自定义自己的Scope
我们都知道spring默认支持的Scope只有两种:
singleton 单例,每次从spring容器中获取到的bean都是同一个对象。
prototype 多例,每次从spring容器中获取到的bean都是不同的对象。
spring web又对Scope进行了扩展,增加了:
RequestScope 同一次请求从spring容器中获取到的bean都是同一个对象。
SessionScope 同一个会话从spring容器中获取到的bean都是同一个对象。
即便如此,有些场景还是无法满足我们的要求。
比如,我们想在同一个线程中从spring容器获取到的bean都是同一个对象,该怎么办?
这就需要自定义Scope了。
第一步实现Scope接口:
public class ThreadLocalScope implements Scope {private static final ThreadLocal THREAD_LOCAL_SCOPE = new ThreadLocal();@Overridepublic Object get(String name, ObjectFactory<?> objectFactory) {Object value = THREAD_LOCAL_SCOPE.get();if (value != null) {return value;}Object object = objectFactory.getObject();THREAD_LOCAL_SCOPE.set(object);return object;}@Overridepublic Object remove(String name) {THREAD_LOCAL_SCOPE.remove();return null;}@Overridepublic void registerDestructionCallback(String name, Runnable callback) {}@Overridepublic Object resolveContextualObject(String key) {return null;}@Overridepublic String getConversationId() {return null;}
}
第二步将新定义的Scope注入到spring容器中:
@Component
public class ThreadLocalBeanFactoryPostProcessor implements BeanFactoryPostProcessor {@Overridepublic void postProcessBeanFactory(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory) throws BeansException {beanFactory.registerScope("threadLocalScope", new ThreadLocalScope());}
}
第三步使用新定义的Scope:
@Scope("threadLocalScope")
@Service
public class CService {public void add() {}
}
四 别说FactoryBean没用
说起FactoryBean就不得不提BeanFactory,因为面试官老喜欢问它们的区别。
BeanFactory:spring容器的顶级接口,管理bean的工厂。
FactoryBean:并非普通的工厂bean,它隐藏了实例化一些复杂Bean的细节,给上层应用带来了便利。
如果你看过spring源码,会发现它有70多个地方在用FactoryBean接口。

上面这张图足以说明该接口的重要性,请勿忽略它好吗?
特别提一句:mybatis的SqlSessionFactory对象就是通过SqlSessionFactoryBean类创建的。
我们一起定义自己的FactoryBean:
@Component
public class MyFactoryBean implements FactoryBean {@Overridepublic Object getObject() throws Exception {String data1 = buildData1();String data2 = buildData2();return buildData3(data1, data2);}private String buildData1() {return "data1";}private String buildData2() {return "data2";}private String buildData3(String data1, String data2) {return data1 + data2;}@Overridepublic Class<?> getObjectType() {return null;}
}
获取FactoryBean实例对象:
@Service
public class MyFactoryBeanService implements BeanFactoryAware {private BeanFactory beanFactory;@Overridepublic void setBeanFactory(BeanFactory beanFactory) throws BeansException {this.beanFactory = beanFactory;}public void test() {Object myFactoryBean = beanFactory.getBean("myFactoryBean");System.out.println(myFactoryBean);Object myFactoryBean1 = beanFactory.getBean("&myFactoryBean");System.out.println(myFactoryBean1);}
}
getBean("myFactoryBean");获取的是MyFactoryBeanService类中getObject方法返回的对象,getBean("&myFactoryBean");获取的才是MyFactoryBean对象。
五 轻松自定义类型转换
spring目前支持3中类型转换器:
Converter<S,T>:将 S 类型对象转为 T 类型对象
ConverterFactory<S, R>:将 S 类型对象转为 R 类型及子类对象
GenericConverter:它支持多个source和目标类型的转化,同时还提供了source和目标类型的上下文,这个上下文能让你实现基于属性上的注解或信息来进行类型转换。
这3种类型转换器使用的场景不一样,我们以Converter<S,T>为例。假如:接口中接收参数的实体对象中,有个字段的类型是Date,但是实际传参的是字符串类型:2021-01-03 10:20:15,要如何处理呢?
第一步,定义一个实体User:
@Data
public class User {private Long id;private String name;private Date registerDate;
}
第二步,实现Converter接口:
public class DateConverter implements Converter<String, Date> {private SimpleDateFormat simpleDateFormat = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss");@Overridepublic Date convert(String source) {if (source != null && !"".equals(source)) {try {simpleDateFormat.parse(source);} catch (ParseException e) {e.printStackTrace();}}return null;}
}
第三步,将新定义的类型转换器注入到spring容器中:
@Configuration
public class WebConfig extends WebMvcConfigurerAdapter {@Overridepublic void addFormatters(FormatterRegistry registry) {registry.addConverter(new DateConverter());}
}第四步,调用接口
@RequestMapping("/user")
@RestController
public class UserController {@RequestMapping("/save")public String save(@RequestBody User user) {return "success";}
}
请求接口时User对象中registerDate字段会被自动转换成Date类型。
六 spring mvc拦截器,用过的都说好
spring mvc拦截器根spring拦截器相比,它里面能够获取HttpServletRequest和HttpServletResponse 等web对象实例。
spring mvc拦截器的顶层接口是:HandlerInterceptor,包含三个方法:
preHandle 目标方法执行前执行
postHandle 目标方法执行后执行
afterCompletion 请求完成时执行
为了方便我们一般情况会用HandlerInterceptor接口的实现类HandlerInterceptorAdapter类。
假如有权限认证、日志、统计的场景,可以使用该拦截器。
第一步,继承HandlerInterceptorAdapter类定义拦截器:
public class AuthInterceptor extends HandlerInterceptorAdapter {@Overridepublic boolean preHandle(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler)throws Exception {String requestUrl = request.getRequestURI();if (checkAuth(requestUrl)) {return true;}return false;}private boolean checkAuth(String requestUrl) {System.out.println("===权限校验===");return true;}
}第二步,将该拦截器注册到spring容器:
@Configuration
public class WebAuthConfig extends WebMvcConfigurerAdapter {@Beanpublic AuthInterceptor getAuthInterceptor() {return new AuthInterceptor();}@Overridepublic void addInterceptors(InterceptorRegistry registry) {registry.addInterceptor(new AuthInterceptor());}
}
第三步,在请求接口时spring mvc通过该拦截器,能够自动拦截该接口,并且校验权限。
该拦截器其实相对来说,比较简单,可以在DispatcherServlet类的doDispatch方法中看到调用过程:

顺便说一句,这里只讲了spring mvc的拦截器,并没有讲spring的拦截器,是因为我有点小私心,后面就会知道。
七 Enable开关真香
不知道你有没有用过Enable开头的注解,比如:EnableAsync、EnableCaching、EnableAspectJAutoProxy等,这类注解就像开关一样,只要在@Configuration定义的配置类上加上这类注解,就能开启相关的功能。
是不是很酷?
让我们一起实现一个自己的开关:
第一步,定义一个LogFilter:
public class LogFilter implements Filter {@Overridepublic void init(FilterConfig filterConfig) throws ServletException {}@Overridepublic void doFilter(ServletRequest request, ServletResponse response, FilterChain chain) throws IOException, ServletException {System.out.println("记录请求日志");chain.doFilter(request, response);System.out.println("记录响应日志");}@Overridepublic void destroy() {}
}
第二步,注册LogFilter:
@ConditionalOnWebApplication
public class LogFilterWebConfig {@Beanpublic LogFilter timeFilter() {return new LogFilter();}
}
注意,这里用了@ConditionalOnWebApplication注解,没有直接使用@Configuration注解。
第三步,定义开关@EnableLog注解:
@Target(ElementType.TYPE)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
@Import(LogFilterWebConfig.class)
public @interface EnableLog {}
第四步,只需在springboot启动类加上@EnableLog注解即可开启LogFilter记录请求和响应日志的功能。
八 RestTemplate拦截器的春天
我们使用RestTemplate调用远程接口时,有时需要在header中传递信息,比如:traceId,source等,便于在查询日志时能够串联一次完整的请求链路,快速定位问题。
这种业务场景就能通过ClientHttpRequestInterceptor接口实现,具体做法如下:
第一步,实现ClientHttpRequestInterceptor接口:
public class RestTemplateInterceptor implements ClientHttpRequestInterceptor {@Overridepublic ClientHttpResponse intercept(HttpRequest request, byte[] body, ClientHttpRequestExecution execution) throws IOException {request.getHeaders().set("traceId", MdcUtil.get());return execution.execute(request, body);}
}
第二步,定义配置类:
@Configuration
public class RestTemplateConfiguration {@Beanpublic RestTemplate restTemplate() {RestTemplate restTemplate = new RestTemplate();restTemplate.setInterceptors(Collections.singletonList(restTemplateInterceptor()));return restTemplate;}@Beanpublic RestTemplateInterceptor restTemplateInterceptor() {return new RestTemplateInterceptor();}
}
其中MdcUtil其实是利用MDC工具在ThreadLocal中存储和获取traceId
public class MdcUtil {private static final String TRACE_ID = "TRACE_ID";public static String get() {return MDC.get(TRACE_ID);}public static void add(String value) {MDC.put(TRACE_ID, value);}
}
当然,这个例子中没有演示MdcUtil类的add方法具体调的地方,我们可以在filter中执行接口方法之前,生成traceId,调用MdcUtil类的add方法添加到MDC中,然后在同一个请求的其他地方就能通过MdcUtil类的get方法获取到该traceId。
九 统一异常处理
以前我们在开发接口时,如果出现异常,为了给用户一个更友好的提示,例如:
@RequestMapping("/test")
@RestController
public class TestController {@GetMapping("/add")public String add() {int a = 10 / 0;return "成功";}
}
如果不做任何处理请求add接口结果直接报错:

what?用户能直接看到错误信息?
这种交互方式给用户的体验非常差,为了解决这个问题,我们通常会在接口中捕获异常:
@GetMapping("/add")
public String add() {String result = "成功";try {int a = 10 / 0;} catch (Exception e) {result = "数据异常";}return result;
}
接口改造后,出现异常时会提示:“数据异常”,对用户来说更友好。
看起来挺不错的,但是有问题。。。
如果只是一个接口还好,但是如果项目中有成百上千个接口,都要加上异常捕获代码吗?
答案是否定的,这时全局异常处理就派上用场了:RestControllerAdvice。
@RestControllerAdvice
public class GlobalExceptionHandler {@ExceptionHandler(Exception.class)public String handleException(Exception e) {if (e instanceof ArithmeticException) {return "数据异常";}if (e instanceof Exception) {return "服务器内部异常";}retur n null;}
}
只需在handleException方法中处理异常情况,业务接口中可以放心使用,不再需要捕获异常(有人统一处理了)。真是爽歪歪。
十 异步也可以这么优雅
以前我们在使用异步功能时,通常情况下有三种方式:
继承Thread类
实现Runable接口
使用线程池
让我们一起回顾一下:
继承Thread类
public class MyThread extends Thread {@Overridepublic void run() {System.out.println("===call MyThread===");}public static void main(String[] args) {new MyThread().start();}
}
实现Runable接口
public class MyWork implements Runnable {@Overridepublic void run() {System.out.println("===call MyWork===");}public static void main(String[] args) {new Thread(new MyWork()).start();}
}
使用线程池
public class MyThreadPool {private static ExecutorService executorService = new ThreadPoolExecutor(1, 5, 60, TimeUnit.SECONDS, new ArrayBlockingQueue<>(200));static class Work implements Runnable {@Overridepublic void run() {System.out.println("===call work===");}}public static void main(String[] args) {try {executorService.submit(new MyThreadPool.Work());} finally {executorService.shutdown();}}
}
这三种实现异步的方法不能说不好,但是spring已经帮我们抽取了一些公共的地方,我们无需再继承Thread类或实现Runable接口,它都搞定了。
如何spring异步功能呢?
第一步,springboot项目启动类上加@EnableAsync注解。
@EnableAsync
@SpringBootApplication
public class Application {public static void main(String[] args) {new SpringApplicationBuilder(Application.class).web(WebApplicationType.SERVLET).run(args);}
}
第二步,在需要使用异步的方法上加上@Async注解:
@Service
public class PersonService {@Asyncpublic String get() {System.out.println("===add==");return "data";}
}
然后在使用的地方调用一下:personService.get();就拥有了异步功能,是不是很神奇。
默认情况下,spring会为我们的异步方法创建一个线程去执行,如果该方法被调用次数非常多的话,需要创建大量的线程,会导致资源浪费。
这时,我们可以定义一个线程池,异步方法将会被自动提交到线程池中执行。
@Configuration
public class ThreadPoolConfig {@Value("${thread.pool.corePoolSize:5}")private int corePoolSize;@Value("${thread.pool.maxPoolSize:10}")private int maxPoolSize;@Value("${thread.pool.queueCapacity:200}")private int queueCapacity;@Value("${thread.pool.keepAliveSeconds:30}")private int keepAliveSeconds;@Value("${thread.pool.threadNamePrefix:ASYNC_}")private String threadNamePrefix;@Beanpublic Executor MessageExecutor() {ThreadPoolTaskExecutor executor = new ThreadPoolTaskExecutor();executor.setCorePoolSize(corePoolSize);executor.setMaxPoolSize(maxPoolSize);executor.setQueueCapacity(queueCapacity);executor.setKeepAliveSeconds(keepAliveSeconds);executor.setThreadNamePrefix(threadNamePrefix);executor.setRejectedExecutionHandler(new ThreadPoolExecutor.CallerRunsPolicy());executor.initialize();return executor;}
}
spring异步的核心方法:

根据返回值不同,处理情况也不太一样,具体分为如下情况:

十一 听说缓存好用,没想到这么好用
spring cache架构图:

它目前支持多种缓存:
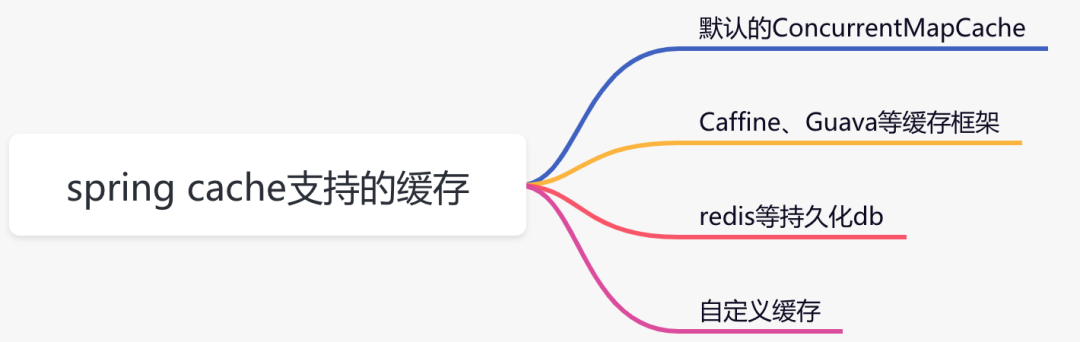
我们在这里以caffeine为例,它是spring官方推荐的。
第一步,引入caffeine的相关jar包
<dependency><groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId><artifactId>spring-boot-starter-cache</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency><groupId>com.github.ben-manes.caffeine</groupId><artifactId>caffeine</artifactId><version>2.6.0</version>
</dependency>
第二步,配置CacheManager,开启EnableCaching
@Configuration
@EnableCaching
public class CacheConfig {@Beanpublic CacheManager cacheManager(){CaffeineCacheManager cacheManager = new CaffeineCacheManager();//Caffeine配置Caffeine<Object, Object> caffeine = Caffeine.newBuilder()//最后一次写入后经过固定时间过期.expireAfterWrite(10, TimeUnit.SECONDS)//缓存的最大条数.maximumSize(1000);cacheManager.setCaffeine(caffeine);return cacheManager;}
}
第三步,使用Cacheable注解获取数据
@Service
public class CategoryService {//category是缓存名称,#type是具体的key,可支持el表达式@Cacheable(value = "category", key = "#type")public CategoryModel getCategory(Integer type) {return getCategoryByType(type);}private CategoryModel getCategoryByType(Integer type) {System.out.println("根据不同的type:" + type + "获取不同的分类数据");CategoryModel categoryModel = new CategoryModel();categoryModel.setId(1L);categoryModel.setParentId(0L);categoryModel.setName("电器");categoryModel.setLevel(3);return categoryModel;}
}
调用categoryService.getCategory()方法时,先从caffine缓存中获取数据,如果能够获取到数据则直接返回该数据,不会进入方法体。如果不能获取到数据,则直接方法体中的代码获取到数据,然后放到caffine缓存中。


方法)



函数以及C ++ STL中的示例)

![[nodejs] 利用openshift 撰寫應用喔](http://pic.xiahunao.cn/[nodejs] 利用openshift 撰寫應用喔)

函数以及C ++ STL中的示例)

?)






